Rome and the Medieval East
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Acropolis
The citadel or fortress of an ancient Greek city, typically built on a hill

Atrium
the formal entrance hall of an ancient Roman house, open to the sky at the center and often featuring a pool for the collection of rain water
in a basilica church, a colonnaded courtyard preceding the entrance
In contemporary architecture, an inner courtyard located near the entrance to a building, often lit with skylights
Arch
In architecture, a curved structural element that spans a space
Nave
the central space of a church. In a basilica church, the nave is usually flanked by aisles
central aisle
the wider, central aisle of a basilica
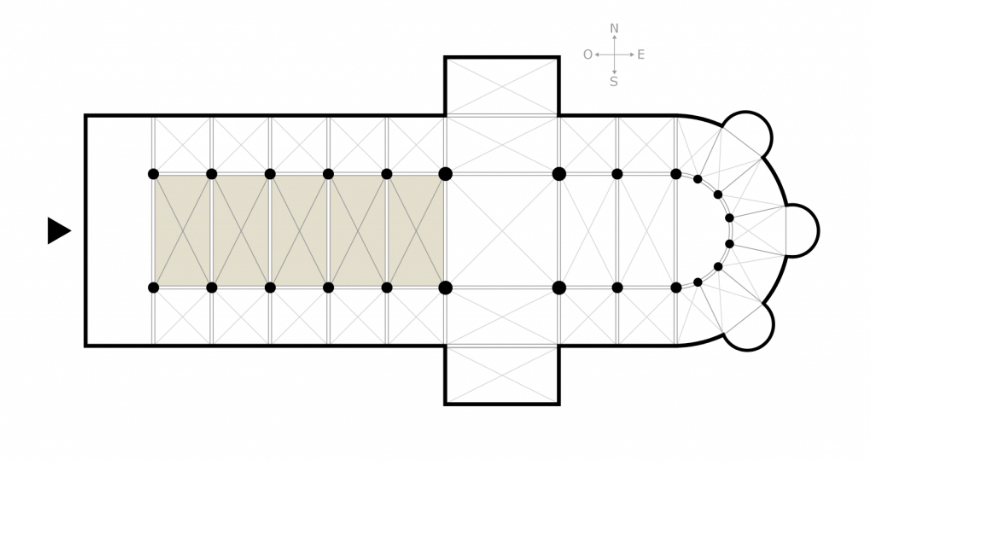
Forum
in ancient Roman urban planning, the city center. An open space used for markets and gatherings of citizens, surrounded by temples and public buildings
a large, rectangular space surrounded on all sides by a colonnade. Used as a gathering space
Roman cities were typically focused on the forum. It was a alrge open plaza surrounded by important buildings
Ionic
a style of classical architecture characterized by its slender, fluted columns and scroll-like ornaments at the capital.
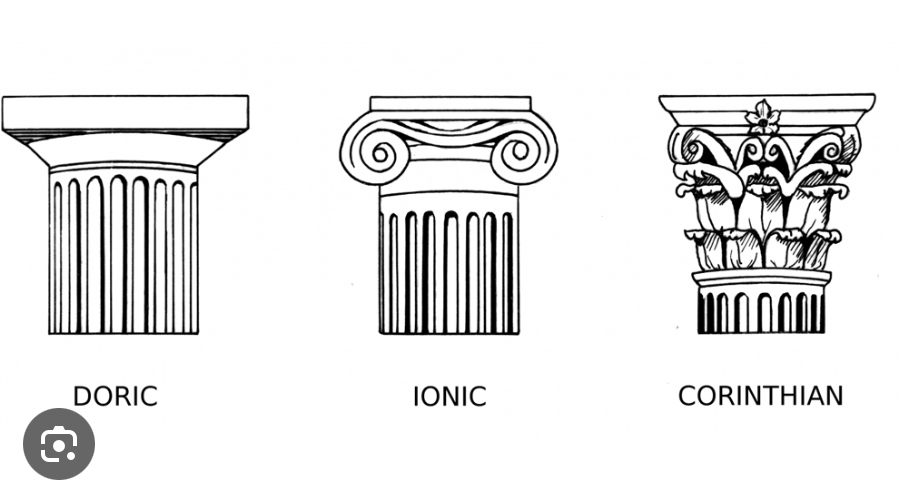
Doric
a style of classical architecture known for its sturdy, fluted columns and simple, plain capitals, representing strength and functionality.
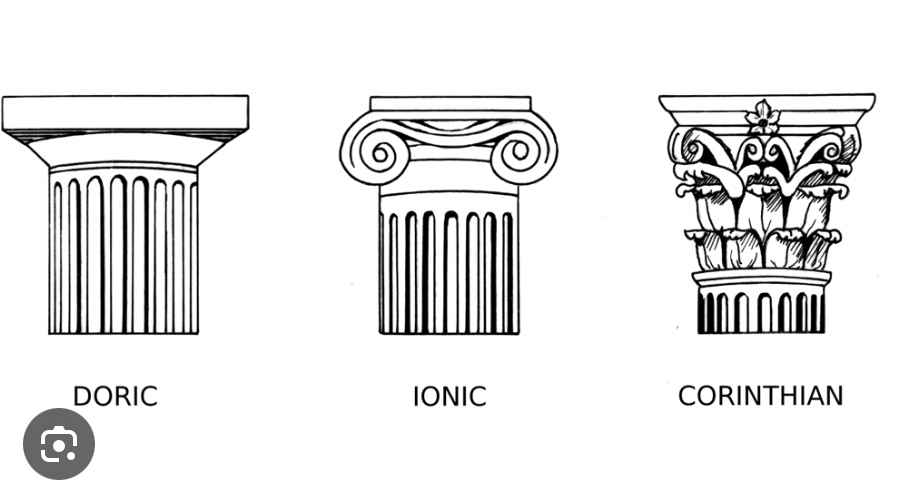
Corinthian
one of the three orders of ancient Greek architecture. The Doric was the earliest of the orders to develop, appearing ca. 580 BCE in the Archaic Temple of Artemis at Corcyra
Mosaic
a medium in which small, roughly cubic pieces of colored material (usually stone or glass) are embedded in mortar to create patterns or images. The small pieces are called tesserae.
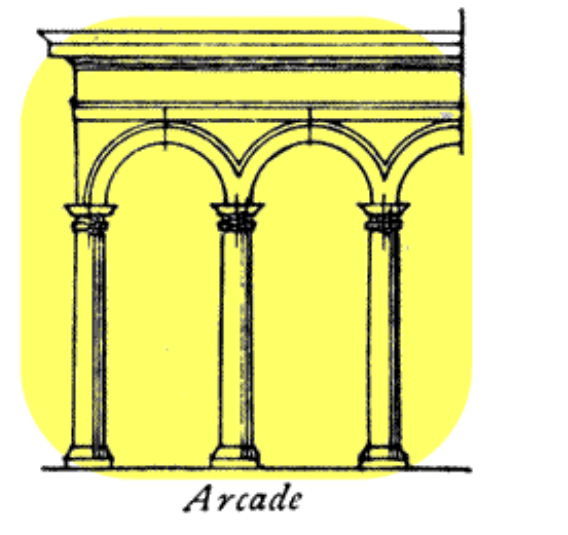
