Chapter 3: Nervous System Organization
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
How many neurons are in the brain?
Approximately 86 billion neurons.
How many connections can a single neuron make?
Up to 30,000 connections with other neurons.
What are groups of neurons in the CNS called?
Nuclei.
What are groups of axons in the CNS called?
Tracts.
What does 'rostral–caudal' mean?
Nose to tail axis (anterior–posterior).
What does 'dorsal–ventral' mean?
Back to front axis (superior–inferior).
What does 'medial–lateral' mean?
Toward the middle or toward the side.
What does 'ipsilateral' mean?
Structures on the same side of the body.
What does 'contralateral' mean?
Structures on opposite sides of the body.
What does 'proximal' mean?
Structures close together.
What does 'distal' mean?
Structures far apart.
What does 'afferent' mean?
Movement toward the CNS.
What does 'efferent' mean?
Movement away from the CNS.
What does the CNS include?
The brain and spinal cord, protected by bone.
What does the PNS do?
Projects to the body; includes somatic and autonomic systems
What does the somatic nervous system do?
Interacts with the external world.
What does the sympathetic branch of the ANS do?
Prepares the body for fight-or-flight.
What does the parasympathetic branch of the ANS do?
Calms the body down.
What protects the CNS structurally?
The skull and vertebral column.
What are the meninges?
Protective layers: dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater.
What does cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) do?
Absorbs shock and removes waste.
What forms the blood-brain barrier?
Astroglia holding blood vessel cells tightly together.
What do neural stem cells give rise to?
Neuroblasts (neurons) and glioblasts (glia).
What are the three types of neurons?
Sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons.
What is the role of sensory neurons?
Transduce environmental information.
What is the role of interneurons?
Connect sensory and motor neurons within the CNS.
What is the role of motor neurons?
Project to muscles to produce movement.
What are astrocytes?
Star-shaped glia with nutritive and support functions.
What are oligodendroglial cells?
Form myelin in the CNS.
What are Schwann cells?
Form myelin in the PNS.
What are microglial cells?
Small, defensive immune-like cells in the CNS.
What are ependymal cells?
Secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What does gray matter contain?
Neuron cell bodies and capillaries.
Where is gray matter usually found?
Outer cortex.
What does white matter contain?
Myelinated axons connecting brain regions.
Where is reticular matter found?
In the brainstem; mixture of gray and white matter.
What are the three embryonic brain enlargements?
Prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon.
What does the prosencephalon become?
Telencephalon (cortex) and diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus).
What does the rhombencephalon become?
Metencephalon (pons/cerebellum) and myelencephalon (medulla).
What fills the brain's ventricles?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Where are the lateral ventricles located?
In the telencephalon.
What are the spinal cord segments?
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral.
What are dermatomes?
Regions of body surface innervated by each spinal nerve.
What are spinal reflexes?
Automatic behaviors without cognitive input.
How many pairs of cranial nerves exist?
Twelve.
What does the sympathetic ganglia location indicate?
They are close to the spinal cord, which means the sympathetic response is quicker than the parasympathetic response.
Where are parasympathetic ganglia located?
Near the target organs
how mahy brain ventricles are there?
4
What are the 2 largest ventricles
Lateral Ventricles
where do the 2 lateral ventricles meet?
Third ventricle, at the midline of the brain
Where is the 4th ventricle between?
cerrebellum and brainstem
What structure connects the third and fourth ventricles?
cerebral aqueduct
True or false: The spinal cord is gray matter surrounded by white matter
true
What do we call a collection of axons in the PNS?
Nerves
what do we call a bundle of axons in the CNS?
