EAPS 106 Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:08 AM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
What is the process that makes subduction zone earthquakes cause tsunamis?
Uplift of the seafloor from elastic rebound during a large subduction zone
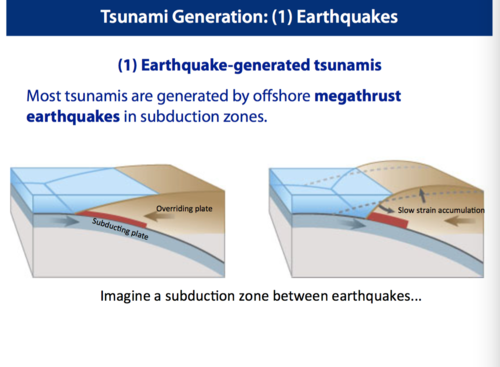
2
New cards
How tsunami and wind-blown waves differ
Tsunami waves can have similar heights to large wind blown waves, but carry a much larger volume of water, have a much longer wavelength (distance from crest to crest), and travel much further inland.
3
New cards
How does a tsunami wave in deep water change when it hits shallow water?
In deep water, long wavelengths, low wave height, and great speed (jet)
Approaching shore, they slow which causes the back of the wave to catch up. Reduces wavelength, but increases wave height.
Approaching shore, they slow which causes the back of the wave to catch up. Reduces wavelength, but increases wave height.
4
New cards
When do water waves typically break?
When the wave height is equal to water depth
Wave Height = Water Depth
Wave Height = Water Depth
5
New cards
What type of earthquakes will cause a tsunami?
strike-slip fault earthquakes
6
New cards
What type of earthquakes will NOT cause a tsunami?
earthquakes between the magnitude of 6.5-7.5
7
New cards
How many people have been killed by tsunamis in the past 1,000 years?
Several Hundred Thousands
8
New cards
What might it mean if you feel shaking near the shore?
Tsunami 20-40 min away
9
New cards
why does the sea level drop before a tsunami?
the ocean is being dragged out when the trough arrives before the crest.
10
New cards
Why is it dangerous to return to the shore after a tsunami wave?
Consists of 3-10 waves and 2nd or 3rd wave is largest
11
New cards
Why did so many people die around the Indian ocean during 2004 tsunami?
1961 Chilean earthquake made tsunamis all over
12
New cards
How does the DART tsunami early warning system work?
1. Pressure sensor on ocean floor measure water pressure
2. Measurements are sent by acoustic signal to a buoy on the surface
3.Buoy sends signal to satellite
4. Signal sent to early-warning stations on land
-can send 15 min after earthquake, including path and size
2. Measurements are sent by acoustic signal to a buoy on the surface
3.Buoy sends signal to satellite
4. Signal sent to early-warning stations on land
-can send 15 min after earthquake, including path and size
13
New cards
Which process has the potential to cause the largest tsunamis?
asteroid and volcanoes
14
New cards
How do the Hawaiian Islands generate tsunamis?
Underwater landslides
15
New cards
What will most likely cause a tsunami in the Atlantic ocean?
Underwater landslides
16
New cards
What caused the largest tsunami run-up in the past 100 years?
1958 Alaska tsunami, generated by an avalanche into Lituya Bay
17
New cards
What are the tectonic settings where the different types of volcanism are found?
1. Mid-ocean ridges
2. Subduction zones
3. Hot spots
2. Subduction zones
3. Hot spots
18
New cards
Is the mantle a subsurface ocean of magma?
No
19
New cards
What process will cause already hot, but not yet melted rocks, to melt?
1. Increase temperature
2. Decrease pressure as rock rises
3. Add water to decrease melting temp
2. Decrease pressure as rock rises
3. Add water to decrease melting temp
20
New cards
What causes hot rocks to melt at each of the tectonic settings where volcanoes are found?
- In subduction zone settings,
water pushed out from subduction plate lowers the melting temp of hot mantle above causing it to melt. (Hydration-induced melting)
- In mid-ocean ridge and hotspot settings,
hot unmelted mantle rises due to convection.
Once near the surface it melts due to lower pressure. (Decompression melting)
water pushed out from subduction plate lowers the melting temp of hot mantle above causing it to melt. (Hydration-induced melting)
- In mid-ocean ridge and hotspot settings,
hot unmelted mantle rises due to convection.
Once near the surface it melts due to lower pressure. (Decompression melting)
21
New cards
Why does hotspot volcanism lead to a chain of volcanoes?