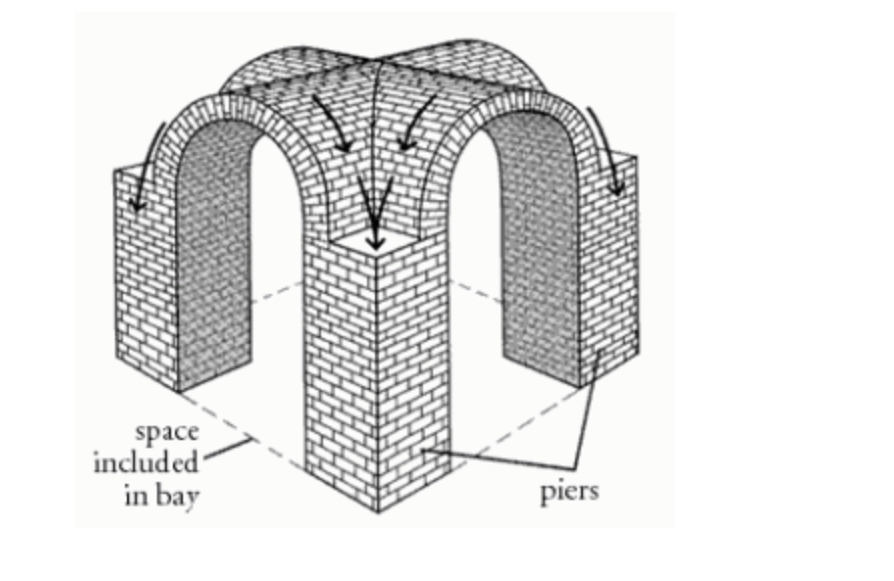
Arcade
a series of arches carried by columns or piers
often created a covered walkway or passage.
Barrel vault
(also known as a tunnel vault.) An elongated or continuous semicircular vault, shaped like a half-cylinder.
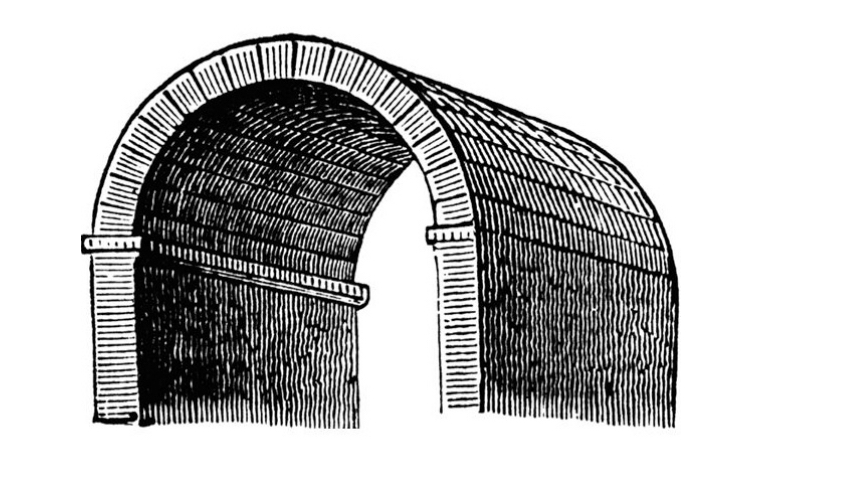
Groin vault
(also known as a cross vault). A vault formed by the intersection of two barrel vaults
Basilica
a large public building, rectangular in plan, normally featuring a nave flanked by aisles, and an apse. In ancient Roman architecture, basilicas were secular buildings, used as law courts and markets, and for public assemblies. The basilica plan was also commonly used for Christian church buildings beginning in the fourth century
For the Catholic church, starting in the 18th century, the term basilica took on a canonical sense, irrespective of the architectural style of the building. Certain churches are granted the status of major or minor basilica, which brings with it privileges and precedence over other churches.
a large public building for legal and other civic proceedings, rectangular in plan, with an entrance usually on a long side
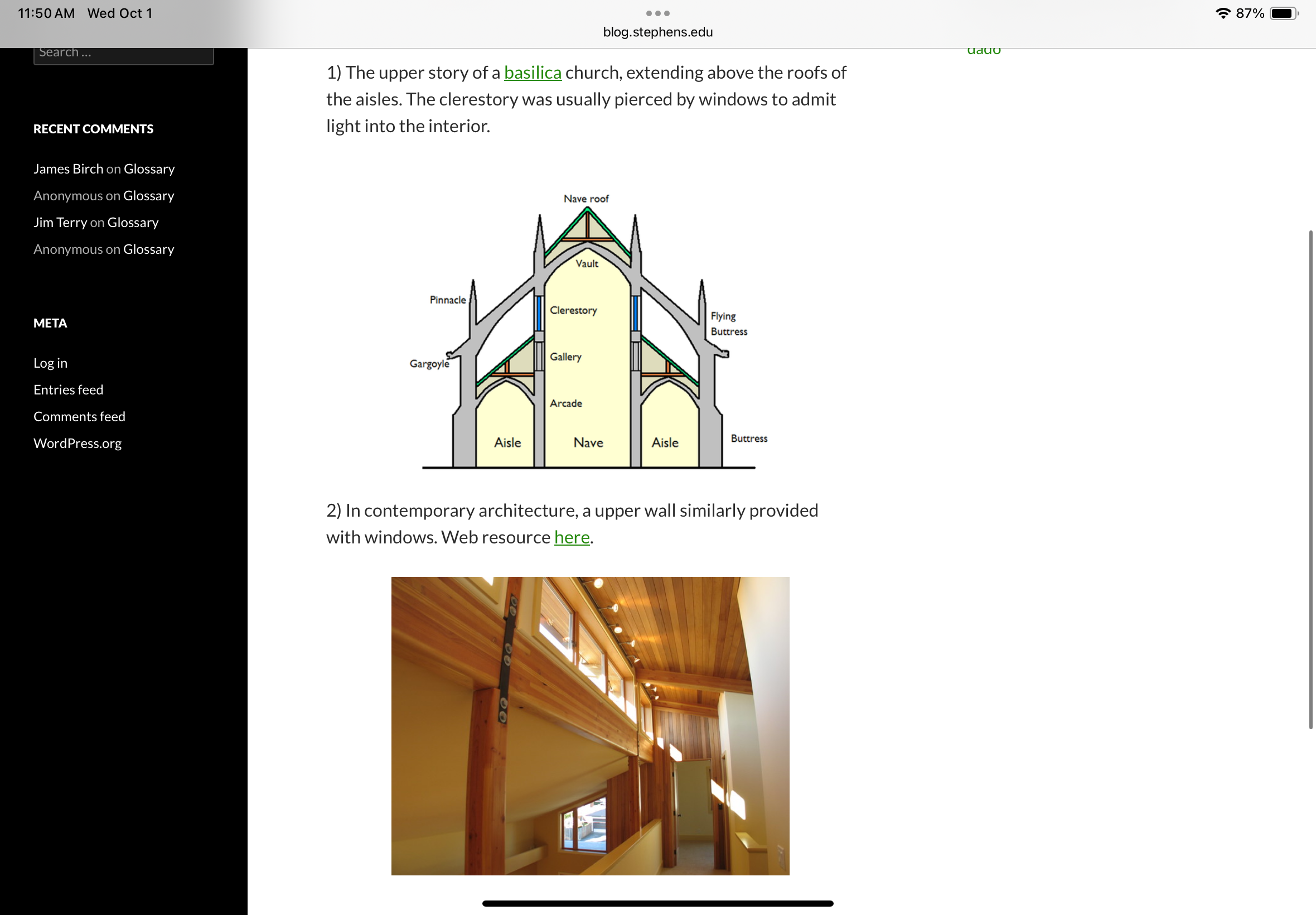
Clerestory
the upper story of the basilica church, extending above the roofs of the aisles. The clerestory was usually pierced by windows to admit light into the interior.
In contemporary architecture, a upper wall similarly provided with windows
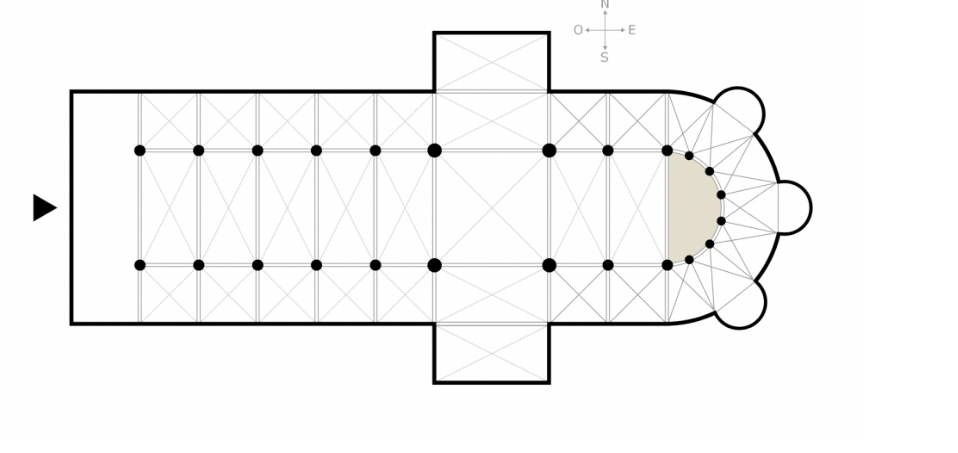
Apse
any semicircular or polygonal recess in a building
In a basilica church, the primary apse is found at the east end of the building, to the east of the chancel
semi-circular recesses in the wall of a building
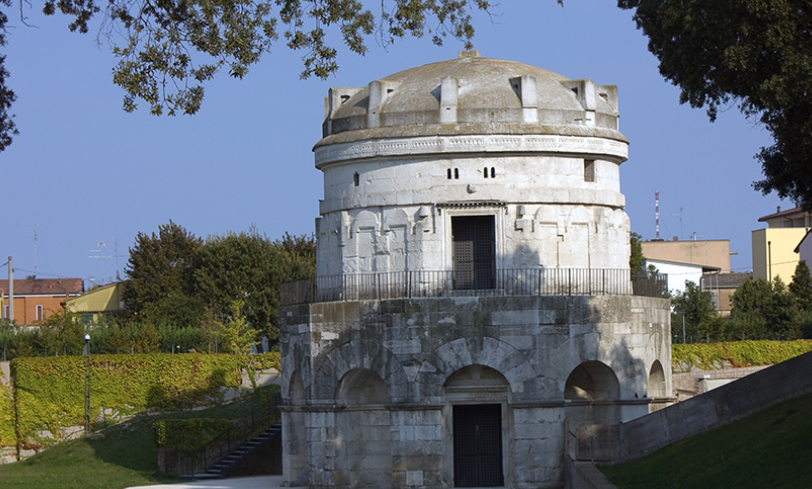
Mausoleum
A freestanding building constructed as a monument and housing the dead body of an important person or the bodies of multiple people

