Macroeconomics
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Longer mark questions sctruture
1) AO1 - knowledge
Outlining point
Defining key terms
2) AO2 - quote examples from extract to support knowledge
2 or more references from the text
essay background knowledge
3) AO3 - use of theory
Explain / develop chain of reasoning
explain what happens and why it happens
4) AO4 - judgement (evaluation)
Counter point for why event might not occur
Specific theory to counter previous points
What are the government objectives?
1) Economic growth
2) Low unemployment
3) Low and stable income
4) Balance of payments equilibrium
5) Balanced government budget
6) Protection of the environment
7) Greater income equality
What is an index number?
An index number is a figure reflecting the value of an asset compared with a base value set at 100.
Index number = (current year) / (base year) * 100
What is a nominal value?
A nominal value is the current monetary worth of an asset at the time it is measured.
The value isn’t adjusted for inflation.
What is a real value?
A real value is an economic measure adjusted for inflation, revealing its true purchasing power over time.
What is national income?
National income is the total spending of goods and services of a country.
What is GDP?
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total monetary value of all goods and services produced by a country over a specific period.
Economic growth is an increase of a country’s GDP.
It is affected by the factors affecting AD - C + I + G + (X-M)
What is nominal GDP?
Nominal GDP is the total monetary value of all goods and services produced in a country calculated using current market prices (not adjusted by inflation).
Nominal GDP per capita = (total GDP / total population)
What is real GDP?
Real GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced in a country adjusted for inflation.
Real GDP = (nominal GDP / price index) * 100
What is the circular flow of income?
The CFoI is an economic model showing how money flows through the economy between firms and households.
It is affected by leakages, injections and household spending habits.

What is an injection?
An injection is the addition of money into the circular flow of income, therefore increasing the amount of money available for spending.
These include government spending, investments, and exports.
What is a leakage?
A leakage is when money is taken out of the circular flow of income, therefore reducing the amount of money available for spending.
These include tax, saving, and imports.
What is aggregate demand (AD)?
AD is the total demand of goods in an economy.
AD = consumption + investment + government spending + (exports - imports)
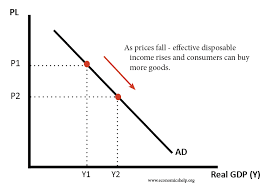
Factors causing a change in AD
1) Changes in fiscal policies
Increase / decrease in tax
Increase / decrease in government spending
2) Changes to monetary policy
Increase / decrease in interest rates
Increase / decrease in exchange rates
3) Changes in consumer confidence
What is consumption (C)?
Consumption is when goods and services are purchased by individuals to satisfy their needs and wants.
It is affected by factors like:
1) Inflation : weaker purchasing power with higher prices so consumption falls if inflation is high
2) Job security : consumption falls if there is a risk of a stable income
3) Consumer confidence : when consumers are confident in future economic growth consumption increases
What is the average propensity to consume (APC)?
APC is the proportion of income that a consumer is willing to spend.
APC = (total consumption expenditure) / (total disposable income)
What is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)?
MPC is the proportion of extra income spent on goods and services following a change in income.
MPC = (change in money spent) / (change in disposable income)
MPCs below 1 are standard.
MPCs above 1 show that the rate of an individual’s spending more that the rate that their income is increasing by.
What is investment (I)?
Investment is the addition of capital stock to the economy (factories / machines / offices).
It is affected by factors like:
1) Income : investment rises as income rises, and falls when income falls
2) Profits : profits provide the finance for investments, so high profits allow more investment and low profits allow less investment
3) Interest rates : interest rates dictate the cost of borrowing so low rates encourages more investment while high rates don’t
What is saving?
Saving is the act of not consuming (spending).
It is affected by factors like:
1) Interest rates: interest rates dictate the cost of borrowing so high rates encourage saving while low rates don’t
2) Job security: people are more likely to save knowing that a stable income is at risk
What is the average propensity to save (APS) ?
The APS the the proportion of income consumers are willing to save.
APS = (total savings) / (total income)
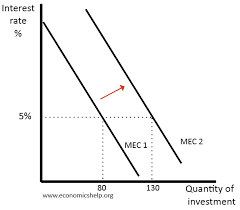
MEC graph
A marginal efficiency of capital (MEC) graph shows the inverse relationship between interest rates and the quality of an investment.
As interest rates fall, the quality of the investment rises.
What is government spending (G)?
Government spending is money spent by the public sector on goods and services.
Examples of areas of spending include infrastructure and benefits.
Scenarios of government performance
1) Budget deficit - occurs when a government’s spending is more than its revenue of tax receipts (G>T)
2) Budget balance - occurs when a government’s spending is equal to its revenue of tax receipts (G=T)
3) Budget surplus - occurs when a government’s spending is less than its revenue of tax receipts (G<T)
What is a benefit?