tracts
true or false: Afferent neurons carry motor signals and their ganlions are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
false; afferent neurons carry sensory information and their ganglions are located in the posterior root, which is outside of the spinal cord
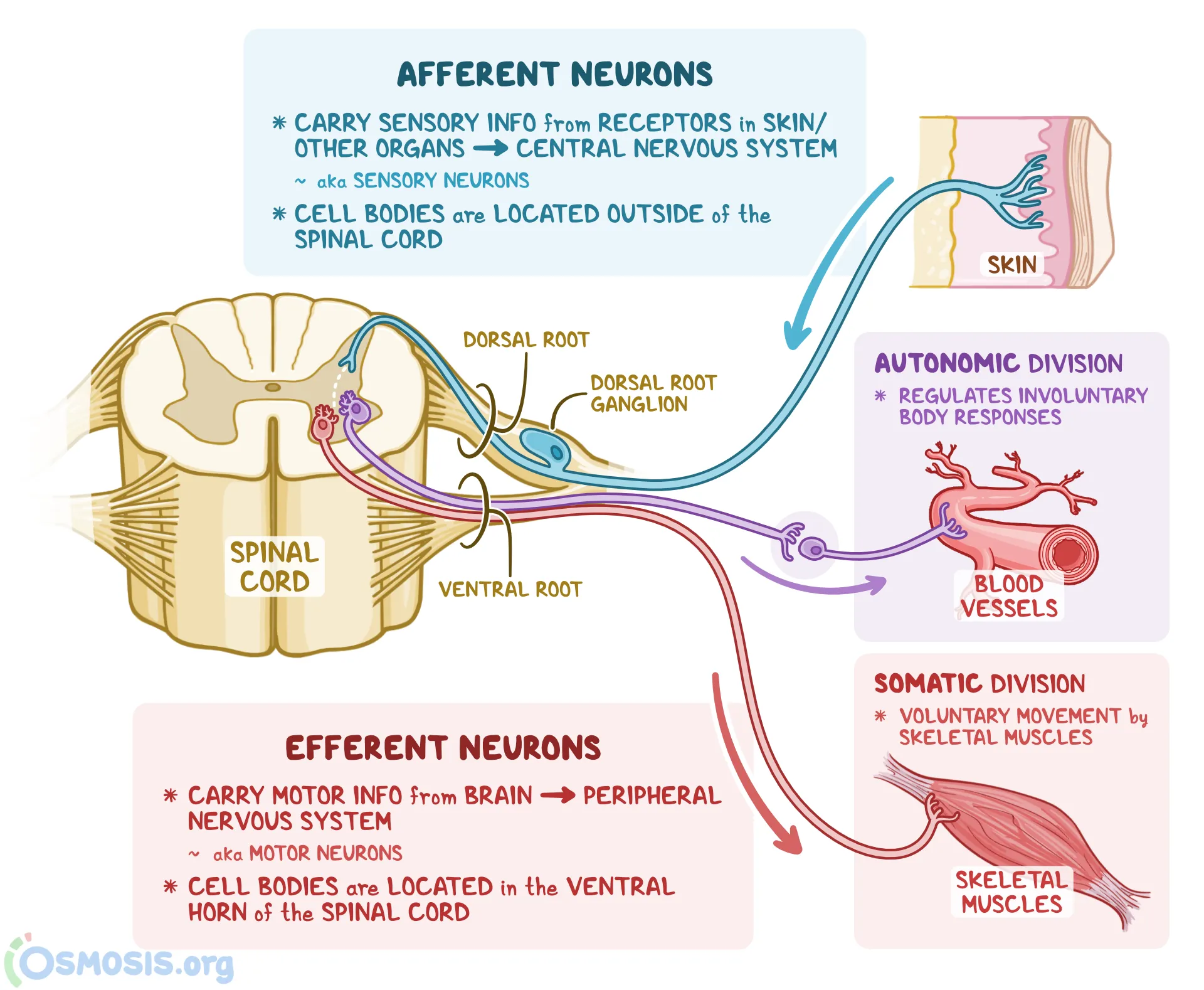
true or false: Efferent neurons carry motor signals away from the CNS, and their ganlions are located in the ventral horn inside of the spinal cord
true
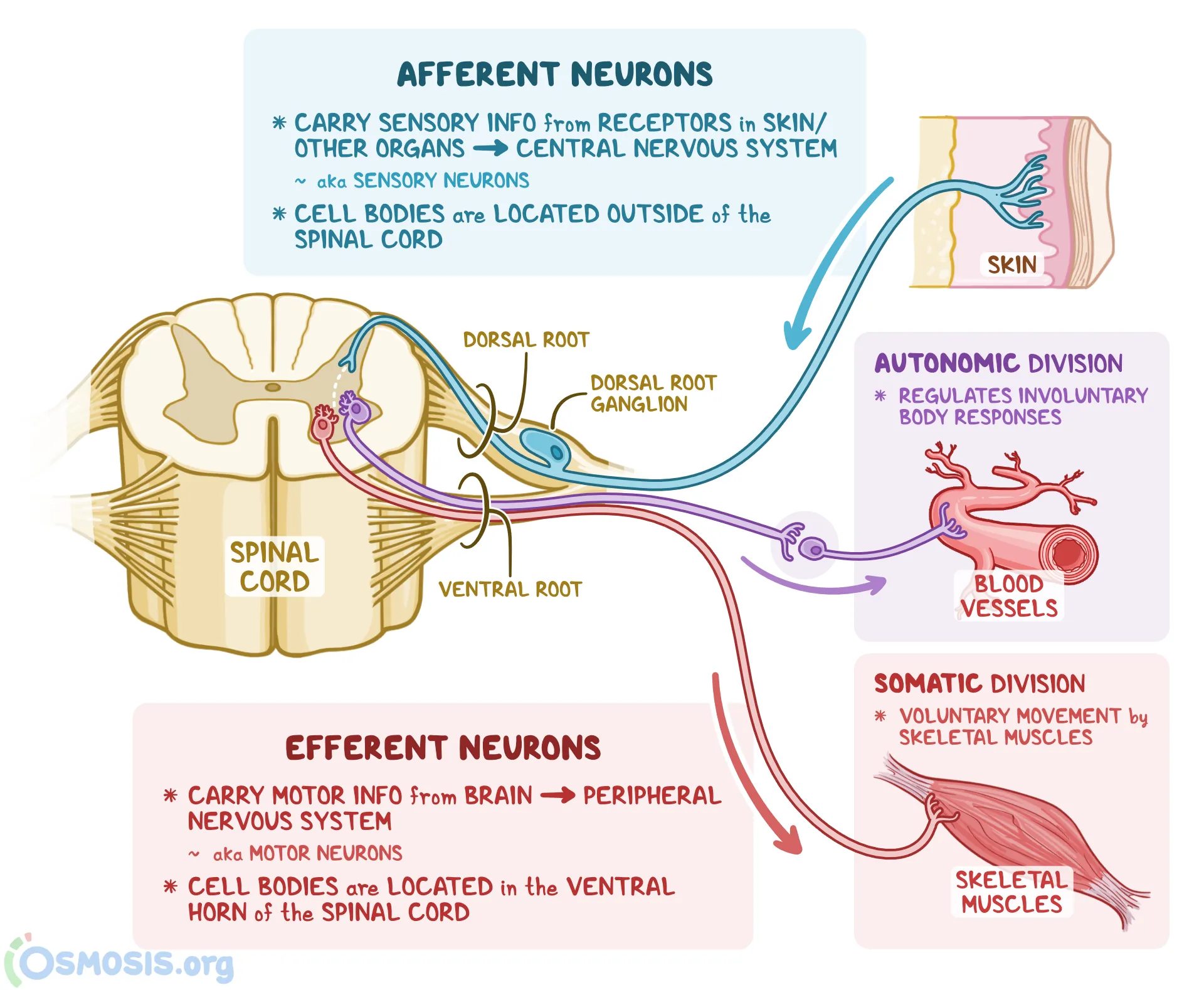
Does a spinal reflex require communication with the brain in order to occur?
No, reflexes are basic behaviours that occur without cognitive input
True or false: All cranial nerves are either sensory or motor, not both
false, some can be sensory, some motor, some both
Pick 2 cranial nerves and describe their function, whether they are motor, sensory, or both, neuropsychological examination method, and sysmptoms typical of dysfunction
Olfactory, smell, sensory, various odours applied to each nostril, loss of smell (anosmia)
Oculomotor, eye movement, motor, reaction to light, lateral movements of eyes, eyelid movement (ptosis), deviation of eye outward, symptoms: double vision (diplopia), large pupil, uneven dilation of pupils, drooping eyelid
what 2 branches does the Autonomic Nervoous system break down into?