Manuscript
a book or document written by hand. A manuscript in which the text is supplemented by paintings is called an illuminated manuscript

Illuminated manuscript
A manuscript that is decorated with gold, silver, or brightly colored illustrations and designs.
books that contain certain artistic decoration
Codex
a manuscript in the form of a bound book (as opposed to a scroll)
a medieval manuscript/book made of pages bound between 2 boards. They’re protected by their cover and have a much greater chance of survival
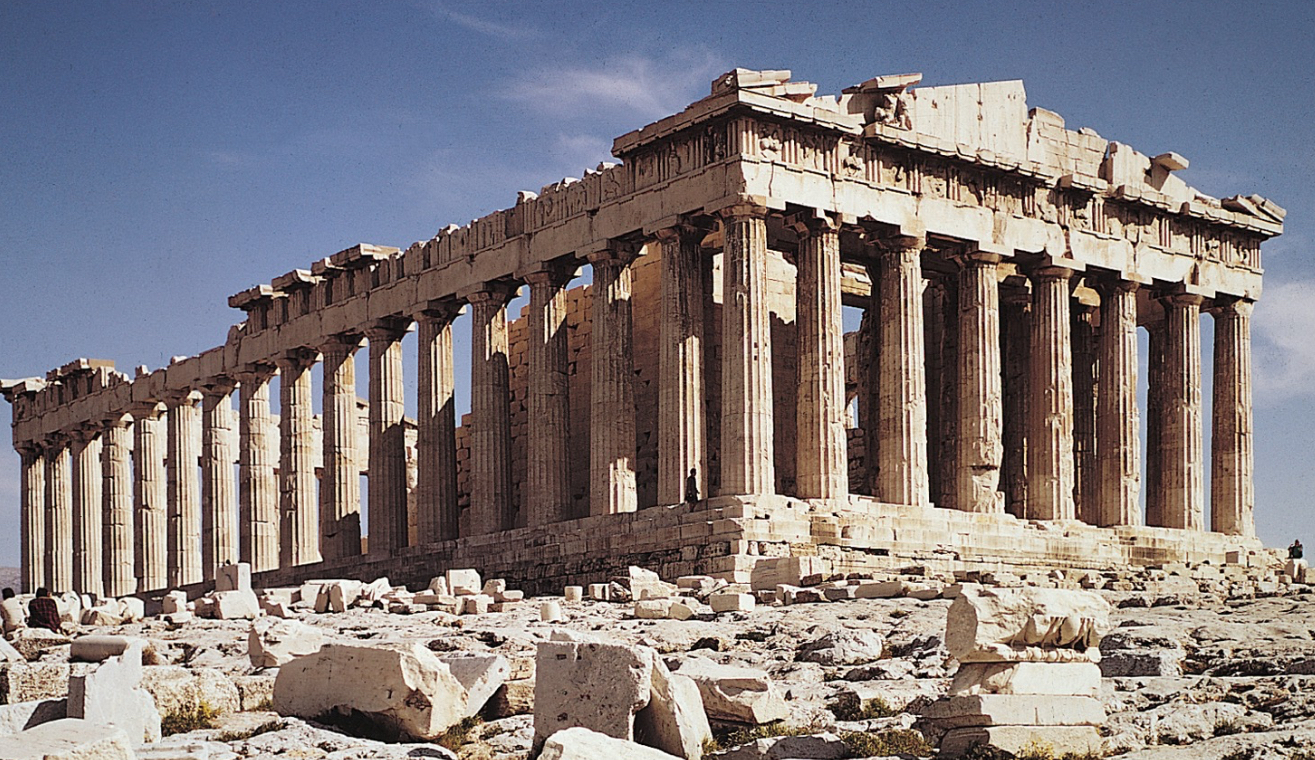


