Biology 1801 Test 2- John Walker (AppState)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What are vacuoles?
large, membrane-bound structures found in plants and fungi
What are some functions of vacuoles?
Some are specialized for digestion, Most are used to store water and ions to help the cell maintain it normal volume- (turgor pressure), May contain pigments, & noxious compounds
Do plant cells have cell walls?
Yes
What are peroxisomes?
Little membrane-bound sphere
What are peroxisomes involved in?
Oxidation reactions (remove electrons) and production of free radicals
Where do peroxisomes originate from?
Buds from the ER
Oxidation often produces what?
Hydrogen peroxide
In peroxisomes, the enzyme catalase ________ it?
detoxifies
What do the mitochondria supply to the cells?
ATP
How many membranes does a mitochondria have?
2 membranes
The inner membrane is folded into a series of sac-like ______ in a mitochondria?
cristae
What is the solution inside the inner membrane of a mitochondria called?
Mitochondrial matrix
The space between the membranes in a mitochondria is called?
Inter-membrane space
Mitochondria have their own DNA called?
mtDNA
What do mitochondria manufacture their own of?
ribosomes
Most plant and algal cells have chloroplasts, where __________ takes place?
photosynthesis
How many membranes does a chloroplast have?
3 membranes
Innermost membrane contains flattened sacs called what?
thylakoids
Internal compartment in a chloroplast is called?
Thylakoid Lumen
Thylakoids are arranged in stacks called
grana
What surrounds the thylakoids ?
Stroma
What two things do chloroplasts do on their own?
Contain their own DNA and manufacture their own ribosomes
What is the endosymbiosis Theory
Bacteria were engulfed and a mutually beneficial relationship evolved
Evidence for the endosymbiosis theory
1. Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA
2. Synthesize their own small ribosomes
3. Grow and divide independently of cell division
4. Phylogenetic relationship to free living bacteria
What is the cytoskeleton composed of?
protein fibers
What does the cytoskeleton give cells?
Their shape and structural ability
What things does the cytoskeleton do?
1. Aids cell movement
2. Transports materials within the cell
3. Organizes the organelles and other cellular structures into a cohesive whole
Which type of cell requires an abundance of mitochondria?
A) Plant Leaf Cell
B) Animal Pancreatic Cell
C) Animal Testes Cell
D) Animal Muscle Cell
Answer- D
Your body's cells use and synthesize approximately ________ ATP molecules per second
10 million
Cellular enzymes can catalyze more than ______ reactions per second
25,000
Each membrane ________ can travel the breadth of its organelle or cell in under a minute
phospholipid
_____________ of mitochondria are completely replaced about every 10 days
Hundreds of trillions
Exocytosis
Export of a substance out of a cell by formation of a membrane-bound vesicle
Lysosomes digest large molecules so ___________ can be used/recycled
monomers
Endocytosis
Materials are brought into the cell by pinching off the plasma membrane
Examples of endocytosis
1. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
2. Phagocytosis - engulfing large particles, bacteria etc.
What are the three types of cytoskeleton elements?
actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
Actin Filaments
Smallest, formed from actins, two twisted strands
Interacts with myosin (motor protein)
Cell shape, movement
Intermediate Filaments
1. Provide structural support for the cell
2. Nuclear lamins Give the nucleus its shape and organize chromosomes
Microtubules
1. Largest, tubular and is composed of tubulin
2. Provide a structural framework for organelles
3. Are involved in movement Separate chromosomes during cell division and serves as "railroad tracks" for vesicle transport
Which cytoskeletal element is involved directly in muscle contraction?
Actin
Cells produce ______________ of distinct proteins
