Week 6 Part 2 - Microbiology of Wastewater Nitrogen Removal in Activated Sludge
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is the primary objective of treating wastewater?
To reduce the amount of harmful forms of nitrogen entering the environment.
What are the inorganic forms of nitrogen that are toxic to aquatic organisms?
NH4/NH3 and NO3.
What environmental issues are contributed by nitrogen compounds like NO2?
Ozone depletion, greenhouse effect, and acid rain formation.
What is 'blue baby' disease and what causes it?
A condition caused by nitrite (NO2) that affects infants, leading to reduced oxygen in the blood.
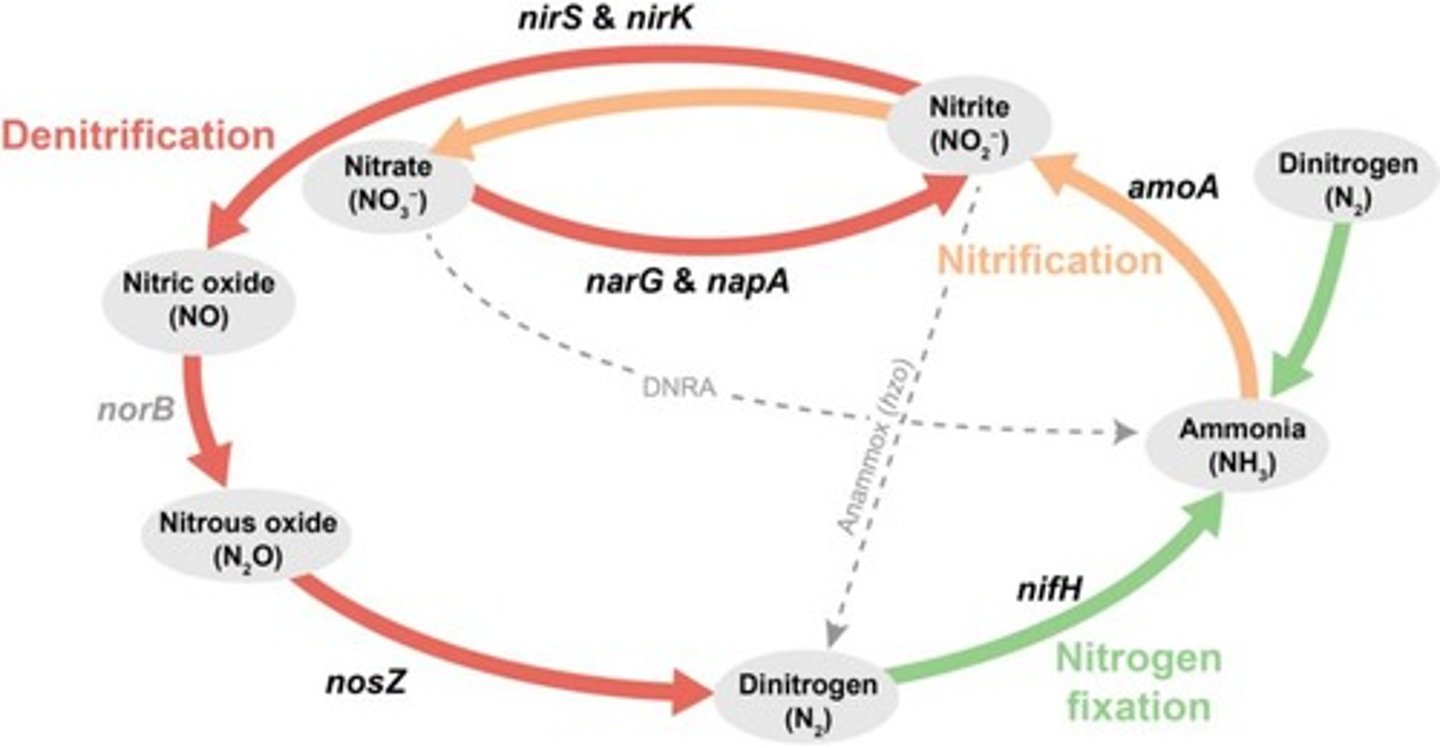
What is the significance of the nitrogen cycle in wastewater treatment?
Microbes convert harmful nitrogen forms into N2, which is less harmful.
What is the range of total nitrogen that enters wastewater treatment plants?
Between 20-80 mg l-1 total nitrogen.
What nitrogen concentration is mandated by EPA regulations in final treated effluent?
5-10 mg l-1 nitrogen.
