9: Mechanics of Translation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
tRNA
Transfer RNA that carries amino acids to ribosomes.
Aminoacyl t-RNA synthetases
Enzymes that attach amino acids to tRNA.
what is the Shine-Dalgarno sequence?
what is it complementary to?
Purine-rich region in prokaryotic mRNA for initiation.
is complementary to the initiator sites of mRNA
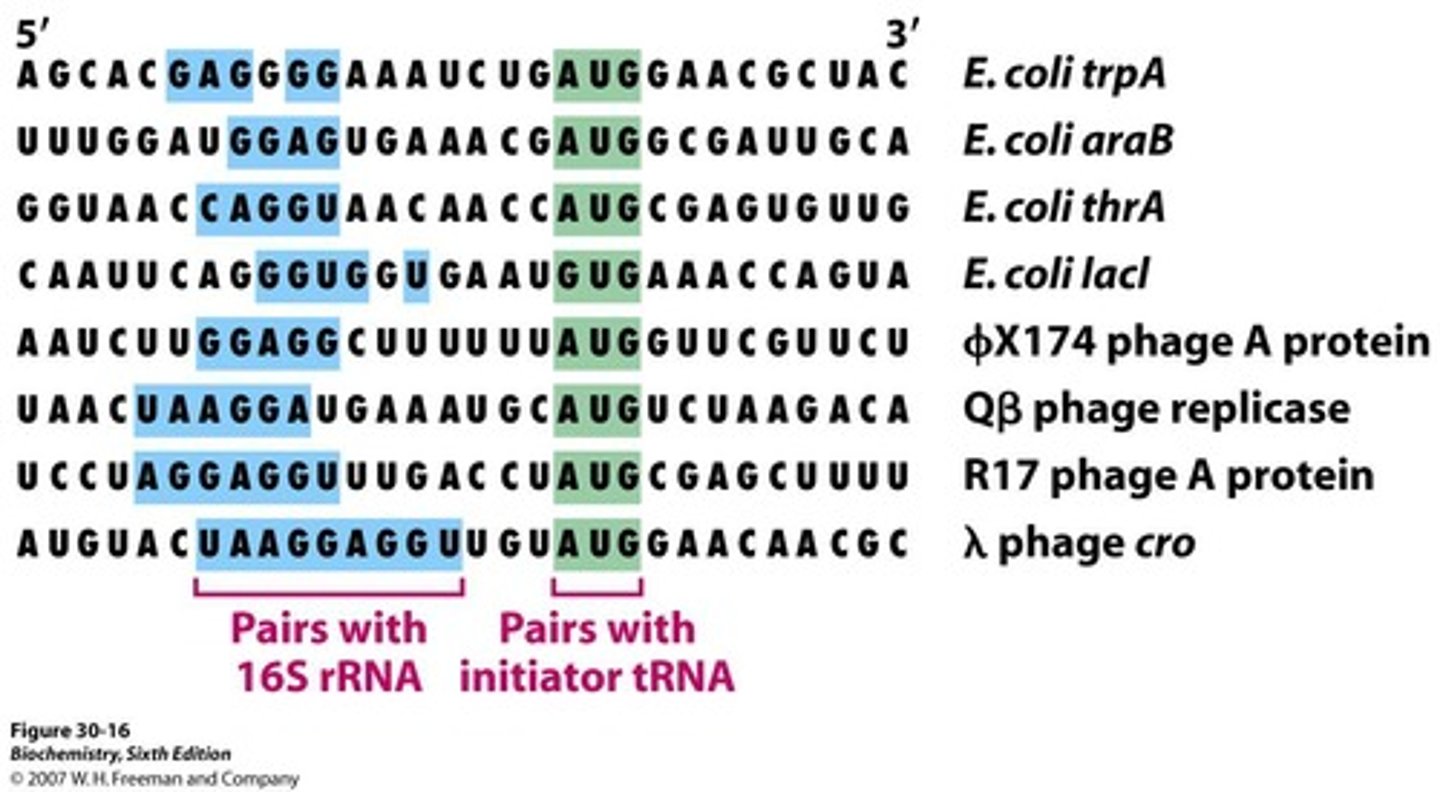
the start signal in prokaryotic mRNA is?
AUG or GUG
tRNAfmet
Formylated tRNA for initiating polypeptide chains.
recognises AUG and GUG
tRNAmmet
Non-formylated tRNA for internal methionine residues.
