AP Physics 2 Full Year
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
Expansion means there is ____ work
NEGATIVE, gas has to do work against its surroundings
Isothermal Expansion
PV=PV, No change in temperature or internal energy, so W=-Q. Graph is downward parabolic and it’s slow movement of pistons with insulation or water bath.
W= 3/2nRT
Isobaric Expansion
Constant Pressure, horizontal line. Positive work and piston is free to move
Q= 5/2nRT because work is negative and it would be delta U - W
Isochoric/volumetric Expansion
Vertical line, volume same so no work. Delta U = Q and piston is locked in place
Adiabatic
Fast expansion so no escape of heat, meaning no Q. Delta U =W
Temperature is proportional to…
Delta U and sqrt(v_rms)
Radiation emission proportion
T^4 is proportional to frequency
Heat lost and gain
Use mc delta T equals -mc delta T
Pressure
F/A, use absolute not gauge. Pab = Po+ pgh
Heat transfer by…
Conduction, convection, and radiation
In written FRQs, remember…
Units, conversions, all formulas with substitution, DIRECTION (negative work, momentum, etc)
At a constant volume and pressure ( a single state) delta U equals
3/2PV
If product of PV is less,
Temperature decreased, meaning delta U increased and then based on the type of compression you can determine the signs of W and Q
The entropy of a full system always
Increases
Reaching thermal equilibrium is a _____ process
Irreversible, increases entropy
Mass does NOT affect ____
Temperature gain
A higher c means
The material maintains heat longer but takes longer to heat up
Entropy is…
Unusable thermal energy spread out throughout something. Highest for a gas because more micro states
Delta s = delta H/T Of cold and delta H/T of hot
In a vacuum…
There is no outside pressure, no exchange of heat, negligible work to expand balloon (if there is work it generates heat which balances out Delta U, meaning no change in T), Boyle: pressure decreases by half, volume doubles. Lose the force on the balloon from particles on the outside
ISOTHERMIC bc no particles to exchange temperature with
What happens to Maxwell Boltzmann at higher temp?
Goes right, spreads out thinner
POSITIVE work means…
work done TO a system, contraction
NEGATIVE work means…
work done BY system, expansion
there is a force that causes pressure from collisions with gas particles because…
there is an impulse or change in momentum, which can only occur with force
When transfering hot to cold, particles with ____
highest KE are transferred most frequently to areas with lower AKE
3 forms of heat transfer
radiation, convection, conduction
In PHYSICS, work is from the perspective of
the system itself
Formula for entropy
delta Q/delta T
1st Law of Thermo
conservation of energy, Delta U = Q+W
Second Law of Thermo
the universe always has positive gain in entropy
processes such as thermal equilibrium are…
irreverisble and lead to an increase in entropy IF considering the ENTIRE system
if there are higher temperatures, then entropy will have
less change
Types of Pressure
Absolute Pressure = Patm+Pgauge. Absolute is the one to use for PV=nRT
absolute pressure uses absolute zero as its zero point, while gauge pressure uses atmospheric pressure as its zero point.
If theres no change in V,
theres no work
if piston is free moving
pressure is constant
Gauge pressure is 0 when…
the gas is at the atmosphere’s pressure (since gauge pressure is additional pressure due to fluid)
