Biology: Cell Biology (Paper 1)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
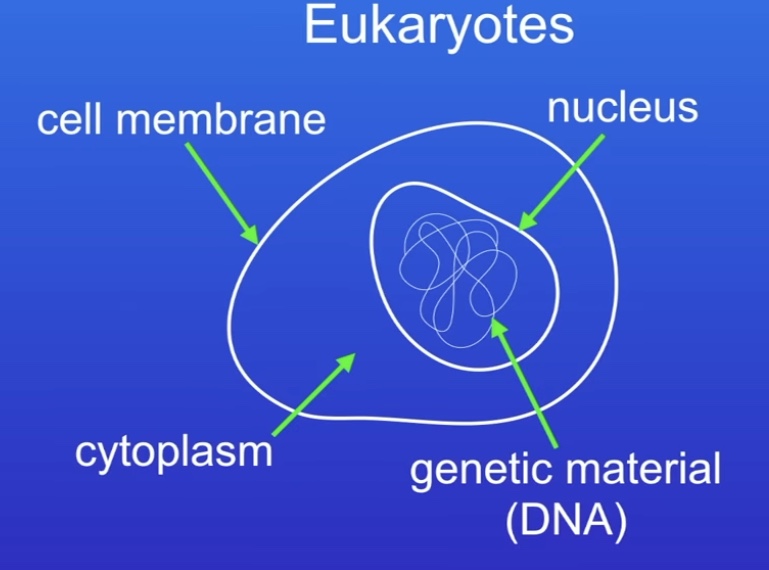
What are eukaryotes?
Contain their genetic material enclosed in a nucleus
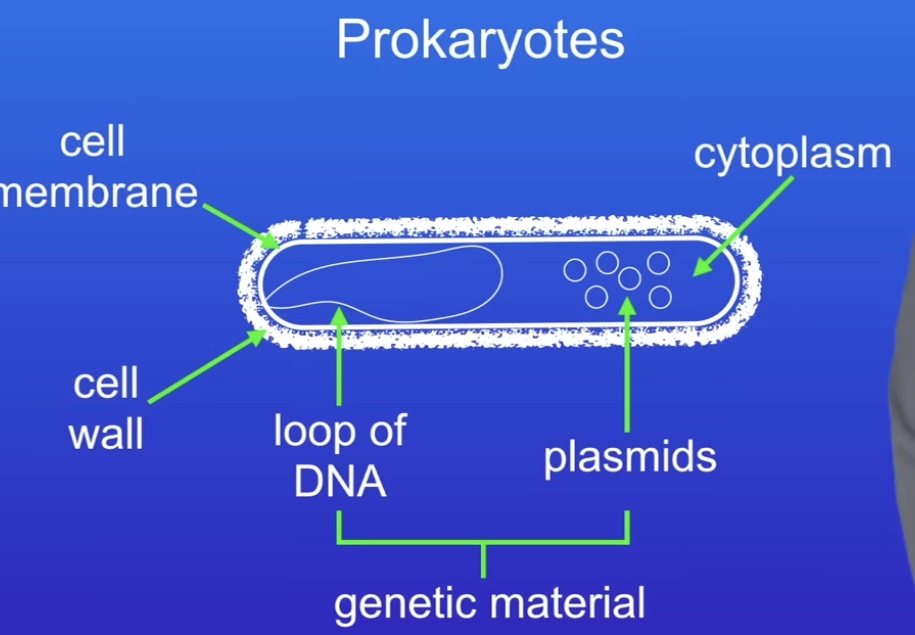
What are prokaryotes?
Don’t contain genetic material enclosed in a nucleus
Much smaller than eukaryotes
Bacterial cell wall
Have a single loop of DNA
What are the sizes of cells:
Prokaryotic much smaller than eukaryotic
centimetre, millimetre, micrometre(cells), nanometre (1 × 10-9) (organelles)
1 micrometer = 0.001 mm

What is order of magnitude?
One order of magnitude means ‘10 times’

How can you calculate order of magnitude?

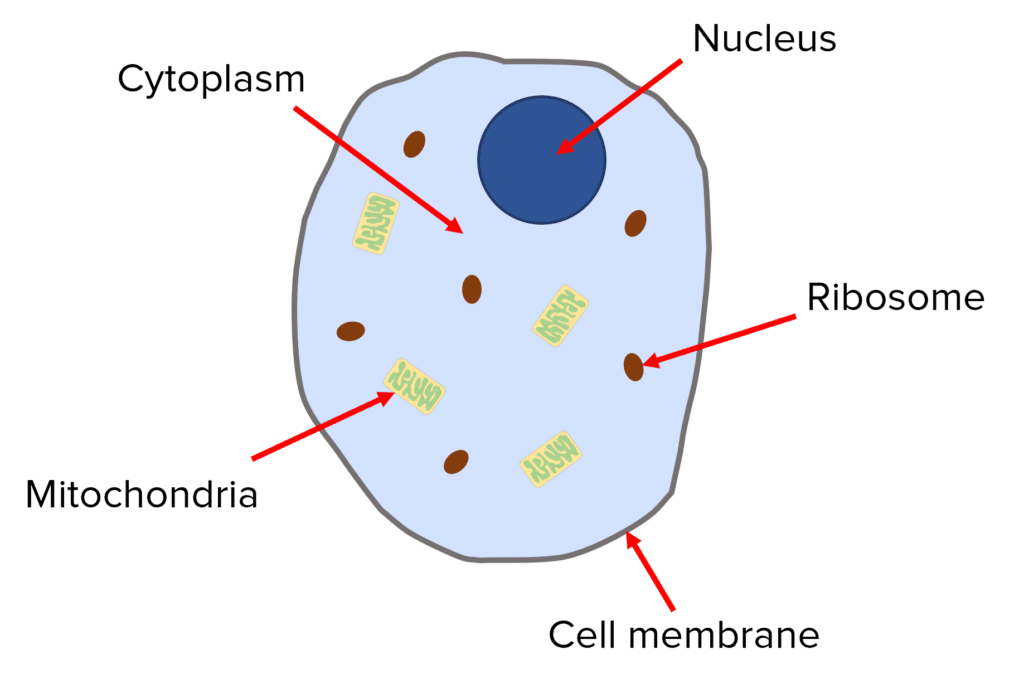
What do the animal cell organelles do? What are they?