recognises AUG only
evidence of protein factors in initiation
protein synthesis requires free 30S subunit
if 30S subunits are in high salt = lose ability to initiate protein synthesis
removing salt = activity restored
chromatography of high salt supernatant = IF-1, IF-2 and IF-3
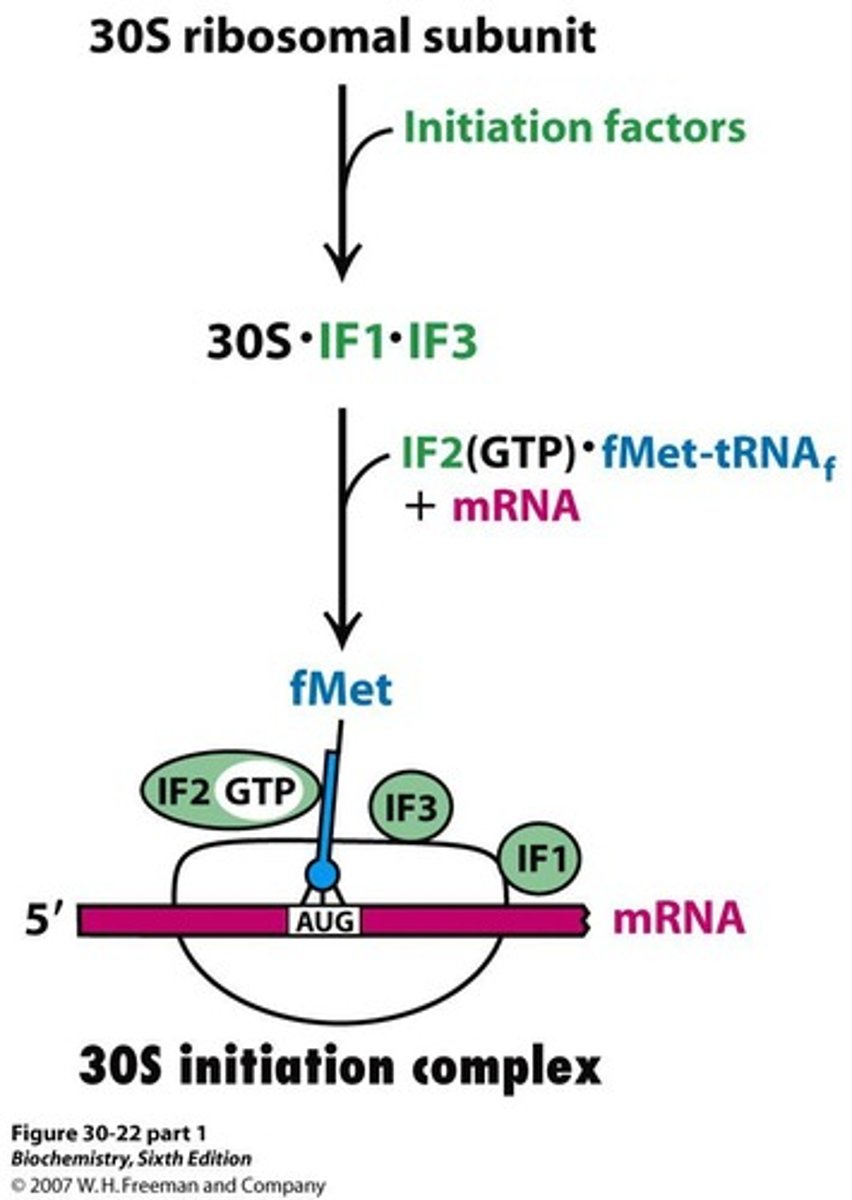
Initiation factors (IFs)
Proteins required for initiation of translation.
IF-1
Binds A site, directs fmet-tRNA to P site.
IF-2
Forms ternary complex with fmet-tRNA and GTP.
delivers this complex and mRNA to the partial P site in 30S subunit-mRNA complex
triggers GTP hydrolysis when 50S joins complex
the now complex does not recognise met-tRNA or any aa tRNA for elongation
IF-3 does what?
Prevents 30S subunit from binding 50S subunit prematurely - before correct mRNA and initiator tRNA are in place (in prokaryotes)
30S initiation complex
Complex formed by 30S subunit and initiation factors.
70S initiation complex
Complex formed when 50S joins 30S initiation complex.
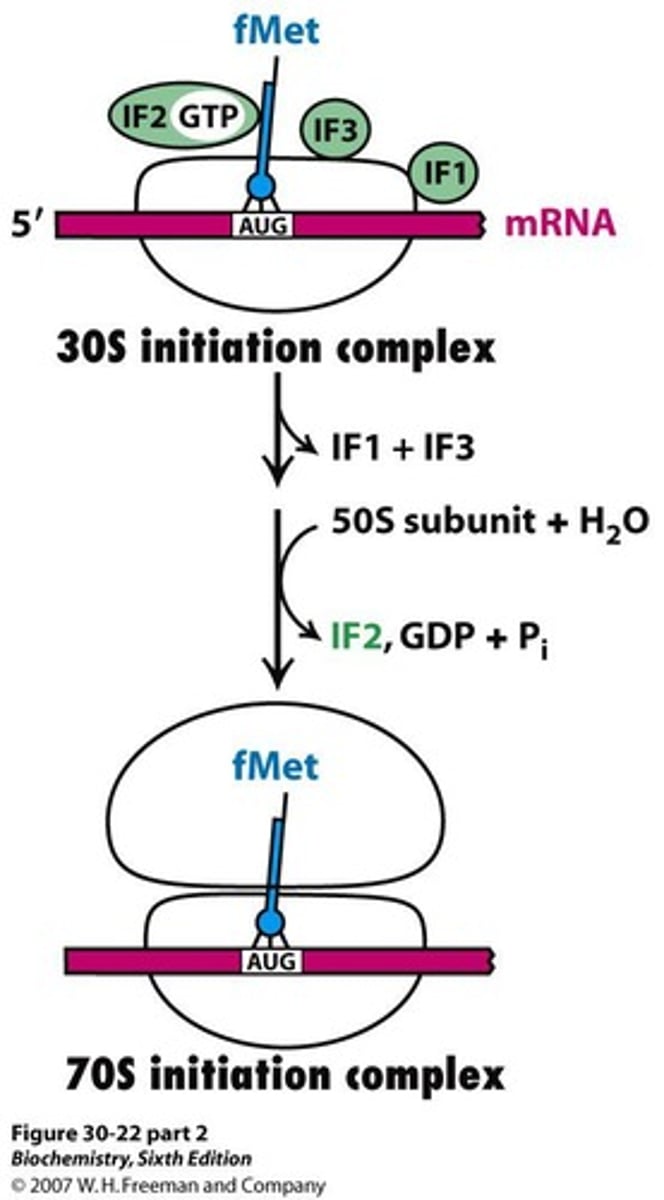
GTP hydrolysis
Energy-releasing reaction during translation initiation.