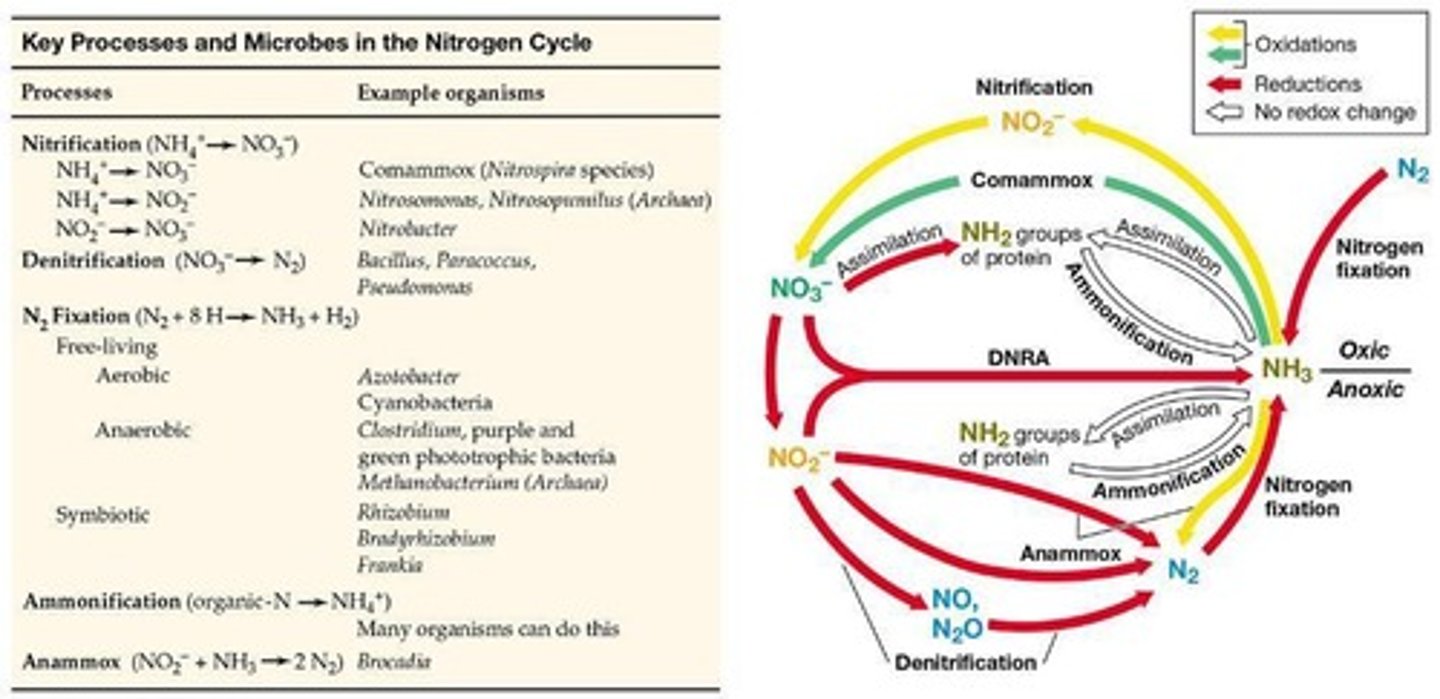
What are the two main processes involved in the microbiological removal of nitrogen?
Nitrification followed by denitrification.
What is nitrification?
The process where reduced nitrogen compounds like NH3 are oxidized to nitrate to supply energy for bacterial growth.
What type of bacteria are involved in ammonia oxidation?
Nitrosobacteria.
What do nitro bacteria do?
They oxidize nitrite to nitrate.
What are the characteristics of the bacteria that carry out nitrification?
They are aerobic chemolithoautotrophs that obtain carbon from CO2 and energy from inorganic nitrogen compounds.
What is the chemical equation for the oxidation of ammonia to nitrite?
2NH3 + 3O2 => 2NO2- + 2H2O + 4H+ + Biomass.
What are the genera of the Betaproteobacteria involved in ammonia oxidation?
Nitrosomonas, Nitrosospira, Nitrosovibrio, and Nitrosolobus.
What is the significance of archaeal ammonia oxidizers in wastewater treatment?
They possess amo genes related to ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and may be present in activated sludge.
What are the two groups of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria mentioned?
Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria.
What is the role of Nitrosomonas in the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrosomonas species are involved in the oxidation of ammonia to nitrite.
What is the energy yield from nitrification?
Very little energy, requiring slow-growing organisms with long residence times.
What is the importance of long sludge ages in wastewater treatment?
They favor the growth of slow-growing nitrifying bacteria.
