Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
1
New cards
Voltage-gated Channel
Sodium Channels
Potassium Channels
Calcium Channels
Potassium Channels
Calcium Channels
2
New cards
Ligand-gated Channel
Nicotinic ACh receptor
GABAA receptor
Glycine receptor
AMPA receptor
GABAA receptor
Glycine receptor
AMPA receptor
3
New cards
Sodium channels
Tetrodotoxin TTX
Batrachotoxin BTX
Batrachotoxin BTX
4
New cards
Potassium Channels
Apamin
Charybdotoxin
Charybdotoxin
5
New cards
Calcium channels
Omega conotoxin
Agatoxin
Agatoxin
6
New cards
Nicotinic CH receptor
alpha-bungarotoxin
7
New cards
GABAA receptor
picrotoxin
8
New cards
Glycine Receptor
Strychnine
9
New cards
AMPA receptor
Philanthotoxin
10
New cards
Source of Tetrodotoxin
Puffer fish
11
New cards
Source of Batratoxin
colombian frog
12
New cards
Source of Apamin
honeybee
13
New cards
Source of Charybdotoxin
scorpion
14
New cards
Source of Omega conotoxin
pacific cone snail
15
New cards
Source of agatoxin
funnel web spider
16
New cards
Source of alphabungarotoxin
marine snake
17
New cards
Source of picrotoxin
south pacific plant
18
New cards
Source of strychnine
indian plant
19
New cards
Source of philanthotoxin
wasp
20
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: Tetrodotoxin
blocks channel from outside
21
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: Batrachotoxin
Slows inactivation, shifts activation
22
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: Apamin
Blocks small Ca-activated K channel
23
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: Charybdotoxin
blocks big Ca-activated K channel
24
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: Omega conotoxin
blocks n-type channel
25
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: Agatoxin
blocks p-type channel
26
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: alpha bungarotoxin
irreversible antagonist
27
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: picrotoxin
blocks channel
28
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: strychnine
competitive antagonist
29
New cards
Mode of Toxin Action: philanthotoxin
blocks channel
30
New cards
↑Na, ↑Ca , ↓K
EPSP
31
New cards
↑K, ↑ Cl postsynaptic, ↓Ca presynaptic
IPSP
32
New cards
depolarizing potential, intracellular less negative
EPSP
33
New cards
hyperpolarizing potential, intracellular more negative
IPSP
34
New cards
E1 + E2
Spatial summation
35
New cards
E1 E1
Temporal summation
36
New cards
large myelinated rapidly conducting fibers
Excitability of CNS
upper lower motor
primary secondary tertiary sensory
Excitability of CNS
upper lower motor
primary secondary tertiary sensory
Hierarchial System
37
New cards
located in small discrete nuclei
different parts of the brain
