Chemistry quizz: Chemical change
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:06 PM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Electronegativity
A measure of an atom’s ability to attract shared bonding electrons to itself.

2
New cards
Nonpolar covalent bond
Occurs when two atoms have the same/similar electronegativity, so the electrons will be in middle, between two nuclei.

3
New cards
Polar covalent bond
Occurs when two atoms have different electronegativity.

4
New cards
Partial negative charge
The most electronegativity atom will have
5
New cards
Electronegativity difference
The difference in the electronegativity values of two atoms that are bonded together.
6
New cards
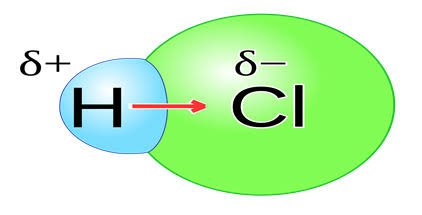
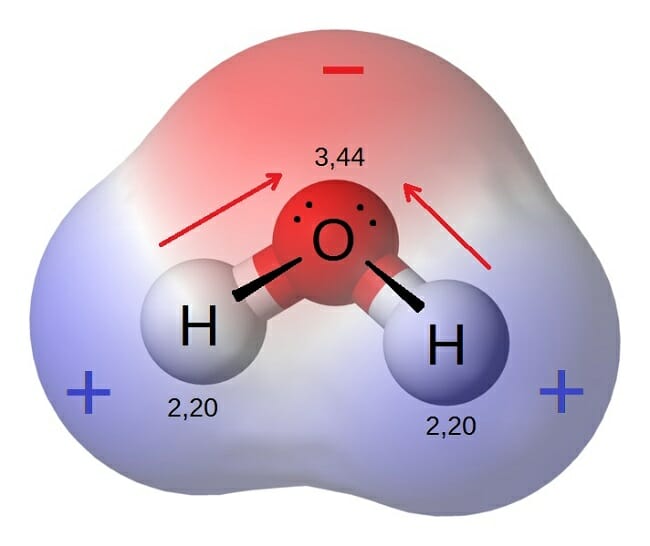
Polar molecule
A molecule where is a partial positive charge on one side of the molecule, and a partial negative charge on the other side.
7
New cards
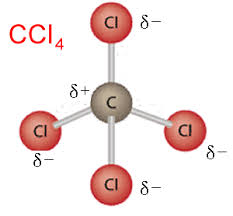
Nonpolar molecule
A molecule where is no different in charge on different sides of the molecule.
8
New cards
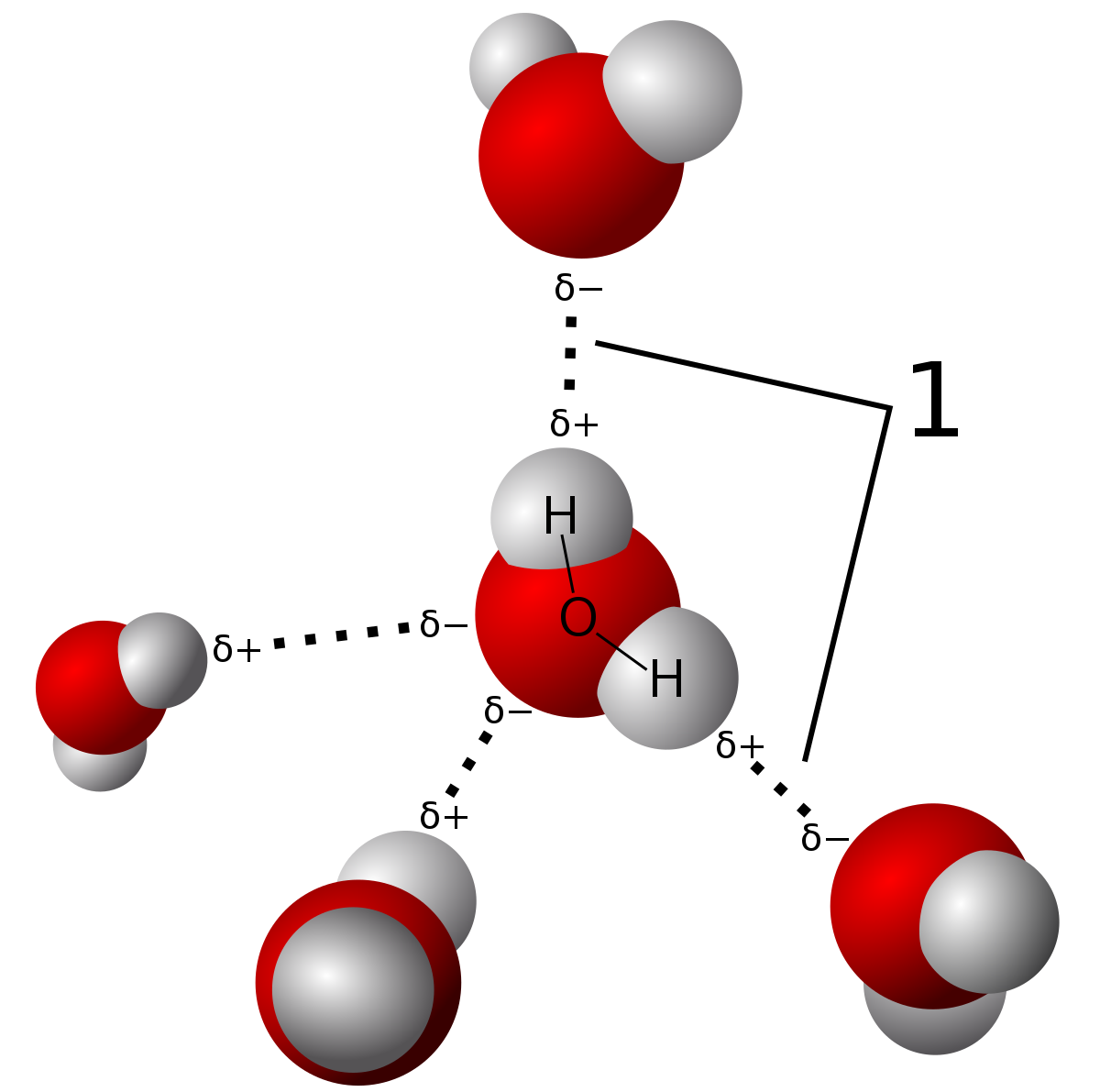
Hydrogen bonding
