development dynamics
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
define development
process of improving peoples lives.
what are the indicators of development
GDP
life expectancy
infant mortality rate
poverty line
dependancy ratio
literacy rate
maternal mortality
access to safe drinking water
define GDP and why does it matter
(Gross domestic product) it is the total value of goods and services produced in a country per year
it matters becuase it shows the economic strength
define literacy rate and why does it matter
the average age that people live in a country
it matter becuase it shows the healthcare and living conditions
define infant mortality rate and why does it matter
number of babies that die before the age of one per 1000 babies
it matter becuase it also shows healthcare
define poverty line and why does it matter
it is the minimum income that is required to meet basic needs
it is important becuase it shows how many people live in poverty
what is dependancy ration and why does it matter
the percentage of population of too young or too old to working age
this matters becuase it shows high ratio = more pressure on working
what is the literacy rate and why does it matter
the percentage of adults that can read and write
it matters because it reflects the education access and the quality of the education
what is maternal mortality and why does it matter
number of mothers per 100000 that die during giving brith
it matters becuase it shows healthcare access
what is access to safe drinking water and why does it matter
it is the percentage of water that is a clean and safe for people to drink
it matters becuase it shows the development for health
define HDI
(human development index) something created by the UN to measure development
the scale is 0-1, the more the number is closer to one, the more developed the country is from that factor
what are the three factors of HDI
life expectancy
literacy rate
GDP per capita
waht is GDP per capita
a persons average economic output in a country
define population pyramid
graph that shows the age and structure of a population
what would it mean if the population graph had a…
wide base
narrow base
bulges
indents
tall pyramid
upside down traingle
wide base = high brith rate
narrow base = low brith rate
bulges = shows immigration
indents = shows possibly disease and people are dying to it
tall pyramid = high life expectancy
upside down triangle = ageing population
define global inequality
uneven distributed of wealth, resources and opportunities in a country.
what are the causes of global inequality
physical environmental
history - colonialism
neo-colonialism
political and economic policies
how is physical environmental a cause of global inequality
landlocked countries
poor climate
frequent natural hazards occurring
how is neo-colonialism a cause of global inequality
rich countries will domiante the poorer countries using debt, trade and political influence.
how is history colonialism a cause of global inequality
colonies were exploited for resources and unequal trade can affect the development of a country.
how is political and economic politics a cause of global inequality
open economies attract investment, corrupted governments can affect the development.
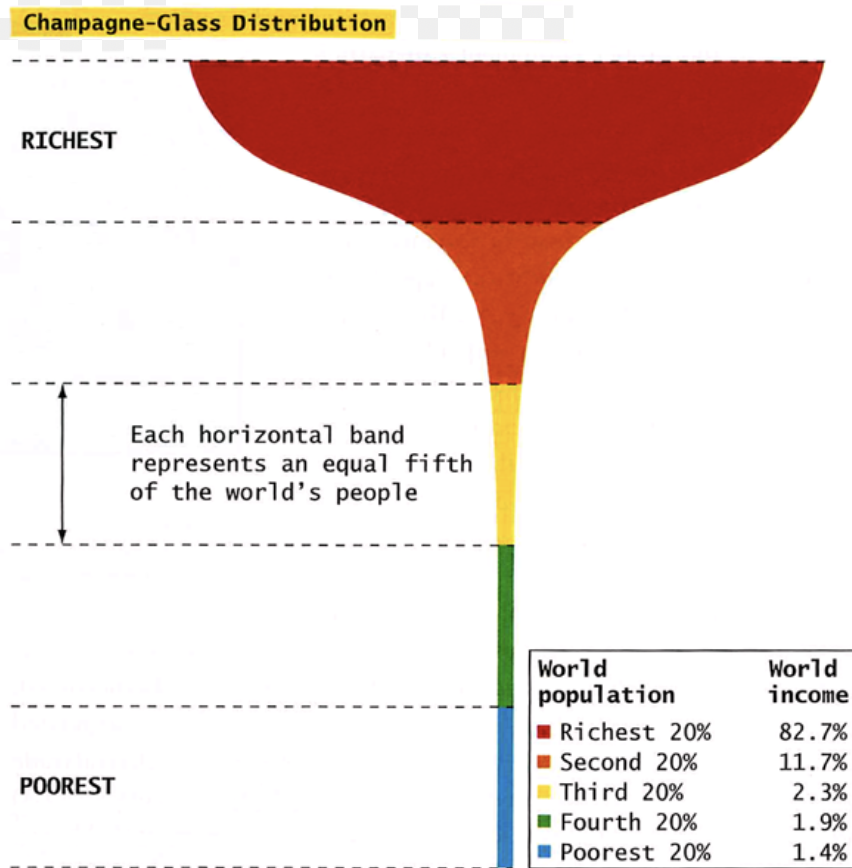
what is the champagne glass distribution
a visual that shows the global income inequality, at the top 20% is the people that holds the top wealth and the bottom 20% have the littlest wealth.