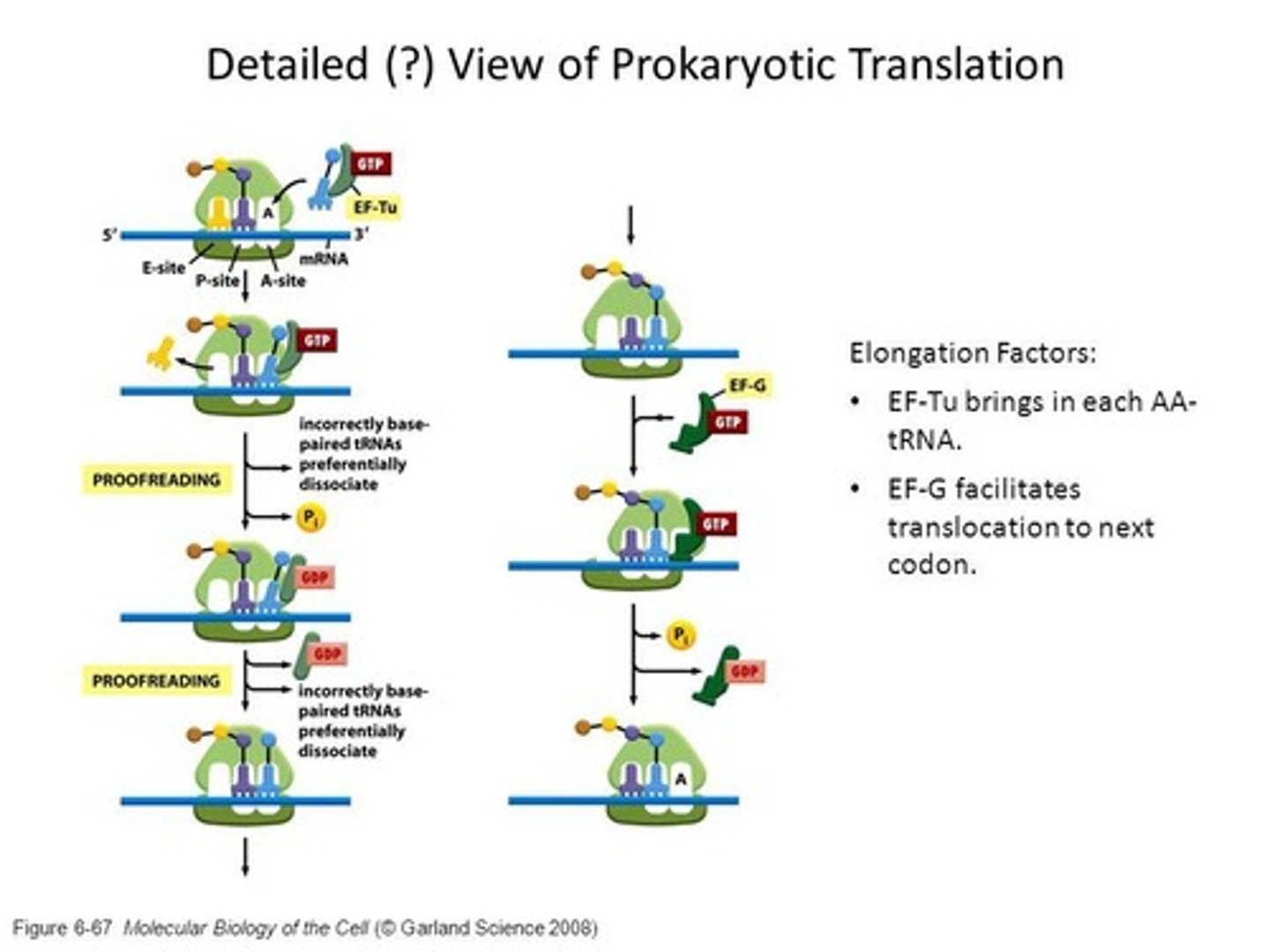
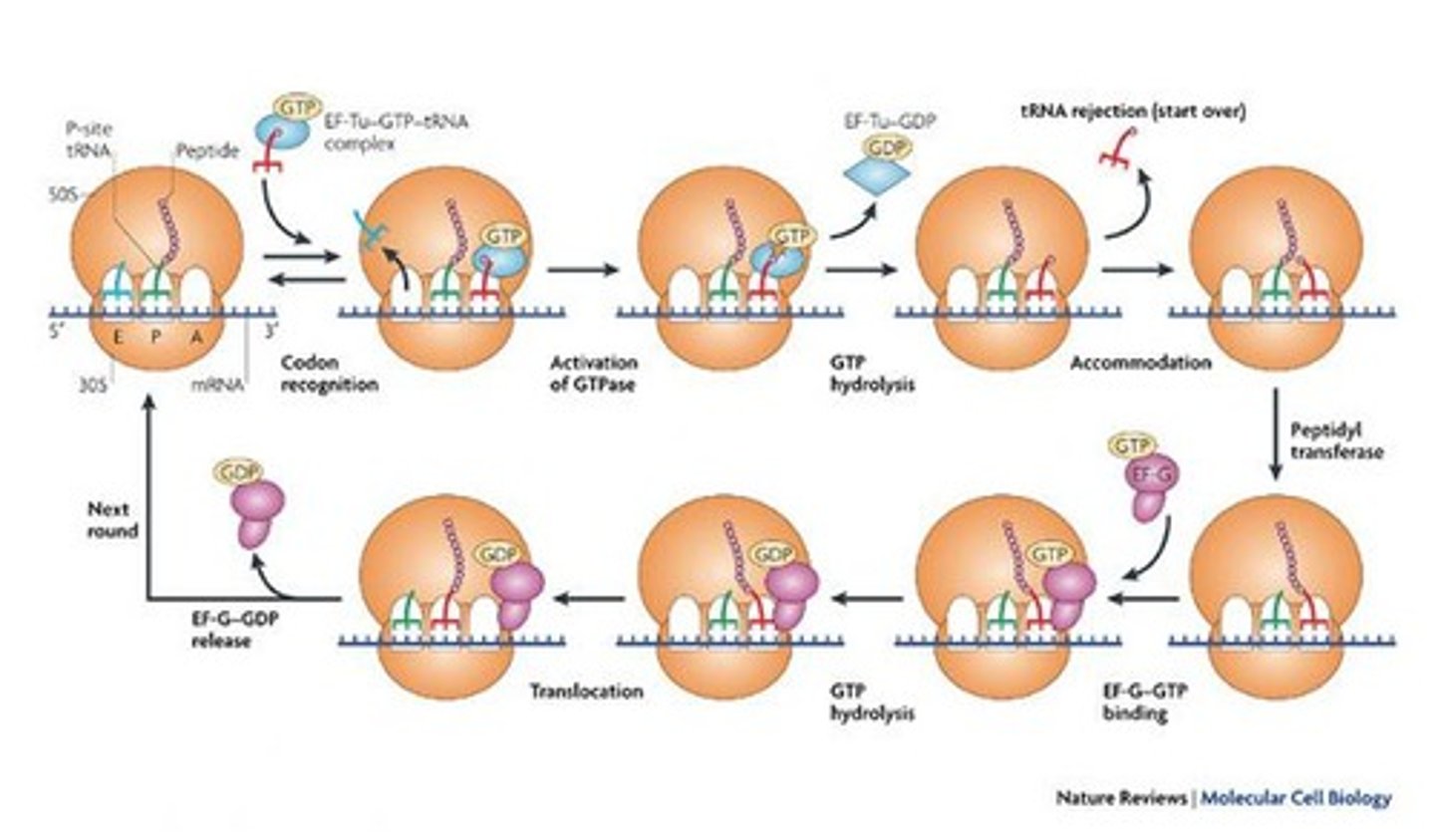
elongation happens in what 3 steps?
codon-directed binding incoming aminoacyl-tRNA
peptide bond formation
translocation of ribosome along mRNA (5’ to 3’ direction)
Codon-directed binding
Process of matching tRNA to mRNA codons.
Peptide bond formation
Linking amino acids via peptide bonds during elongation.
Translocation
Movement of ribosome along mRNA during elongation.