A particularly strong intermolecular attraction which occurs between molecules in which hydrogen is bonded to the most electronegative atoms.
9
New cards
Polar
A molecule that has a charge on one side of the molecule, that is not cancelled out.
10
New cards
Partial positive charge
The less electronegativity atom will have
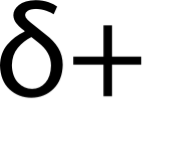
11
New cards
Chemical reaction
The kind of reaction where one kind of matter turns into a different kind of matter, with a different chemical formula.

12
New cards
Chemical equation
Short way to write the chemical reaction, by using chemical formulas and symbols. There are equal number of each type of atom on the reactant and product sides of the equation.
13
New cards
Reactant
Substances that to into a reaction (go down).
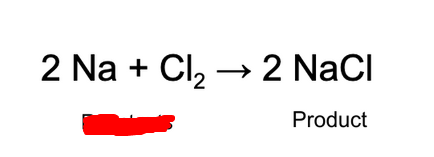
14
New cards
Coefficient
A whole number multiplier placed in front of a formula in an equation to have the same number of each type of atom on the reactants and products.

15
New cards
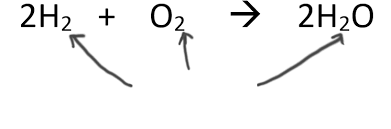
Subscript
Total number of each type of atom.
16
New cards
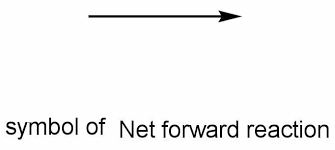
Yield arrow
A sign used to seperate products from reactants and show the direction of a reaction.