what is the rostows model
it is a theory that shows the things that a country needs to go through to develop economically
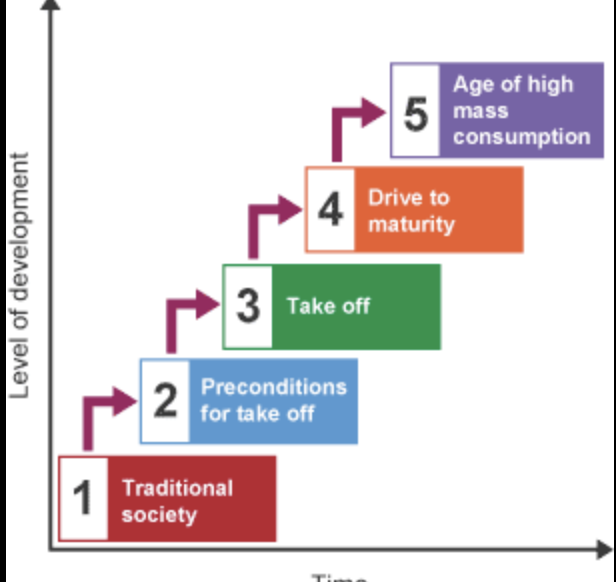
what are the 5 stages in the rostows model and what is each stage about
traditional society
agriculture based, little trading
preconditions before take off
investing in industries and infrastrcuture
take off
more trading, investing and technology creates manufacturing industries
age of high mass consumption
wealth society, lots of goods and services being sold.
what are the strengths of the rosters model
easy to understand
show how countries can develop over time
what are the criticisms of the rostows model
assume all countries start equally
ignores countries that experience inequality
what is franks theory
shows how inequality is caused by the exploitation of poorer countries (peripheral) by richer countries (core)
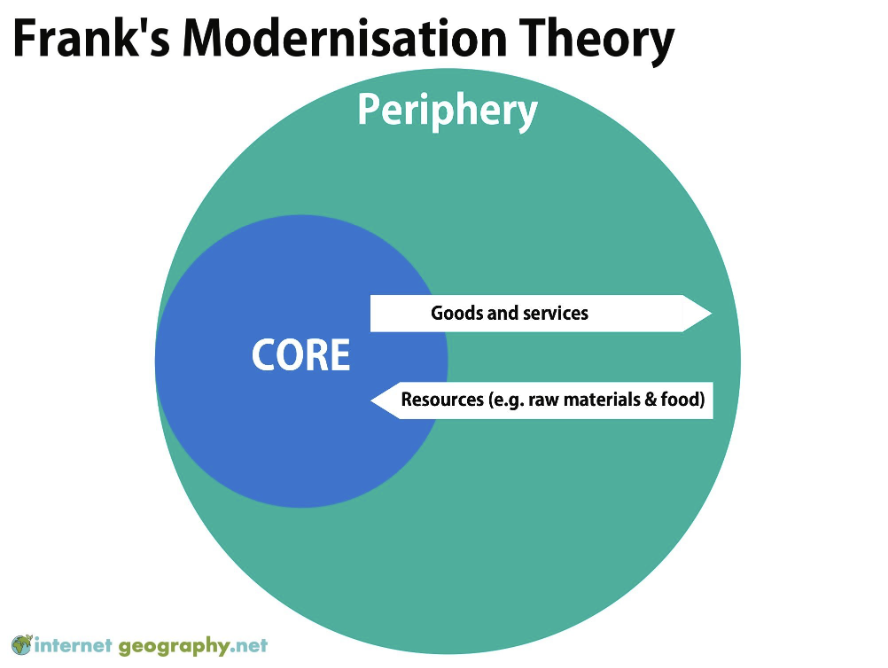
what is the process of the franks theory
when periphery sells the raw materials to the core, the core turns it into a product for a high price that the periphery has to buy. This makes the periphery unable to develop since they are buying expensive imports form the core.
what are the strengths of the franks model
explains why global inequality happens
highlights exploitation and Neo colonialism
what are the criticisms of the franks model
some developing countries develop successfully
ignores factors such as government is corrupted
not all countries are colonised
define colonised
when a country is taken over by another country that is more powerful than them
what are the consequences of global inequality
economic
1 in 5 people live on less that one dollar a day , it is hard for the country to develop.
social
775 million people cannot read or write and 1 billion people lack of clean water access
environmental
poorer countries are more vulnerable to natural hazards.