What are the environmental impacts of nitrogen compounds in wastewater?
They can lead to eutrophication, acid rain, and health issues like 'blue baby' disease.
What is the relationship between nitrogen compounds and ozone depletion?
Nitrogen oxides contribute to the degradation of ozone in the atmosphere.
What is the role of microbes in the nitrogen cycle within activated sludge plants?
They convert harmful nitrogen forms into nitrogen gas (N2) through various biochemical processes.
What is the significance of the chemical reactions involving nitrogen in wastewater treatment?
They are crucial for reducing nitrogen levels and preventing environmental harm.
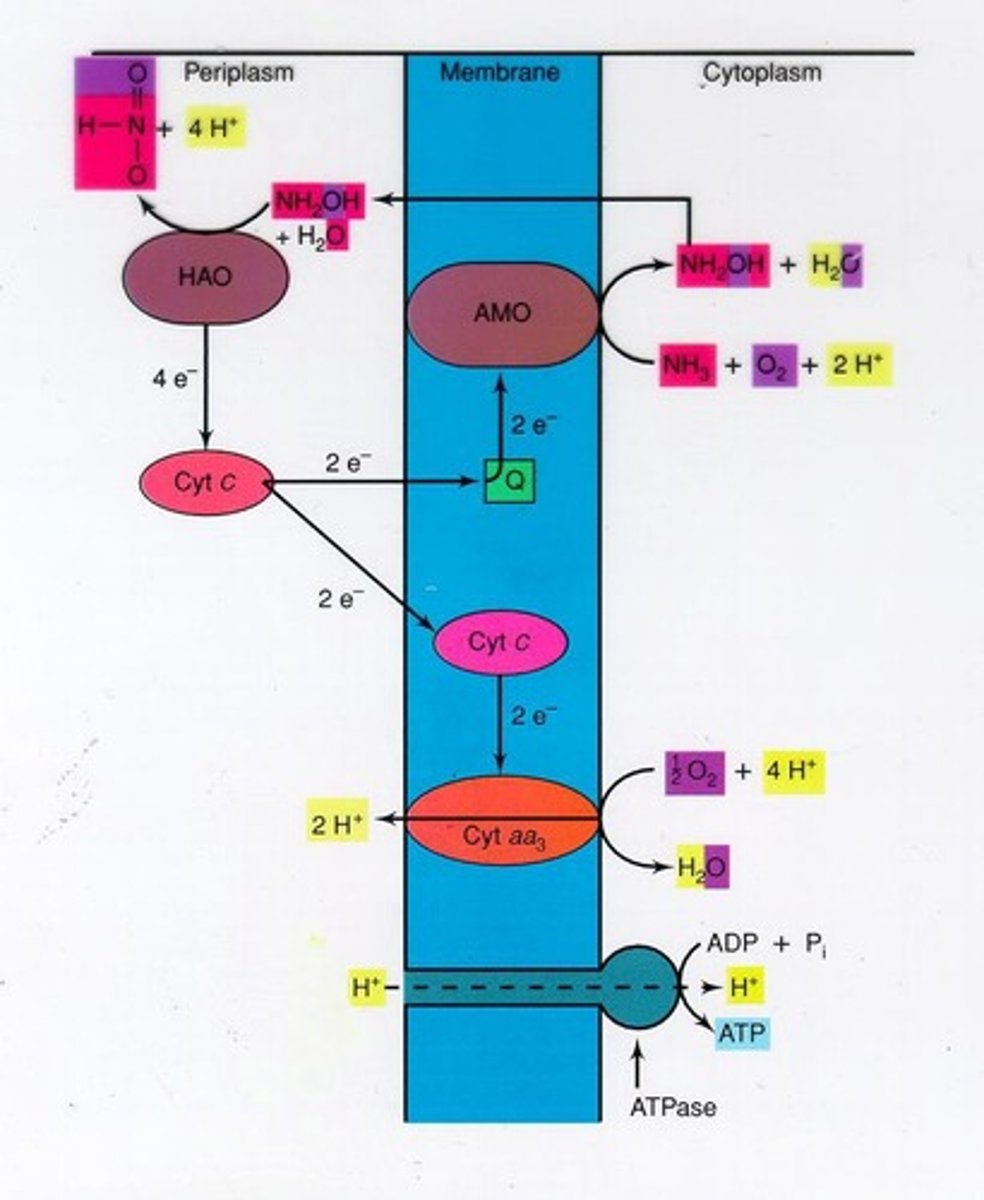
What is the first step in the biochemistry of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB)?