Peptidyl transferase
Ribozyme that catalyzes peptide bond formation.
peptide bond formation by peptidyl transferase
fMet-tRNA is initially in the P site
new aminoacyl-tRNA enters A site
amino acid group attack fMet in the P site
fMet is transferred to A site
peptide bond is formed from moving peptide chain from P site to A site.
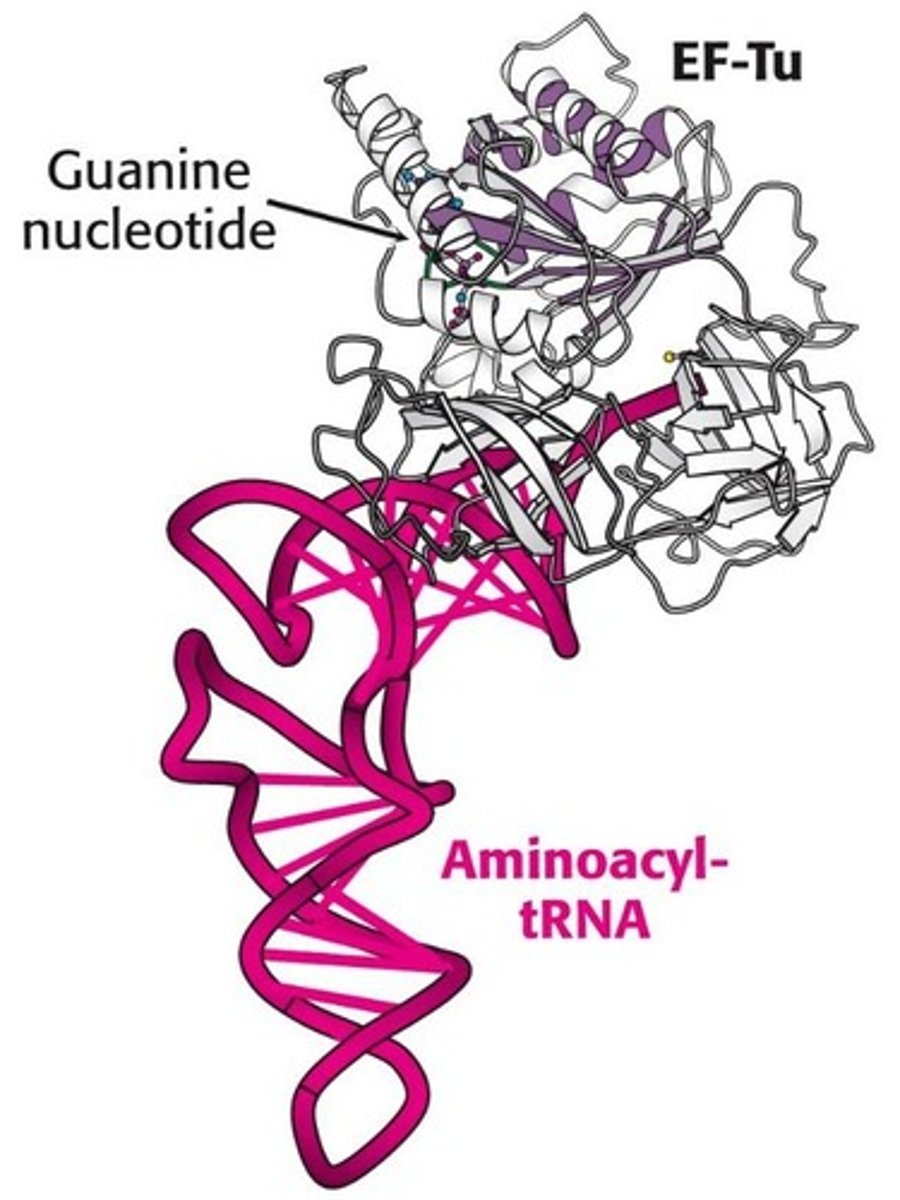
EF-Tu
is heat ______
Elongation factor that binds incoming aminoacyl-tRNA.