in rate of heat flow… ___ doesn’t matter
moles and size of gas molecules
How to view forces at angles/corners of a shape
Look at distance as d√2 NOT F√2
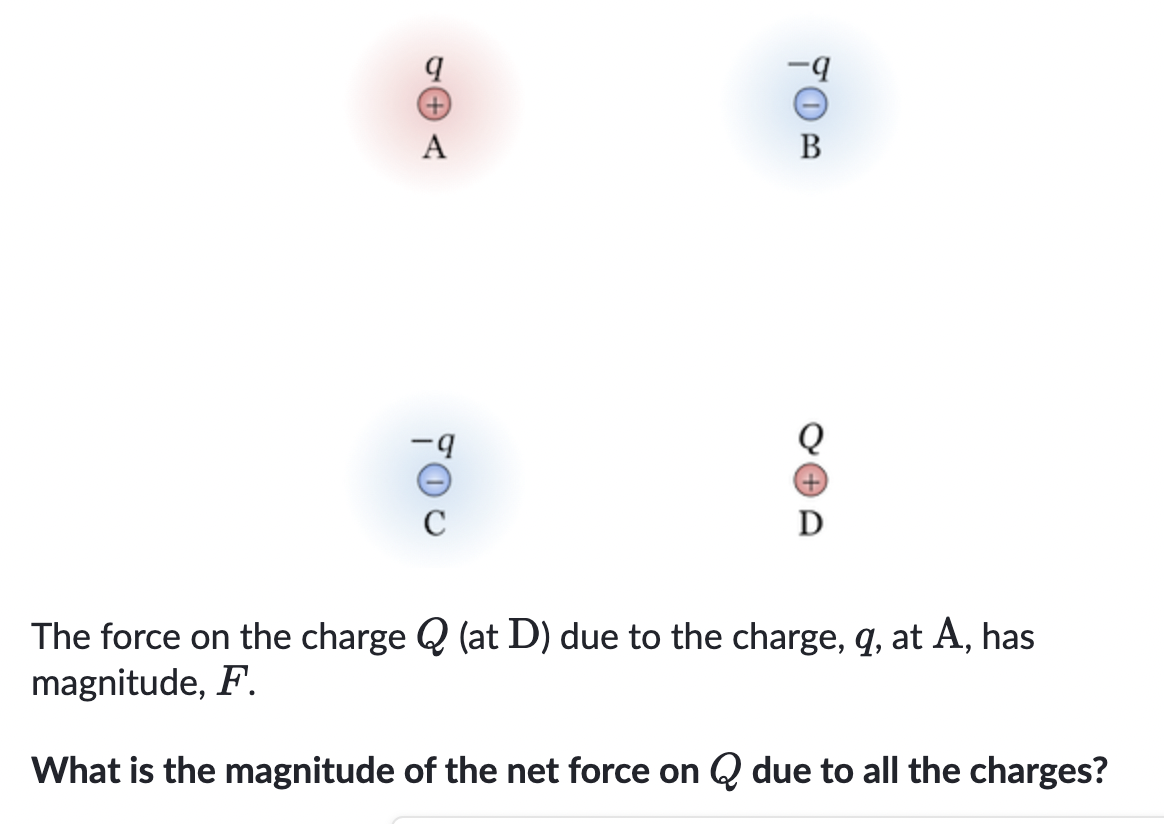
which way do fields go and where does a negative go in a field?
Away from positive, towards negative. Electrons move AGAINST field
Charge
Remember NEGATIVE or positive, if its in e or C and nano or micro
Electric field lines point toward more/less potential
LESS potential, closer to negative has less potential (more neg)
How to find KE of a particle in system
Conservation of Energy: Delta K = NEGATIVE Delta U
How to find distance or velocity of a particle in system
Conservation of ENERGY
remember mass, mass of electron is much less so it has more ACCELERATION and thus velocity than proton
Moving positives together….
Requires the input of work into the system, increases potential because positive charge and closer distance
The magnitude of an E field of a single particle…
has the SAME magnitude and SAME direction on ALL other particles, regardless of the other particles’ sign of charge or magnitude of charge.
Think of it like F=mg, mass does not affect g
Closer to a negative charge has more/less potential
LESS, more negative
E-field in capacitor
UNIFORM (exception is end points)
Do NOT treat the field the same as a sphere using the Coulomb Law-derived equation
Definition of Capacitance
Amount of voltage/potential stored in a capacitor per a certain distance.
Capacitance has its own PE designated as U_c
As distance of the capacitor plates get _____ and as area _____, the U_c/C increases
smaller, increases
Keeping a capacitor plugged in to a battery maintains
constant voltage
Removing a capacitor plugged in to a battery maintains
constant charge
What impacts Capacitance?
The physical properties of the plates, such as area, distance, material (dielectric constant or presence of dielectric)
Capacitance is dependent on _____
charge
IN a capacitor, electric field is dependent on
the strength of flux lines, or CHARGE
If a position has MORE potential energy, then that state is…
LESS favorable, has MORE V
More PE for negative charges means…
HIGHER V
Relationship between V and U_e
Can have OPPOSITE signs bc it depends on sign of charge
which particle has the highest potential?
Positive
How to find total V or PE of a system
SCALAR addition, NOT vector
Charge inside a conductor
NONE, all on surface
In conduction, the potential difference afterwards is…
0, both have same potential
If there’s no delta V, then there’s no
No Delta U_e, no E and no FE (like having only constant velocity and no acceleration)
How to find field from equipotential lines
perpendicular, towards lower potential
How does distance impact voltage?
NOT constant distance per change in voltage, exponential change according to 1/r
Moving perpendicular to a field
does NOT change V
A system defined as a SINGLE particle
has NO PE on its own
A positive charge attracts
a negative AND a neutral
Difference between insulator and conductor
insulator only gets polarized as atomic level, conductor gets polarized on large scale because electrons can move around
Electric Permitivity (ε)
degree to which a material can be polarized
Electroscope
leaves outward means charged, could be positive or negative
Charge by Induction
NOT touching. Gives the material OPPOSITE charge if connected to ground wire, but nothing if not touched only temporary polarization. Ground not rod HAS to be removed first.