Mitochondria (energy)
Ribosomes (protein synthesis)
Cell membrane (Controls in&out)
Nucleus (contains genetic material)
Cytoplasm (chemical reactions)
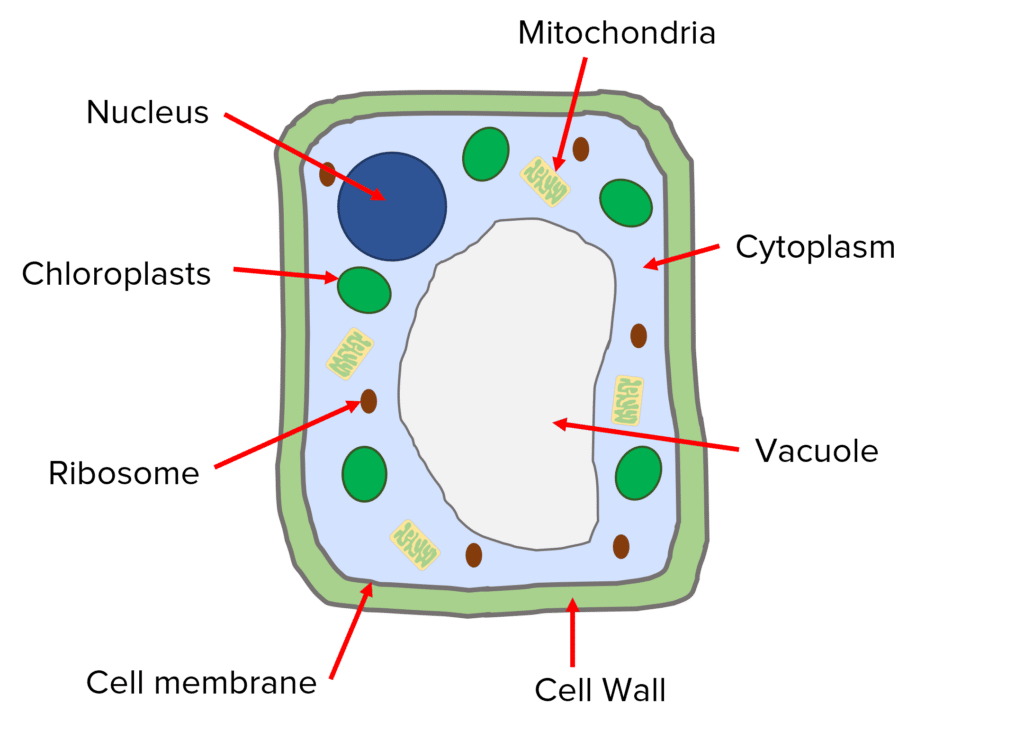
What do the plant cell organelles do? What are they?
Cell wall , cellulose (Structure)
Mitochondria (energy)
Ribosomes (protein synthesis)
Cell membrane (Controls in&out)
Nucleus (contains genetic material)
Cytoplasm (chemical reactions)
Permanent Vacuole (Fluid/ cell sap)
Chloroplasts (photosynthesis)
How are sperm cells specialised?
Sperm cell
½ genetic info,
tail,
enzymes (digest ovum),
mitochondria
How are muscle cells specialised?
Muscle cells
contract, protein fibres to change length,
mitochondria,
cells work together to form muscle tissue
How are nerve cells specialised?
Nerve cell
Long axon [carry impulses]
myelin [insulates & speeds up transmission of impulses],* exam answer
synapses [impulses move from nerve cell to another],
dendrites [increase SA for nerve cells to connect]
What is a specialised cell?