unstable
Diphtheria toxin inhibits ______ synthesis by acting during _________
protein
elongation
Overall Keq ~1
Indicates no net energy input required for translation.
Eukaryotic mRNA
Has distinct initiation and termination regions compared to prokaryotic.
Prokaryotic mRNA
Contains specific sequences for translation initiation.
EF-Ts
it is heat ____
Facilitates GDP to GTP exchange for EF-Tu.
stable
Cryo-EM
Technique for visualizing ribosome-tRNA complexes.
A/T site
Site for aminoacyl-tRNA during translation.
P site
Peptidyl site where tRNA holds growing peptide.
E site
Exit site for deacylated tRNA.
GTP hydrolysis
Process that triggers EF-Tu-GDP release.
Peptide bond formation occurs when?
Occurs after EF-Tu-GDP dissociates.
Translocation
Ribosome movement along mRNA by one codon.
EF-G/GTP acts in bacteria & does?
what does the same in eukaryotes?
Elongation factor that facilitates ribosome translocation.
EF-2
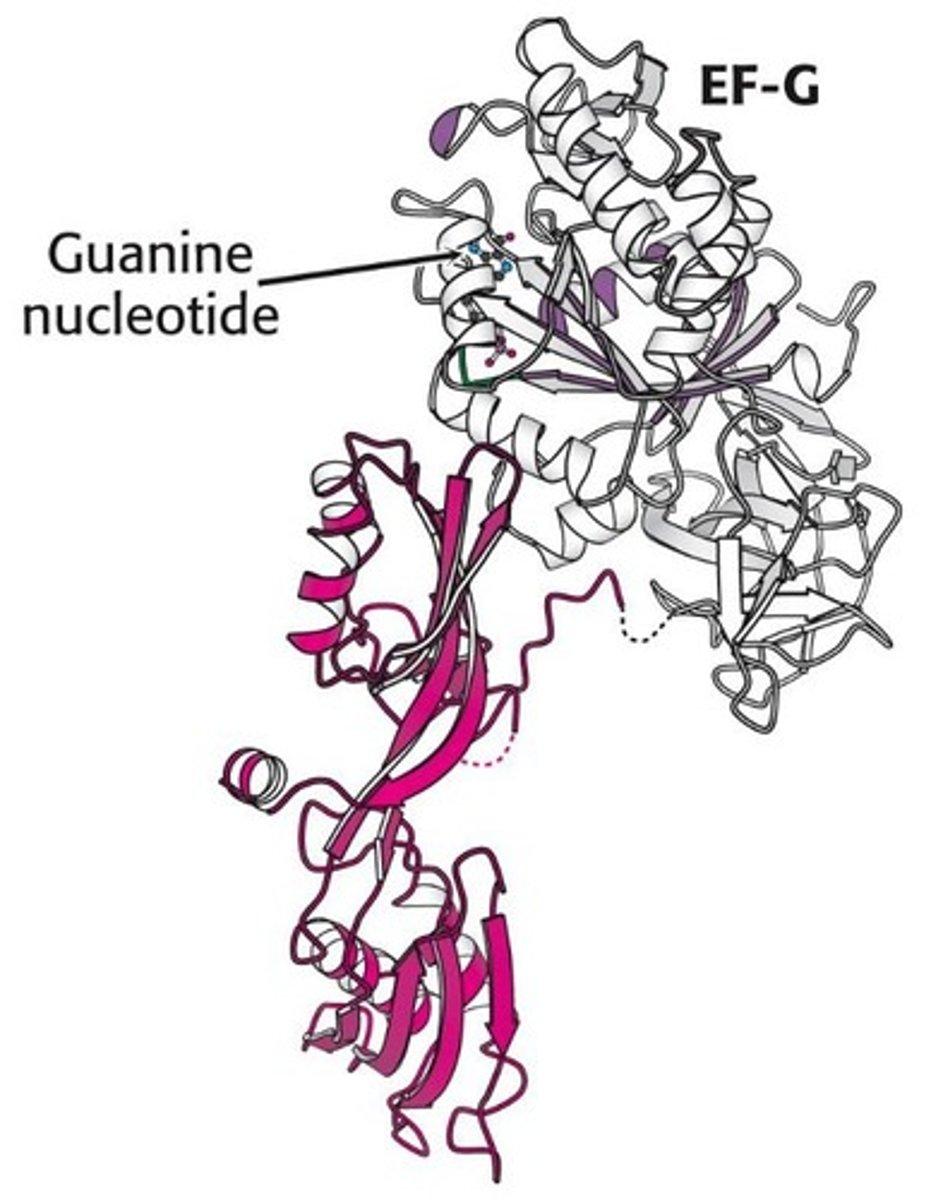
N-terminal region of EF-G mimics what and why?