Triboelectric effect
rubbing/friction moving electrons, higher affinity (ε) takes electrons
Conduction
charges split, equal charge density
ρ
charge density, could be of surface area or volume, Q/A or Q/V
Kirchoff’s Junction Rule
Conservation of charge
Electric Flux (Φ)
E∆A, density of field/lines
What is Φ in between two like charges?
0, asymptotic
How to find strength of E in system
VECTOR not scalar addition
If there’s a charge
then there’s also a FIELD
*****For work, remember that
only the one component matters bc work is qEd*cosØ
If you are moving a charge in its normal direction, the field is doing or getting work done?
DOING
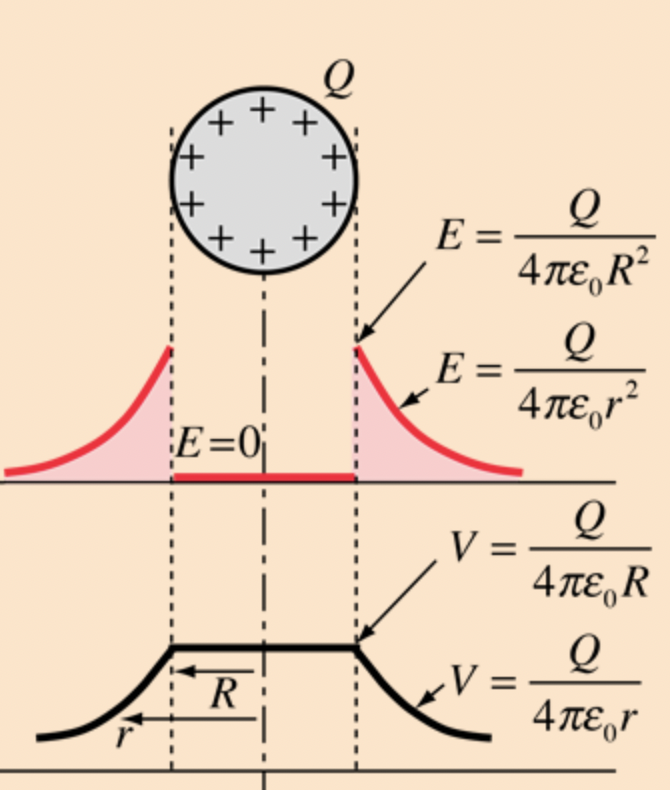
How does the potential of a sphere compare at different parts?
the V of sphere is SAME throughout, different as you get outside of it
The potential line of a field is VERTICAL/striaght when
it is going directly from a positive to negative, i.e. equipotential lines of capacitor
Which formula has a radius squared?
F and E, NOT V or U
Work moving inside a sphere
ZERO, equipotential and NO FIELD inside
When you are finding the potential away from a sphere, you do NOT have to add
the distance from the center bc same everywhere in sphere
How does a dielectric work?
The dielectric is typically an insulator that gets polarized and weakens the electric field because it creates an opposite field when polarized. This allows for the capacitor to store more charge. This reduces voltage and increase capacitance, thus meaning charge has to increase
Unit for Capacitance
F (farad)
How to find how much distance a particle travels before hitting a plate when sent through capacitor
Calculate force, F=ma, kinematics to find t, t*v = distance traveled
if capacitance and voltage increase, how does this impact Uc?
Increases from both according to Uc = 1/2C(deltaV)^2
How to find distance of added charge between two other charges
treat distance as (r-d) and other as d in Fe formulas
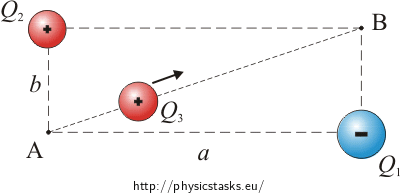
If a charge is on an angle from another charge…
then take that distance and plug it into force formula. THEN take components. Distance on a diagonal is MORE than straight component so LESS force. Remember DIRECTION of each force
What force dominates at the following levels? Microscopic, macroscopic, planetary/universal size
strong, electrostatic, gravity
How can a capacitor transfer charge in a circuit?
Induction only, no conduction or electrons “jumping” across gap
At what point of a charge do you measure its force?
From the CENTER, unless its a conducting sphere, then the OUTSIDE
When finding the net electric field or force, what should you be careful with?
VECTOR ADDITION DIRECTION
How to find spot where field is greatest from equipotentials
point where lines are closest together NOT closest to charge
motion of proton in capacitor
accelerates toward neg plate at CONSTANT rate
internal energy of a capacitor is equal to
Uc= QV = 1/2CV²
Every FRQ you must remember…
Units, show all work, use formulas, label
Experimental design show replication, use slope of graph and explain what is represents