Specialised cells have adaptations to carry out a function (differentiation)
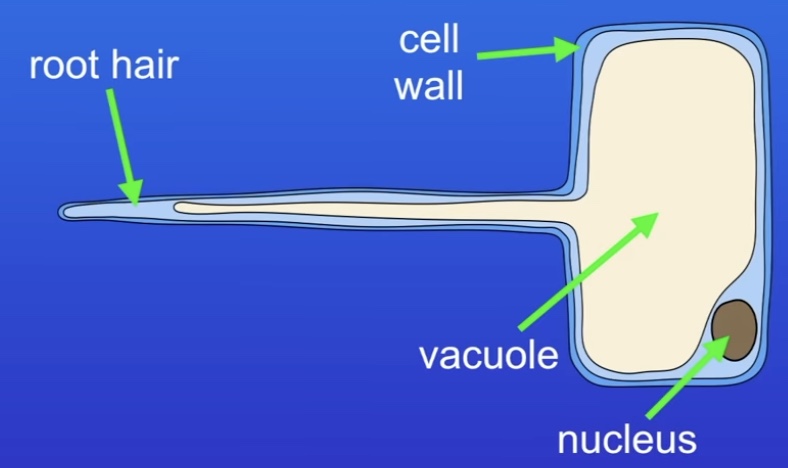
How are root hair cells (plant) specialised?
No chloroplasts (underground)
Root hair increases surface area
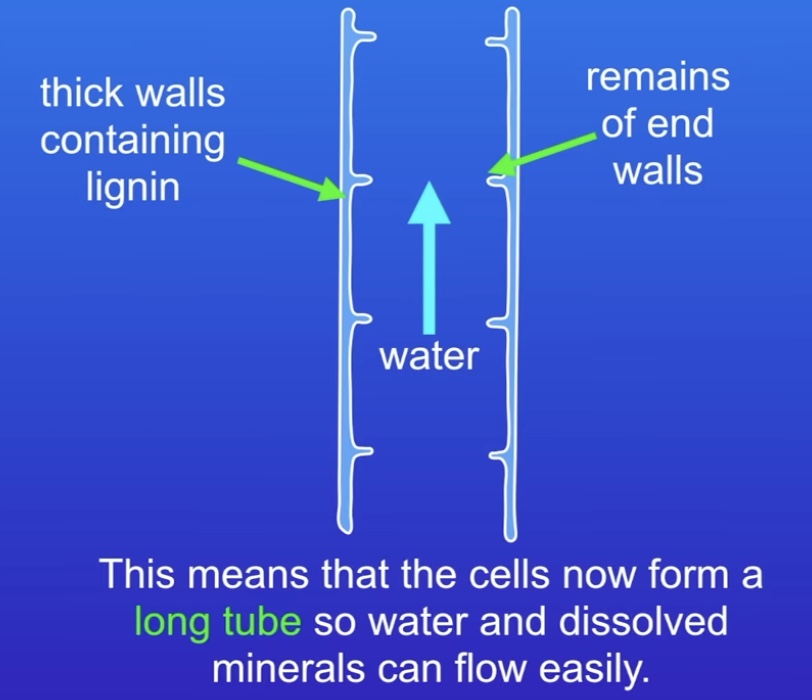
How are Xylem cells (plant) specialised?
In plant stem. Long tubes which carry water & dissolved minerals up
Thick walls contain lignin - structure
End walls are broken for easy access
No internal structures / Hollow (more room for minerals & water)
Made of dead cells
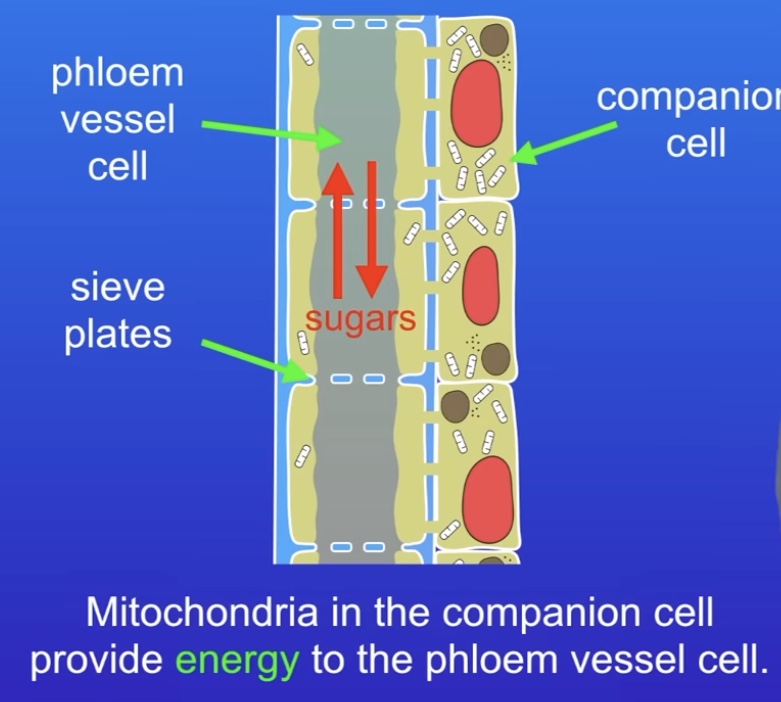
How are Phloem cells specialised?
Carry dissolves sugars up & down the plant.
