Academic Team Science Quick Recall
1/384
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
385 Terms
lev landau
this russian scientist developed a model of magnetism for solids and developed the theory of fermi fluids, superconductivity, and won the nobel prize for superfluids
lavoisier
this "father of modern chemistry" disproved phlogiston theory, named oxygen and hydrogen, and made the law of conservation of mass.
adiabatic
type of process in which heat neither enters nor leaves the system
carapace
chitinous upper exoskeleton of certain organisms such as arthropods and turtles
tri state tornado
deadliest tornado in US History
barrier islands
long, thin, low offshore islands of sediment that generally run parallel to the shore along some coasts and protect against tsunamis
law of octaves
this law states that the same properties appear every eighth element when the elements are listed in order of their atomic masses
third law of thermodynamics
AKA Nernst Heat theorem. entropy of a perfect crystal is zero at absolute zero.
bathymetric map
map showing depths of body of water
agnatha
class of jawless fish
plasmids
small DNA molecules that can build up resistance against a drug
massif
one is named Sancy in southern france. mountain group with many faults.
translation
at the start of this, the ribosome binds to the shine-dalgarno sequence
flagella
move in runs and tumbles
photoelectric effect
when light shines on metal, charge (e-) is created
coelom
cavity formed in gastrulation. not in platyhelminthes and cnidarians.
stroma
calvin cycle takes place in this.
acetylcholine
curare inhibits a receptor for this neurotransmitter
pterophyta
phylum that includes ferns
electron transport chain
without oxygen, this process is replaced by fermentation
abscission
the process by which cells physically separate after cytokinesis.
ohms law
diodes dont obey this law
bilateral symmetry
echinoderms in larvae stage show this property
black hole
extracting energy from spinning ones of these is called Blandford-Zjanek process. surrounded by accretion disk.
biennial
examples of this kind of plant are parsley and black-eyed susans
batholith
made of many plutons making a big expanse of felsic rock. examples are found in sierra nevadas and coast mountains.
pH
first proposed by Soren Sorenson. name refers to power of certain ion. logarithmic scale.
conjugate
in an acid-base reaction, one base and conjugate are formed by proton transfer. term for related acid-base pairs
calvin cycle
conducted in plants at day. makes glucose from captured CO2
schwann cells
type of glial cell only in peripheral nervous system. provide support for neurons by forming myelin sheath of PNS
dirac
he quantized the gravitational field and discovered positrons
tombaugh
he researched ballistics and discovered pluto
morgan
biologist best known for fruit fly genetics
moon
soil called regolith, and famous site called sea of tranquility
clausius
his thesis on how refraction makes the sky blue was proven by Rayleigh to be scattering. introduced idea of entropy and second law of thermodynamics
primitive streak
this linear structure establishes bilateral symmetry in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
hookes law
deals with elasticity. force to stretch a spring is proportional to movement distance
krebs cycle
this process occurs in cytosol and makes FADH2 + 3NADH
beaufort scale
scale ranging from calm to hurricane (0-17). determines wind speed from sea's appearance
mycology
study of fungi
nematodes
this phylum includes c. elegans and roundworms. it has bilaterally symmetric bodies and radially symmetric heads.
feynman
won nobel prize for contributing to quantum electrodynamics
residue
leftover product of a chemical reaction or unit of a larger molecule
dioecious
plants that require cross-pollination. male and female reproductive organs are separate plants
halophytes
salt tolerant plants
mesophyll
photosynthesis happens most strongly in this type of spongy plant tissue.
alkane
single bond
salt dome
an inverted bowl hiding oil or natural gas. form in saline environments.
lepton
Family of particles (electrons, muons, and neutrinos) that experience no strong forces. type of fermion.
glycogen
liver is most significant source of this molecule. stores energy in animals
second law of thermodynamics
law by clausius. entropy always increased so no process can fully 100% efficient
xray
radiation type discovered by Roentgen. between gamma and ultraviolet.
induction
phenomenon present in certain coiled circuit components. a change in the magnetic field makes an electric field.
