4) Intro to Musculoskeletal Loading
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
The amount of mass that can be accelerated is proportional to the force acting on it
F = ma
what is a force
Newtons (N) = 1 kg x 1m*s^2
standard international units for force are
vector
force is what type of quantity
magnitude and direction (represented by arrows)
a vector has a
load
a force that acts on the body tissue is often referred to as a
healthy; harmful
tissues all respond to force in diff ways and NEED force to be _____ ; however, forces can also be ____
hyaline/articular cartilage
needs to be loaded to be healthy - squeezes fluid out and absorbs it back in
loading magnitude
Loading rate
loading type
important factors that impact musculoskeletal loads
loading magnitude
how much a tissue is loaded
loading rate
speed at which a tissue is loaded
loading type
the way in which a tissue is loaded
time
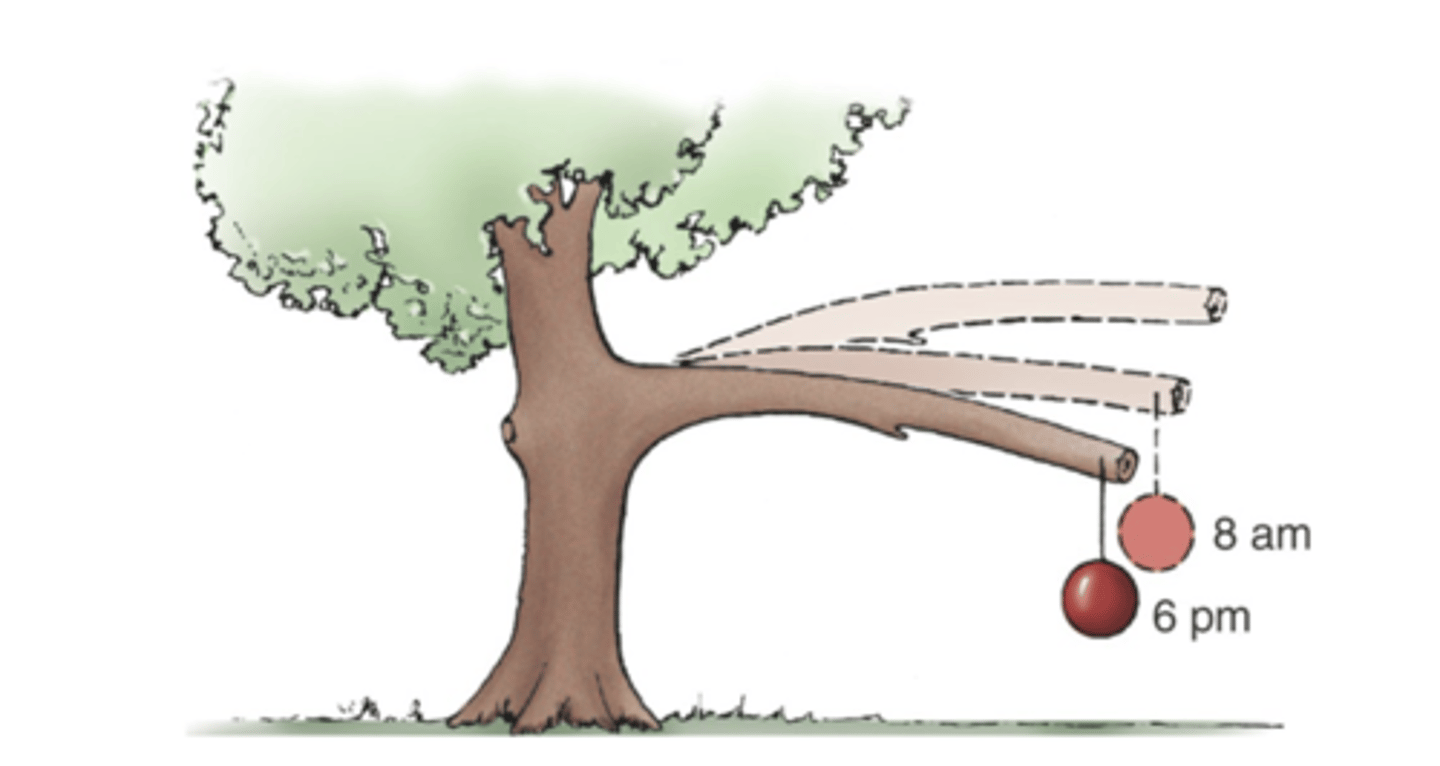
The loading rate is a function of
the rate at which they are loaded/how quickly they get loaded
biologic tissues are sensitive to
different loading-rate conditions