1. Base of mantle is heated by outer core, causing hot/solid plume of mantle to rise
2. When plume head reaches shallow, it melts by depressurizing, causing volcanism
3. As plate moves across plume, volcanoes go extinct and new ones arise, creating a chain
2. When plume head reaches shallow, it melts by depressurizing, causing volcanism
3. As plate moves across plume, volcanoes go extinct and new ones arise, creating a chain
22
New cards
What is viscosity a measure of?
measure of how easily a fluid flows
23
New cards
How do stratovolcanoes form?
Alternating layers of pyroclastic flows (explosive) and lava flows (effusive)
24
New cards
Which combinations of magma viscosity and gas content leads to effusive and explosive eruptions?
effusive: low gas and low viscosity
Explosive: high gas and high viscosity
Explosive: high gas and high viscosity
25
New cards
What happens to dissolved gas when it rises near the surface?
The gas expands to form a vapor phase (bubbles) and stream
26
New cards
What are the four main types of eruptions and their relative explosiveness?
1. Hawaiian 6,500 ft
2. Strombolian
3. Vulcanian
4. Plinian 180,400
2. Strombolian
3. Vulcanian
4. Plinian 180,400
27
New cards
How many volcano-related deaths have occurred in the past 500 years?
250,000
28
New cards
What are the basic characteristics of the various volcanic hazards and which one causes the most and least fatalities near and far from a volcano?
Least: lava, lightning, flood
Most fatal: Pyroclastic flow, indirect, and tsunamis
Most fatal: Pyroclastic flow, indirect, and tsunamis
29
New cards
What are some basics of volcanic ash?
1. Volcanic glass from gas bubbles
2. Smaller than sand
3. Hard electrical conducting
4. Wet ash can destroy roof
5. 5 cm can kill crops
2. Smaller than sand
3. Hard electrical conducting
4. Wet ash can destroy roof
5. 5 cm can kill crops
30
New cards
What is a pyroclastic flow?
A fast-moving avalanche of hot rock, ash and glass fragments
31
New cards
What is a lahar?
Mudflow avalanche of ash, soil, rock, and water. Can occur days or months later
32
New cards
Can volcanic eruptions be predicted?
yes, but never straightforward
33
New cards
What are harmonic tremors?
A continuous release of seismic energy typically associated with the underground movement of magma (long duration)
34
New cards
Why is Pompeii so interesting?
-2,00 people died
-buried under 30 ft of ash and lost from history for 1500 years
-ash preserved the dead
-buried under 30 ft of ash and lost from history for 1500 years
-ash preserved the dead
35
New cards
What was Pliny the Younger famous for?
-Description of Pompeii written by Pliny the Younger
-Plinian eruptions were named after him
-Plinian eruptions were named after him
36
New cards
What can a volcano look like before an eruption? What can it not look like?
-Pressure cannot build with lava at surface
37
New cards
What is the Volcano Explosivity Index (VEI) a measure of?
The volume of ash and other rock ejected
38
New cards
What is the relative size difference in size of eruptions at different VEI levels?
small 0-1, moderate 2-3, large 4-5, VERY large 6-7, SUPER 8
39
New cards
Why do geysers erupt but hot springs do not?
Geysers erupt because the water is trapped and becomes superheated until finally the pressure builds enough for it to break the seal.
40
New cards
How do we know Yellowstone is a hotspot?
By the trail of extinct volcanoes that lead up to it
41
New cards
How do calderas form?
Calderas form when the summit of a volcano collapses.
42
New cards
Have many large explosive eruptions occurred at Yellowstone in the last 2.1 million years?
3
43
New cards
How much of the US was covered by ash from Yellowstone's supereruptions?
Most of the West (stops at midwest) (missouri) 5,790 square miles with ash
44
New cards
How is the current size of the magma chamber under Yellowstone measured?
Seismic network
45
New cards
How do we monitor pressure changes in a magma chamber?
GPS on ground measure uplift (ground elevation)
46
New cards
What are the global consequences of large explosive volcanic eruptions?
-Global cooling
-SO2 reacts with oxygen and water vapor to create sulfuric acid droplets
-The ash and acid block the sun
-SO2 reacts with oxygen and water vapor to create sulfuric acid droplets
-The ash and acid block the sun
47
New cards
What is the connection between the Tambora eruption and monsters?
1816 cold summer in Switzerland
Mary Shelley Frankenstein
John Polidori came up with the Vampyre, Stoker used to make Dracula
Mary Shelley Frankenstein
John Polidori came up with the Vampyre, Stoker used to make Dracula
48
New cards
Why was the Toba eruption an important event in our species history?
Toba is a super-eruption lead to global cooling and almost wiped out humanity.
49
New cards
What are the global consequences of giant flood basalts?
-Might cause mass extinctions.
-Large amounts of greenhouse gases led to global warming and acid rain
-Large amounts of greenhouse gases led to global warming and acid rain