Parthenon, by architects Iktinos and Kallikrates, 5th century BCE (Ancient Greece)
is a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena, symbolizing the power and culture of Athens.
building using old building technologies. The structure features Doric columns and uses a post and lintel.
was built on the site of early temples that were destroyed by the Persians
Hellenistic and Roman adapatations
In Late Antiquity the Parthenon became the Christian Church
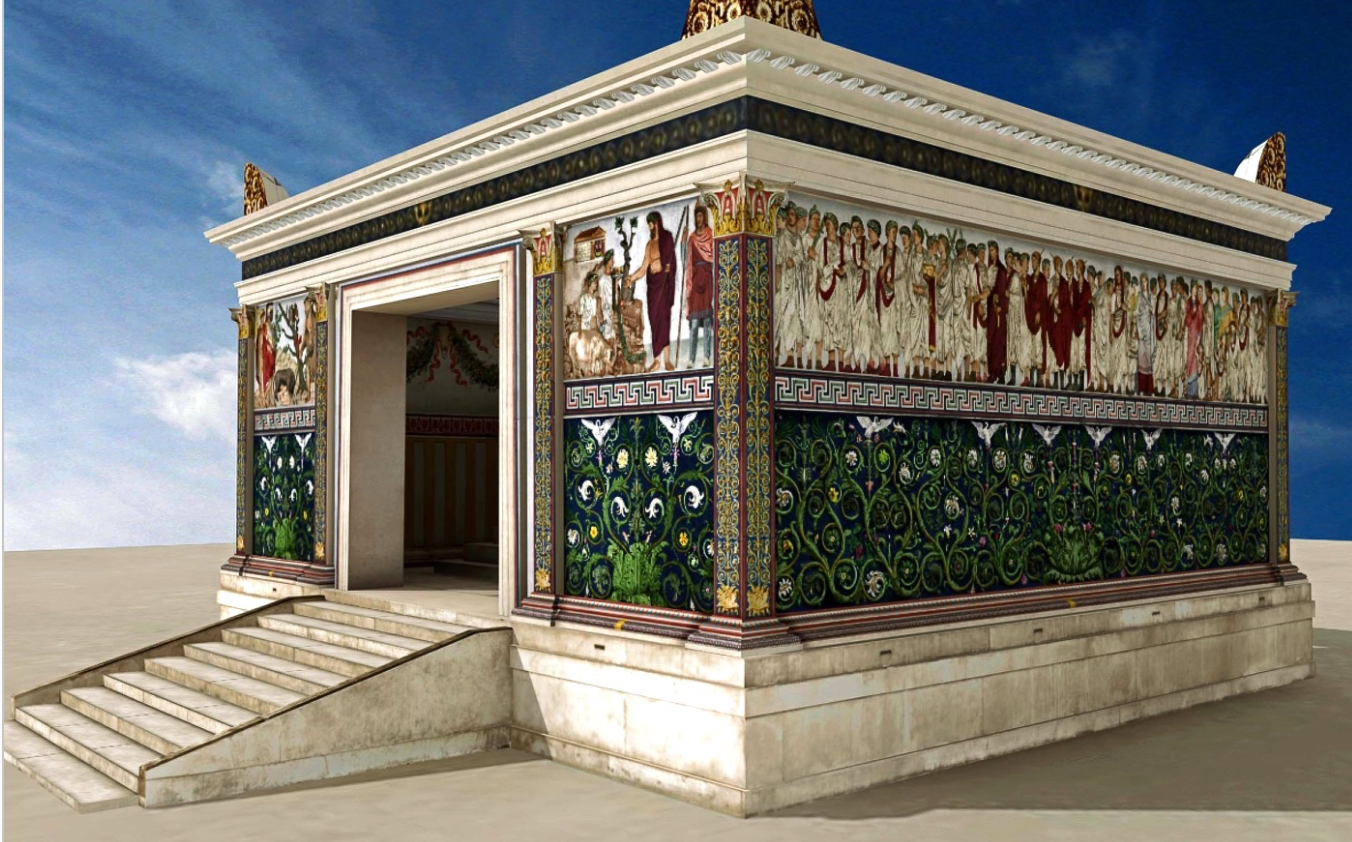

Ara Pacis, Rome, early 1st century BCE (Ancient Rome)- color reconstruction
of the Altar of Peace, celebrating Emperor Augustus' victory and promoting peace in the Roman Empire.
Also used a program of propaganda to convey Augustus' positive image and legitimacy as ruler/propaganda for Augustus and his family.
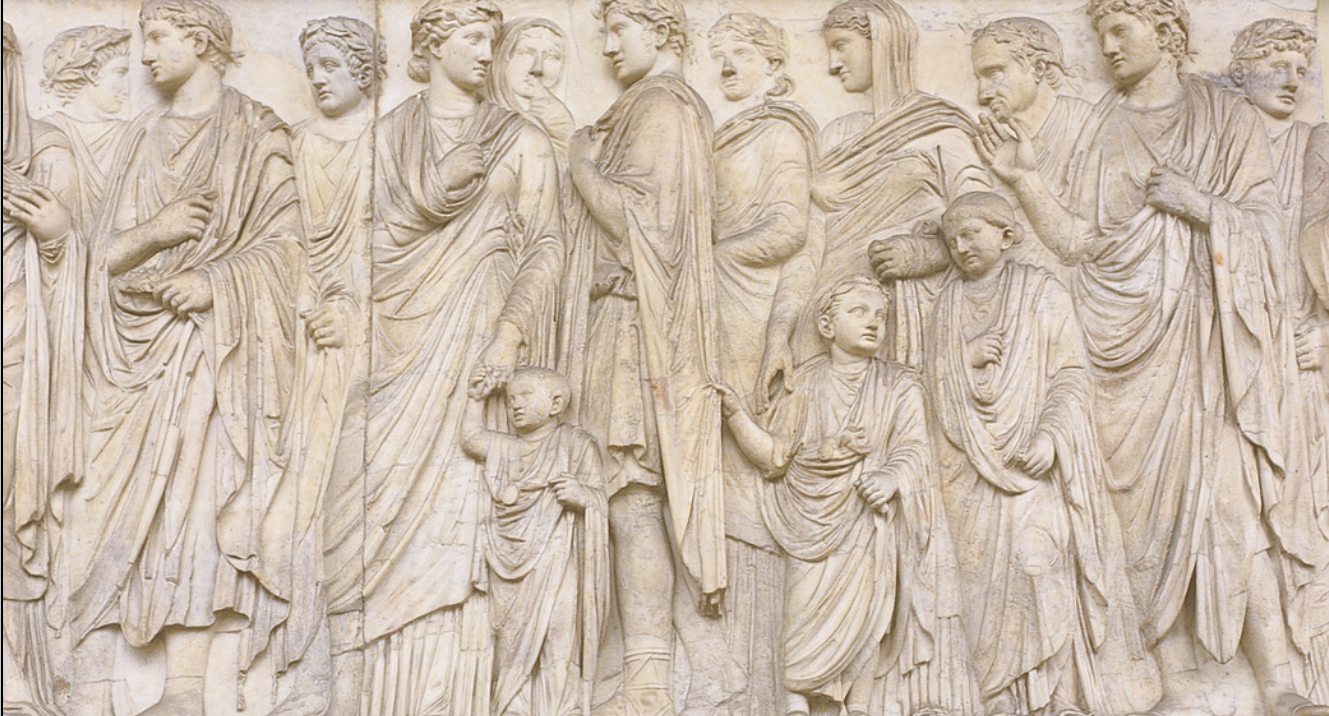