ideal gas constant
one measurement for this constant was found by finding speed of sound of argon at water's triple point. denoted R
pleura
membranes in thorax that surround the lungs
beryl
hardness 7-8, blue variants of this mineral are called aquamarine. namesake lightest alkaline earth metal.
faraday cage
first made by benjamin franklin. discovered with ice pail experiment. wire meshes that don't allow electromagnetic signals smaller than their gaps to pass
mutagens
phenylalanine is a type of this. physical and chemical agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations.
microtubules
structures that help pull the cell apart during mitosis. provide support to cell and dispersed through cytoplasm.
lignin
lacks formal primary structure like most structural plant compounds. stretchy polymer in plant cell walls.
endosymbiosis
a theory explaining the separation between eukaryotes and prokaryotes and the existence of organelles being from evolved ingested unicellular organisms.
aerosols
inhalation of these can cause diseases like black lung. these colloids are made of solid particles or liquid drops dispersed in a gas.
anemia
this disorder is more likely in females. lack of red blood cells.
twin paradox
a thought experiment in special relativity explained by einstein to be the result of time dilation. this paradox says that 2 identical objects in different reference frames age at different rates.
buckminsterfullerene
one of the largest known compounds to show wave-particle duality. 60+ carbon atom structure. namesake scientist made geodesic dome.
seaborg
this berkeley scientist discovered 10 elements and hypothesized actinide series. has element Sg named after him.
cavendish
discovered that nitrogen makes up most of atmosphere. did namesake experiment to measure density, mass, and special gravity of Earth. discovered hydrogen.
boltzmann
his theorem for statistical mechanics supplements the second law of thermodynamics. his equation is basis of transport-processes theory. Austrian physicist.
zika
this retrovirus was first isolated in a rhesus monkey in Uganda. brazil outbreak in 2015.
energy level
quantum numbers corresponding to position of electron in atom. particles have a discrete amount of energy in these distinctions.
meninges
the innermost of these tissues is the pia mater, impermeable to fluids. these membranes cushion CNS
planck
made system of units derived only from universal constants like his namesake time and length. german pioneer of quantum mechanics.
osteichthyes
this class contains bony fish
cinnabar
a toxic substance. distilling/roasting this yields mercury. mercury sulfide mineral with namesake red-orange color.
impulse
airbags try to minimize this. time integral of force. time derivative of momentum.
azeotropes
a mixture of multiple liquids unable to be separated through distillation. form mechanically inseparable phases
galvanic cell
the 2 halves of this device are connected by glass tube/filter paper called salt bridge. this type of cell uses chemical reactions to make electricity.
anammox
this process in the nitrogen cycle is short for anaerobic ammonia oxidation
loess
fine grains consisting mainly of quartz. loosely packed sediments created by wind or glaciers.
coulombs law
physics law with namesake constant: 8.987*10^9. describes interaction between charged particles. explains why like charges repel.
proteomics
study of proteins
gay-lussacs law
gas law: pressure and temperature are directly related.
oncogenes
genes that influence the development and growth of tumor cells, causing cancer
cosmological constant
represented by capital lambda. constant in Einstein's equations of space and time representing a repulsion force. allows for static universe.
molality
concentration of a solution expressed in moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. deals with mass.
epistasis
gene at one locus alters the expression of a gene at a second locus
superacids
acids stronger than 100% sulfuric acid including
fluoroantimonic, magic, and perchloric acids.
james clerk maxwell
derived namesake electromagnetism equations. first to unify electricity and magnetism.
cyclosis
movement of cytoplasm around the cell
colligative properties
Properties of solutions affected only by number of solute particles dissolved.
enthalpy
the heat/energy content of a system. symbolized H.
pauling
proposed alpha helix and though DNA was triple helix. created namesake 4-point scale for electronegativity
pyridine
makes up half of nicotine molecule. forms niacin when carboxylic acid is added. formula C5H5N with similar shape to benzene
isobaric
type of thermodynamic process in which total pressure of the system is constant
esters
this functional group has general formula RCOOR. notable fruity scent.
