PHY 1.3 Thermodynamics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
zeroth law of thermodynamics
states that objects are in thermal equilibrium when they are at the same temperature.
Objects in thermal equilibrium experience no net exchange of heat energy.
temperature
is a qualitative measure of how hot or cold an object is;
quantitatively, it is related to the average kinetic energy of the particles that make up a substance.
thermal expansion
describes how a substance changes in length or volume as a function of the change in temperature

linear expansion
ΔL is the change in length, α is the coefficient of linear expansion, L
is the original length, and ΔT is the change in temperature (final - initial)
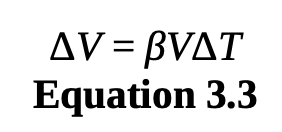
volumeric thermal expansion
ΔV is the change in volume, β is the coefficient of volumetric
expansion, V is the original volume, and ΔT is the change in temperature (final - initial)
thermodynamic system
is the portion of the universe that we are interested in observing, whereas the surroundings include everything that is not part of the system
isolated systems
do not exchange matter or energy with the surroundings.
closed systems
exchange energy but not matter with their surroundings.
open systems
exchange both energy and matter with their surroundings.
state functions
are pathway independent and are not themselves defined by a process.
Pressure
density
temperature
volume
enthalpy
internal energy
Gibbs free energy
entropy
process functions
describe the pathway from one equilibrium state to another.
work
heat
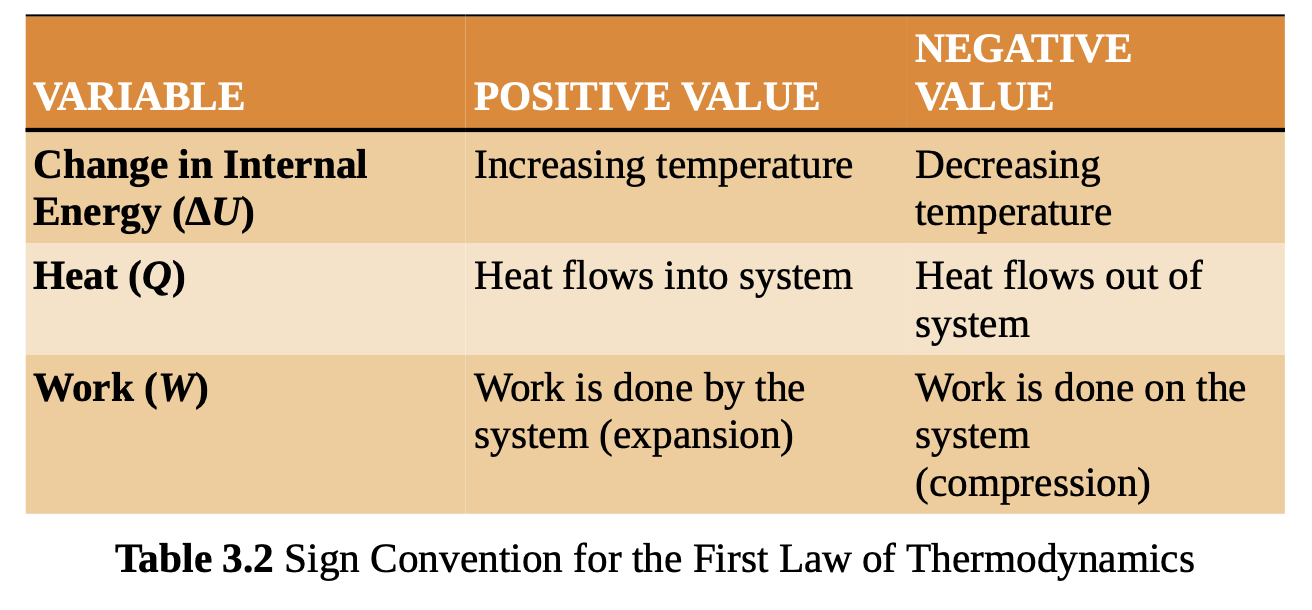
first law of thermodynamics
is a statement of conservation of energy: the total energy in the universe can never decrease or increase.