tens of thousands
8 vital, tremendously versatile components of cells
1. Hair and Nails
2. Blood
3. Brain and nerves
4. Enzymes
5. Cellular construction workers
6. Muscles
7. Cellular messengers
8. Antibodies
Parts of Amino Acid: central C, amino, carboxyl, residue or side chain
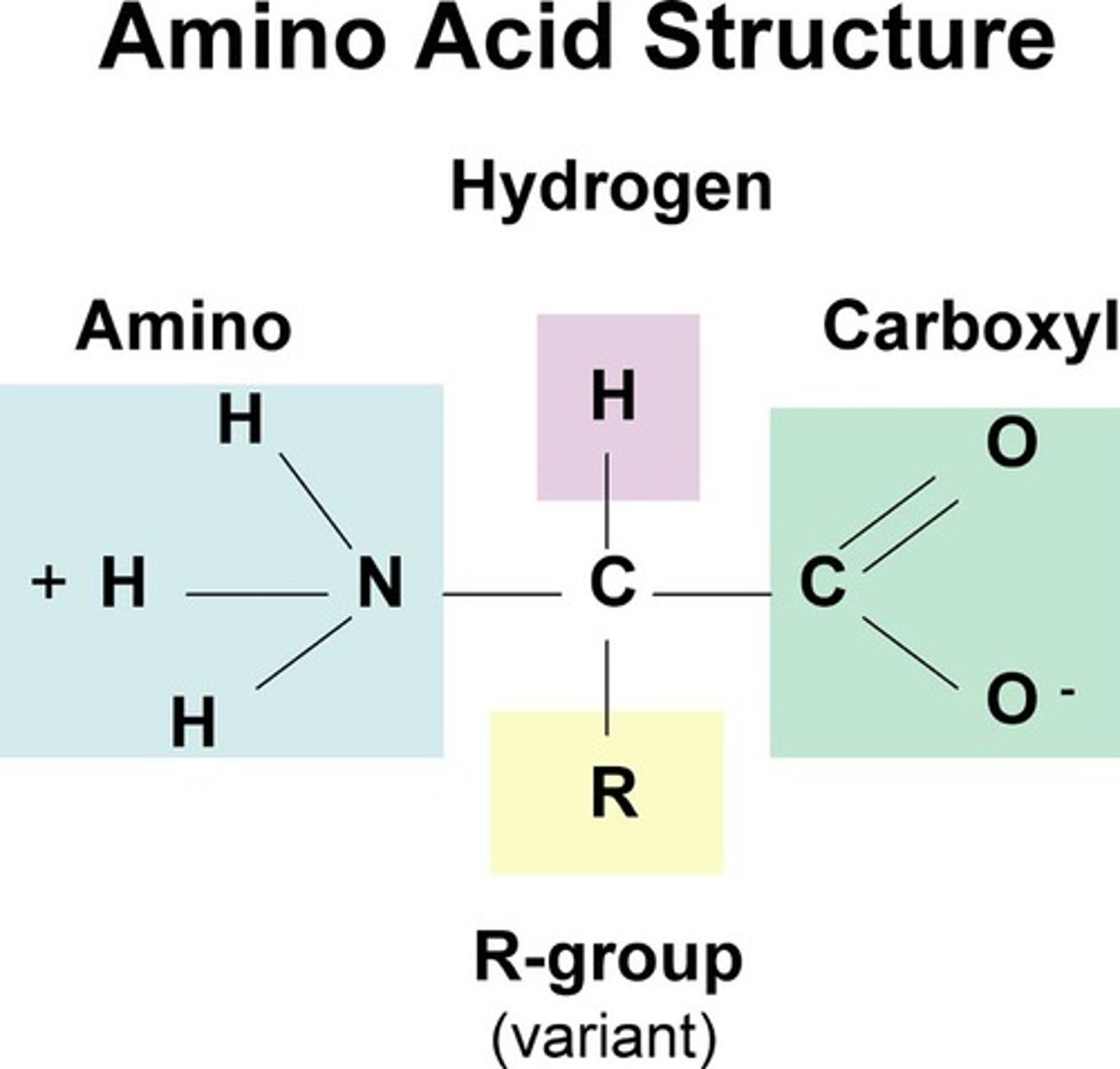
The properties of amino acids are determined by their _________
R-groups
Side chains can be grouped into what three types?
1. Charged—includes both acidic (-) and basic (+)
2. Uncharged polar
3. Uncharged non-polar
Charged and polar side chains are hydrophilic or hydrophobic: They interact readily with water
Hydrophilic
Non-polar side chains are hydrophobic or hydrophilic: They do not interact with water
Hydrophobic
There are 20 common amino acids. The distinguishing feature that makes each one unique is?
The nature of the R-group
Are proteins macromolecules?
Yes
Macromolecules are large molecules made of smaller subunits
Subunits are called _______ ("one-part")
Monomers link together (polymerize) to form ________ ("many-parts")
monomers, polymers
Amino acids are the __________ that make up proteins
monomers
Monomers polymerize through _______________, which results in the loss of a water molecule and hydrolysis is the inverse reaction
condensation (dehydration synthesis) reactions
Dehydration reaction is a type of ___________ reaction.
condensation
Amino acids ________ when a bond forms between a ________ group of one amino acid and an _________ group of another
polymerize, carboxyl, amino
The resulting C-N bond is called a?
peptide bond
Peptide bonds are formed by hydrolysis
False
Peptide bonds form a "backbone" with?
1. R-group orientation
2. Directionality
3. Flexibility
A chain of many amino acids is a ___________ ("many-peptides")
polypeptide
___________ are the complete, functional form of the molecule
Proteins
What do proteins look like?
unparalleled diversity of size, shape, and chemical properties
Proteins have just four basic structures:
1. Primary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
4. Quaternary
Protein _______ _______ is its unique sequence of amino acids
primary structure
The amino acid ___________ affect a polypeptide's properties and function
R-groups
A single amino acid change can radically alter ________ function
protein
Protein secondary structure is formed by ________ bonds between certain amino acids (carbonyl group - amino group)
hydrogen
2 Types of secondary structure in proteins
1. α-helices
2. β-pleated sheets
Which level of protein structure includes α-helices & β-pleated sheets?
Secondary structure
The tertiary structure of a polypeptide results from?
1. Interactions between R-groups
2. Or between R-groups and the peptide backbone
3. Bending and folding contribute to the distinctive three-dimensional shape of the polypeptide
Five important types of R-group interactions:
1. Hydrogen bonds
2. Hydrophobic interactions
3. Van der Waals interactions—weak electrical interactions between hydrophobic side chains
4. Covalent disulfide bonds—form bridges between two sulfhydryl groups
5. Ionic bonds
The bonding of two or more distinct polypeptide subunits produces _______________
quaternary structure
Some cells contain _______________ - Groups of multiple proteins that carry out a particular function
molecular machines
The bonding of two or more distinct polypeptide subunits produces which level of structure?
Quaternary
Protein folding is often spontaneous or non-spontaneous?
spontaneous
Proteins called __________ help proteins fold correctly in cells
molecular chaperones
A ____________ (unfolded) protein is unable to function normally
denatured
__________ in proteins can be "infectious"
Misfolding
________ are improperly folded forms of normal proteins
Prions
__________ may be the most important protein function
Catalysis
An _________ is a protein that functions as a catalyst
enzyme
The location on an enzyme where substrates bind and react is the?
active site