PSYC 301 Neuroanatomy
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what is the basic structure of the brain?
cerebral cortex
diencephalon
midbrain
pons
medulla
cerebellum
spinal cord
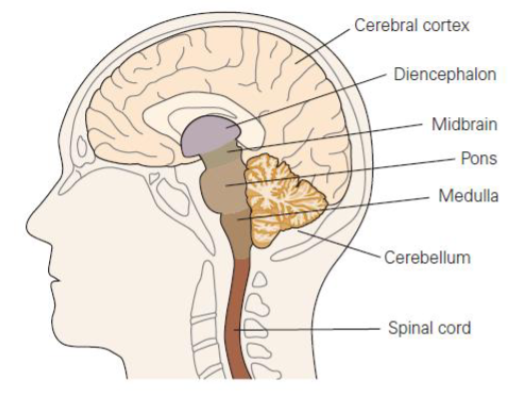
what are the divisions of the NS & what it a part of them?
CNS located skull & spine
brain & spinal cord
PNS located outside skull & spine
what are the divisions of the PNS & describe them?
somatic nervous system: interacts w/ environment
autonomic nervous system: regulates body’s internal environment
what is the role of afferent & efferent nerves in the somatic nervous system?
afferent nerves carry sensory signals from the skin, skeletal muscles, joints, eyes, ears to the CNS
efferent nerves carry motor signals from the CNS to the skeletal muscles
what is the role of afferent & efferent nerves in the ANS?
Afferent nerves that carry sensory signals from internal organs to CNS
see’s bear & send’s to brain=> danger
Efferent nerves that carry motor signals from the CNS to internal organs
heart rate increases
what are the 2 kinds of efferent nerves in the ANS & describe them?
Sympathetic nerves: mobilize energy in threatening situations (e.g., via adrenal glands)
Parasympathetic nerves: act to conserve energy or “rest and digest” (e.g.,
stimulate gut motility)
how are neurons 2-stage?
Neurons project from CNS go part of the way then synapse on other neurons that carry the signal the rest of the way
Sympathetic neurons synapse on 2nd-stage neurons further away from target organs
Parasympathetic neurons synapse closer to targeted organs
what are the 3 principles of the conventional view of sympathetic & parasympathetic nerves?
1) sympathetic nerves stimulate, organize, mobilize energy resources in threatening situations & parasympathetic acts to conserve energy
2) each autonomic target organ receives opposing sympathetic & parasympathetic & activity is controlled relative to both activity input ex: symp increases HR while para decreases it
3) sympathetic changes relate to psyc arousal & parasympathetic relate to psyc relaxation
=> Exception: Most nerves in the PNS project from the spinal cord but…
=> 12 pairs of cranial nerves – project from brain
· Sensory nerves: brain - olfactory (I), optic (II), vagus (x – to & from gut)
in the CNS, what is a nucleus & tract?
nucleus: a cluster of cell bodies
tract: a bundle of axons
in the PNS, what is a ganglion & nerves?
ganglion: cluster of cell bodies
nerve (fibres): bundle of axons
what are meninges?
brain & spinal cord are encased in bone & covered by 3 protective membranes (protect CNS)
what are the 3 meninges & explain them?
dura mater: tough, thick, protective layer
arachnoid membrane: middle layer, delicate, web-like
contains the subarachnoid space where CSF circulates
pia matter: innermost layer, thin layer that covers brain & spinal cord
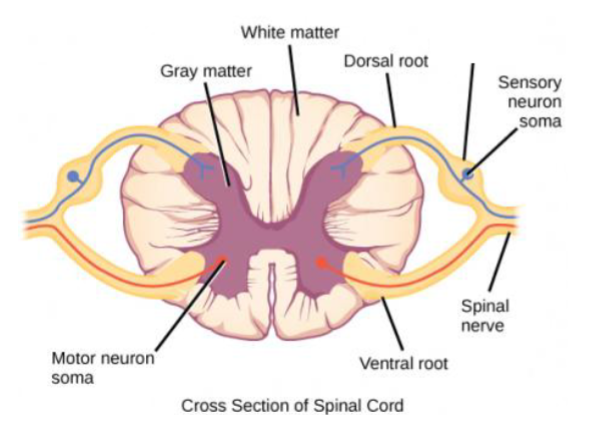
what does the spinal cord consist of?