Mimics tRNA structure for effective binding.
Sarcin/ricin loop
Part of 23S rRNA involved in EF-G binding.
mechanism of translocation
EF-G/GTP binds to pre-translocation ribosome
tRNA-like domain interacts with 30S close to partial A site
GTP hydrolysis = conformational change in EF-G = forces arm deep in 30S
peptidyl tRNA forced from A site to P site carrying mRNA and deacylated RNA
ribosome move along mRNA by length of one codon
Probability of error-free protein synthesis
p = (1-ɛ)n, where ɛ is frequency of inserting a wrong amino acid.
Elongation process
Involves EF-Tu-GTP and aminoacyl-tRNA delivery.
fMet-tRNAf
First tRNA in prokaryotic protein synthesis.
Initiation factors
Proteins IF-1, IF-2, IF-3 aid in translation start.
Labile ester bond
Bond between tRNA and amino acid, protected by EF-Tu.
Decoding centre
Region where codon-anticodon matching occurs.
Pre-translocation ribosome
Ribosome state before tRNA movement.
GTPase-associated centre (GAC)
Region involved in GTP hydrolysis during translation.
Translocation
Process requiring elongation factor EF-G/GTP.
Termination is simply…
Transfer of polypeptide to water ends translation.
termination steps [4]
release factors bind to vacant A site
peptidyl transferred to water rather than aminoacyl tRNA
hydrolysis of RF3-GTP to GDP dissociates everything
Initiation Factors
Proteins aiding the start of translation.
IF-1
Prevents premature tRNA binding to A site.
IF-2
Guides fMet-tRNAfMet to 30S subunit.
IF-3
Prevents premature 50S subunit association.
eIF1
Guides Met-tRNAi to 40S subunit.
eIF2B
Facilitates binding of initiation factors.
eIF3
First binder in eukaryotic translation initiation.
eIF4A
RNA helicase unwinding secondary structures.
eIF4B
Binds mRNA, facilitating scanning process.
eIF4E
Binds 5' cap of mRNA.
eIF4G
Links eIF4E and pol(A) binding protein.
eIF5
Promotes dissociation of initiation factors.
eIF6
Promotes dissociation of 80S into subunits.
AUG Codon
Common initiation codon for protein synthesis.
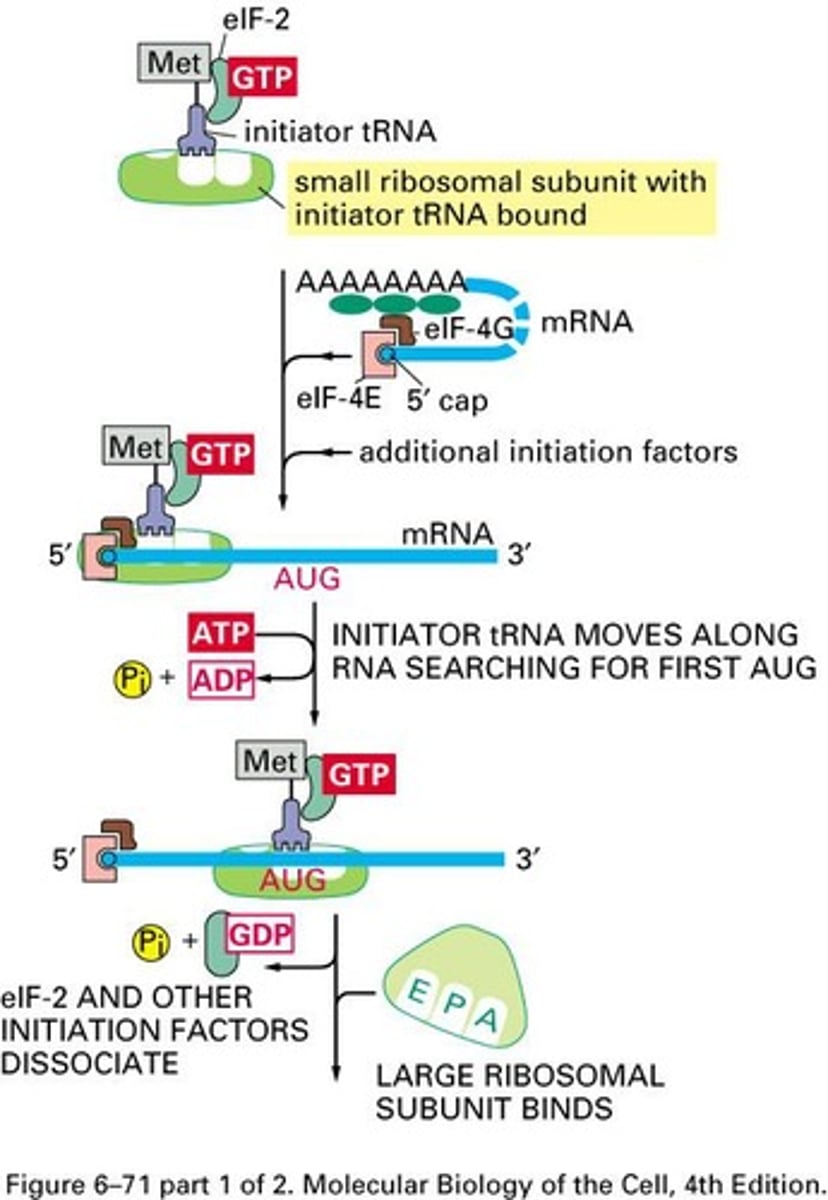
tRNAimet
Special initiator tRNA for eukaryotic translation.
