Lecture 9 -- Vertebral Column
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the regional variations of the vertebral column?
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal.
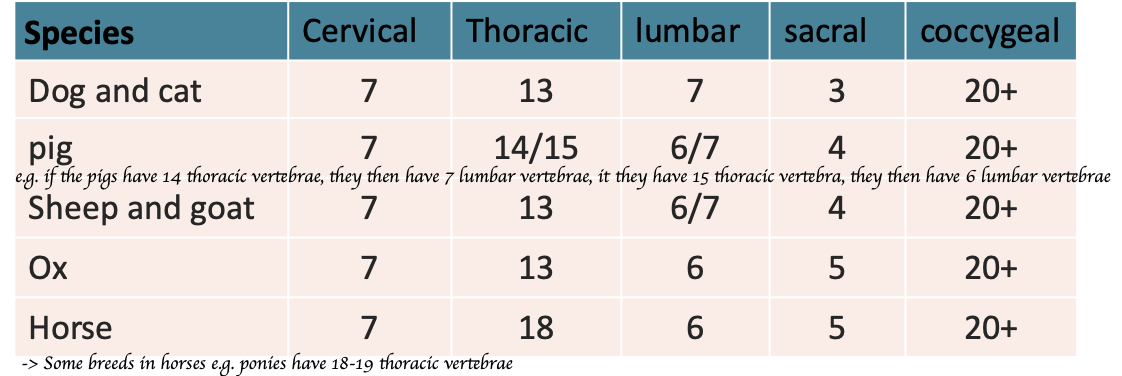
List out the number of each vertebral column of different species (Dogs and cats, pigs, sheep, ox and horse)?
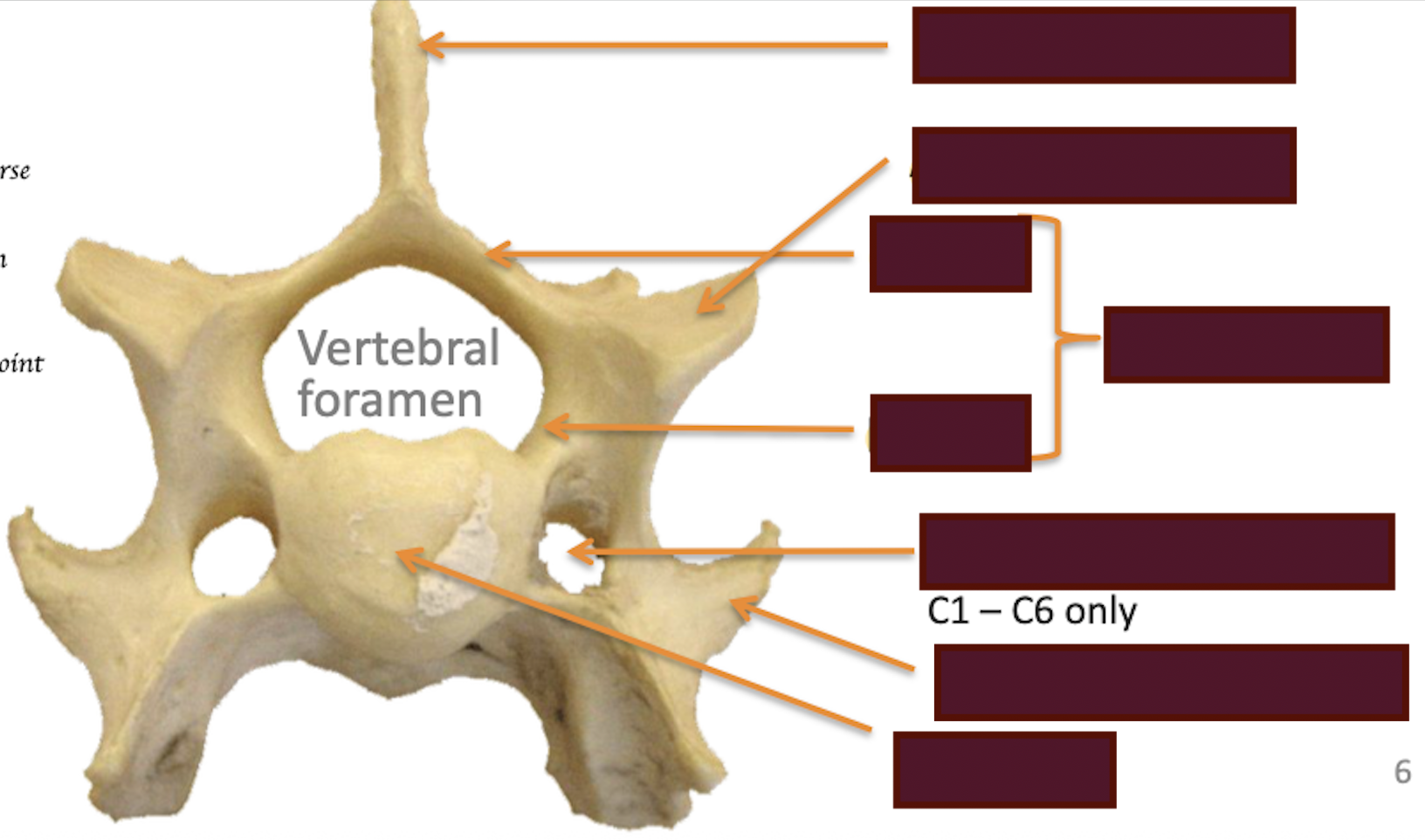
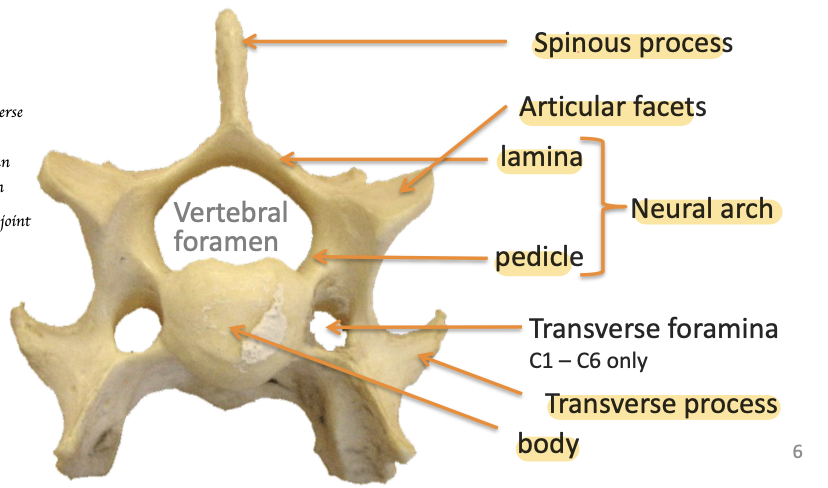
Label the key structure of typical vertebra
Through which joints do adjacent vertebrae articulate?
Synovial joints
What structures form the intervertebral foramen?
Cranial and caudal notches
What passes through the intervertebral foramen?