inner H-shaped core of gray matter: cell bodies and unmyelinated axons
surrounding area of white matter: myelinated axons
what does a cross section of the spinal cord look like & where are the dorsal & ventral roots?
where is cerebrospinal fluid produced?
cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexuses (network of capillaries, or small blood vessels that protrude into the ventricles from the pia mater)
where does the cerebrospinal fluid flow?
excess cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed from the subarachnoid space into dural sinuses (large blood-filled spaces) which runs through the dura mater & drain into the large jugular veins of the neck
what are the functions of CSF?
cushions the brain
provides nutrients
removes waste
protects against physical injury
what is gray matter & white matter made of?
gray: cell bodies & capillary blood vessels
white: myelinated axons
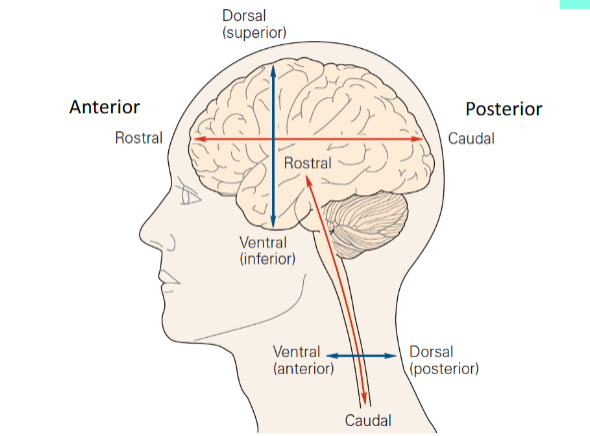
what are the directions of a mouse body?
dorsal towards the top
ventral towards the bottom
rostral toward the nose
caudal towards the tail
anterior towards the front
posterior towards the back
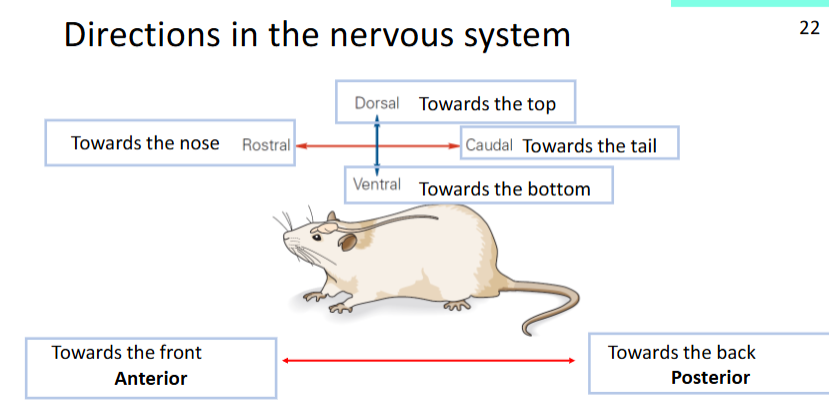
what are the directions of a human brain?
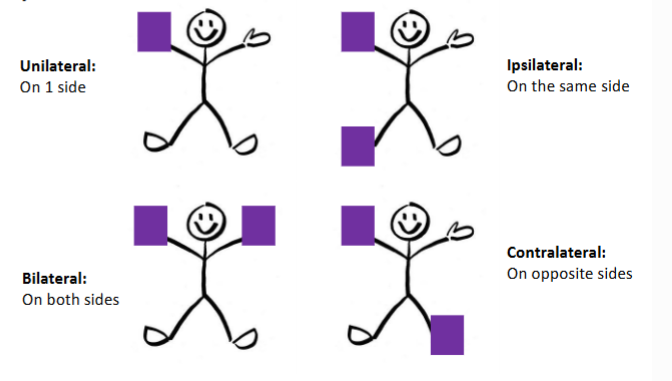
what are the 4 different types of laterality?