sympathetic and parasympathetic branches
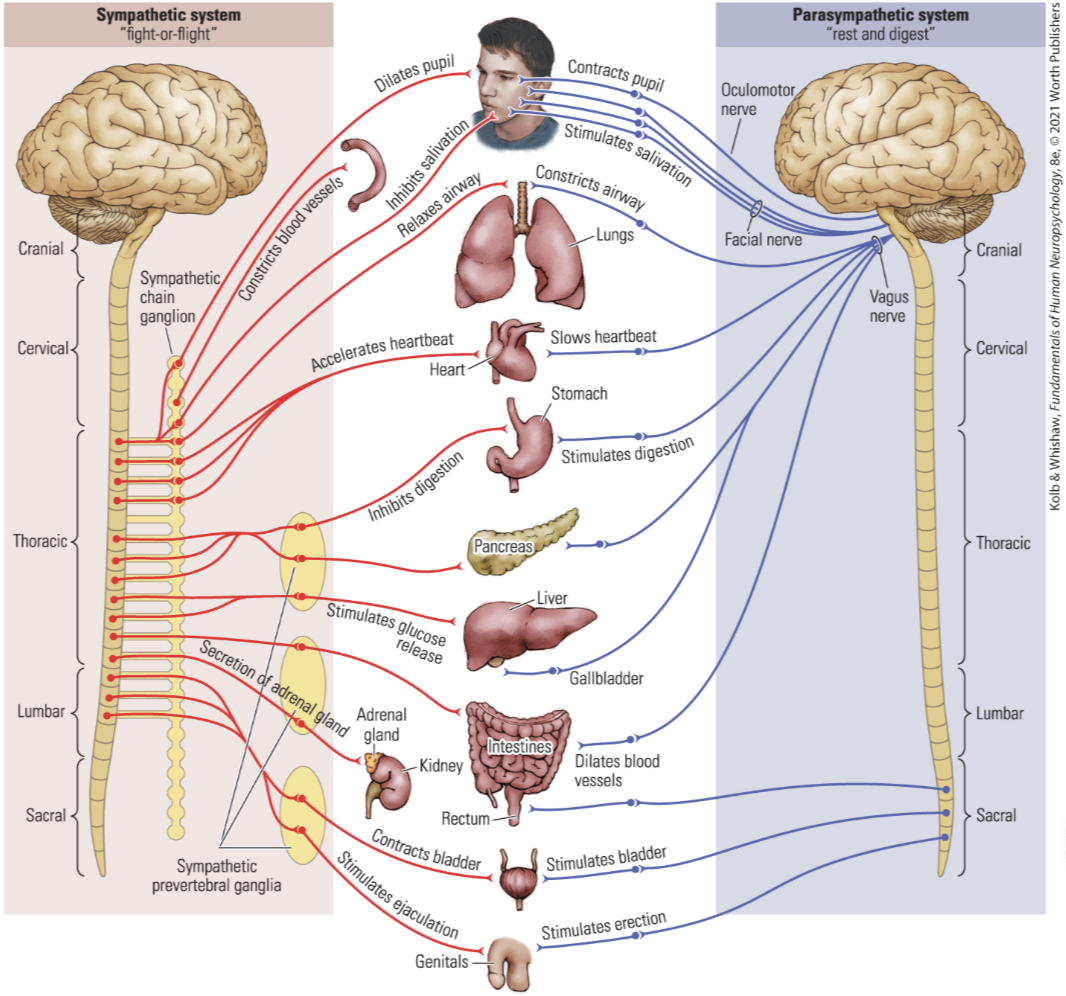
What do the locations of the ganglions tell us about the sympathetic and parasympathetic processes
The sympathetic system is composed of a chain of ganglia that run parallel to the spinal cord, connecting the spinal cord to body organs. This acts almost like a primative brain to. control the internal organs. Since it is closer to the spinal cord, the process is quicker. In contrast, the parasympathetic system connects with parasympathetic ganglia near the target organs, meaning they are further from the spinal cord. This means that the process takes longer.
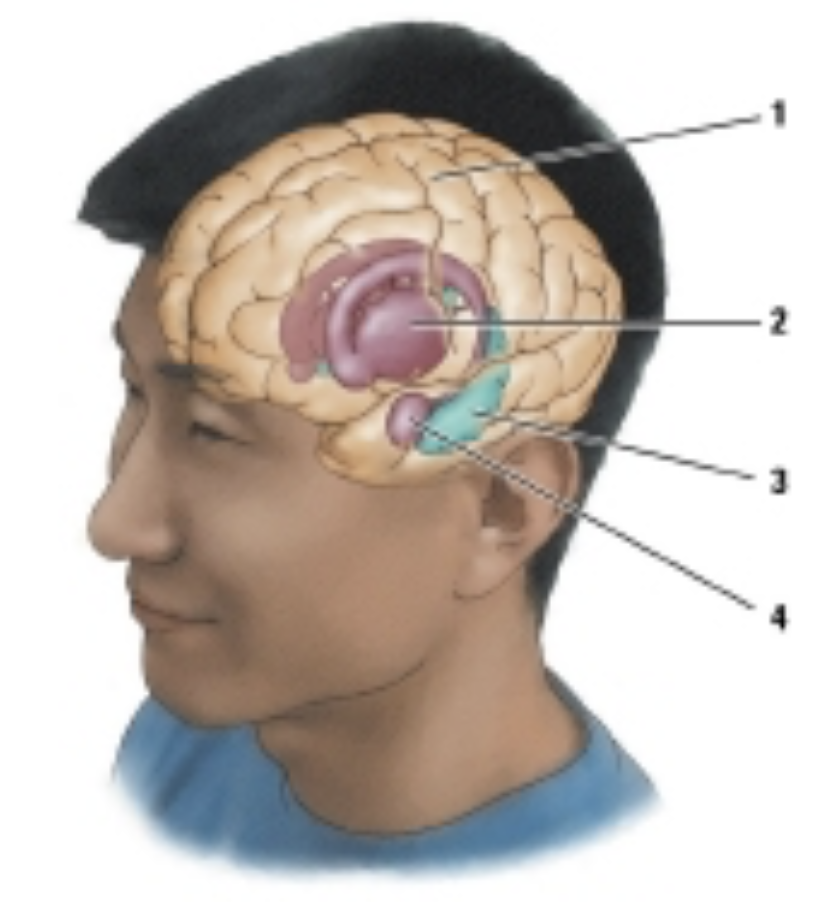
which of the following structures is labelled #1 in the drawing?