Spinal nerves
How do the brachial plexus and lumbosacral plexus form?
Spinal cord has dorsal branches and ventral branches
→ Dorsal branches: Supply the muscle of the backbone of vertebral structure e.g. intercostal muscle, abdominal muscle
→ Ventral branches: Extend to the pelvis to form lumbosacral plexus + extend to forelimb to form brachial plexus
What are the two main components of an intervertebral disc?
Annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus.
What is the function of the annulus fibrosus?
Allow attachment to adjacent vertebrae + Provides stability
What is the function of the nucleus pulposus?
Gelatinous cushion → Shock absorption
Which cervical vertebrae are considered atypical?
C1 and C2
What are the unique features of the atlas (C1)?
Reduced body and no spinous process
Describes the other key structure of atlas (Dorsal aspect) and axis (C2)
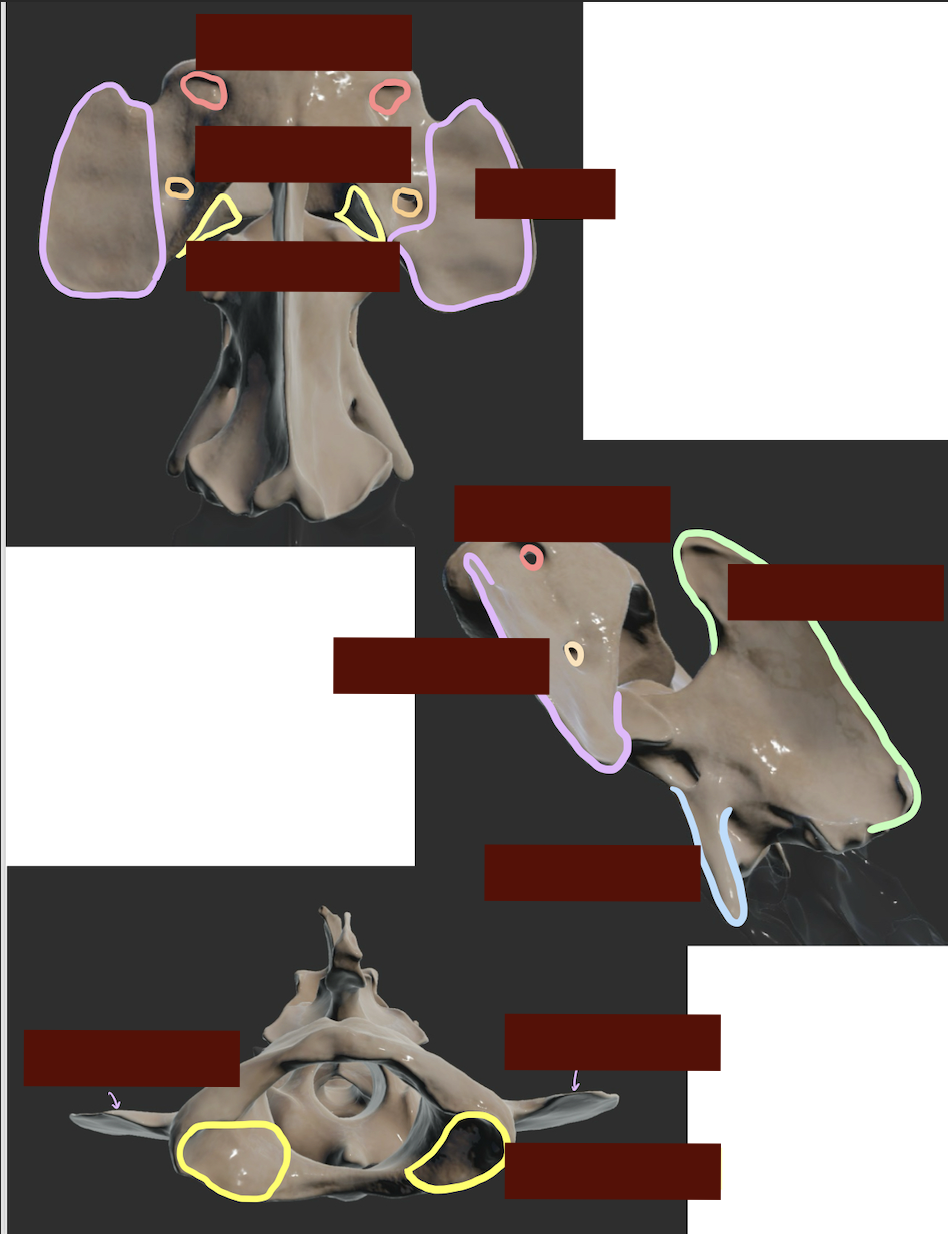

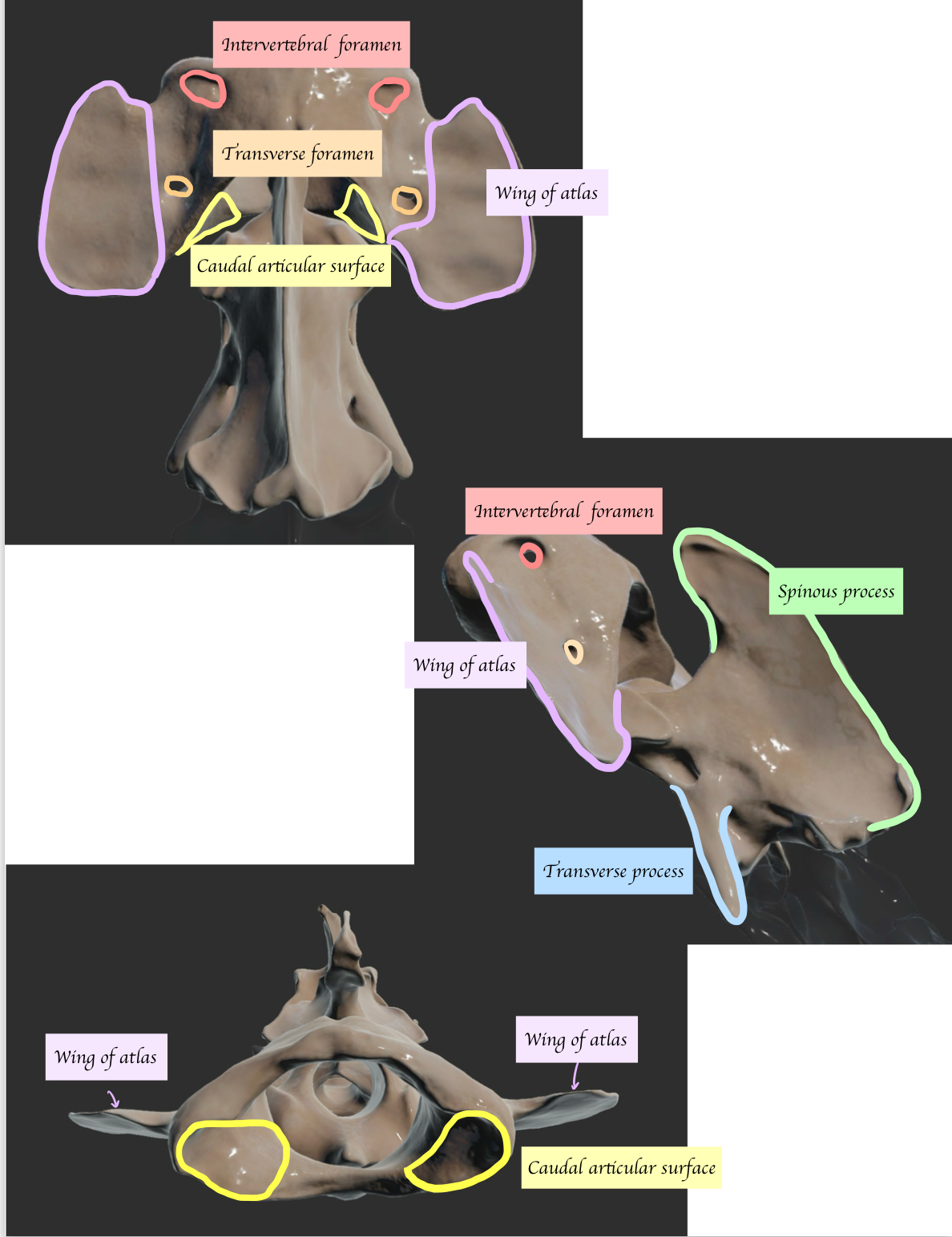
C2 has two body. What is the name of the extension of main body
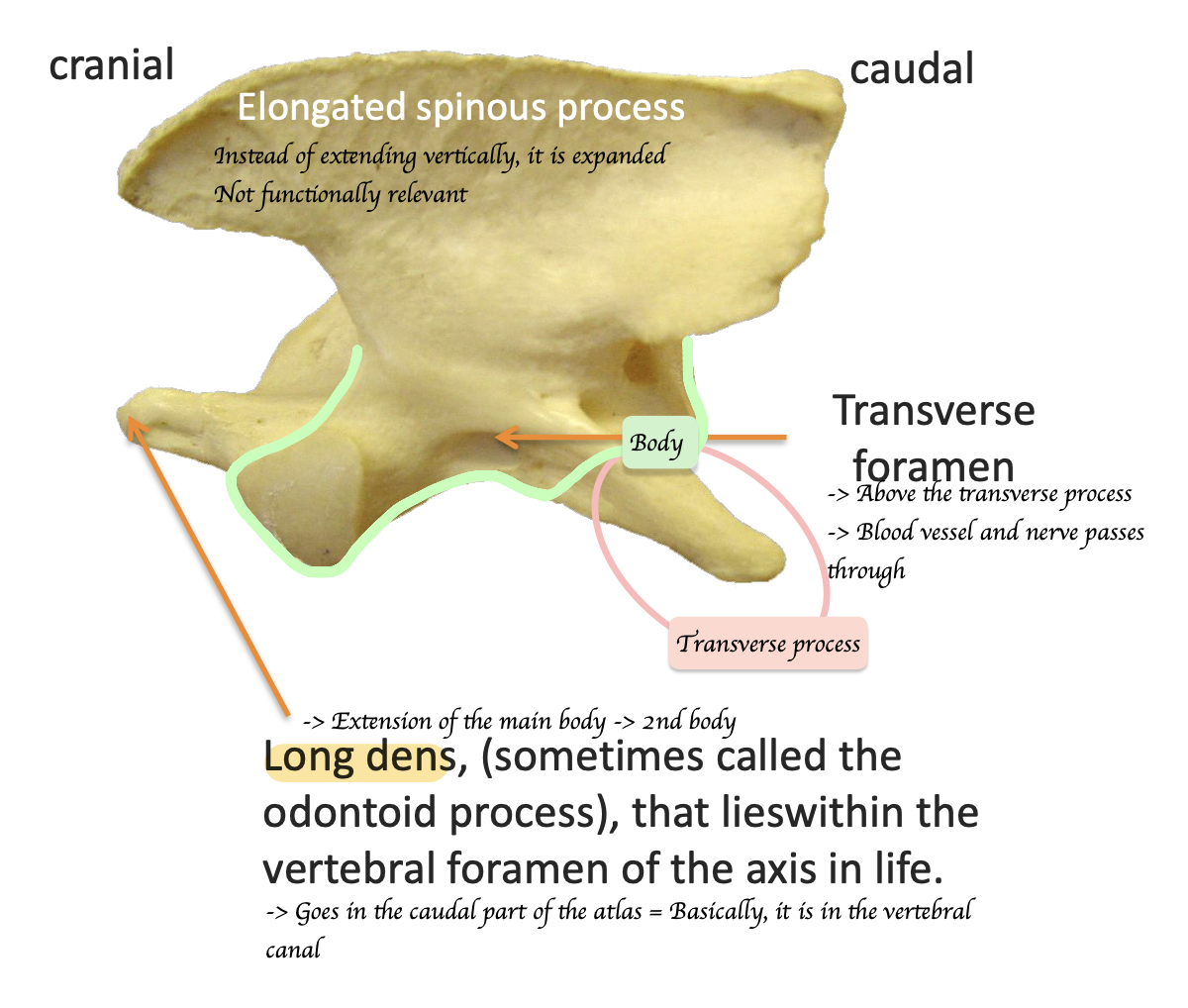
Long dens = Odontoid process
What movement is allowed by the atlanto-occipital joint = Yes joint?
Flexion and extension of the head
What type of movement does the atlanto-axial joint = No joint allow?
Lateral rotation
What does the transverse foramina carry?
Vertebral vessels and the vertebral nerve.
What is a distinguishing feature of the C7 cervical vertebra?
It lacks the transverse foramen
Why there are only seven cervical vertebrae but eight cervical spinal nerves?
In cervical region, each spinal nerve exits from the vertebral canal cranial to the vertebra of the same no.
In thoracic region each spinal nerve exits caudal to the vertebra of the same no.
A spinal nerve between the caudal C7 and cranial T1 = C8
What limits motion in the thoracic region of the vertebral column?
Ribs
Which part of the thoracic vertebrae has the most movement?
Thoraco-lumbar junction
What are the key features of thoracic vertebrae?