political
some governments are corrupted
define migration
movement of people going from a place to another
why does migration occur
escape poverty
globalisation
transport improvements
what factors affect to development
aid
fair trade
remittance
debt relief
define globalisation
the interconnectedness of countries through trade, communication and migration
define aid
when grants or loans are given to the country to help develop
define trade
allows producers to sell directly to richer countries.
define remittance
money sent home by the immigrants
define debt relief
when the rich countries cancel the poor countries debt if they invest in sustainability
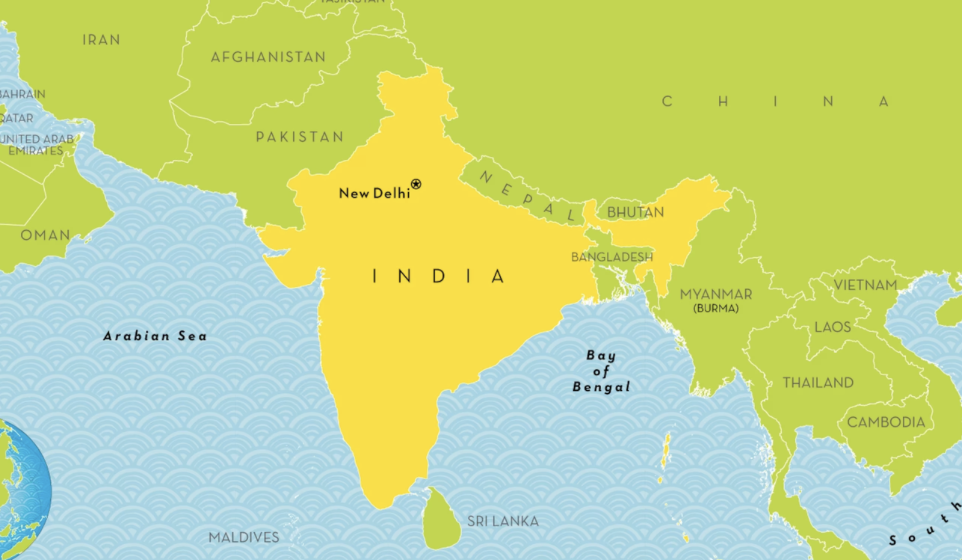
where is india around
nepal
china
pakistan
Indian Ocean
Arabian Sea
wahat is the environment of India
contains lots of biodiversity
one of the largest greenhouses gases producers
waht is the culture in india
80% are hindu
15% are muslim
3% are christian
2% of sikh
what is the politics in india
one of the largest democracy
what is the society of india
1 billion people in india
16 million in mumbai
40 million live in slums
define economic liberalisation
where economy is opened up to private businesses and global trade
how did globalisation change Indias economy
reduced tariffs, taxes and monetary controls encouraging FDI (foreign direct investment) this is economy liberalisation
growth in containerisation and shipping increased exports
define TNC
(transational corporation)
where a buisness is in more than one country
how do TNCs operatie in india
by doing outsourcing
wokrers gain 3000 pounds per year (this is 20% of UKs average pay)
some workers earn more than doctors so brain fear occurs
define outsourcing
when TNCs move services to countires that have cheaper labour
define brain drain
when there is a loss of skilled workers from key sectors such as healthcare sector (eg doctor)
what industries are in india due to TNC
BT’s call centre is in Bangalore
Walmart, zara etc garment factories are in India
how did TNC change Indias economy
80 million employees were employed
300 billion pounds GDP
this makes india the 2nd largest GDP country
Indias economy increased by 7%
is there inequality on working Pay and how
yes, 70 percent of women workers are having the lowest salary
what are the development indicator for India
(GDP per capita, GNI per capita, HDI)
GDP per capita 1200 —> 6000 dollars
GNI per capita 2500 → 5500 dollars
HDI 0.5 → 0.6
what are the sector changes in the economy (for agriculture, manufacturing and services)
agriculture 40%→ 20%
manufacturing 17%→18%
services 45%→ 67%
what does india export
gems and jewlery
transport equipment
petroleum products
50% of it goes to India
waht does india import
oil
gold and silver
electronics
mainly comes from china
how much money has been invested into india (FDI)
250 billion dollars
what are the social impacts due to the economy change
rural to urban migration has increased
lots of demographic changes
birth rate fell 30 → 20 per 1000
life expectancy increased 60 →68
infant mortality rate fell by 50%
what are the environmental impacts due to the economy change
increases air pollution
increases water pollution
increase in deforestation
increase climate change sicne idnai as the 2nd largest greenhouse affect producer
what is the GDP per capita for Maharashtra and Bihar and where does it come from
2500 pounds (Maharashtra)
from series such as call centres
700 pounds (bihar)
comes from farming