Phloem vessel cells - no nucleus, limited cytoplasm
Sieve plates - pores
Both allow dissolved sugars to move through the cell interior
Companion cells (containing mitochondria for phloem vessel cell)
Made of living cells
Microscope required practical process & result
Place slide onto stage & clip in place
Lowest power objective lens
Turn coarse focus dial till lens almost touches slide
Look through eyepiece
Turn coarse focus dial until cells come into focus
Use fine focus dial for clear focus
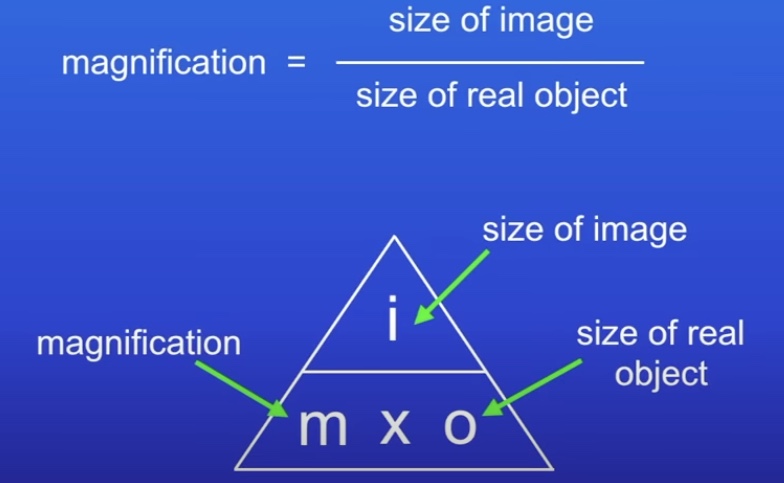
Calculate magnification: Eye piece magnification x objective lens magnification
Label a microscope
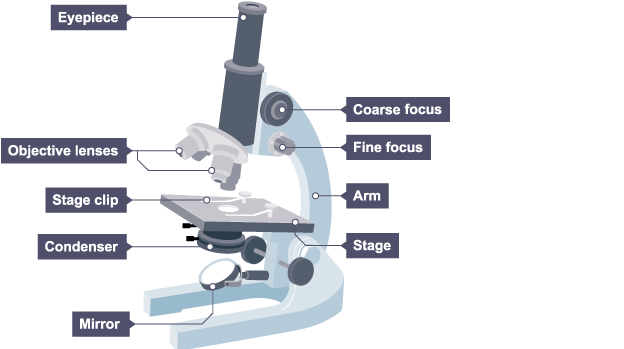
What is the method of using a microscope? How to calculate magnification?
Put slide onto stage & clip in place
Lowest power objective lens - turn coarse focus dial until almost touches slide
Look through eyepiece, turn coarse focus dial until cell in focus
Fine focus dial for clear focus
Eyepiece lens magnification x objective lens magnification
Why are electron microscopes better than light microscopes?
Greater magnification
Greater resolution
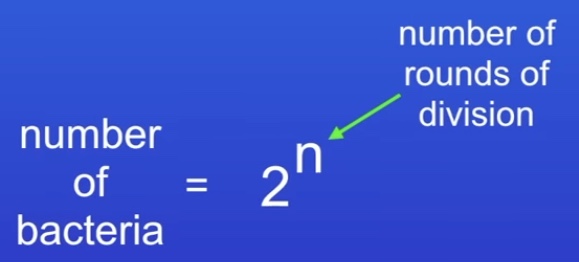
How do Bacteria use Binary Fission?
Bacteria multiply by simple cell division. One cell splits into two.
Bacteria can reproduce every 20 mins
Amount of time / 20(mins) = rounds of division
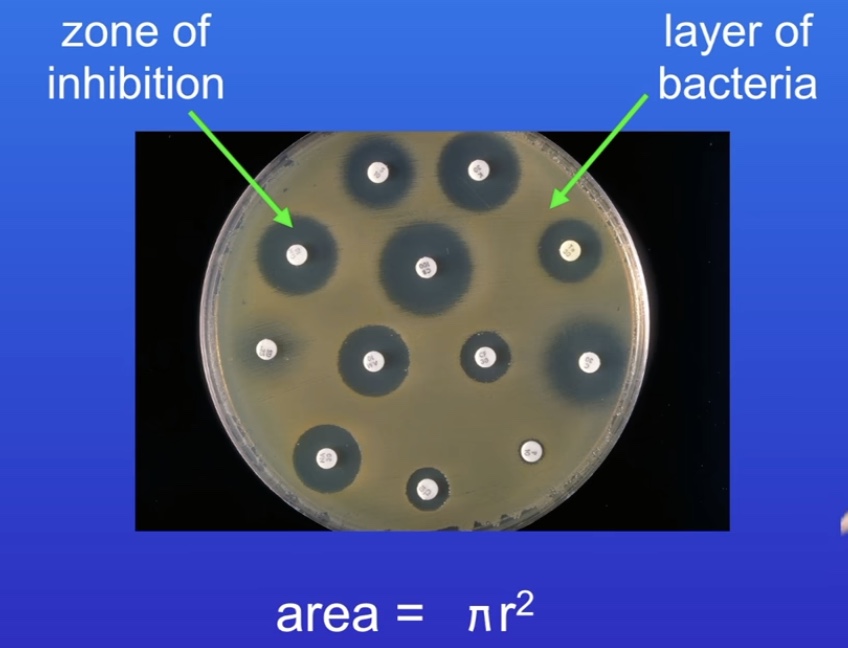
How can we prevent contamination of a culture?