Short body
Large dorsal spinous process
Reduced transverse process
Costal fovea (Cranial + caudal costal fovea for articulation with the head of ribs)
Describe the other key features of thoracic vertebra
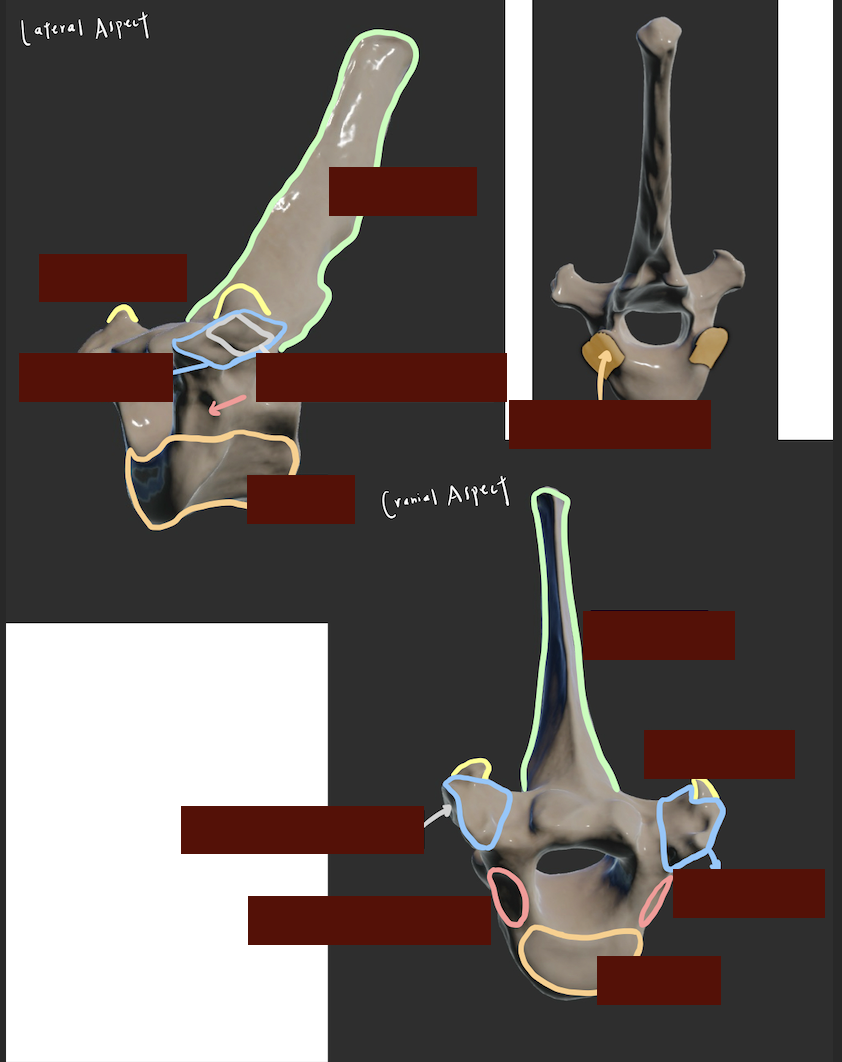
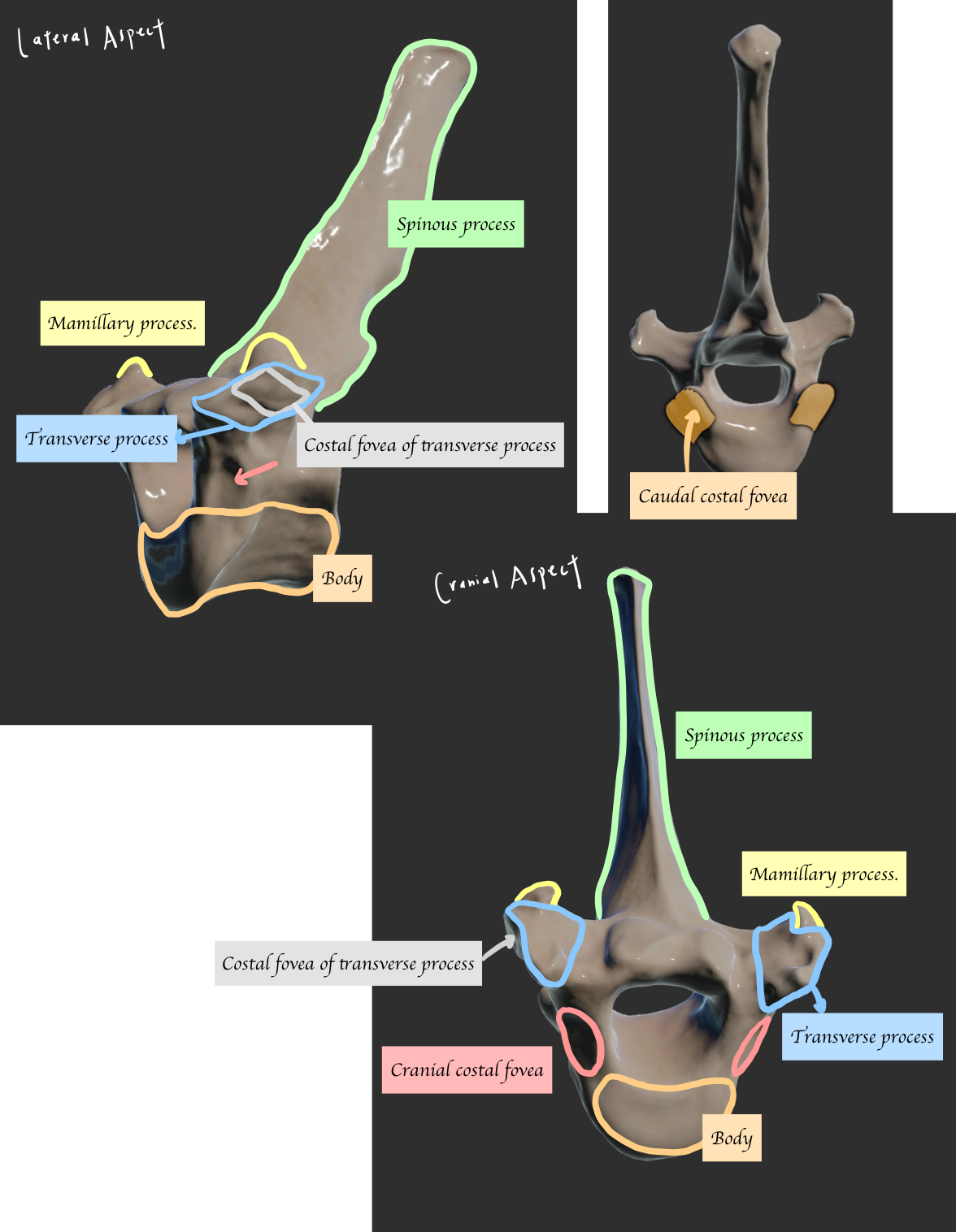
Why thoracic vertebrae has reduced transverse process?
Accommodate the ribs
Describe how ribs attaches to the thoracic vertebrae
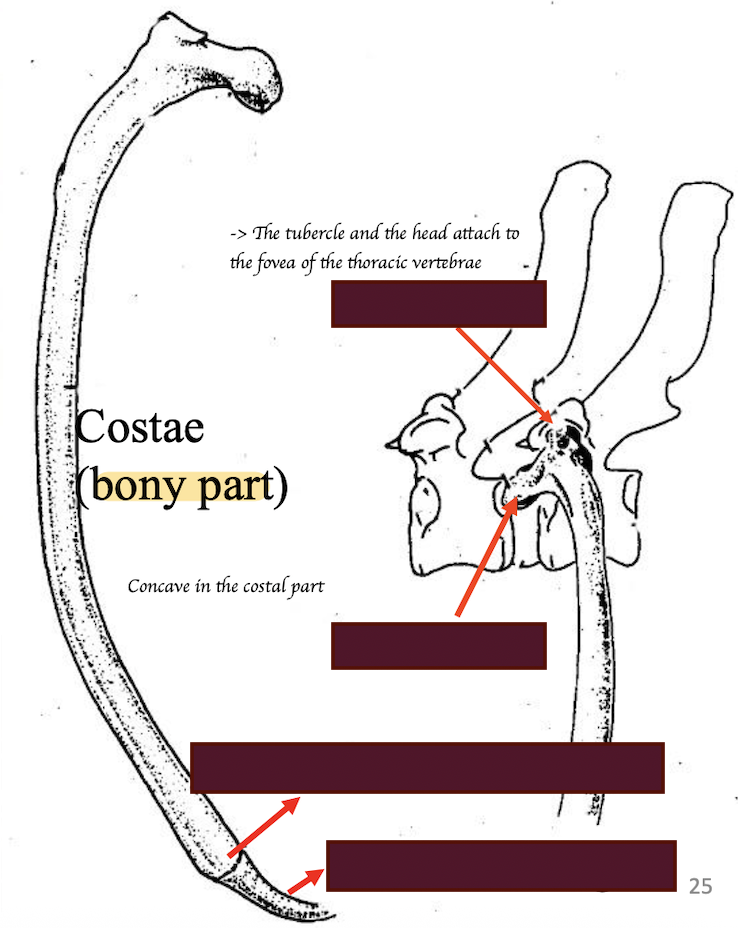