tissues behave differently under
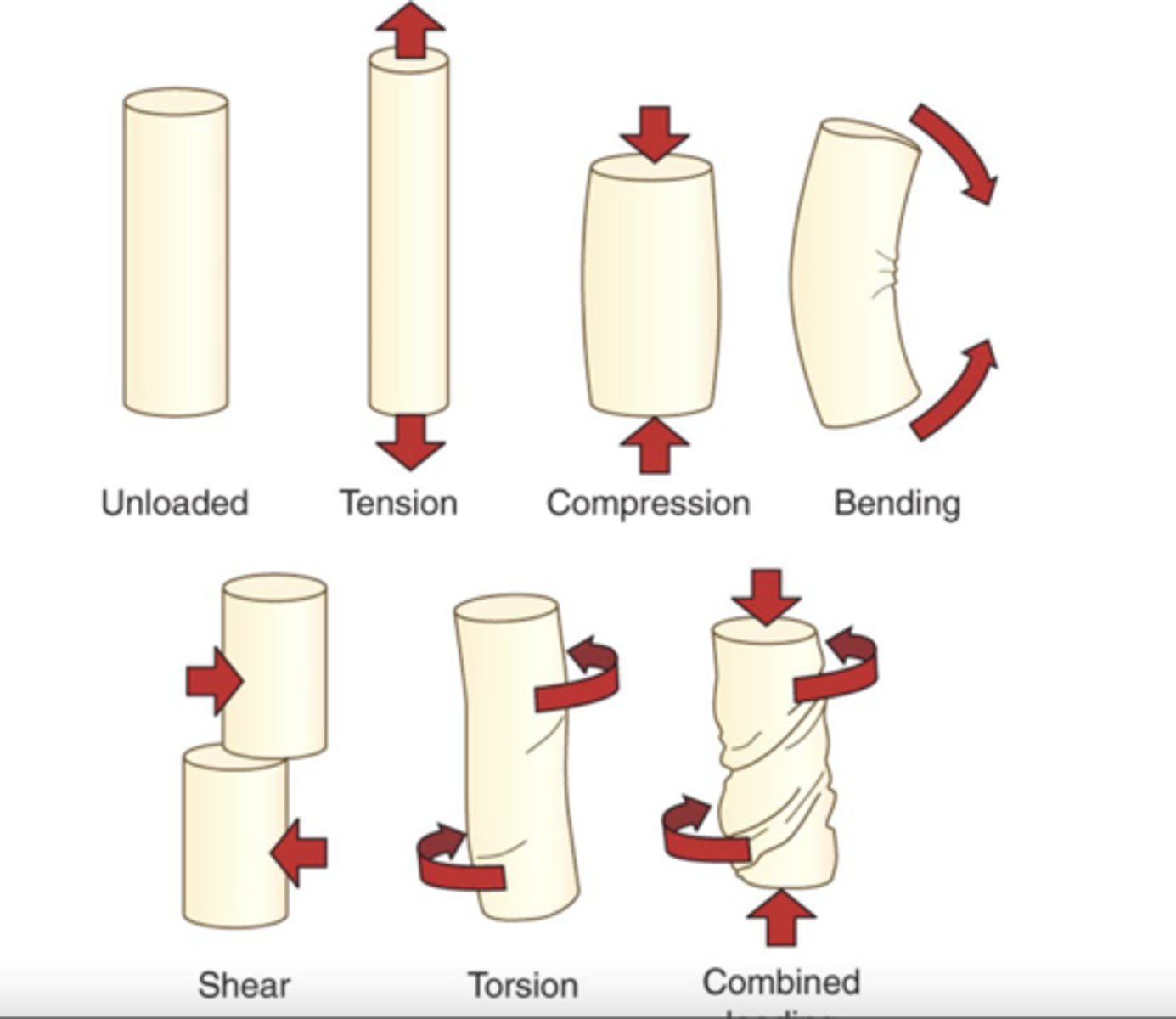
unloaded
tension
compression
bending
shear
torsion
combined loading
types of musculoskeletal loads
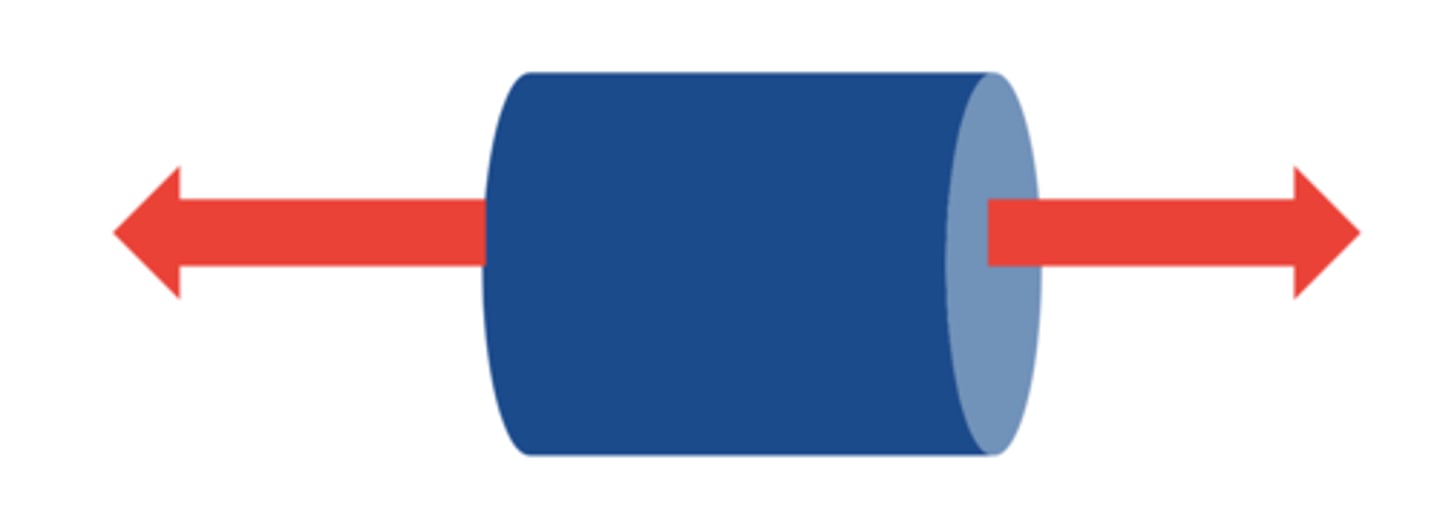
tension loading
two forces pull on an object in different directions
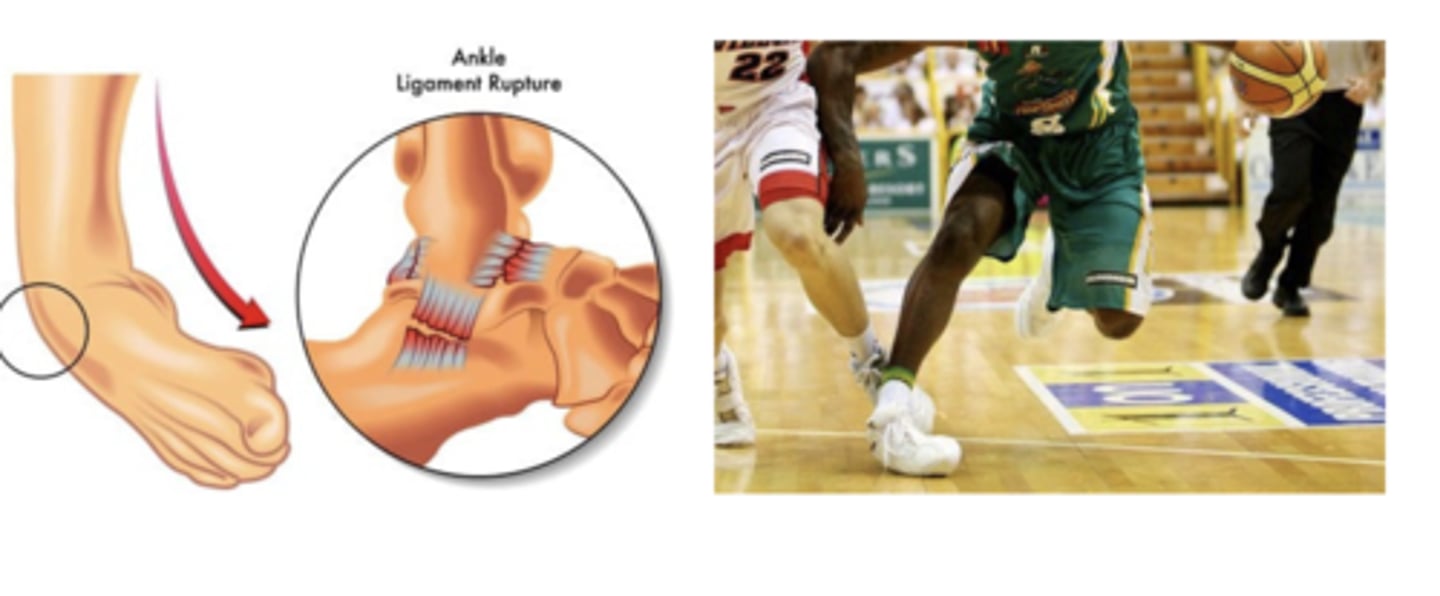
tension loading injury example
The lateral ankle ligaments (most commonly torn) are severely tensioned as the foot rotates inward
compression loading
forces that push or pull the surfaces of objects together or brings the end of an object closer