For a closed system, the total internal energy is equal to the heat flow into the system minus the work done by the system.

heat
is the process of energy transfer between two objects at different temperatures that occurs until the two objects come into thermal equilibrium (reach the same temperature).
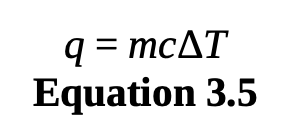
specific heat
is the amount of energy necessary to raise one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius or one kelvin.
heat of transformation
During a phase change, heat energy causes changes in the particles’ potential energy and energy distribution (entropy), but not kinetic energy. Therefore, there is no change in temperature.
isobaric
pressure is held constant
adiabatic
no heat is exchanged
isothermal
the temperature is constant, and the change in internal energy is therefore 0
isochoric
the volume is held constant and the work done by or on the system is 0
second law of thermodynamics
states that in a closed system (up to and including the entire universe), energy will spontaneously and irreversibly go from being localized to being spread out (dispersed)
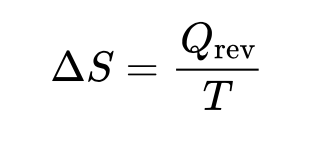
entropy
is a measure of how much energy has spread out or how spread out energy has become
On a statistical level, as the number of available microstates increases, the potential energy of a molecule is distributed over that larger number of microstates, increasing entropy.
where ΔS is the change in entropy, Qrev is the heat that is gained or lost in a reversible process, and T is the temperature in kelvin.
Every natural process is ultimately irreversible; under highly controlled conditions, certain equilibrium processes such as phase changes can be treated as essentially reversible
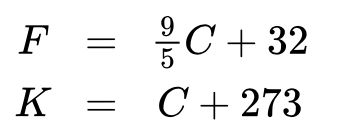
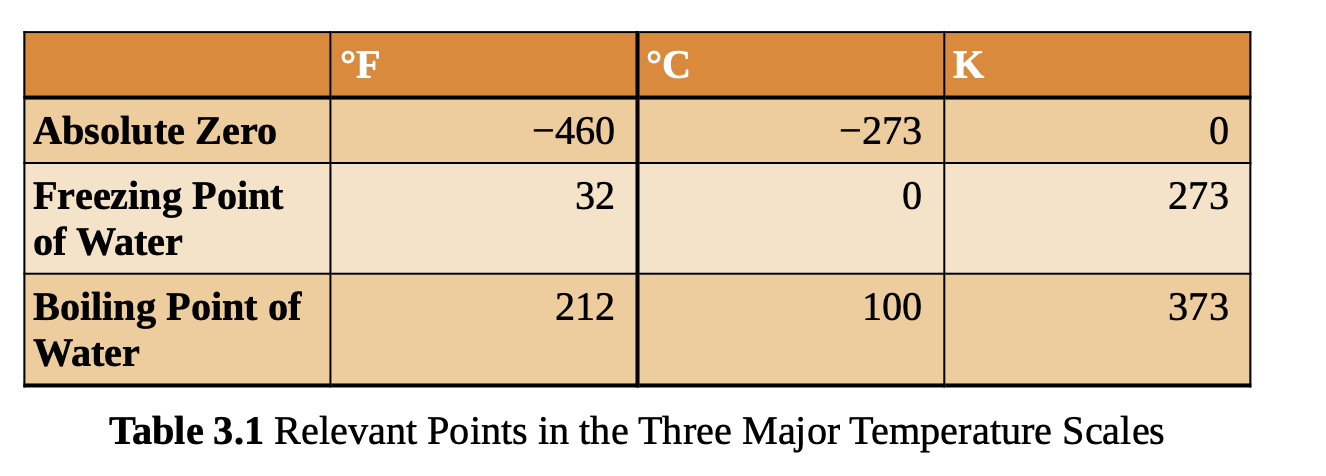
3 Major Temperature Scales
a change of 1 degree celsius = 1 unit kelvin
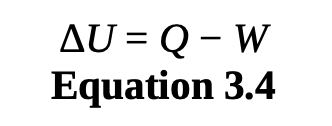
internal energy
conduction
direct transfer of energy from molecule to molecule through molecular collisions
convection
is the transfer of heat by the physical motion of a fluid over a material.
radiation
is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves
can transfer energy through a vacuum.