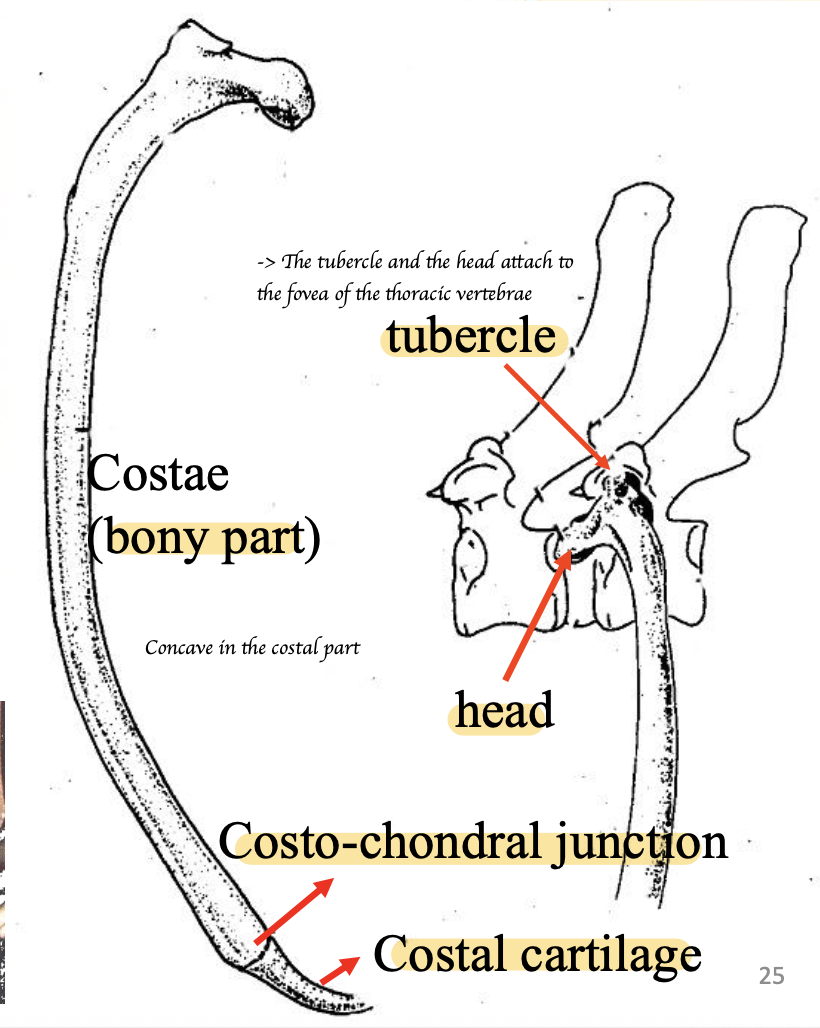
What are the ligaments of the vertebral column and ribs
Costotransverse ligament (Attach the tubercle of rib to the transverse process of vertebrae)
Intercapital ligament = Intercapital ligament (Attaches the two heads of left and right ribs)
Dorsal longitudinal ligament (Attaches intervertebral disk and vertebral body)
Ventral longitudinal ligament
Which thoracic vertebra is referred to as the anticlinal vertebra?
T11
