Chapter 18.3: Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Alcohols
alcohols are a homologous series of organic compounds which contain the hydroxyl functional group
Functional group of alcohol
hydroxyl group or —OH
alcohols are ________ liquids at room temperature and pressure
volatile
solubility of alcohols in water
they are soluble in water
but their solubility decreases and boiling point increases as their molecular size increase
why does the solubility of alcohols decrease
this is due to the forces of attraction increasing between the alcohol molecules
acidity of alcohols
they are neutral
alcohol + oxygen
carbon dioxide + water vapour
how can alcohol be oxidised to carboxylic acids
heat the alcohol with an oxidising agent like acidified potassium manganate (VII)
alcohol + oxygen from oxidising agent
carboxylic acid + water
how is ethanol manufactured
by the fermentation of carbohydrates
fermentation
a chemical process in which microorganisms such as yeast act on carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide
equation for fermentation of carbohydrates
C6H12O6 —> 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2
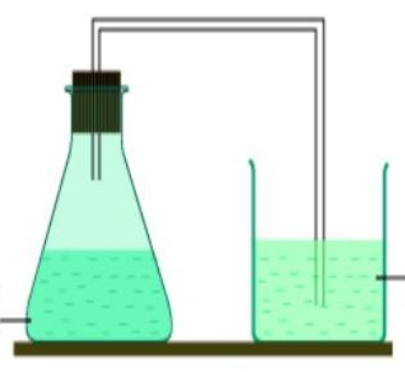
whats this setup for
the preparation of ethanol in the laboratory
purpose of limewater in prep of ethanol setup
to ensure that carbon dioxide was produced and that fermentation was taking place.
also to act as an airlock
how is ethanol extracted from the solution of carbon dioxide and a dilute solution of ethanol
fractional distillation
what happens when ethanol is exposed to oxygen
ethanol would be oxidised to ethanoic acid by bacteria in the air.
word equation for:
ethanol would be oxidised to ethanoic acid by bacteria in the air.
ethanol + oxygen from air —> ethanoic acid + water
how is the set up for fermentation of carbohydrates made air-tight
the rubber bung is secured tightly to the flask
limewater in the test tube prevent oxygen from entering the apparatus
functional group of carboxylic acids
carboxyl group -COOH
general formula for carboxylic acids
CnH2n+1COOH
carboxylic acids solubility in water
they are soluble
why are carboxylic acids weak acids
they ionise partially in water, therefore the concentration of H+ ions is low
carboxylic acids + reactive metal
salt + hydrogen
ethanoic acid + magnesium
magnesium ethanoate + hydrogen
carboxylic acid + carbonate
salt + carbon dioxide + water
carboxylic acid + base
salt + water
ethanoic acid + copper(II) oxide
copper(II) ethanoate + water
how can ethanoic acid be produced
oxidation with acidified potassium manganate(VII) or by atmospheric oxygen