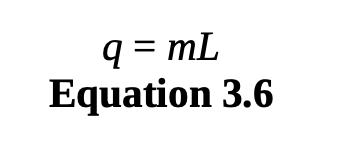
calculates heat added or removed
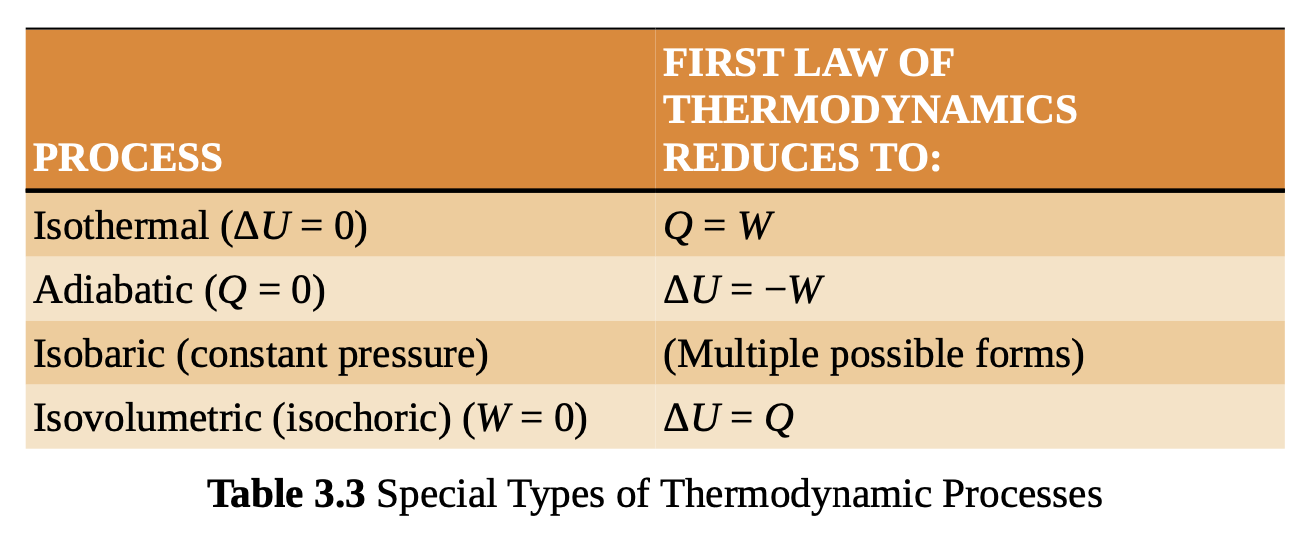
thermodynamic processes
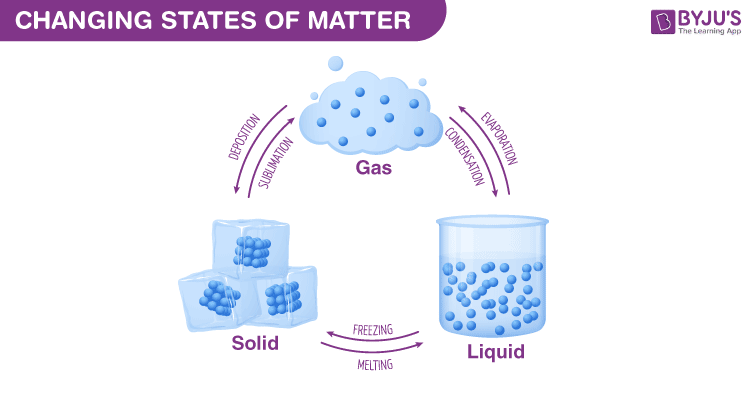
change in states of matter
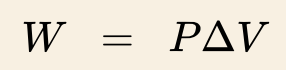
measure work done by / on a gas
V (final - initial)
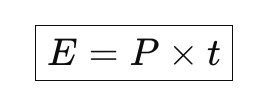
is used to calculate energy consumed or produced by a device over a period of time.