Procession of imperial family, detail from the Ara Pacis Augustae, Rome, late 1st century BCE (Ancient Rome)
This commemorates a historical event that celebrated the peace brought by Augustus after civil wars.
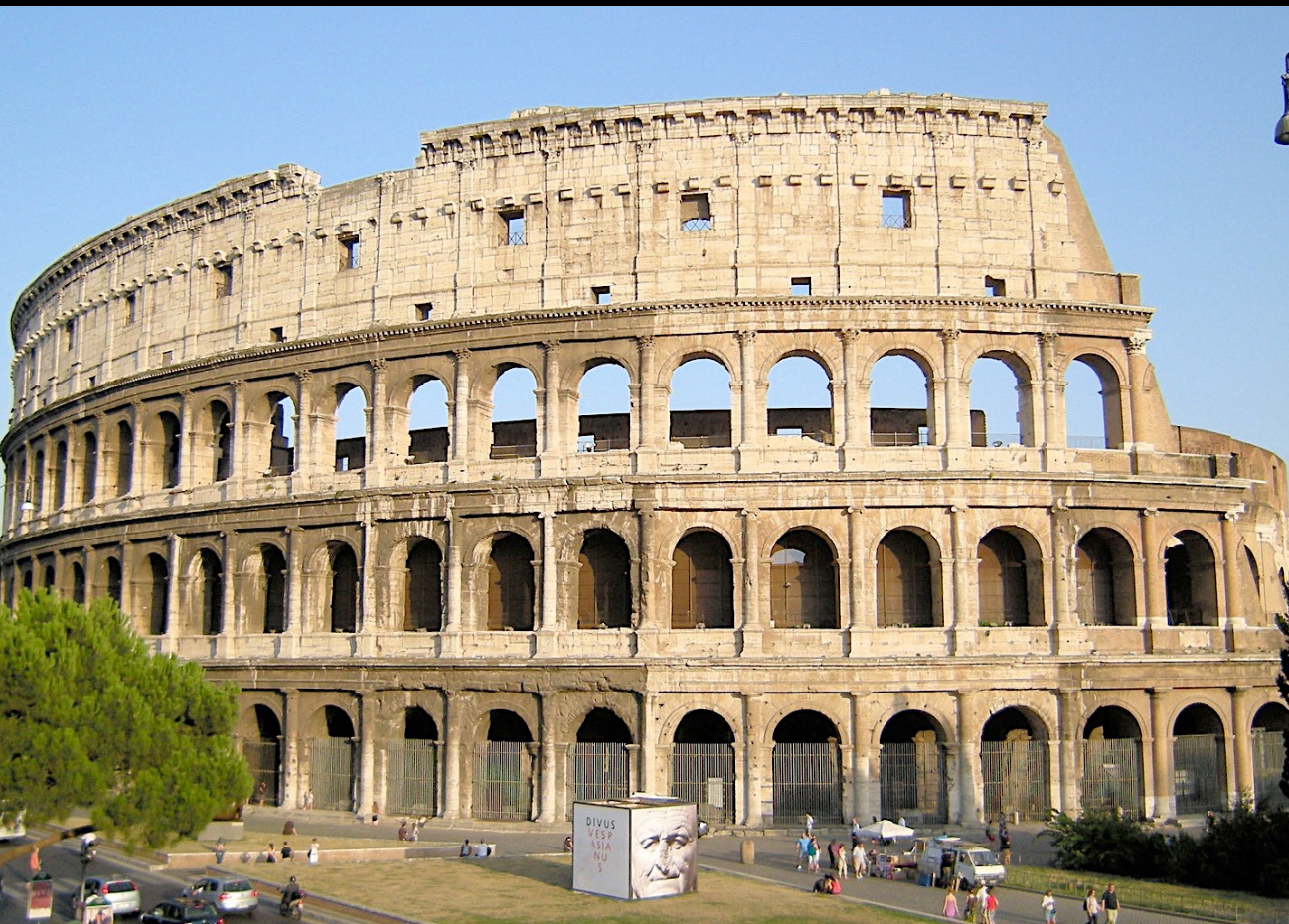

The Colosseum, Rome, 1st century CE (Ancient Rome)
also known as The Flavian Amphitheatre
It hosted various public spectacles, including gladiatorial contests and animal hunts.
has 3 tiers and it gets more complex as it goes up
advanced engineering with its elliptical shape and complex series of vaults. It could seat tens of thousands of spectators, demonstrating the grandeur of Roman entertainment.
has barrel vaults and groin vaults
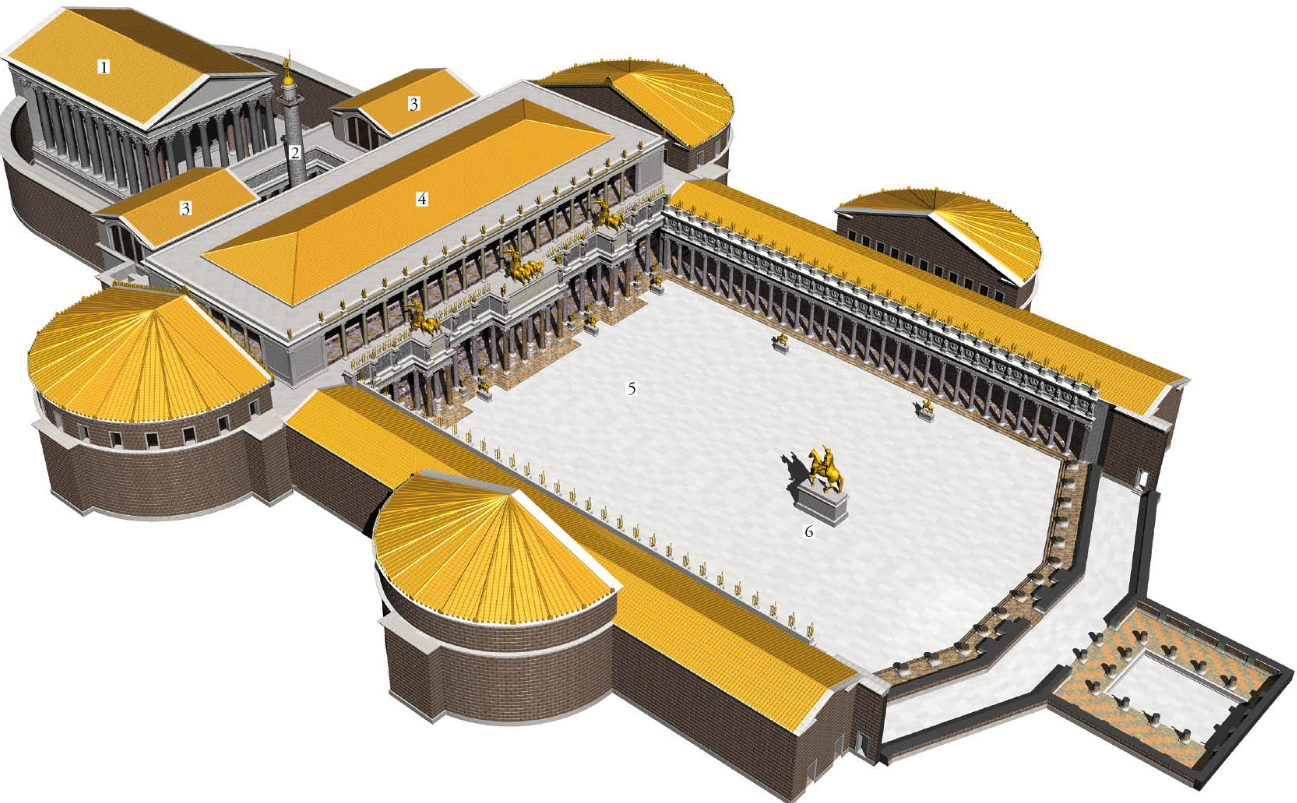
Forum of Trajan, (reconstruction) architect Apollodorus of Damascus, Rome, 2nd century CE (Ancient Rome)