Sterilise agar*, Petri dish & bacterial nutrient broth
Sterile inoculating loop (flame)
Attach lid with tape*
Store upside down in incubator (stops moisture disturbing culture)
Stored at 25ºC (reduces harmful bacteria)
*exam answer
What Is the method of making a bacteria culture?
Clean the bench with disinfectant solution. (kills contaminants)
Sterilise an inoculating loop by passing it through a Bunsen burner flame.
Open a sterile agar gel plate near a Bunsen burner flame. The flame kills bacteria in the air.
Now use the loop to spread the chosen bacteria evenly over the plate.
Place sterile filter paper discs containing antibiotic onto the plate.
Incubate the plate at 25°C.
What is the zone of inhibition? How do you calculate this?
Area where bacteria didn’t grow
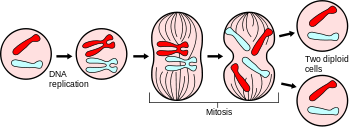
What is mitosis?
Chromosomes duplicate
Sub-cellular structures duplicate
Chromosomes are pulled to each side of cell
The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide (into two identical daughter cells)
What is meiosis?
DNA replicates, grows & copies internal structures
One set of chromosomes are pulled to each side of cell, Nucleus divides
Divide cell into non-identical haploid cells
Growth & development for multi-cellular organisms
Repair
Asexual reproduction
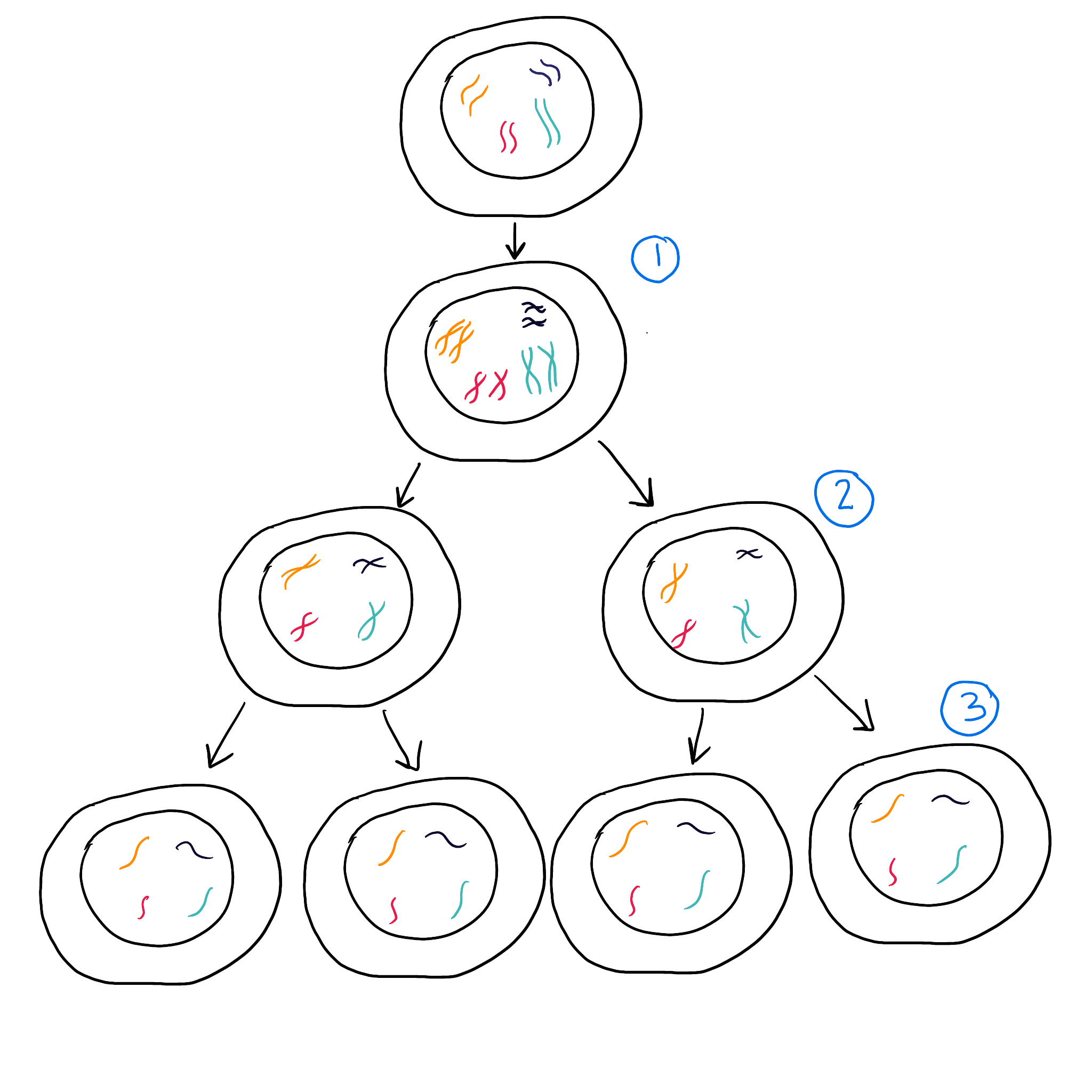
What are stem cells?