17
New cards
Product
Substances that come out of the reaction (go up).
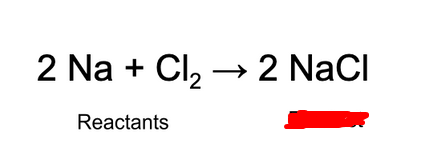
18
New cards
Balancing
Adding coefficient to a skeleton chemical equation to make the numbers of each type of atom the same on either side.
19
New cards
Multiplier
Includes coefficient and subscript, indicates how many particular atoms or functional groups are attached at a particular point in a molecule.
20
New cards
Conservation of mass
The law states that matter cannot be created or destroyed. There must be the same number of each type of atom on the reactant and product sides of a chemical reaction.
21
New cards
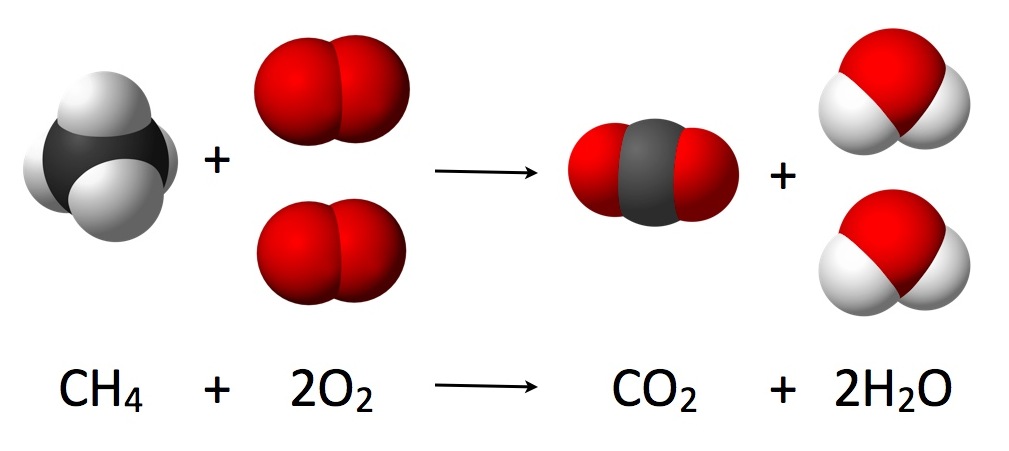
Combination reaction
A chemical change where two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
22
New cards
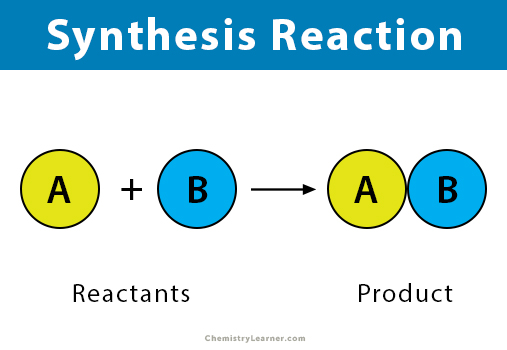
Decomposition reaction
A chemical change where one reactant breaks down to form two or more products.
23
New cards
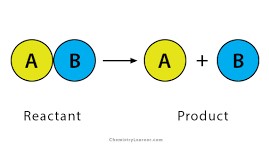
Single-replacement reaction
A chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound.
24
New cards
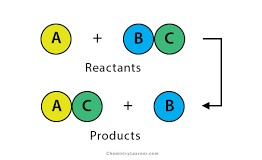
Double-replacement reaction
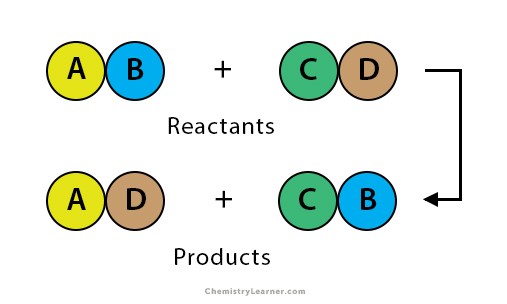
A chemical change in which two ionic compounds swap cations.