Kozak Sequence
Sequence surrounding AUG for translation initiation.
Cap Binding Complex
eIF-4F complex binding to mRNA cap.
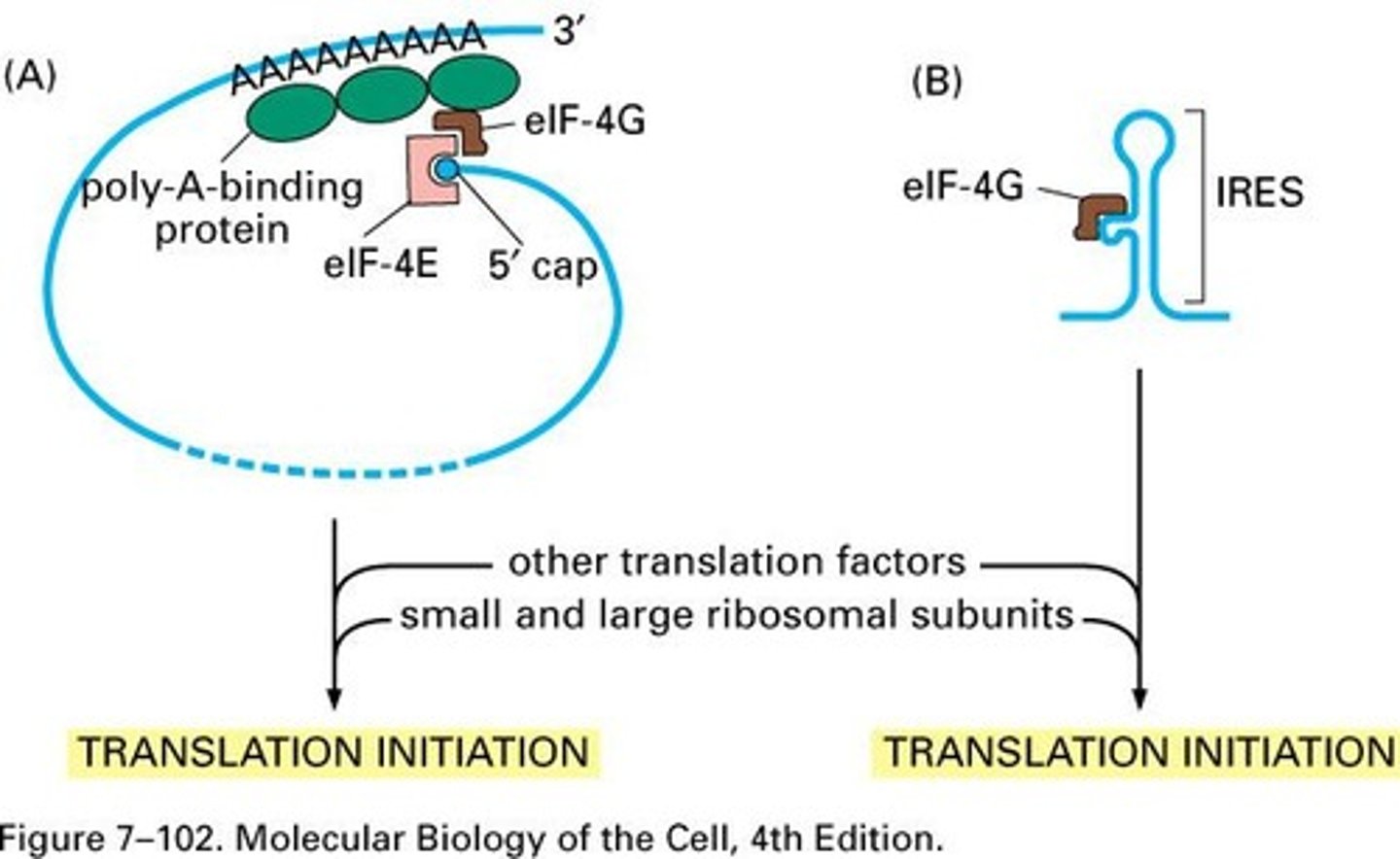
PAB1
Interacts with eIF4G and eIF4E at cap.
Internal Ribosome Entry Sites (IRES)
Alternative translation initiation lacking 5' cap.
Picornaviruses
Viruses using cap and IRES-dependent initiation.
