Biology: exam style questions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Explain what happens to animal cells when their tissue is placed in water.
The cells burst because of the water entering the cell through osmosis.
A student investigates how the type of fertiliser affects the rate of growth of a plant.
Give two abiotic variables that should be controlled in this investigation.
Type of soil
Volume of fertilizer
Give the balanced chemical symbol equation for aerobic respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Explain why carbon monoxide is harmful to humans.
Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin more strongly than oxygen. This reduces oxygen transport.
Define tissue.
A group of similar cells working together for a shared function.
Explain three adaptations of a red bloods cell for the transport of oxygen.
Biconcave shape which provides a large surface area.
Lots of haemoglobin to bind to oxygen
No nucleus which provides more space for haemoglobin
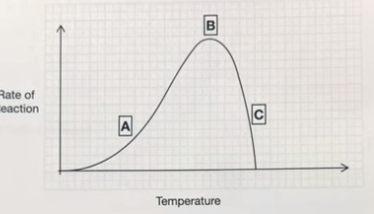
The graph shows how the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction changes with temperature. Explain the shape of the graph at area C
The enzyme is past its optimum temperature which instantly decreases the rate of reaction because the enzymes have become denatured. This means that substrate molecules can no longer bind to the active site.
Define diffusion.
The movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Define osmosis
The movement of water particles from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane.
Define active transport
The movement of ions from a region of lower to higher concentration using energy from respiration.
Explain the consequences for living organisms of air pollution by sulphur dioxide.
Sulfur dioxide dissolves in water vapour and forms sulfuric acid, which falls as acid rain. This causes damage to plants and aquatic organisms.
Give the balance chemical symbol equation for photosynthesis.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Describe the safe procedure to test a drink for the presence of reducing sugars.
Wearing safety goggles, add 2cm3 of Benedict’s reagent to 2cm3 of the drink sample. Place it into a hot water bath. A colour change from blue to green/yellow/orange (or a brick red precipitate forming) indicates the presence of reducing sugars.
Explain why the wall of an artery is thicker than the wall of a capillary.
Arteries carry blood at higher pressure and carry more blood. They have more muscle and elastic tissue. Arteries also need to be able to expand.
Explain how human tissue allows efficient gas exchange.