neocortex
which structure regulats vital autonomic functions (e.g, breathing, heartrate)?
medulla
which structure is involved in the regulation of pain
periaqueductal gray matter
which structure is found in the medulla, pons, and midbrain?
recticular formation
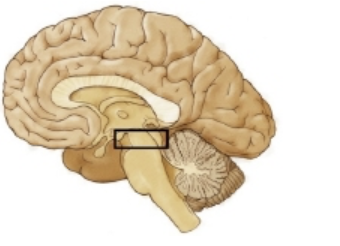
which region is outlined in the figure?
midbrain
The superior and inferior colliculi are components of the:
tectum
which structure regulates the release of hormones through its connection with the pituitary gland?
hypothalamus
True of False: The basal ganglia is a structure found in the hindbrain
false
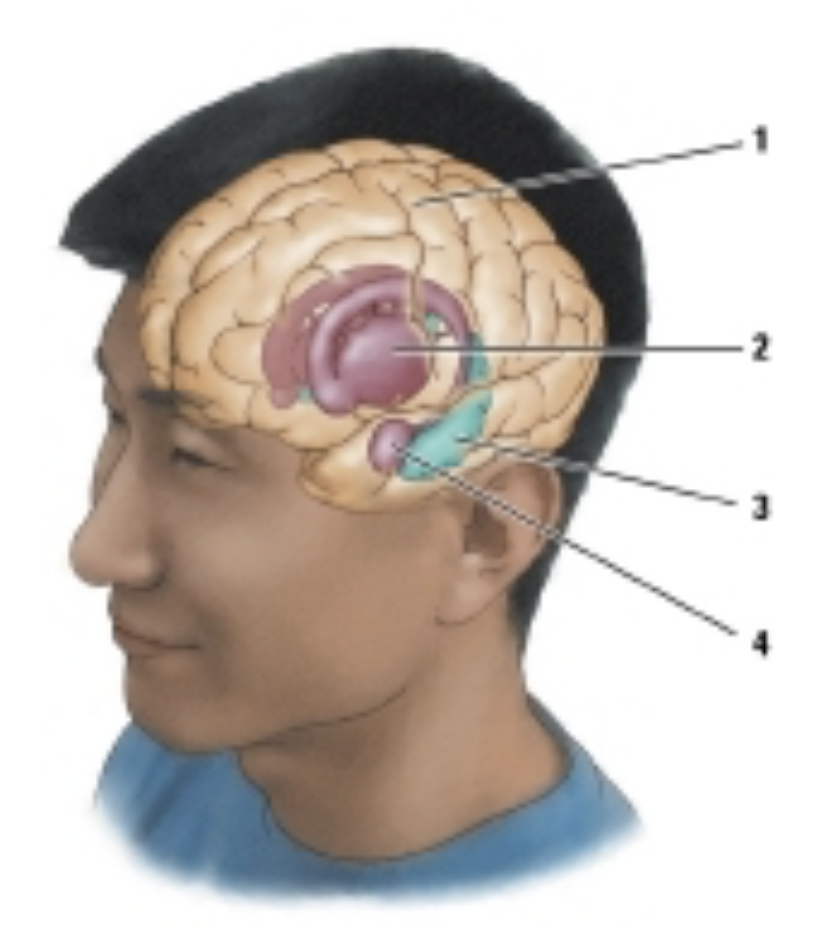
which structure is labeled #4?
amygdala
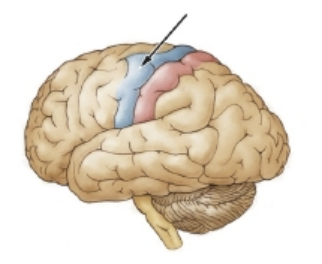
The arrow in the drawing is pointing to the primary ________ cortex
motor