unilateral: one side
bilateral: both sides
ipsilateral: on the same side
contralateral: on opposite sides
what is the blood-brain barrier?
impedes the passage of many toxic substances from the blood into the brain
what are the functions in the body & brain?
body: cell that make up the walls of blood vessels are loosely packed so nutrients can easily pass
brain: cells of blood vessels are tightly packed, affecting the degree to which drugs/recreational drugs can influence brain activity
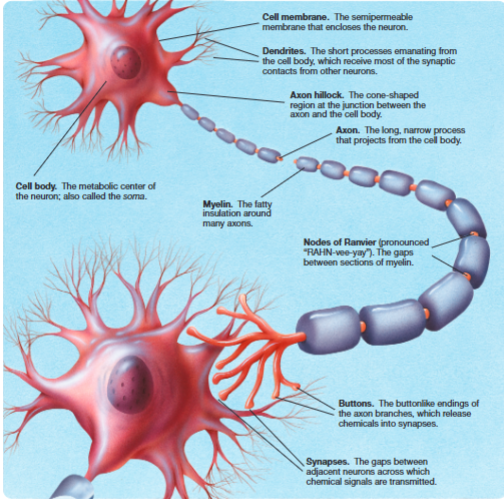
what are the external features of a multipolar neuron?
cell membrane: semipermeable membrane that encloses the neuron
dendrites: short processes emanating from the cell body, which receives most of the synaptic contacts from other neurons
cell body: metabolic center of the neuron (soma)
axon hillock: cone-shaped region at the junction between the axon & the cell body
axon: long, narrow process that projects from the cell body
myelin: fatty insulation around axons
nodes of ranvier: gaps between sections of myelin
what makes up a neuron’s cell membrane?
composed of lipid bilayer (2 layers of fat molecules)
protein molecules forming the basis of cell membrane functional properties
channel proteins: certain molecules may pass
signal proteins: transfer signal to the inside of the neurons when particular molecules bind to them on the outside of the membrane
what are the classes of neurons?
multipolar: more than 2 processes extending from its cell body
unipolar: neuron w/ 1 process extending from its cell body
bipolar: neuron w/ 2 processes extending from its cell body
what are the 4 kinds of glial cells?
oligodendrocytes
schwann cells
microglia
astrocytes
what are oligodendrocytes?
glial cells w/ extension that wrap around the axons of some neurons of the CNS
extensions are rich in myelin & myelin sheath to increase the speed & efficiency of axonal conduction
what are schwann cells?
function similarly to oligodendrocytes but on the PNS
only 1 myelin segment
guide axonal regeneration (regrowth) after damage
what is the 3rd class of glial cells?
microglia respond to injury/ disease by multiplying, engulfing cellular debris or even entire cells, & triggering inflammatory responses
shown to play a role in regulation of cell death, synapse formation, & synapse elimination
what are the 4th class of glial cells?
astrocytes are the largest
some extensions outer surfaces of blood vessels in the brain & make contact w/ neurons
play a role in allowing some chemicals from the blood into CNS neurons & blocking other chemicals & have the ability to contract or relax blood vessels based on blood flow demands of certain brain regions
control establishment & maintenance of synapses between neurons, to modulate neural activity, to form functional networks w/ neurons & other astrocytes, to control blood-brain barrier, & to respond to brain injury
what are the 5 major divisions of the brain?
telencephalon
diencephalon
mesencephalon
metencephalon
myelencephalon
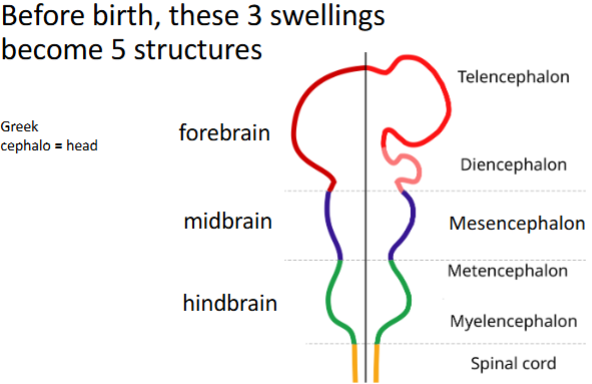
what is the brain made up of?
