Behaviourist approach : Approaches
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
When did the behaviourist movement begin and who by?
John Watson (1913)
What is the behaviourist approach?
A theory of learning which states all behaviours are learned through interaction with environment through conditioning.
What are the 5 basic assumptions of the behaviourist approach?
1. All behaviour is learned from the environment
2. Psychology should be seen as a science
3. Behaviourism is primarily concerned with observable behaviour, as opposed to internal events; thinking and emotion.
4. Little differences between learning in humans and animals
5. Behaviour is a result of stimulus response.
What are the 2 types of behaviourism?
1. Methodological Behaviourism
2. Radical Behaviourism
Who is Pavlov?
He discovered classical conditioning
What is classical conditioning?
A type of learning in which an existing involuntary response is associated with a new stimulus.
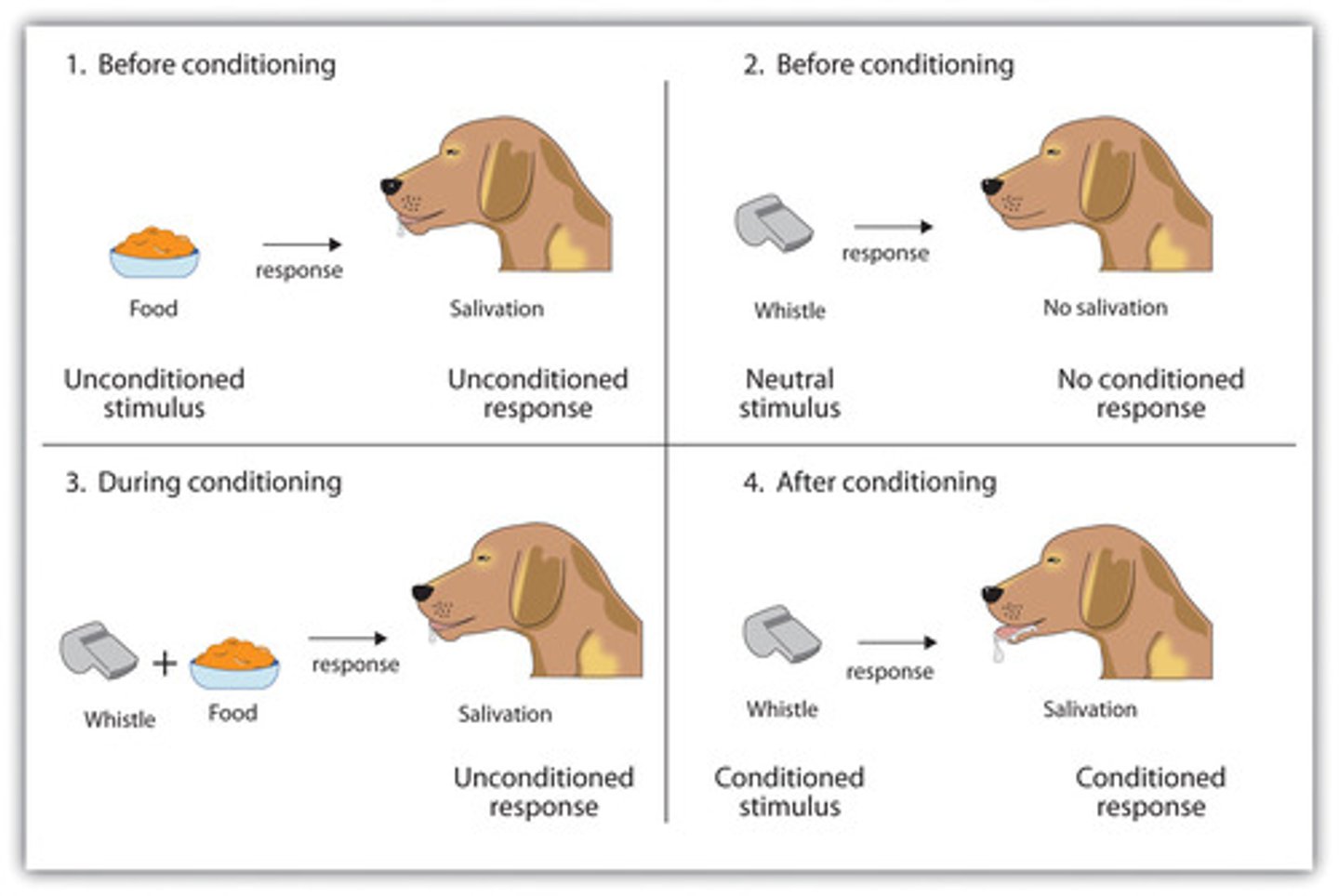
Outline Pavlov's experiment?
Classically conditionened dogs to salivate to the sound of a bell if that sound was repeatedly presented at the same time as they were given food they eventually associate the bell with food
Who is Skinner?
He discovered operant conditioning
What is operant conditioning?
a type of learning in which a new voluntary behaviour is associated with a consequence - positive reinforcement makes the behaviour more likely to occur, while punishment makes it less likely to occur.