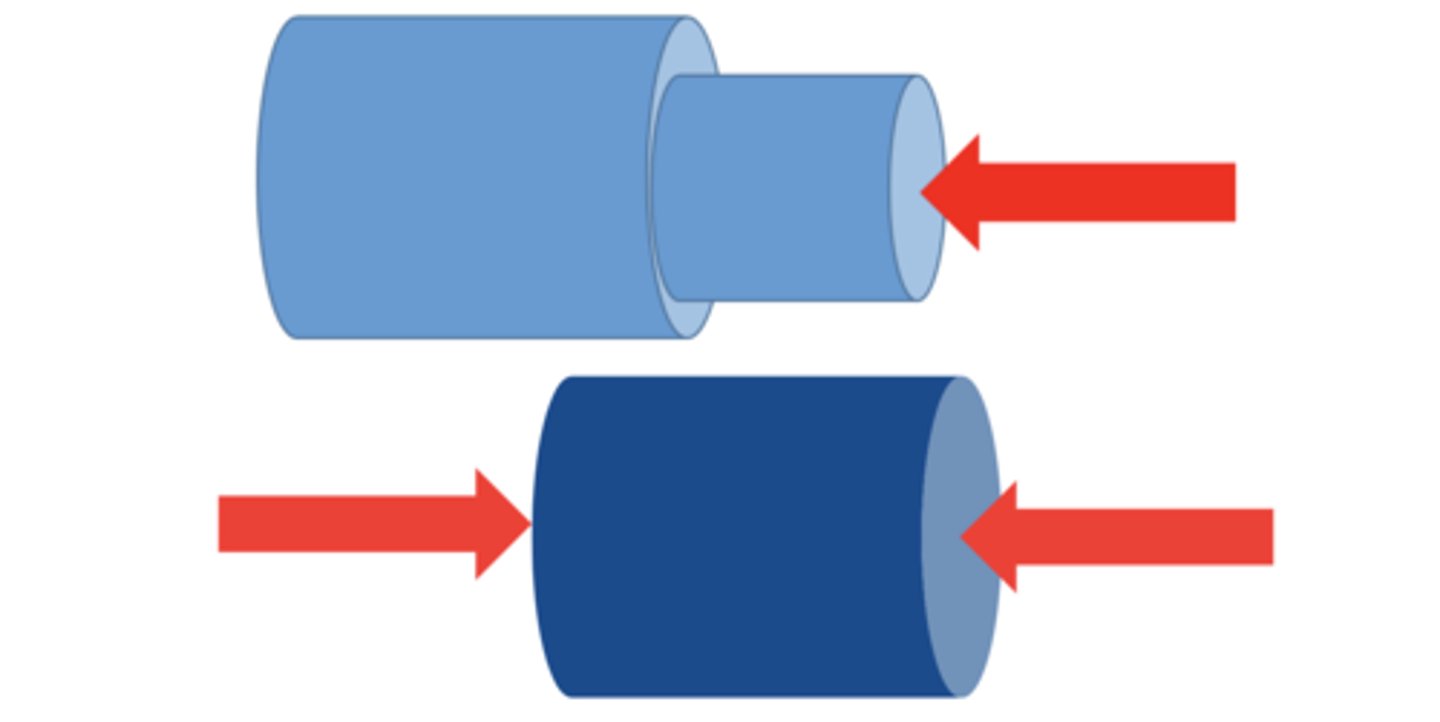
Compression loading example
The humerus is pulled against the glenoid by the deltoid muscle, creating a compressive load between the joint surfaces of the bones
bending load
deformation of tissue that occurs at right angles to its longitudinal axis
concave side undergoes compression load
convex side undergoes tension load
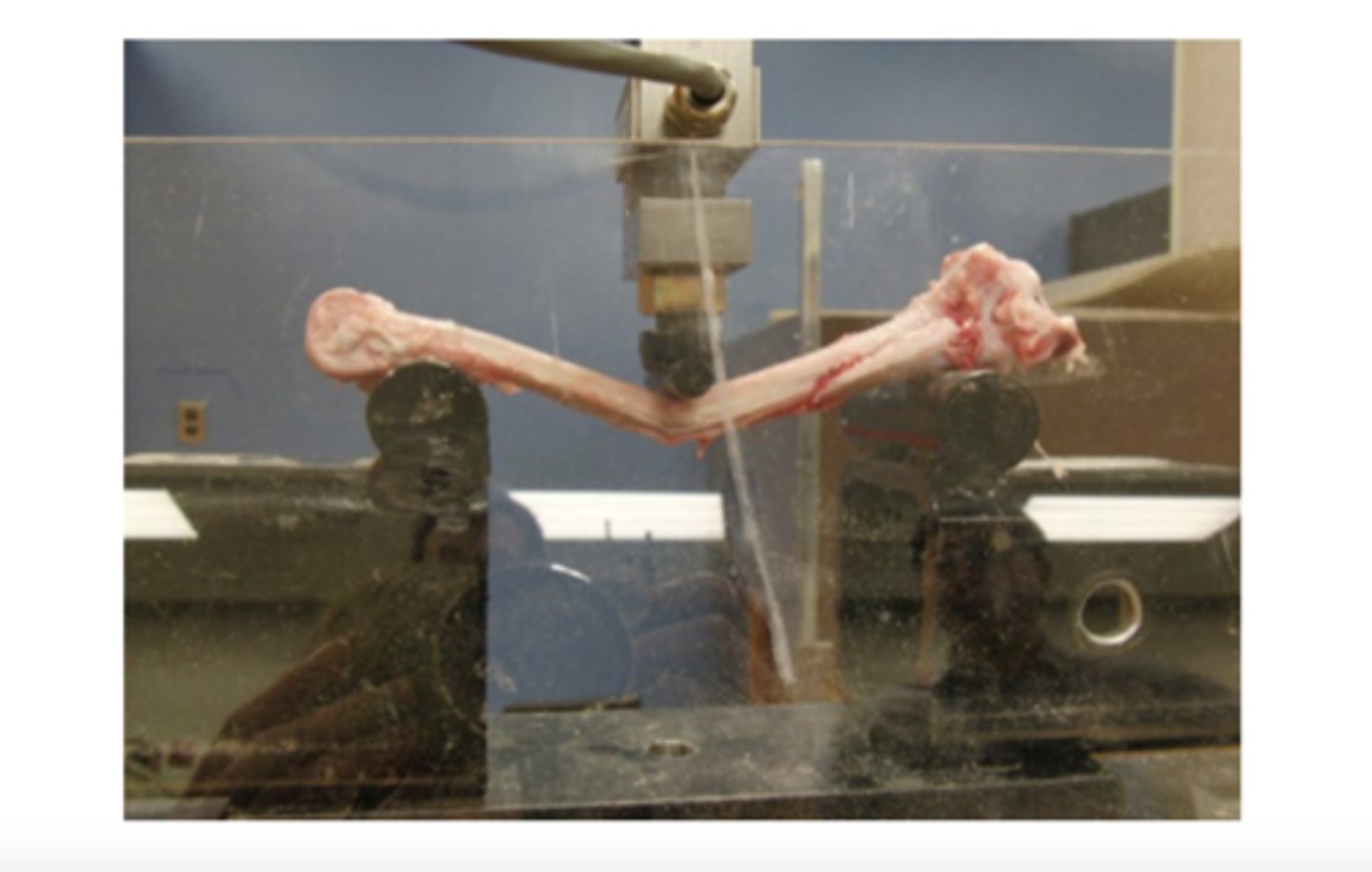
bending load injury example
coxa vara results in an increased bending load on the neck of the femur
shear load