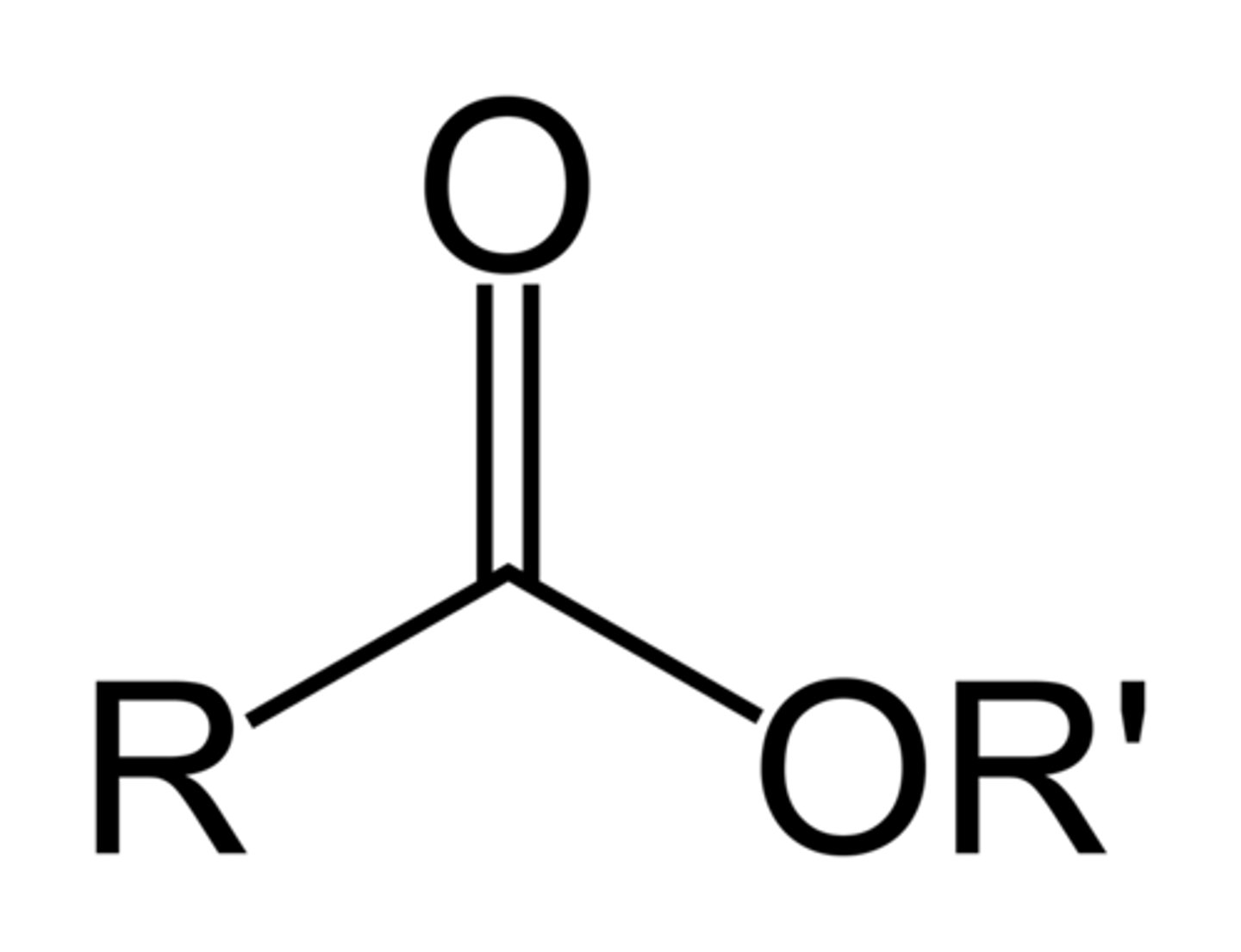
standard candle
class of celestial objects including cepheids with constant known luminosities used to identify astronomical distances
punnett
wrote first textbook on genetics and butterfly mimicry. namesake rectangular tool to predict genotypes.
la nina
cooling of western pacific ocean around december. name means "Little Girl"
acetone
simplest ketone, used in labs to clean glassware, found in nail polish remover.
rosalind franklin
this scientist researched the structure of the tobacco mosaic virus and used x-ray diffraction to determine the structure of DNA