25
New cards
Activity series
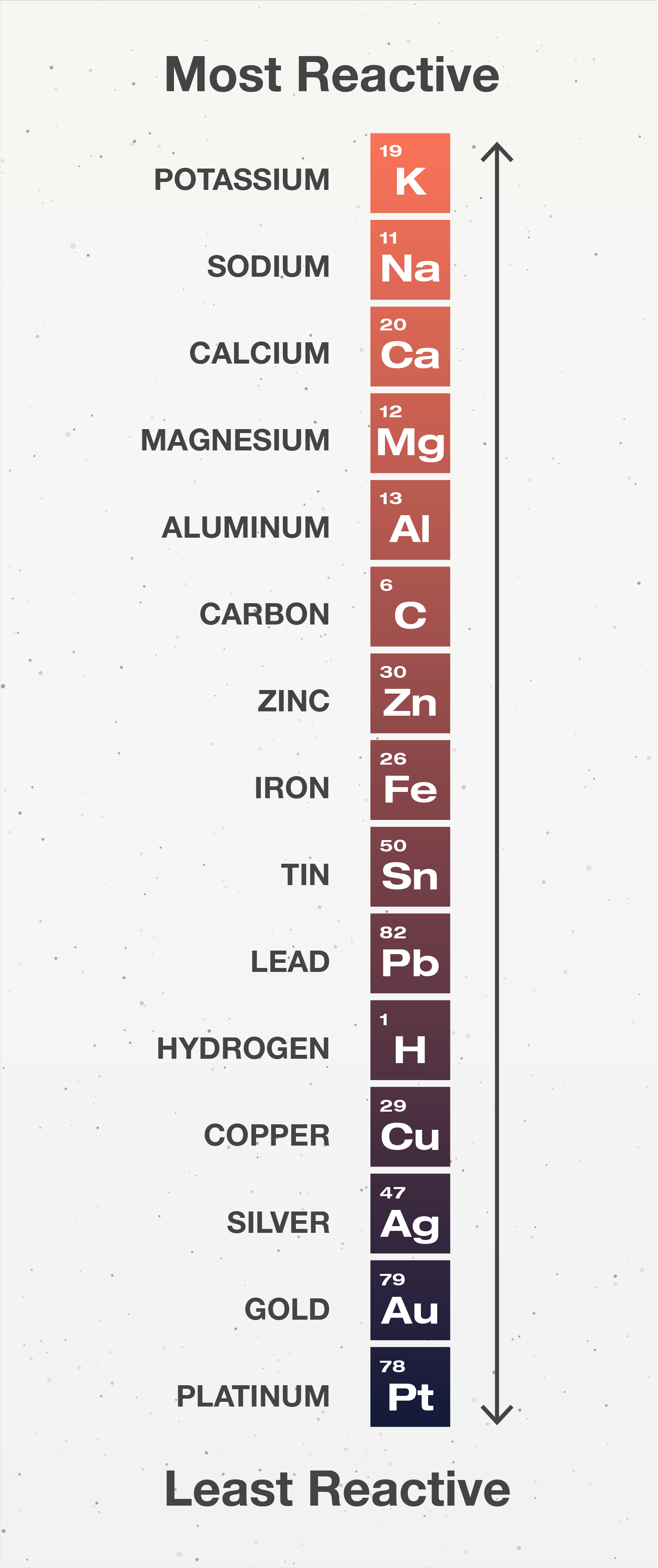
A list of elements in order of reactivity.
26
New cards
Combustion reaction
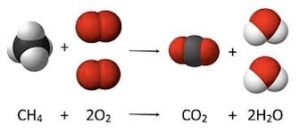
A chemical change in which an element or compound reacts with oxygen O2.
27
New cards
Hydrocarbon
Compounds made only of C and H.