Unaligned parallel forces that move on part of a body in one direction and another part in the opposite direction (created by friction)
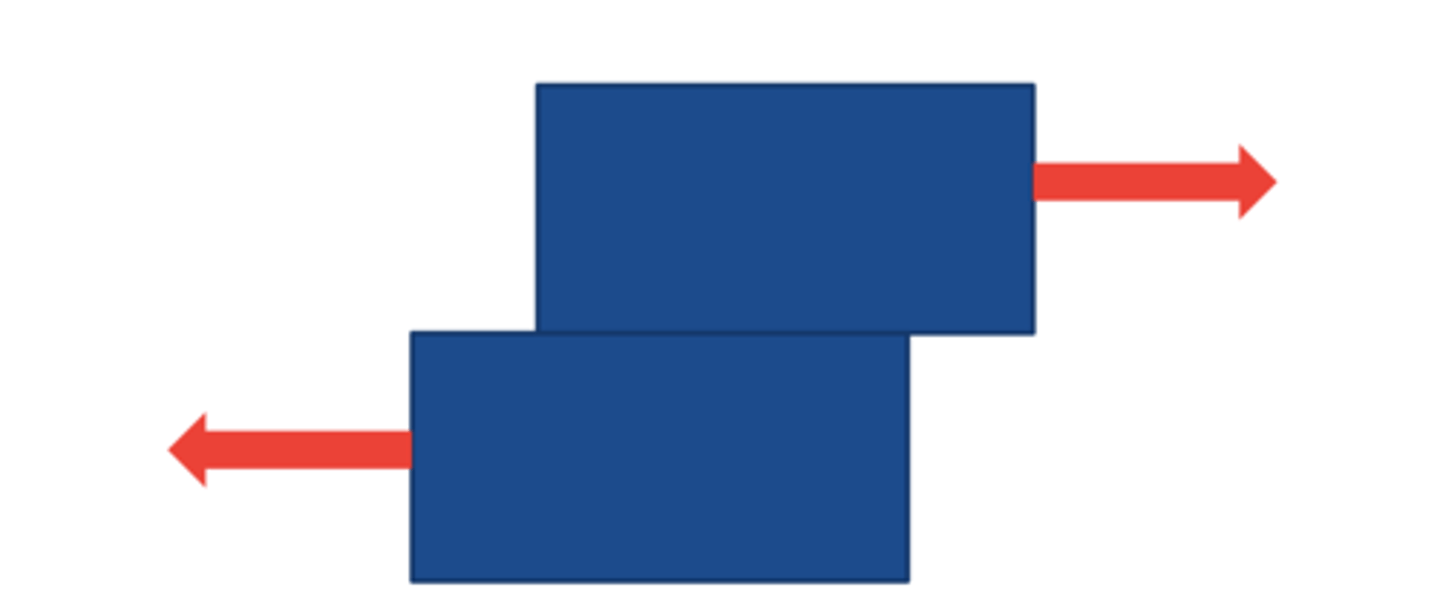

shear load injury example
cam type morphology in femoroacetabular impingement syndrome creates abnormal shear load between the femur and acetabulum
torsion load
twisting force applied to tissue around its longitudinal axis (one segment moving one way, other moving the opposite)
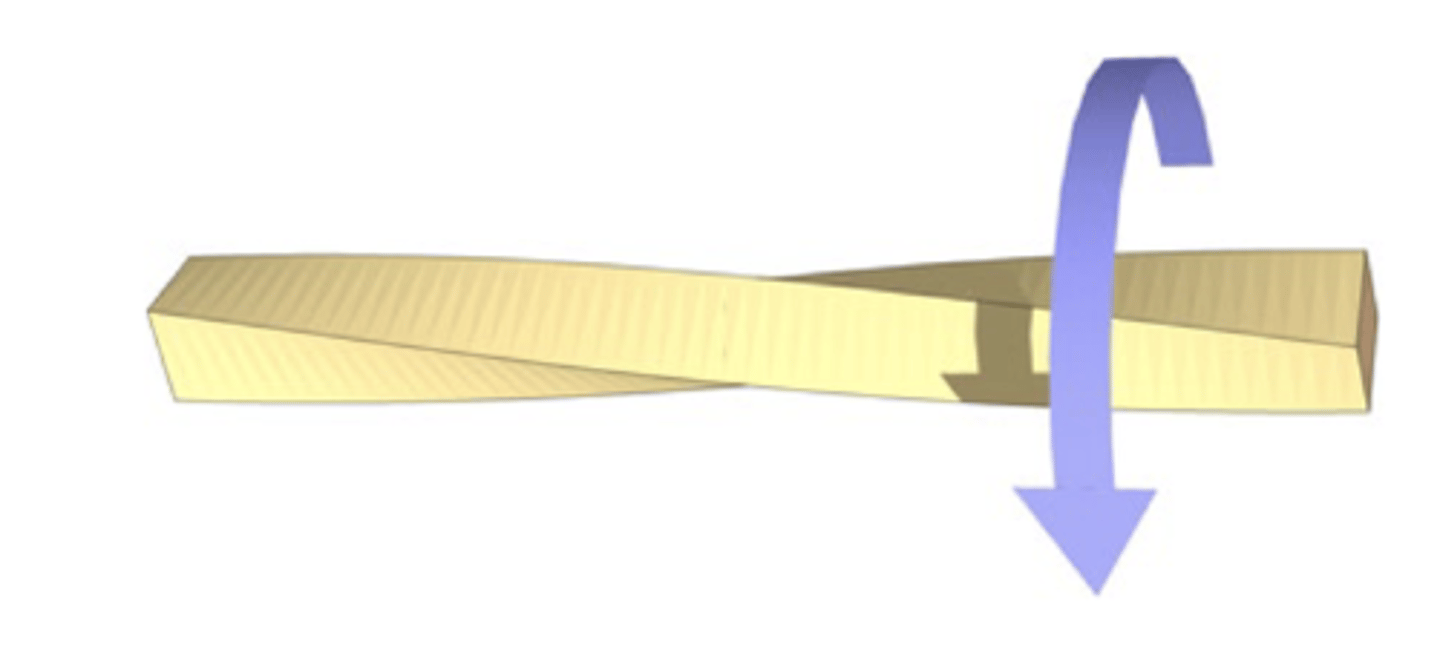
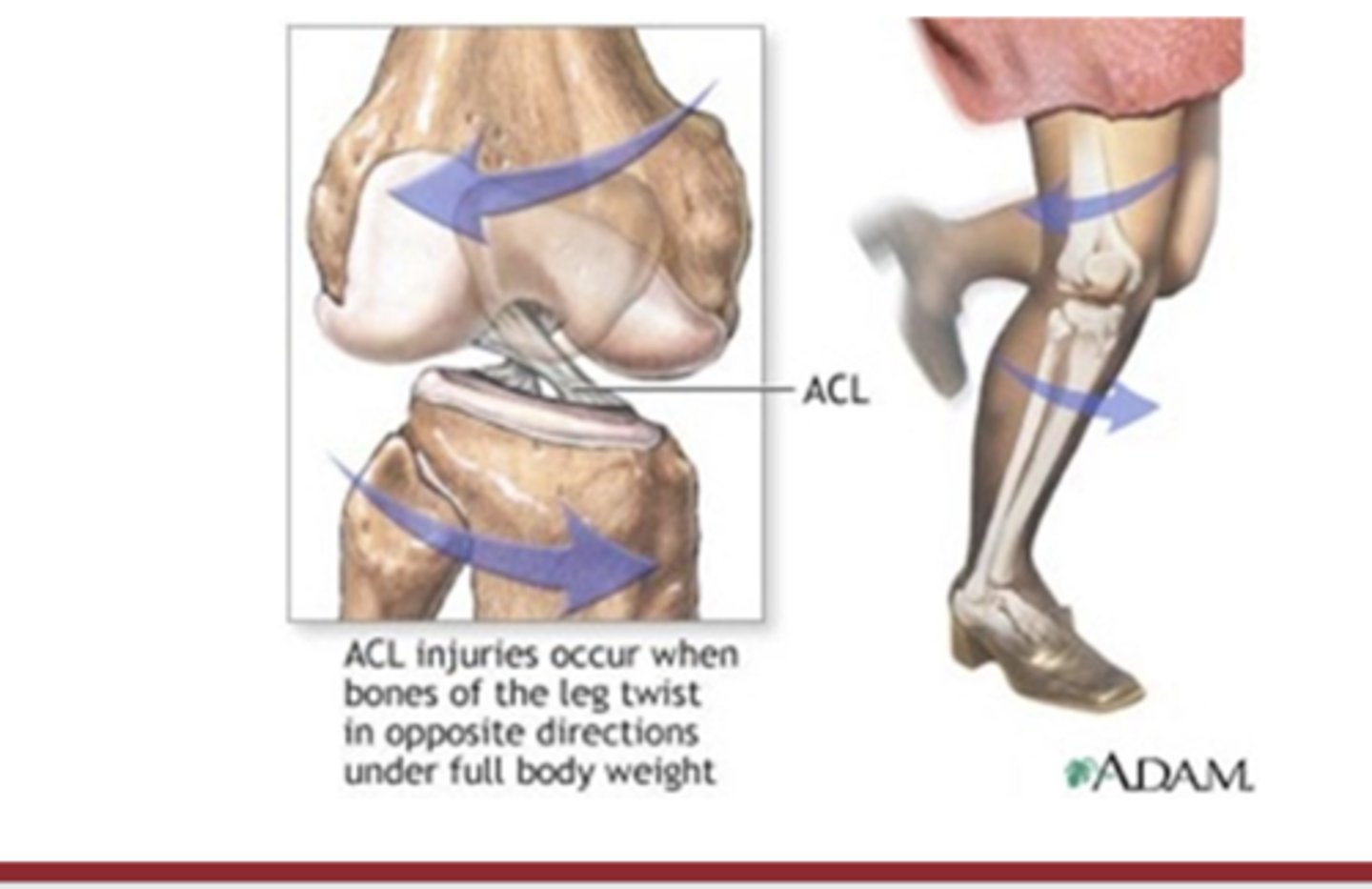
torsion load injury example