Cells which have not differenciated
Embryonic stem cells & can form any type of cell
Adult stem cell (bone marrow) - can form cells found in blood
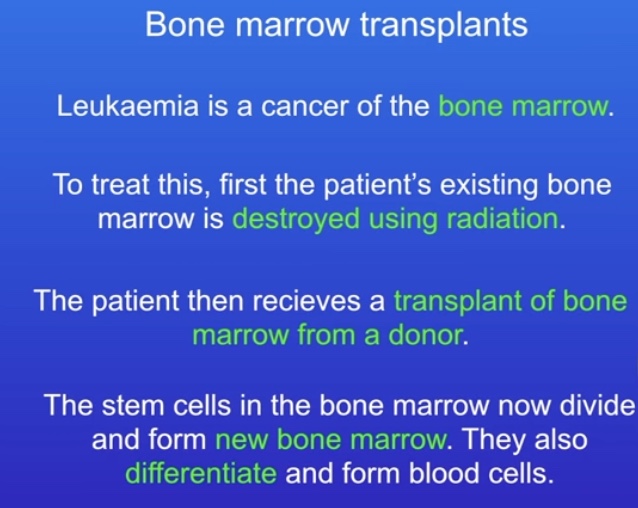
How are stem cells used in bone marrow transplants?
Patient & donor have to be compatible
can spread viruses
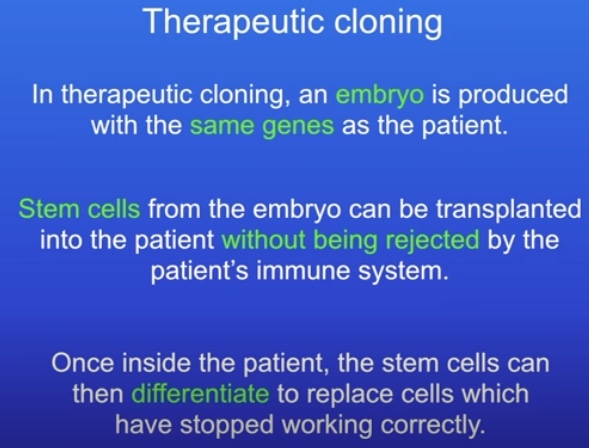
How are stem cells used in therapeutic cloning?
Diabetes, paralysis
Ethical objections
How can plants be cloned?
Contian meristem tissue
Which differentiate into any type of plant tissue at any point in plants life
Clone plants to stop extinction or for farmers
How do molecules move in and out of cells?
Though cell membrane, diffusion
Spreading out of particles from higher to lower concentration
e.g. oxygen, CO2, urea
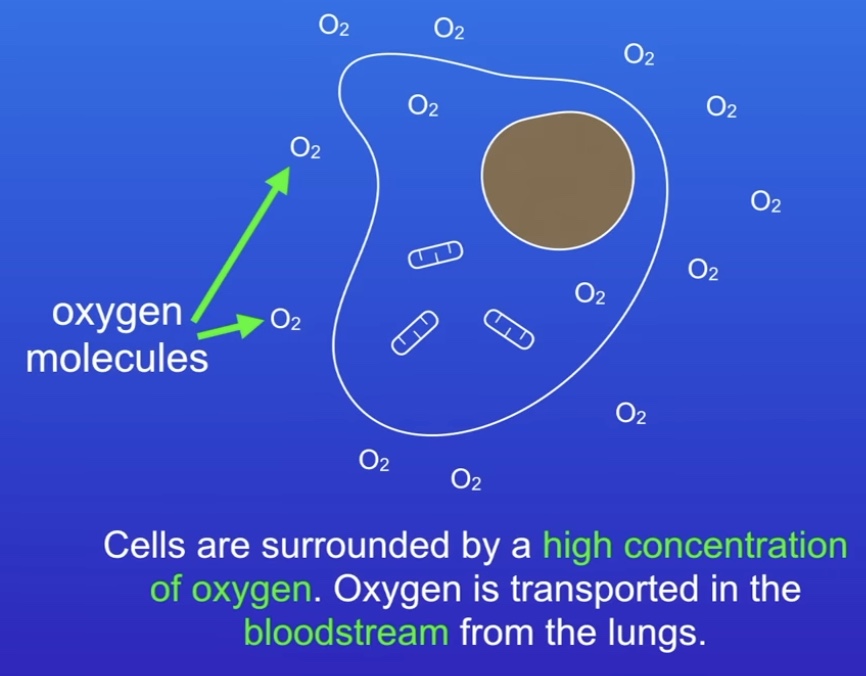
What effects the rate of diffusion?
Concentration gradient (high = faster vice versa)
Temperature (higher, more kinetic energy, faster)
Surfacer area (larger = faster)
What is surface area: volume ratio? How do you calculate it?