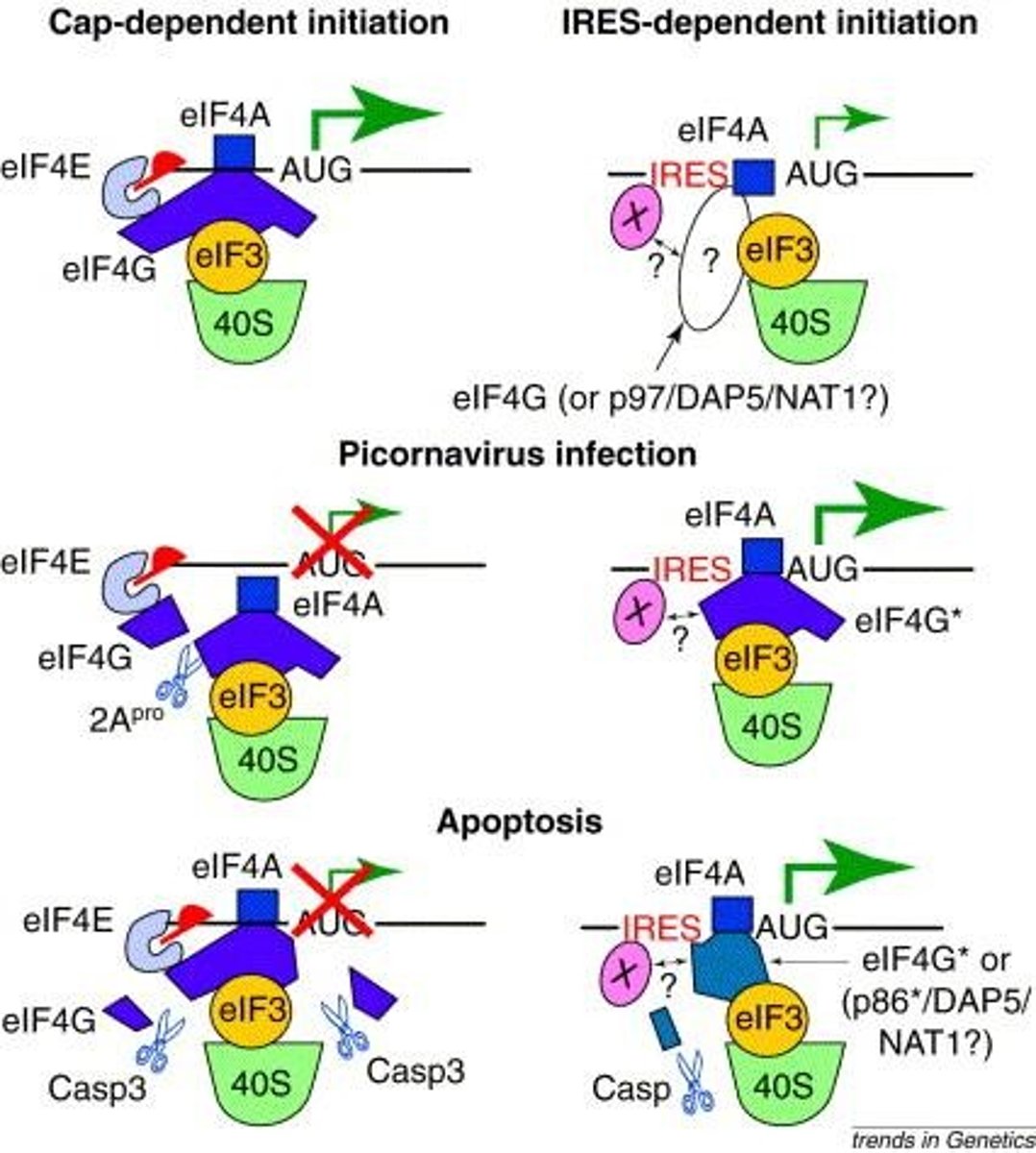
IRES
Internal Ribosome Entry Site; allows translation independent of cell cycle.
Eukaryotic release factor
Mimics tRNA's acceptor stem structure for polypeptide release.
Peptidyl transferase center
Ribosomal site where peptide bond formation occurs.
Kozak sequence
Sequence that facilitates recognition of start codon.
Met-tRNA
Methionine-carrying tRNA pre-bound to ribosomal subunit.
eIF4E
Initiation factor that binds to the 5' cap.
Polysomes
Multiple ribosomes translating a single mRNA simultaneously.
Hydrolysis of ester bond
Water molecule cleaves bond, releasing polypeptide.
Translational control mechanisms
Regulation of translation via initiation and elongation factors.
Autogenous regulation
Gene product binds mRNA to prevent its translation.
Differential stability of mRNA
Variability in mRNA lifespan affects protein synthesis.
eIF2a phosphorylation
Regulates initiation of translation in eukaryotes.
eIF4E phosphorylation
Target for cancer drugs, regulates translation initiation.
R-protein synthesis
Regulated by growth rate and coupled to rRNA synthesis.
Operons
Groups of genes transcribed together, often in prokaryotes.
Iron-response element (IRE)
Sequence that regulates mRNA translation based on iron levels.
Aconitase
Protein that binds IRE under iron starvation conditions.
Ferritin
Cytosolic protein that stores iron, preventing toxicity.
Transferrin receptor
Cell surface protein for iron uptake regulation.
mRNA decay
Process of mRNA degradation after poly(A) tail shortening.
Decapping
Removal of the 5' cap leading to mRNA degradation.
Endonuclease cleavage site
Location in 3' UTR where mRNA is cleaved.
EF-Tu-GTP
Elongation factor that brings aminoacyl tRNA to ribosome.
EF-G/GTP
Elongation factor required for ribosome translocation.
Termination of translation
Process where polypeptide is transferred to water.