non-contact ACL rupture (tears by ____) … tibia sticks, femur twists
internal muscle forces
what counteracts the external loads on the body
active muscle forces
passive tissue deformation
viscoelastic
tissues in the human body are
viscosity
fluid-like component to the behavior of tissue ("gooeyness")
- honey = high
- water = low
time-dependent behavior… wants to return to original shape but is time-dependent
fluid-like behavior =
Elasticity
ability of material to return to its original state after loading
it can deform but resist change in structure and shape
healthy tissue can resist loads,
resist the external forces placing the tissue under the load
internal forces that arise w/in the structure under load can
tissue dependent
load response is
tissue stress
- force/load divided by cross-sectional area
- a measure of load or energy that is stored within a tissue
force (newtons) / area (m^2)
pressure =
tissue strain
the amount a tissue deforms under a force or load
usually expressed as a percent change in length or distance
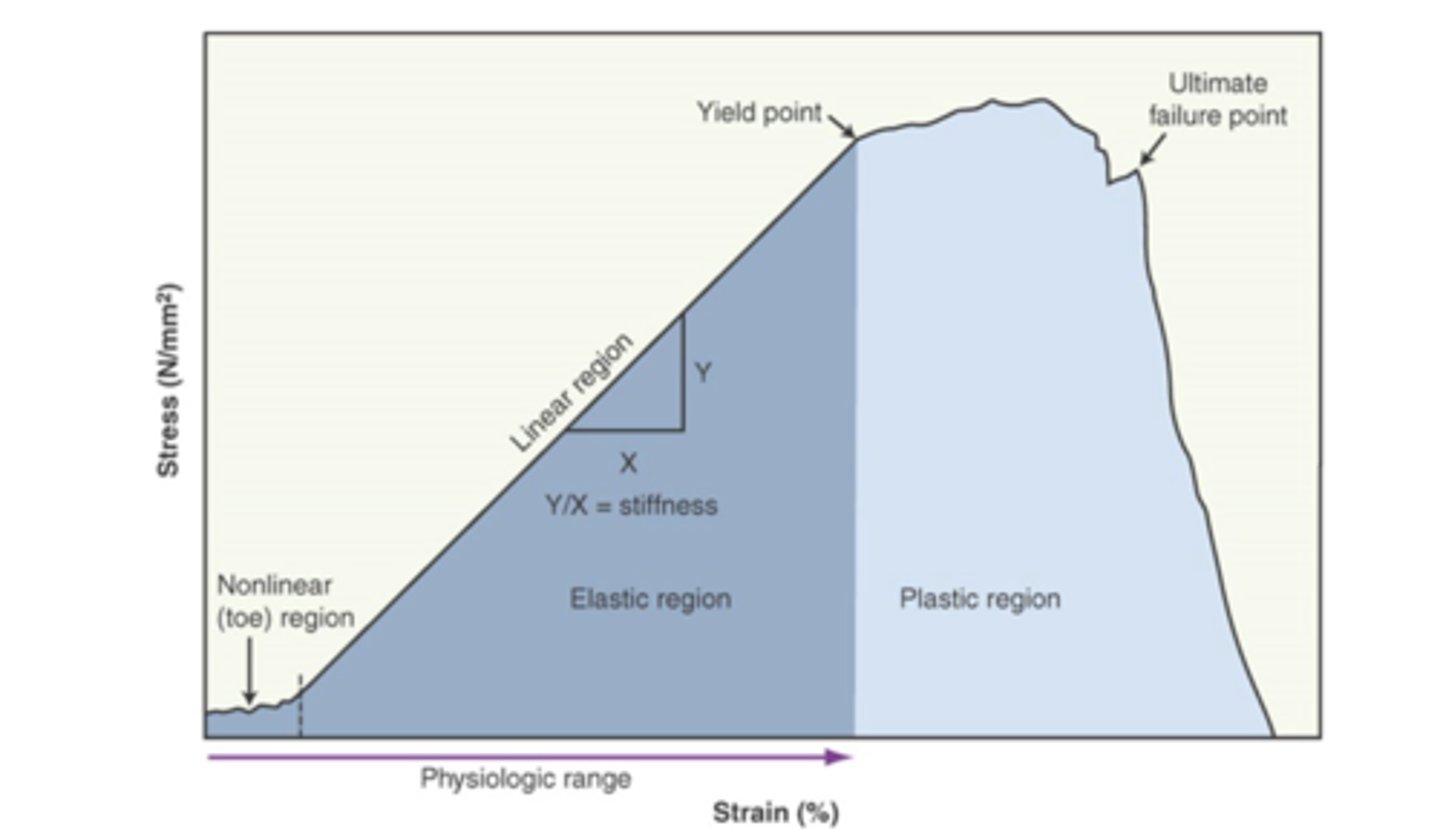
elastic deformation energy