Used within single-celled organisms (amoeba)
Use diffusion for transport of molecules in & out
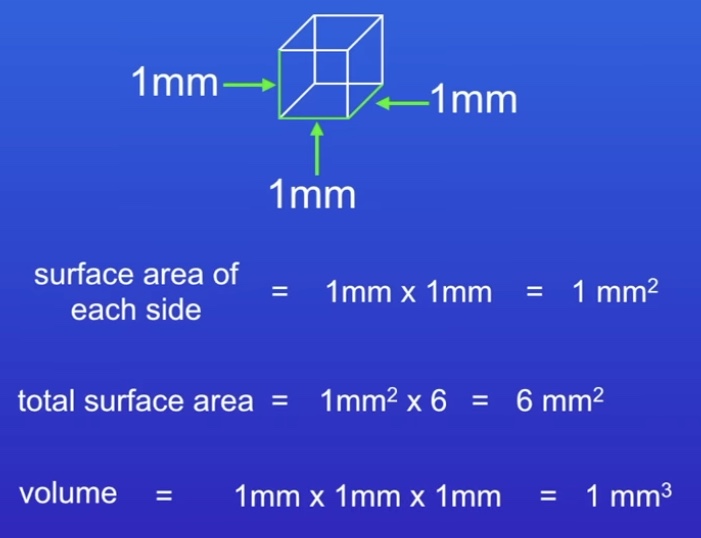
Why does diffusion not work for multi-cellular organisms?
Larger the organism , the smaller surface area : volume ratio
Their SA is not large enough for their volume
Cells on surface get oxygen via diffusion, internal cells are too far
(Animals use lungs/gills)
How do fish breathe?
Oxygen in water flows over gills
Transported into the blood stream
Gills covered in fine filament so oxygen can flow
Filament has a thin membrane(easy diffusion pathway), large surface area and efficient blood supply (take oxygenated blood away) & always high concentration gradient
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of water from dilute to concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane.
E.g plants absorbing water
What happens during osmosis of an animal cell?
Water diffuses in and cell expands (could burst)
In concentrated solution, water will move out and shrink
What happens during osmosis of a plant cell?
Water move in through osmosis and cell expands (doesn’t burst because of cell wall & becomes turgid)
In concentrated solution, water moves out and shrinks, (becomes flaccid)
Osmosis required practical method
Peel potato skin
Use cork borer to prode 3 cylinder
Cut to 3cm
Measure mass
Add solution to test tubes
Roll potato onto paper towels