Ammonia + Oxygen + H → Hydroxylamine + Water, catalyzed by ammonia monooxygenase.
Where is the enzyme ammonia monooxygenase located in AOB?
In the cell membrane.
What is produced in the second step of AOB biochemistry?
Nitrite + Water + ATP, from Hydroxylamine + Oxygen, catalyzed by hydroxylamine oxido-reductase.
What is the source of oxygen in the second step of AOB biochemistry?
Water.
How do nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) differ from AOB in terms of energy requirements?
NOB require lots of ATP and often grow as heterotrophs using organic compounds.
What are the four recognized genera of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB)?
Nitrobacter, Nitrospira, Nitrococcus, and Nitrospina.
Which genus of NOB is considered the most diverse?
Nitrospira.
How many described species does Nitrospira have?
Two: N. marina and N. moscoviensis.
What is the significance of uncultured Nitrospira sequences found in various habitats?
They indicate phylogenetic diversity unrelated to other NOB and in a separate phylum.
What is the overall reaction catalyzed by nitrite oxido-reductase in NOB?
2NO2 + O2 → 2NO3.
What is the energy yield from the reaction catalyzed by nitrite oxido-reductase?
The energy yield is low.
What is the Modified Ludzak-Ettinger Process in nitrification?
It involves ammonia being converted to nitrite and then to nitrate in anoxic and aerobic zones.
What is the role of Nitrosomonas in activated sludge systems?
They are organized into clusters and can dominate depending on treatment plant conditions.
Which Nitrosomonas species are commonly detected in activated sludge?
Nitrosomonas europea and N. oligotropha.
What factors influence the distribution of Nitrosomonas AOB in treatment plants?
Type of treatment plant and operating conditions.
Why is Nitrosospira rarely detected in activated sludge plants?
It has a lower growth rate and is better adapted for low substrate concentrations.
What was previously thought about the main nitro bacteria in activated sludge?
Nitrobacter spp. were thought to be the main nitro bacteria.
What did FISH with probes targeting Nitrobacter reveal?
It failed to detect Nitrobacter in activated sludge.
How do NOB interact with AOB in activated sludge systems?
NOB remove toxic nitrite produced by AOB, creating a syntrophic relationship.
What does the 16S rRNA clone library reveal about NOB in activated sludge?
It indicates the presence of Nitrospira spp.
What is the significance of the phylogenetic diversity found in Nitrospira?
It suggests a complex evolutionary history and adaptation to various environments.
What is the ecological role of Nitrosococcus in treatment plants?
It is seen in plants receiving high ammonia loads.
What is the relationship between AOB and NOB in terms of energy supply?
AOB supply nitrite as an energy source for NOB.
What is denitrification?
The process where nitrate and/or nitrite are reduced to nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, and nitrogen gas.
What types of bacteria carry out denitrification?
Many phylogenetically different chemoorganoheterotrophic bacteria.
What is another name for denitrification?
Dissimilatory nitrate reduction.
What are the gaseous products of denitrification?
N2, NO, or N2O.
Why is the accumulation of N2O harmful?
N2O is 300 times worse than CO2 as an air pollutant.
What conditions are required for denitrification to occur?
An anoxic zone with no O2, plenty of NO3, and an organic carbon source.
What is the sequence of nitrate reduction in denitrification?
NO3 → NO2 → NO → N2O → N2.
What is the Anammox process?
A microbiological process for nitrogen removal where nitrite is converted to dinitrogen gas using ammonia as the electron donor.