What are the key features of T11 that are clinically significant?
Distinctive perpendicular spinous process = Good radiographic landmark
→ After T11, the spinous process points cranially until it gets to the lumbar vertebrae
What are the key features of lumbar vertebrae?
Longer bodies and large transverse processes
Why lumbar vertebrae has a large transverse process?
Abdominal muscle attachment
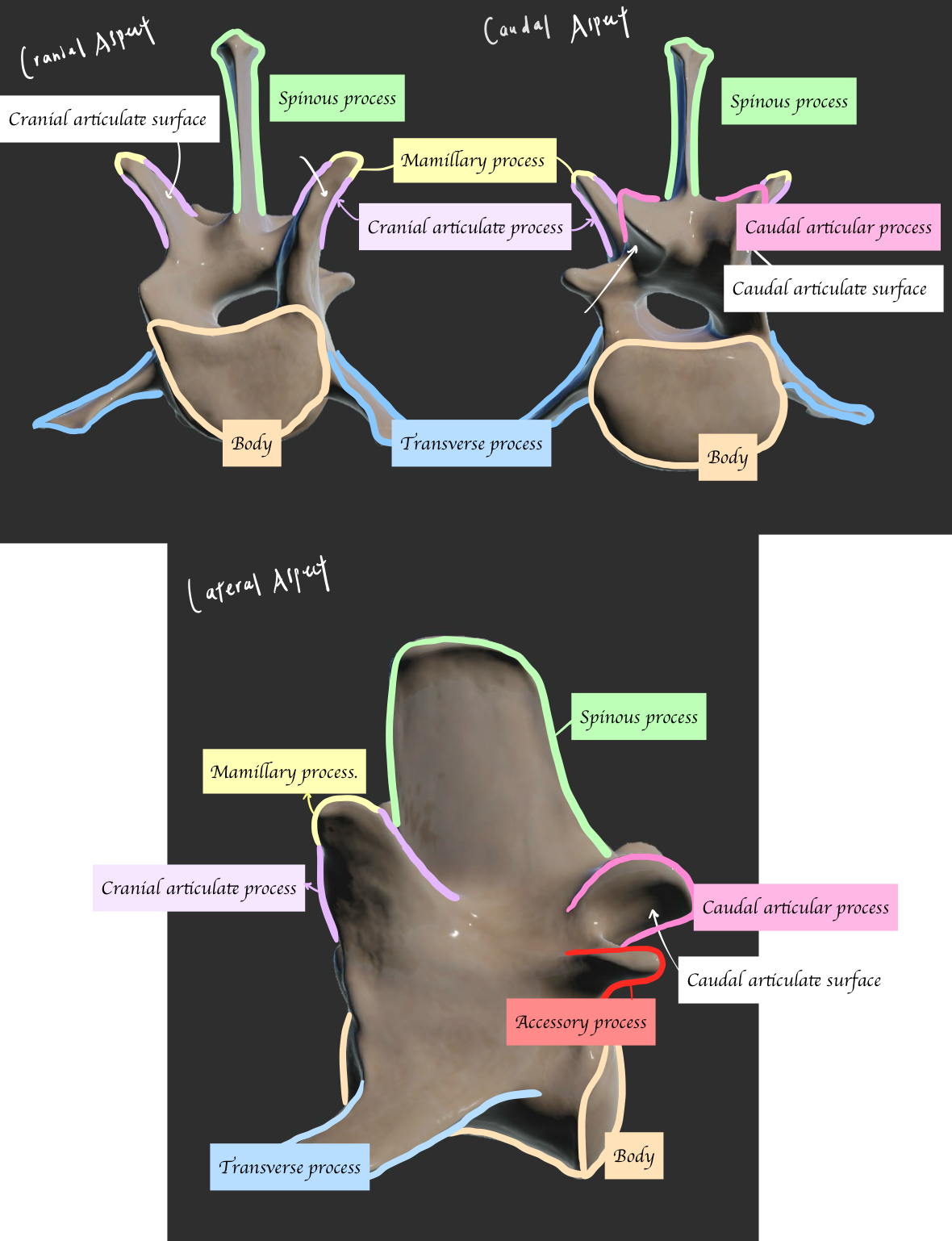
Label the key structure of lumber vertebrae.