2-3% of body weight, ~3 lbs
Consumes ~20% of body’s energy
Made up of neurons, neural stem cells, glia, blood vessels
60-100 billion neurons; ~half in cerebellum
Brain size is weakly related to
body height
what are the components of the myelencephalon?
Composed largely of tracts carrying
signals between the rest of the
brain and the body
what are the components of the metencephalon?
Pons: houses many fibre tracts and part of reticular formation
Cerebellum:50% of all neurons in the
brain!
Massively connected to cortex -- multiple cerebro-cerebellar systems
Involved in movement & timing
what are the components of the mesencephalon?
Composed of:
the tectum (“roof”), which contains
nuclei that receive and relay: visual information (superior colliculi) & auditory info (inferior colliculi)
the tegmentum (“floor”), which
contains nuclei related to: motor function (substantia nigra & red nucleus) & pain-reducing effect of opiods - analgesic (periaqueductal grey)
what is the reticular formation?
In the myel-, met- and mesencephalon (midbrain + hindbrain)
Many nuclei that play roles in arousal, attention, cardiac and respiratory reflexes, and other jobs
what are disorders of the midbrain & hindbrain?
dejerine syndrome (bilateral medial medullary stroke)
chiari malformation
pontine tegmental cap dysplasia
what are symptoms of dejerine syndrome?
Respiratory failure
Paralysis of all four limbs
Tongue dysfunction
what is chiari malformation & its symptoms?
Compression & distortion of cerebellum due to skull shape
Headache
Neck pain
Coordination issues
Swallowing issues
what is pontine tegmental cap dysplasia & symptoms affected?
A rare genetic disorder of pons & cerebellum formation due to a developmental error in axon growth & guidance
Hearing, gaze, swallowing, facial
movements
what are the components of the diencephalon?
thalamus
hypothalamus
what is the role of the thalamus?
2-lobed structure @ top of brainstem
Many different types of nuclei – some process & relay info between receptors & cortex
Nuclei may be specific to one sense or non-specific & involved in multimodal integration
how does the thalamus play a role in general anesthetics?
tend to act upon the nonspecific nuclei of the thalamus (as well as other structures)
Abnormal synchronization in the thalamo-cortical network can cause absence seizures
what is the role of the hypothalamus?
below anterior thalamus
Plays an important role in behaviours such as feeding, sex, sleeping, temperature, emotion, & movement
Acts upon the body’s endocrine (hormone) system via the pituitary gland
what are symptoms of hypothalamic & pituitary tumours?
Headache, seizures
Feeding & weight changes: Failure to thrive, loss of appetite, weight gain or loss
Energy and mood changes: euphoria, hyperactivity, fatigue, aggression
Cognitive changes: disrupted attention, memory problems
Hormonal changes like early puberty, sexual problems
where is the brainstem?
mesencephalon to myelencephalon
sometimes diencephalon is included
cerebellum isn’t a part of the brainstem
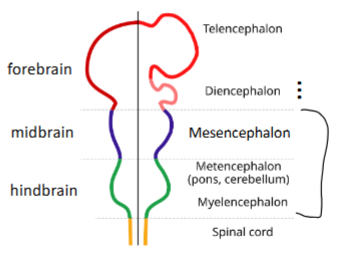
what are the components of the telencephalon?
is the cerebrum
basal ganglia
limbic system
cerebral cortex
what are the functions of the telencephalon?
largest division of the brain
mediates complex functions
initiates voluntary movement
interprets sensory input
mediates complex cognitive processes ex: learning, speaking, & problem solving