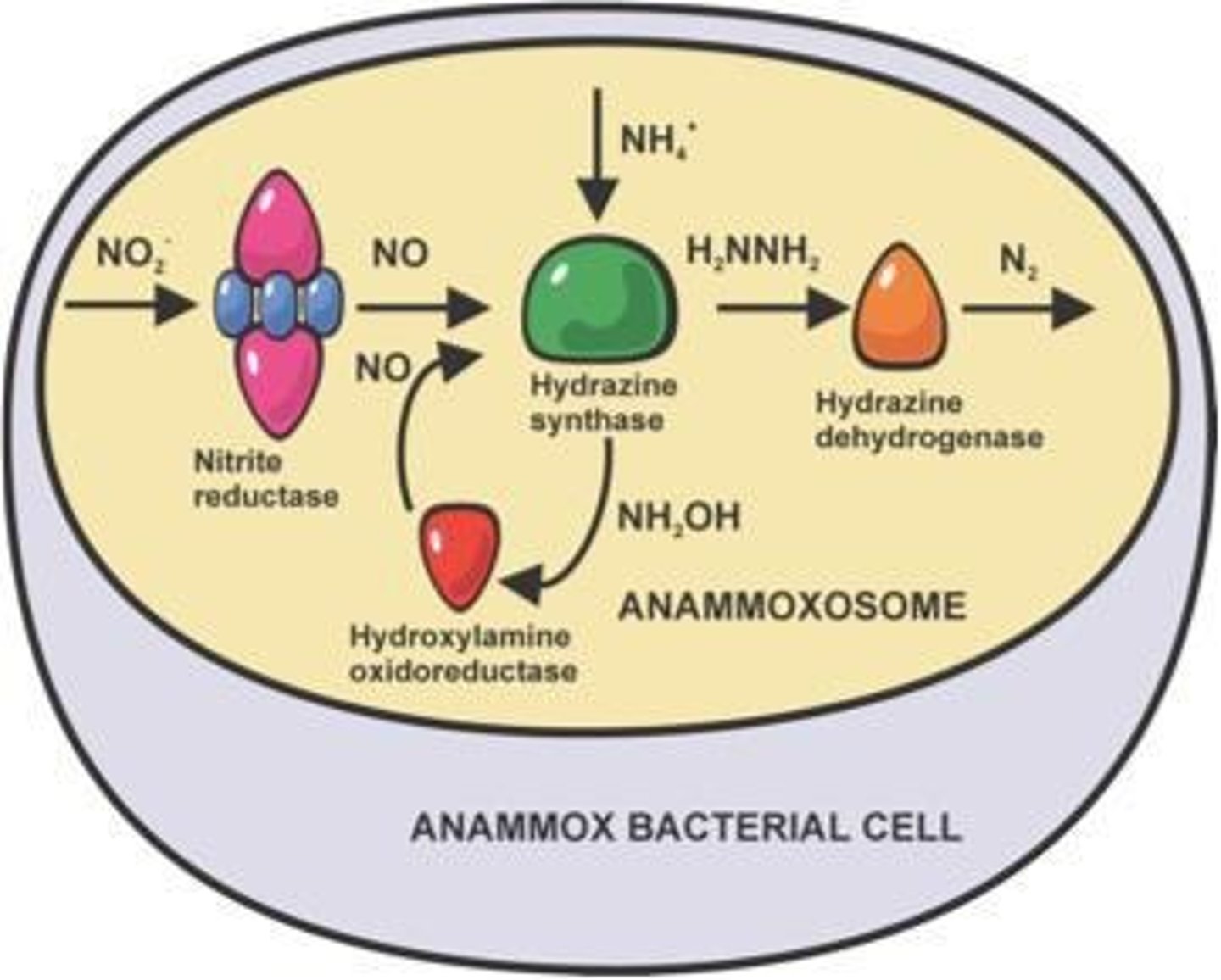
What is the chemical reaction for the Anammox process?
Ammonia + Nitrite → Dinitrogen + H2O (via hydrazine).
What unique cellular structure do Anammox bacteria possess?
An anammoxosome, which is surrounded by a membrane with unique lipids called ladderanes.
What is the role of hydrazine in the Anammox process?
Hydrazine is formed from NO and ammonium and is then oxidized to N2.
What is the significance of the genes nirS and nirK?
They encode nitrate reductase enzymes important for denitrification.
How can molecular methods be used in studying denitrification?
By profiling gene fragments using techniques like targeted Next-Gen sequencing or qPCR.
What is the Modified Ludzak-Ettinger Process?
A process involving denitrification and nitrification in an anoxic and aerobic zone.
What are the two zones involved in the nitrogen removal process?
Anoxic zone and aerobic zone.
What is the role of AOB in the Anammox process?
AOB can supply nitrite as an energy source for Anammox bacteria.
What is the significance of Planctomycetes in Anammox?
They are novel bacteria involved in the Anammox process and have not been grown in culture.
What is the environmental benefit of using Anammox for wastewater treatment?
It requires no carbon addition or aeration and is suitable for nitrogen removal from high ammonium content wastes.
What is the impact of denitrification on the nitrogen cycle?
It contributes to the removal of nitrogen from ecosystems by converting nitrates to gaseous forms.
What are the implications of using different carbon sources in denitrification?
Different carbon sources can favor different denitrifying populations, such as methylotrophic or Azoarcus/Thauera.
What is the relationship between denitrification and activated sludge systems?
Activated sludge systems can harbor various organisms capable of denitrification, but their importance in situ can be assessed with molecular methods.
What is the role of nitrite reductase in the Anammox process?
It oxidizes nitrite to nitric oxide (NO), which is a key step in forming hydrazine.