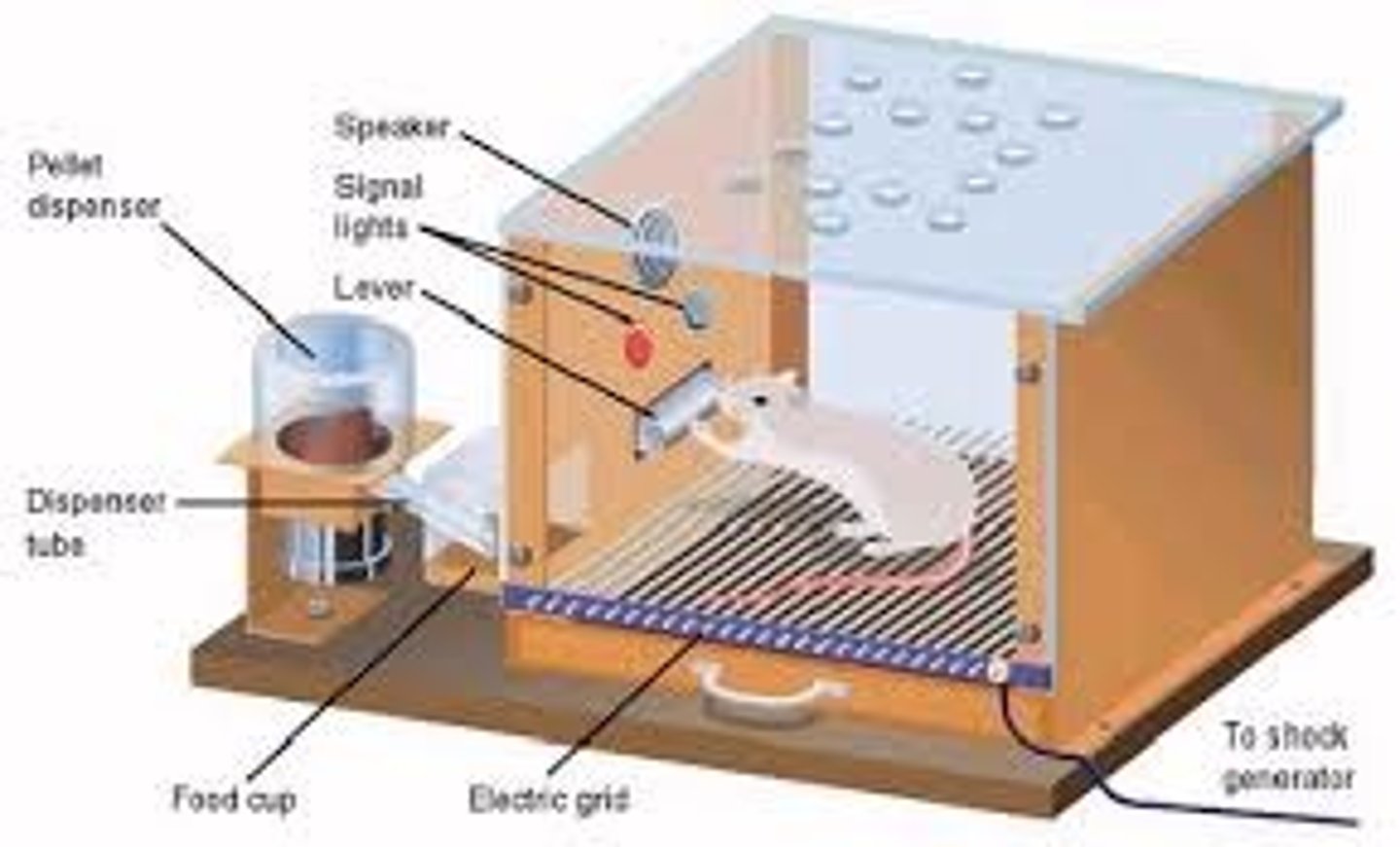
Outline Skinner's research?
- researched reinforcement using the Skinner box, where rats were positively reinforced with food when they pressed a lever, and some negatively reinforced when they pressed the lever an electric shock would disperse, this meant that the rats repeated the desired behaviour and would not push lever in negative condition
- also found that if the rat was not enforced regularly, they forgot the operant conditioning, this is known as extinction.
What are the 3 types of responses in operant conditioning?
1. Neutral operants
2. Reinforcers
3. Punishers
What are neutral operants?
responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of a behavior being repeated.
What are reinforcers?
Responses from the environment that increase the probability of a behavior being repeated. Reinforcers can be either positive or negative.
What are punishers?
Responses from the environment that decrease the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. Punishment weakens behavior.
What is positive reinforcement?
adding something into the situation that increases the tendency to repeat the preceding behaviour.
What is negative reinforcement?
taking something away from the situation that increases the tendency to repeat the preceding behaviour.
What is positive punishment?
adding a stimulus to stop a behavior from happening.
What is negative punishment?
removing a stimulus to stop a behavior from happening.
What are the 5 schedules of reinforcement?
1. Continuous
2. Fixed Ratio
3. Fixed Interval
4. Variable Ratio
5. Variable Interval
What is a strength of the behaviourist approach
Research is scientific, meaning it can be replicated, adding sustanance to the theory
What is a weakness of the behaviourist approach
Hard to generalise, samples are small and the control groups are animals making it difficult
What is a study done linked to humans
Little albert, white rats, conditioned to be scared of them as they were repeatedly paired with a loud bang.
What is an issue with the behaviourist approach
Hard deterministic approach, suggests humans have no free will of their behaviour and that all behaviour is determined from our upbringing. Also ignores biological factors such as genes