different parts of the brain
Diffuse/ Nonspecific neuronal system
38
New cards
1. Action potential in presynaptic fiber
2. Synthesis of transmitter
3. storage
4. metabolism
5. release
6. reuptake into the nerve ending or uptake into a glial cell
7. degradation
8. receptor for the transmitter
9. receptor induced increase or decrease in ionic conductance
10. retrogade signaling
2. Synthesis of transmitter
3. storage
4. metabolism
5. release
6. reuptake into the nerve ending or uptake into a glial cell
7. degradation
8. receptor for the transmitter
9. receptor induced increase or decrease in ionic conductance
10. retrogade signaling
sites of drug action
39
New cards
Excitatory: ↓ K conductance, ↑IP3 DAG
pirenzepine, astropine
\[*acetylcholine*\]
\[*acetylcholine*\]
40
New cards
Inhibitory: ↑ K conductance, ↓cAMP
atropine, methoctramine
\[*acetylcholine*\]
\[*acetylcholine*\]
41
New cards
Excitatory: ↑ cation conductance
dihydro-b-erythroidine, alpha bungarotoxin
\[*acetylcholine*\]
\[*acetylcholine*\]
42
New cards
Inhibitory: ↑ cAMP
phenothiazines
\[*dopamine*\]
\[*dopamine*\]
43
New cards
Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓ Ca
Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K conductance ↓ cAMP
Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K conductance ↓ cAMP
phenothiazines, butyrophenones
\[*dopamine*\]
\[*dopamine*\]
44
New cards
Inhibitory: ↑ Cl conductance
bicuculline, picrotoxin
\[*GABA*\]
\[*GABA*\]
45
New cards
Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓Ca conductance
Inhibitory (postsynaptic) ↑K conductance
Inhibitory (postsynaptic) ↑K conductance
2OH saclofen
\[*GABA*\]
\[*GABA*\]
46
New cards
Excitatory: ↑cation conductance particularly Ca
2 amino 5 phosphonovalerate dizocilpine
\[*Glutamate*\]
\[*Glutamate*\]
47
New cards
Excitatory: ↑Cation conductance
NBQX
\[*Glutamate*\]
\[*Glutamate*\]
48
New cards
Excitatory: ↑cation conductance
ACET
\[*Glutamate*\]
\[*Glutamate*\]
49
New cards
Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓Ca conductance ↓cAMP
Excitatory: ↓K conductance ↑IP3 Dag
Excitatory: ↓K conductance ↑IP3 Dag
MCPG
\[*Glutamate*\]
\[*Glutamate*\]
50
New cards
Inhibitory: ↑Cl conductance
strychnine
\[*Glycine*\]
\[*Glycine*\]
51
New cards
Inhibitory: ↑K conductance, ↓cAMP
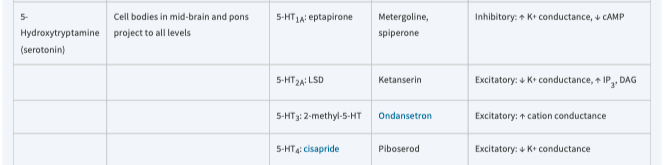
metergoline, spiperone
\[*Serotonin*\]
\[*Serotonin*\]
52
New cards
Excitatory: ↓K conductance ↑IP3 Dag
ketanserin
\[*Serotonin*\]
\[*Serotonin*\]
53
New cards
Excitatory: ↑cation conductance.
ondansetron
\[*Serotonin*\]
\[*Serotonin*\]
54
New cards
Excitatory: ↓K conductance
piboserod
\[*Serotonin*\]
\[*Serotonin*\]
55
New cards
Excitatory: ↓K conductance ↑IP3 DAG
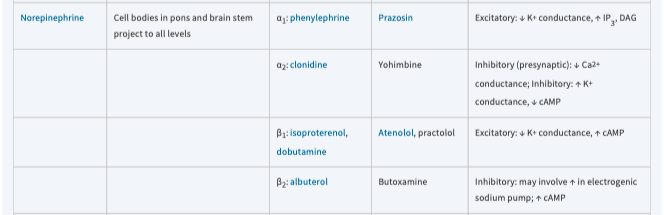