A benefit is a fiscal policy (use of government’s spending) put in place to try to stabilise the economy by ensuring there is full employment, therefore reinstating AD and reducing poverty.
Benefits are also known as automatic stabilisers as they are used during slumps or recessions, allowing consumption to increase.
What is an export (X) ?
An export is a good sold abroad.
Exports are injections into the circular flow of income.
What is an import? (M) ?
An import is a good bought from abroad.
Imports are leakages from the circular flow of income.
What is net trade?
Net trade = exports - imports (X-M)
Scenarios of trade performance
1) Balance of payments deficit - occurs when a country imports more than its exports (M>X), resulting in a negative net trade
2) Balance of payments equilibrium - occurs when a country imports the same as it exports (M=X), resulting in a net trade of 0
3) Balance of payments surplus - occurs when a country imports less than its exports (M<X), resulting in a positive net trade
Factors affecting trade
1) Price - how goods are priced influences supply, demand and competitiveness
2) Degree of protectionism - tariffs decrease frequency of imports of priced high
3) Exchange rates - WPIDEC , SPICED
4) Non-price factors - high quality products are likely to have a high demand and so will be priced high
What is SPICED?
SPICED - Strong Pound = Imports Cheaper = Exports Dearer
A rise in the value of a currency causes import prices to fall and export prices to rise.
What is WPIDEC?
WPIDEC - Weak Pound = Imports Dearer = Exports Cheaper
A fall in the value of a currency causes import prices to increase and export prices to fall.
Demand for exports increase as foreign consumers need less of their money to purchase them.
What is an economic system?
An economic system is a group of organisations used to resolve the problem of what, how much, how and whom to produce.
Types of market
1) Free market (private ownership)
Prices and production are determined by supply and demand
Limited role of state (no taxes, subsides, regulations)
2) Mixed economy
Mix of state and private ownership
Government intervention (essential services are provided)
Government has some influence of prices
3) Command economy (state ownership)
Government controls all economic activity
Government authority owns factors of production
What is the multiplier effect?
The multiplier effect is a concept coined by John Maynard Keynes stating:
A £1 injection leads to more than a £1 increase in AD (positive)
or
A £1 withdrawal leads to more than a £1 decrease in AD (negative)
Injections into the economy (like investment and government spending) encourage consumers to increase their spending, therefore increasing AD.
Withdrawals from the economy (like saving and tax) encourage consumers to reduce their spending, therefore decreasing AD.
Multiplier = (1 / 1-MPC) = (1 / (MPS + MPT + MPM) = (1 / MPW)
What is aggregate supply (AS) ?
Aggregate supply is the total amount of goods and services firms and businesses are willing to produce and sell in an economy.
The Yf line represents ‘full employment output’ - this shows the economy is working to full capacity and cannot produce any more goods.
Y lines before the Yf show that the economy is working below full capacity (unemployment)
An increase in the cost of production shows inefficiency while a decrease shows efficiency.
An outward shift shows an increases in capacity so more products can be made, while an inward shift shows a decrease in capacity so less products can be made.
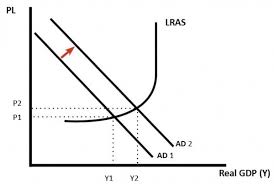
AD-AS graphs combined
At optimum, AD curve intersects when economic growth is at its highest and there is full employment - this is at the top of the Yf line.
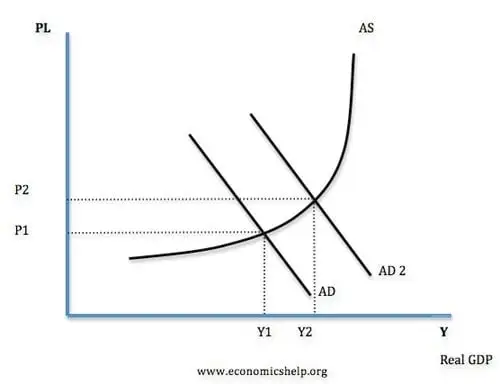
AD-AS curves scenarios
1) Unemployment
AD line before Yf line
Distance from Yf to Y1 represents unemployment
There is a negative output gap as not all possible workers are working
2) High inflation
Price level rises so AD lines shift outwards (positive output gap)
Rise in AD also causes rise in GDP/RNI
When AD intersects at full employment output it can no longer shift outward - prices continue to rise without GDP increasing
3) High unemployment
AD continues to shift inwards if nothing is done to try to reduce unemployment
More unemployment means consumption falls
More people put out of jobs (negative multiplier)