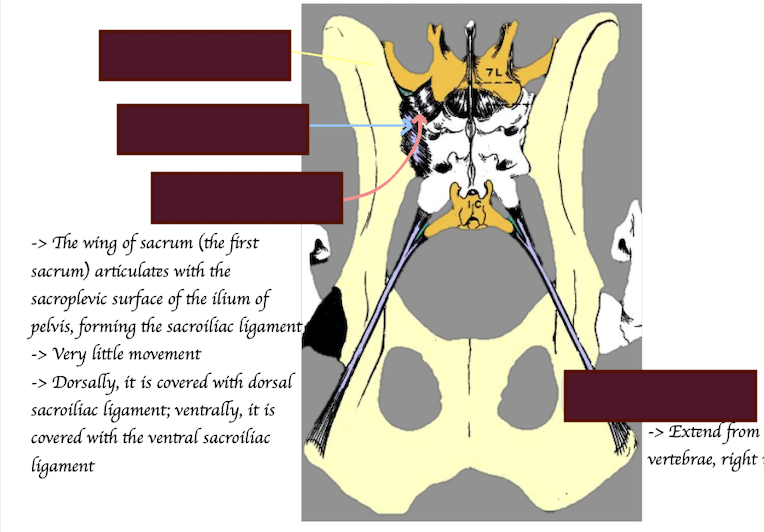
How is the sacrum formed?
Fusion of 3 vertebrae
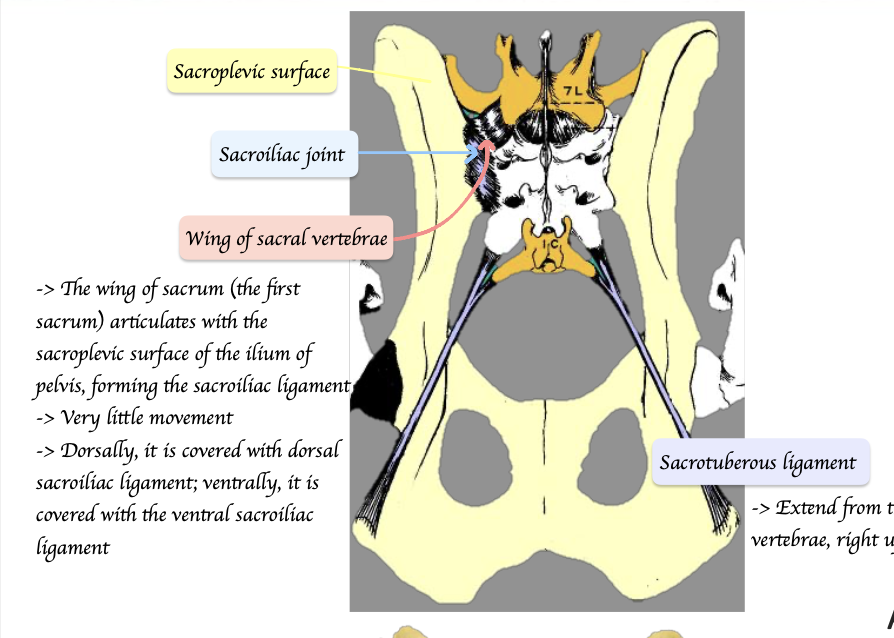
Describe the key structure of sacrum and pelvis
What structures are found on the ventral aspect of the first few coccygeal vertebrae? What is the function of that structure?
Hemal arches → Protecting the coccygeal artery.
When do the vertebral canal disappear?
After C5-C7
Which intervertebral discs have the most movement? Which have the least movement?
Most movement: Cervical region; thoracolumbar junction; lumbar region
Least movement: Sacral + T1-T10 due to strong inter capital ligament
What is the difference between the nuchal ligaments in dogs and horses?
Dogs: Continuation of dorsal supraspinous ligaments → Only attached to caudal aspect of axis (C2)
Horses: Fenestrated sheet → Attaches on all individual cervical vertebrae (Laminar part of nuchal ligament) + Continues attaching to the occipital bone (Funicular part)