Column of Trajan, Forum of Trajan, architect Apollodorus of Damascus, Rome, 2nd century CE (Ancient Rome)
monumental structures of Rome.
Trajan ashes are at the bottom
has long series of stories of his military campaigns
the story starts at the bottom and continues upward in a spiral
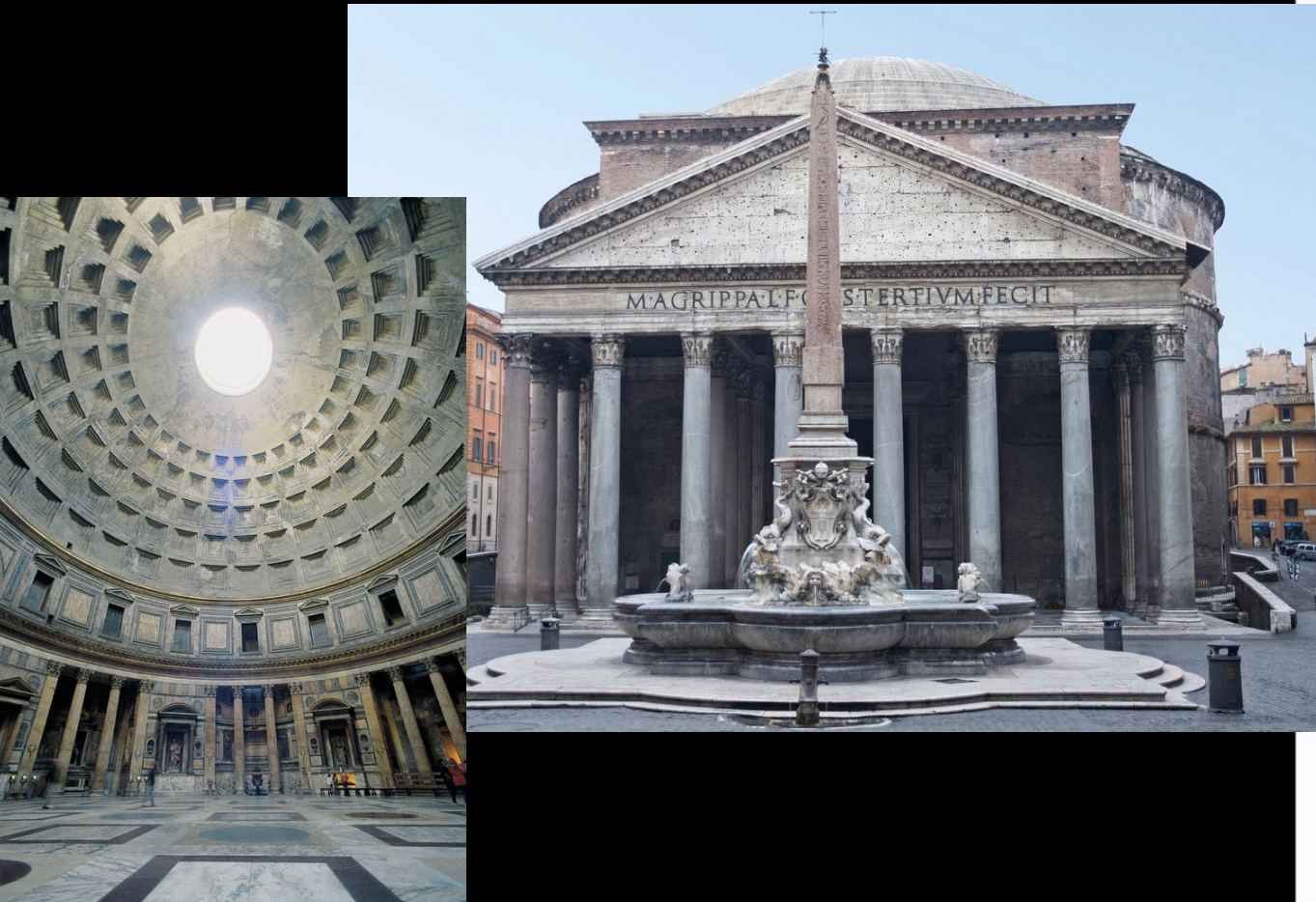

Pantheon, Rome, 2nd century CE (Ancient Rome)
“Temple of Gods”
for centuries was the largest dome shape in Europe
It’s a perfect globe of space
Dome with interior coffers and central oculu
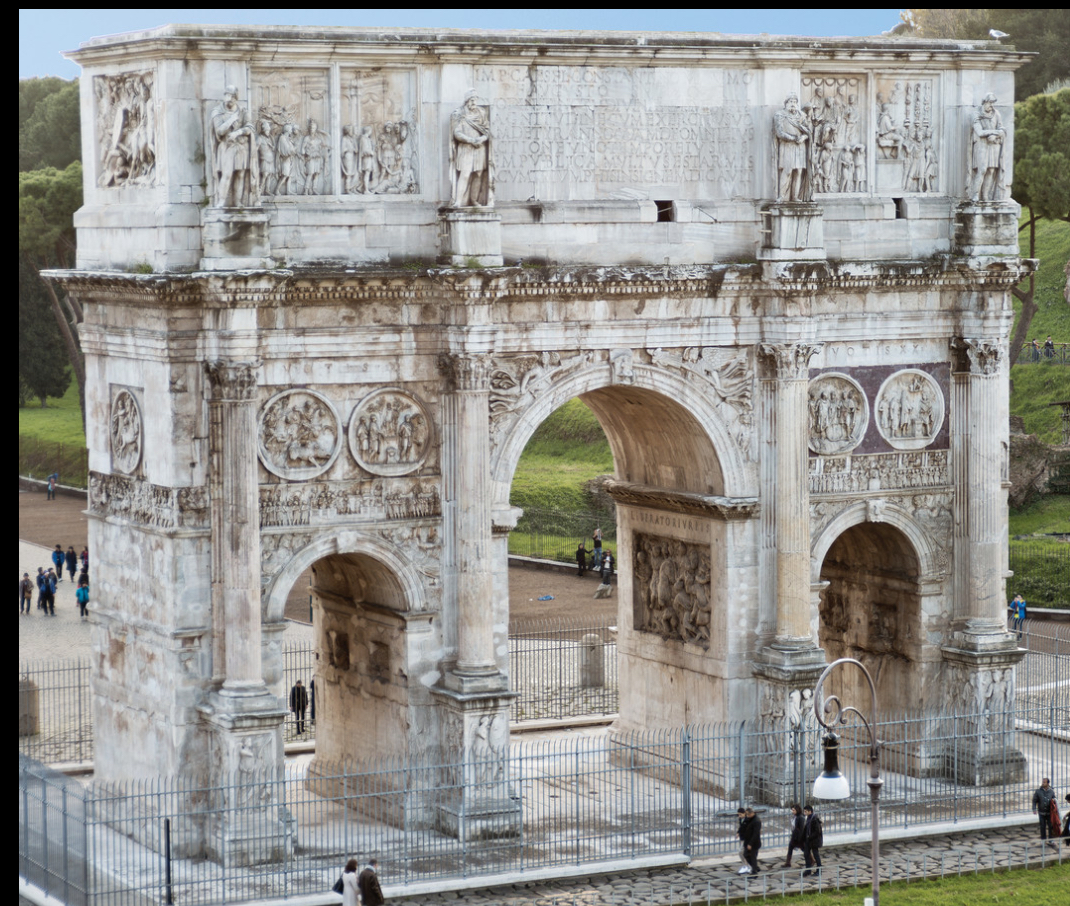

Triumphal Arch of Constantine, Rome, early 4th century (Ancient Rome)
“Arch of Constantine”
used for triumphal victory like a parade
framework for empirical perspectives
Other places did this as well
Ex. Triumphal Arch, Paris, France, early 19th century (Neoclassicism)
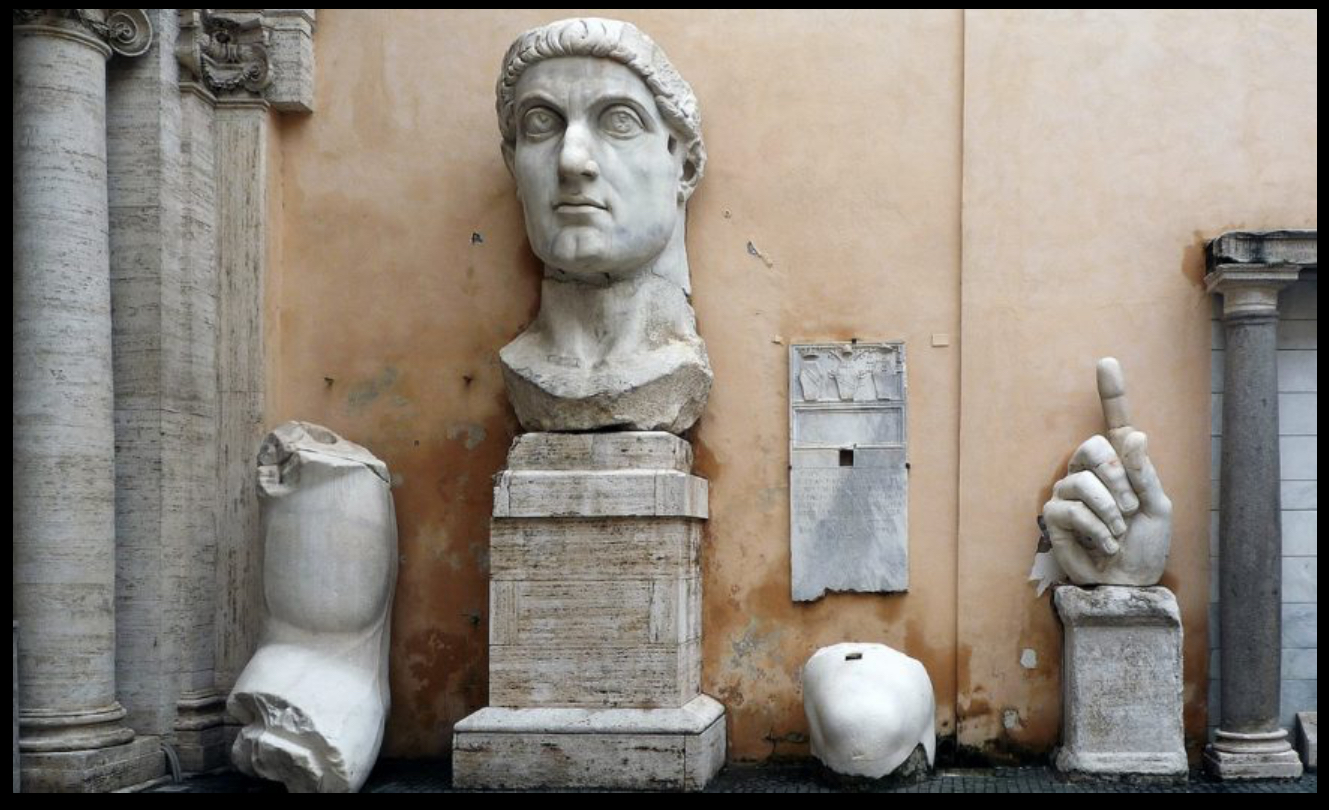