prazosin
\[*Norepinephrine*\]
\[*Norepinephrine*\]
56
New cards
Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓ Ca
Inhibitory:↑ K conductance ↓cAMP
Inhibitory:↑ K conductance ↓cAMP
yohimbine
*[Norepinephrine]*
*[Norepinephrine]*
57
New cards
Excitatory: ↓ K conductance ↑ cAMP
atenolol, practolol
*[Norepinephrine]*
*[Norepinephrine]*
58
New cards
Inhibitory: may involve in ↑ electrogenic sodium pump ↑ cAMP
butoxamine
*[Norepinephrine]*
*[Norepinephrine]*
59
New cards
Excitatory: ↓ K conductance ↑ IP3 DAG
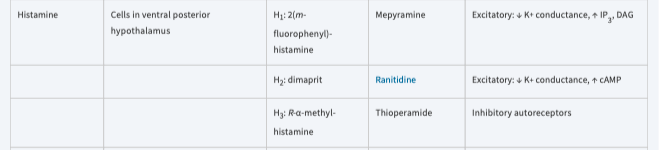
mepyramine
*[histamine]*
*[histamine]*
60
New cards
Excitatory: ↓ K conductance, ↑ cAMP
ranitidine
*[histamine]*
*[histamine]*
61
New cards
Inhibitory autoreceptors
thioperamide
*[histamine]*
*[histamine]*
62
New cards
Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓ Ca conductance ↓ cAMP
Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K conductance ↓ cAMP
Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K conductance ↓ cAMP
Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K conductance ↓ cAMP
Inhibitory (postsynaptic): ↑ K conductance ↓ cAMP
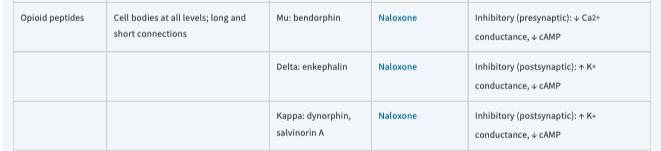
Naloxone
*[opioid peptides]*
*[opioid peptides]*
63
New cards
Excitatory: glutamate co-release
Suvorexant
*[orexins]*
*[orexins]*
64
New cards
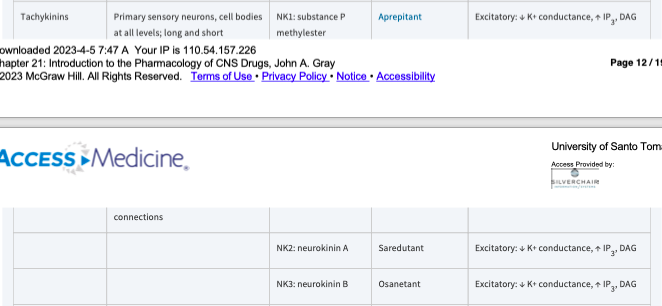
Excitatory: ↓K conductance ↑ IP3 Dag
Aprepitant, Saredutant, Osanetant
*[Tachykinins]*
*[Tachykinins]*
65
New cards
Inhibitory (presynaptic): ↓Ca conductance ↓cAMP
Rimonabant
*[Endocannabinoids]*
*[Endocannabinoids]*
66
New cards
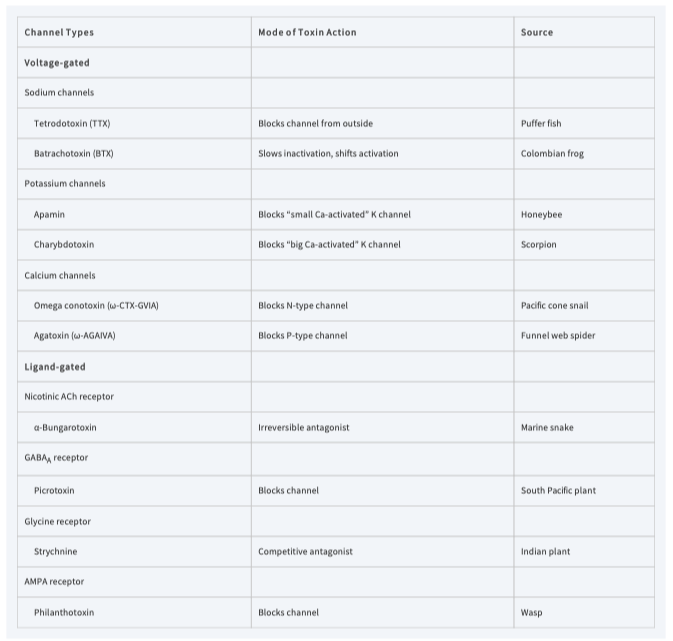
Table 1
Some toxins used t o characterize ion channels.
67
New cards

Acetylcholine
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
68
New cards
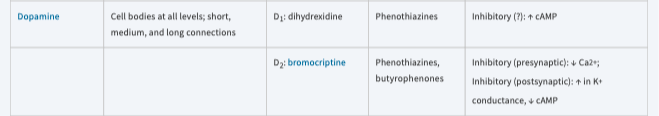
Dopamine
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
69
New cards
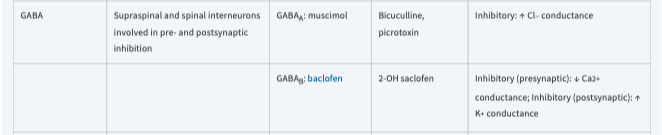
GABA
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
70
New cards
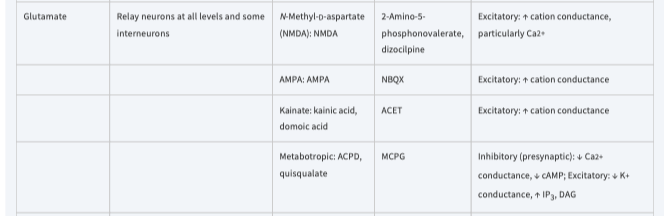
Glutamate
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
71
New cards

Glycine
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
72
New cards
Serotonin
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
73
New cards
Histamine
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
74
New cards
Norepinephrine
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
75
New cards
Opoid peptides
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
76
New cards

Orexins
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
77
New cards
Tachykinins
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*
78
New cards

Endocannabinoids
*Anatomy, Receptor, Mechanisms*