- tissue returns to its original shape and all stored energy is released once unloaded
elastic energy represents
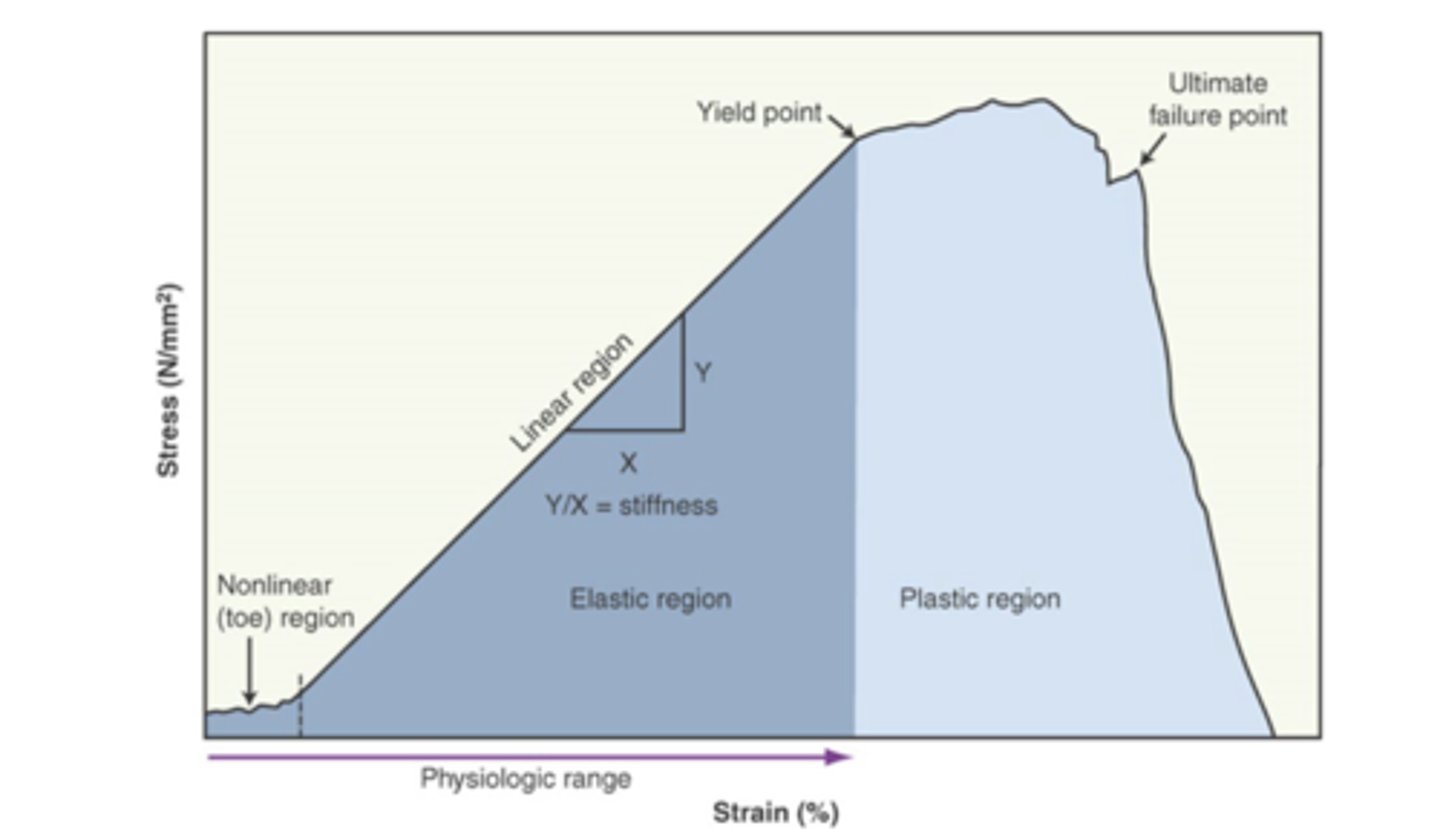
transition between elastic and plastic behavior
- additional load results in a marginal increase in stress
yield point is the
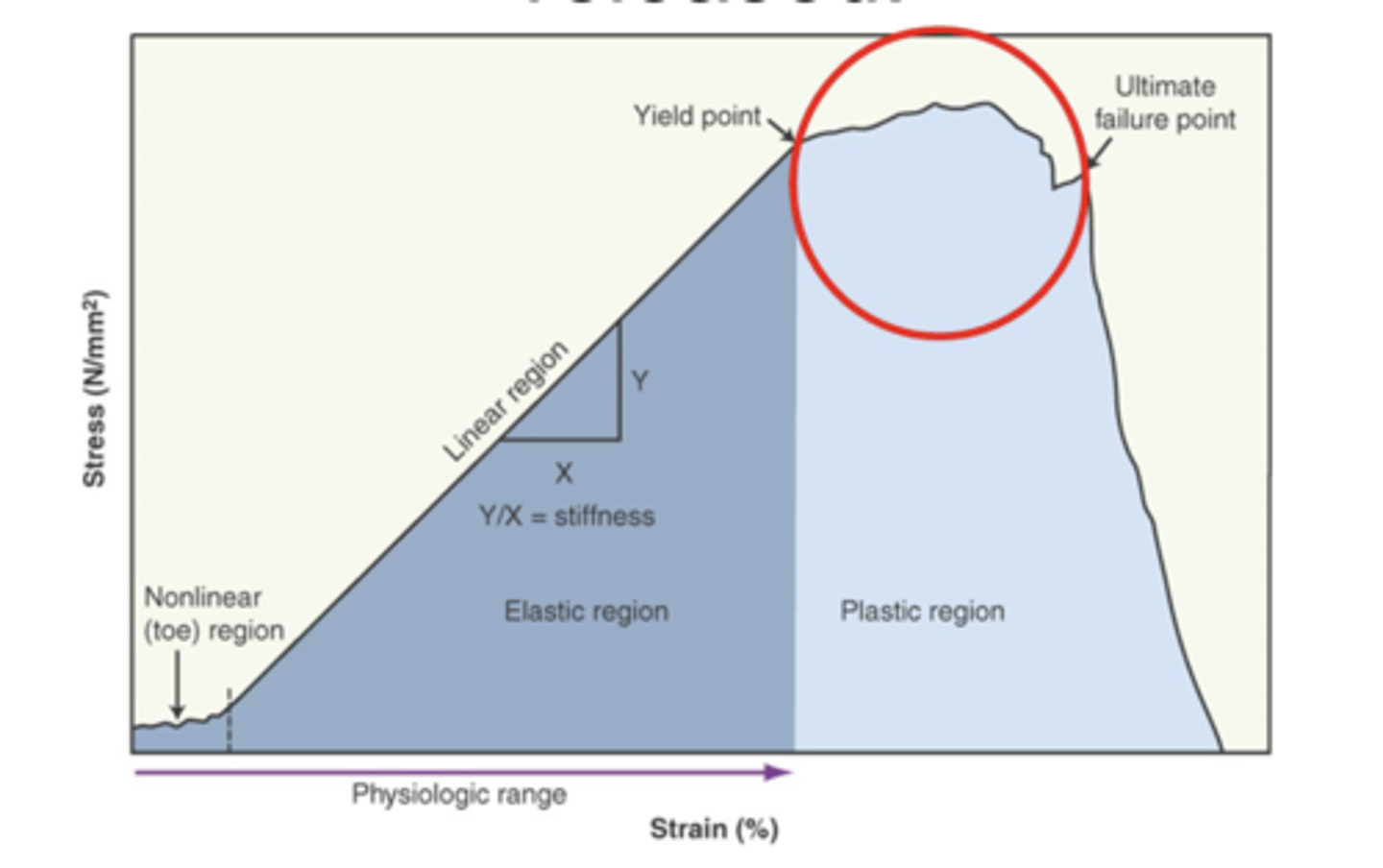
plastic deformation
- overstrained tissue is permanently deformed and energy cannot be recovered once load is released
micro-failure of tissue under continued load results in
creep
continued deformation of a material over time as it is subjected to a constant load