Colossal Statue of Constantine, Rome, early 4th century (Ancient Rome)

Old St.Peter’s, Rome, 4th century (Late Antiquity)
was a significant early Christian basilica built over the site believed to be the burial place of Saint Peter. It served as a major pilgrimage destination and influenced later church architecture.
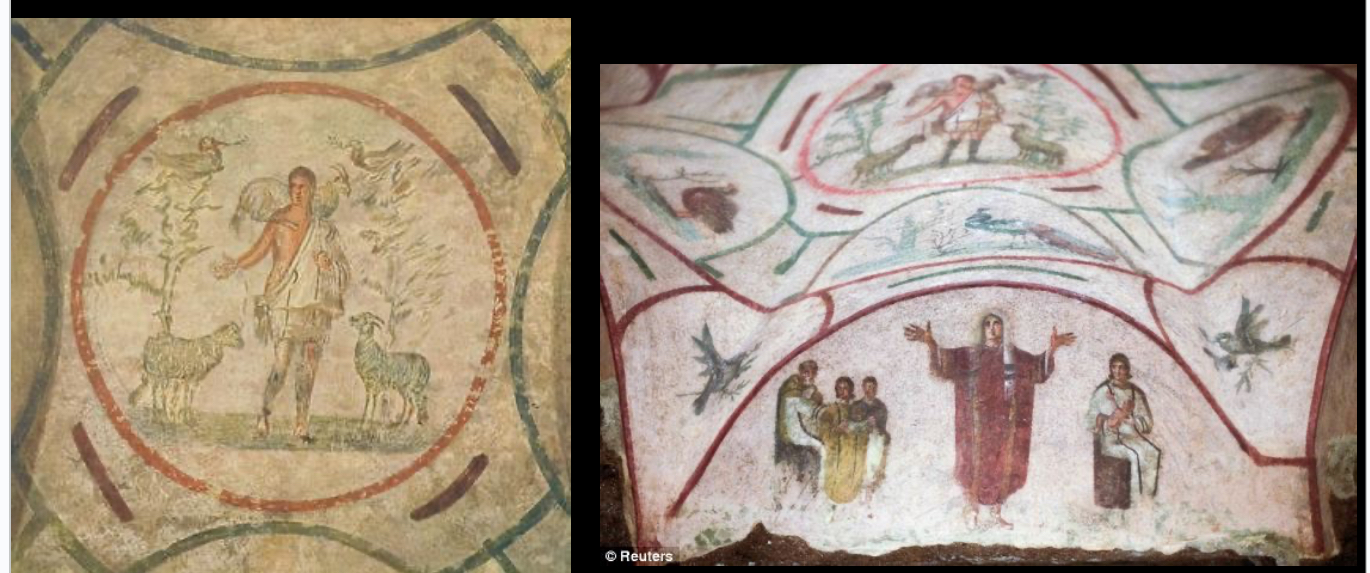

Christ as the Good Shepherd and other scenes, from The Catacomb of Priscillia, Rome, 3rd century CE
Christianity is becoming more of a conceptual art and not perceptual (perceptual is forbidden in the 10 commandments)
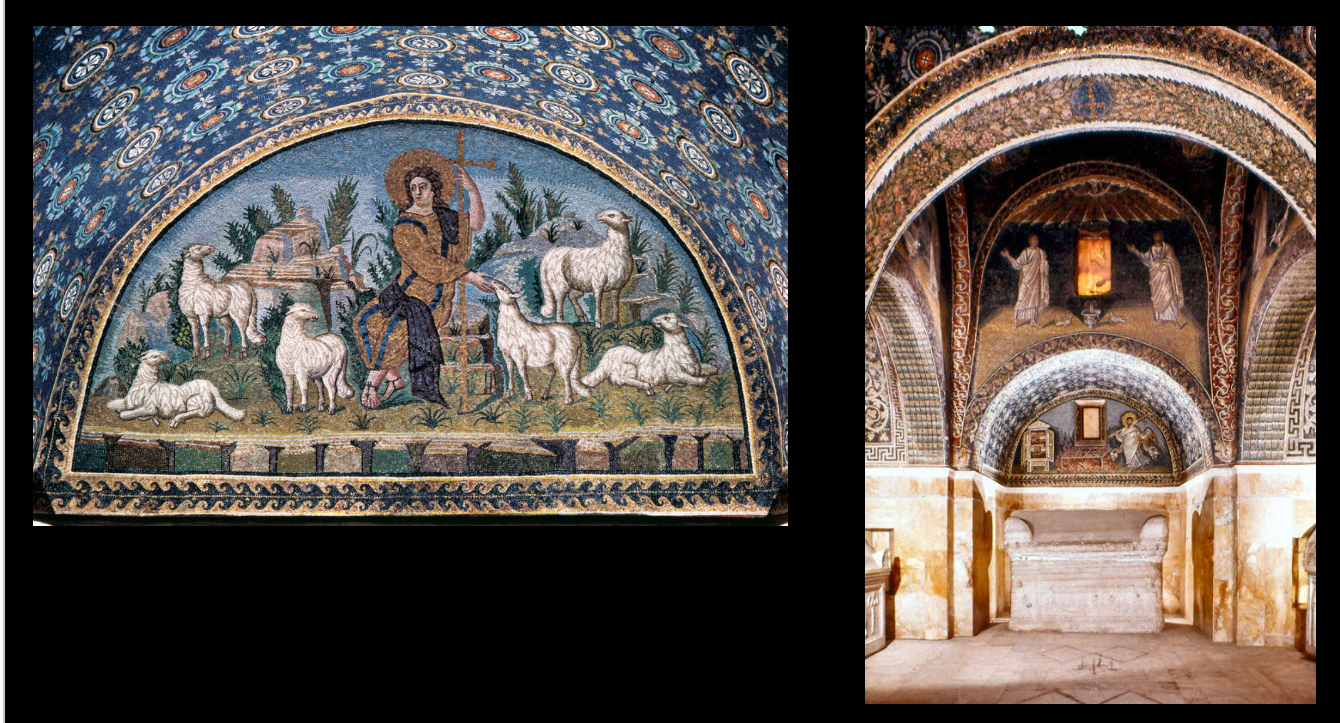

Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna, 5th century (Late Antiquity)

Icon of the Virgin and Child with Saints, 6th century, from St.Catherine’s Monastery, Mt.Sinai, Egypt (Byzantine)
icon=Greek for image
eyes of the figures are very large
they aren’t there to represent bodies they are meant to be abstract
Mt.Sinai is one of the oldest Christian monasteries

Rebecca at the Well, From the Vienna Genesis, 6th century (Byzantine)
this is probably one of the most famous pages from Noah and the Rainbow, from Vienna Genesis, 6th Century (Byzantine)

Koran (Qu’ran), folio showing beginning of Surah 18, 10th century (Islamic)
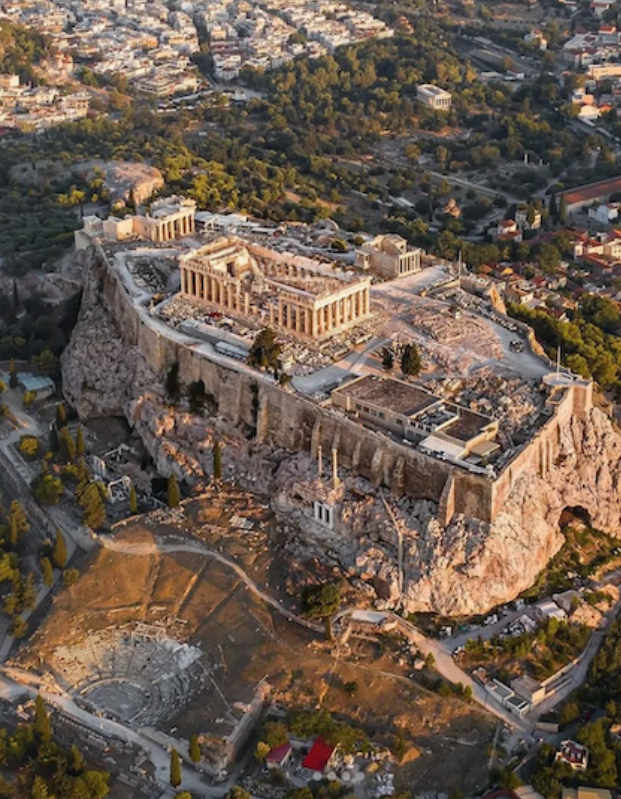
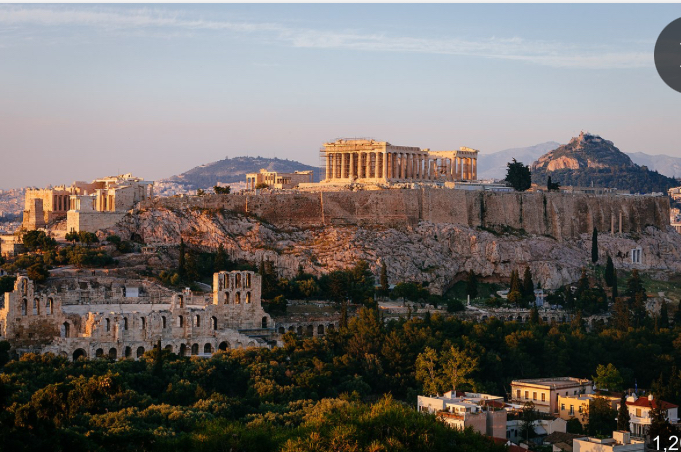
The Acropolis of Athens
An ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, it includes several historic buildings of great cultural significance, notably the Parthenon, and serves as a symbol of Ancient Greece.
rebuilt later 5th century BCE
it’s not the original

Compare: Flavian Amphitheater (Colosseum) vs. Amphitheater at Pompeii
The Flavian Amphitheater, known as the Colosseum, is a large ancient arena in Rome built in the 1st century CE, renowned for its gladiatorial contests. In contrast, the Amphitheater at Pompeii is an earlier structure from the 2nd century BCE, which is smaller and predates the Colosseum. And at Pompeii the Amphitheater land is built up to support the walls
Compare: Column of Trajan vs. Standard of Ur
The Column of Trajan is a monumental column in Rome that commemorates Emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars, featuring intricate reliefs that depict scenes from the campaigns. In contrast, the Standard of Ur is an artifact from ancient Mesopotamia, often interpreted as a musical instrument or a display of wealth, showcasing a narrative of war and peace through its elaborate scenes.
Mizzou columns refers to the Greek architecture order known as
ionic order
Prostyle
is a type of architectural column arrangement characterized by columns positioned in front of a building
Amphiprostyle
is an architectural style featuring columns at both the front and back of a structure, typically without columns along the sides.
Peripteral
is a classical architectural style characterized by a single row of columns surrounding the entire structure
Dipteral
is an architectural form consisting of a double row of columns on all sides of a building
Tholos
is a circular building with a conical or domed roof, often used in ancient Greek architecture for various purposes, including tombs and temples.
Stoa
is a covered walkway or porch, typically supported by columns, commonly found in ancient Greek architecture and used for public gatherings often farming the agora (public market place)
post-and-lintel system
used two upright posts, like columns, with a horizontal block, known as a lintel, laid flat across the top
opus caementicium
is a Roman concrete used in construction, made from a mixture of lime mortar, water, and aggregate. Its durability and versatility allowed for the construction of various architectural structures in ancient Rome.
the romans built aqueducts which are
structured to transport water over long distances using gravity.
amphitheaters
large circular or oval open-air venues used for public spectacles such as gladiatorial contests, theater performances, and other events in ancient Rome.
naturalism
the faithful depiction of the visible world
basilica style
large interiors for worship and to show authority
refers to a type of church building characterized by a rectangular floor plan, a central nave, and side aisles, originally modeled after Roman public buildings.
Compare: Pantheon and the Parthenon
Both are architectural masterpieces; the Pantheon is a Roman temple known for its large dome, while the Parthenon is a Greek temple dedicated to Athena, showcasing Doric order.
Pantheon, Rome, 2nd century CE (Ancient Rome)
Parthenon, (Ancient Greece, 5th century BCE)
Hellenistic art vs roman art
Hellenistic art → highly dramatic, emotional, dynamic poses (e.g., Laocoön Group).
Roman art → practical but very inspired by Hellenistic works, with more emphasis on realism, portraits, and propaganda (emperors, triumphs).
Constantine
The first Christian emperor of Rome, known for the Edict of Milan, which granted religious tolerance, and for founding the city of Constantinople.
he legalized Christianity
He became the main guy
built churches in Rome, the Holy Land, and Constantinople
Early churches in Rome looked like houses but Constantine’s churches were basilica style

Colossal Head of Constantine, Rome, early 4th century (Roman Empire)
found inside the Basilica of Maxentius/ Basilica of Nova
Compare the Colossal Head of Constantine to Augustus as General
The Colossal head seemed to be pointing up. The head was more idealized by using different parts of the face to show an idealized ruler, like his larger eyes speak of wisdom, etc
In contrast, Augustus as General was depicted with a focus on youthful vigor and idealized perfection, showcasing his authority and divine approval with realism and heroic attributes.
tessera
A small, individual tile or piece used in creating mosaics or decorations, often made of stone, glass, or ceramic, arranged to form elaborate patterns or images.
Iconoclasm
The destruction or rejection of religious images and icons, particularly in the context of Byzantine and medieval Christianity, where such acts were driven by theological and political motives.
Parchment is
a writing material made from animal skin, commonly used for manuscripts and documents in the medieval era, known for its durability and smooth surface.
Vellum is
a fine-quality parchment made from calfskin or lambskin, used for writing and illumination.
Scrolls are normally stored in ____ and are _____
boxes and are vulnerable