Measure length & mass
Calculate % change

How do you calculate % change?

What is happening at each stage of osmosis RP?
Water - gains mass
Sugar solution - loses mass
On x axis, no change same concentration inside & outside
What is active transport?
Movement of particles from lower to higher concentration (moving against concentration gradient) which requires energy from respiration
E.g. Plants absorbing mineral ions
What are some active transport examples?
Lumen of small intestine absorbing sugars
Root hair cells - mineral Ions into plant from soil. Transported into xylem.
Both have lots of mitochondria
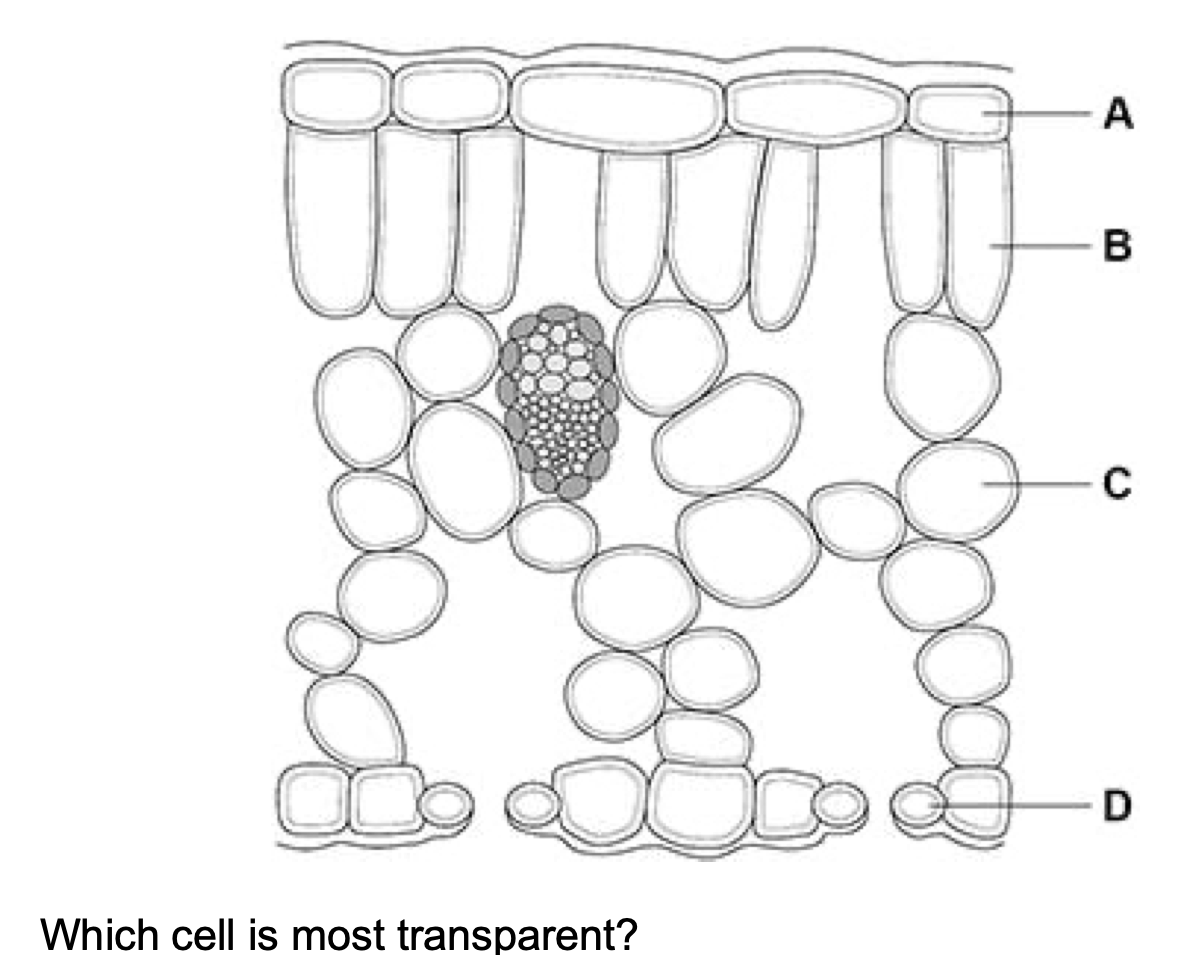
A
Because it must allow light to enter
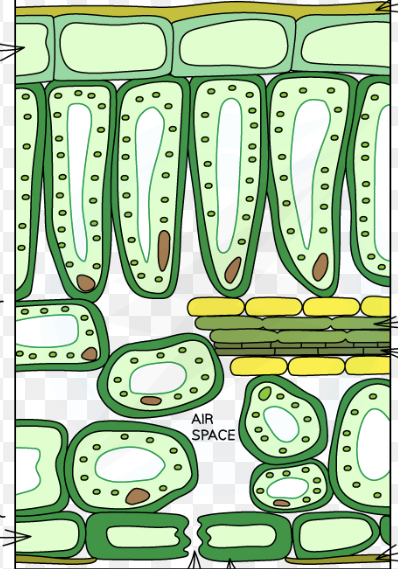
Label this leaf cross section
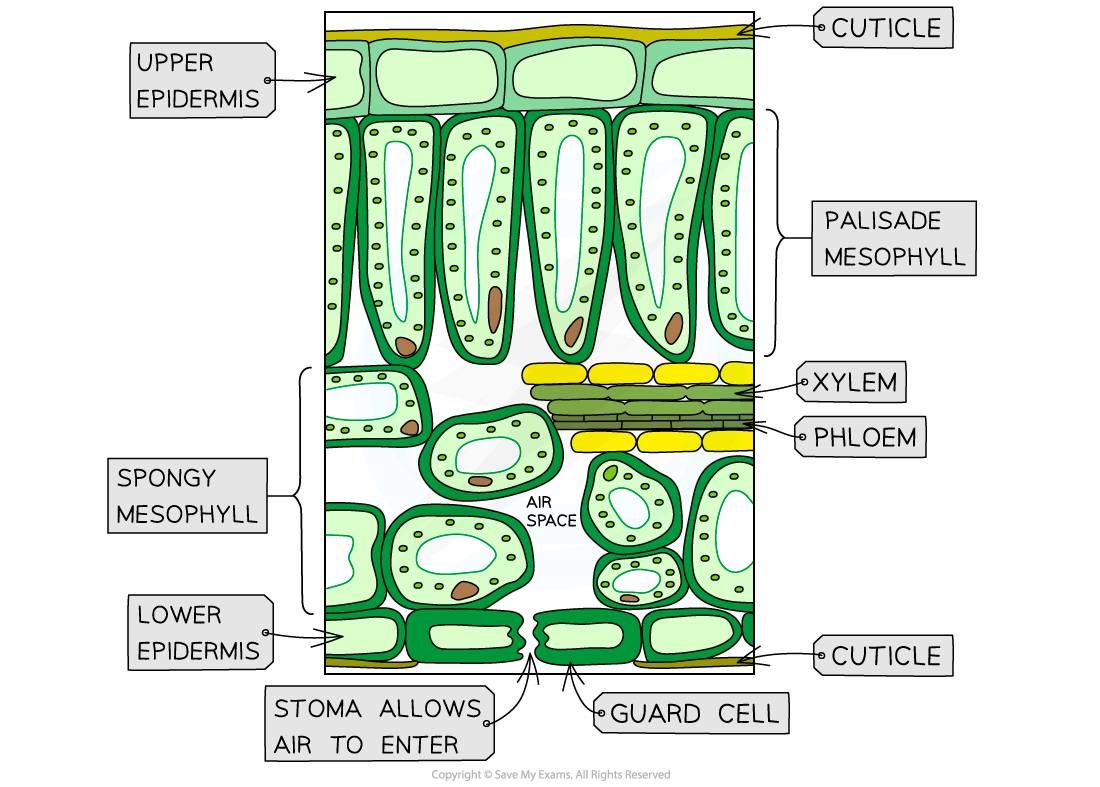
What is a transpiration stream?
The roots take in water, it is transported up the stem and lost by the leaves.
What decreases the rate of water loss from a plants leaves?
Increased humidity
How does the stomata’s width change in low CO2 concentration to help it survive?
The stomata is open wider for longer
To allow more CO2 to be absorbed for photosynthesis.
In the osmosis practical, why is a thin layer of epidermis and iodine solution used? And why is the cover slip lowered at an angle?
Thin layer - Help see individual cells
Iodine solution - To stain parts of the cell
Cover slip at angle - prevent air bubbles.