business finance unit 3.7, 3.8, 3.9
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
cash definition
money that comes into the firm through sales, borrowing and investment
cash flow definition
the amount of money that flows in and out of the business over a given period of time
cash inflow definition
money received by business
cash outflow definition
money paid out by the business over a period of time
difference between profit and cash flow
businesses may make sales on credit, they will have made profit but the cash flow position at that time will differ
net cash flow calculation
= total cash inflow - total cash outflow
first problem with differentiating profit and cash flow and its causes
insolvency
business can be profitable but have little or no cash which can be caused by allowing a long credit period, paying suppliers too early and purchasing too much stock with cash
second problem with differentiating profit and cash flow
a business can have a positive cash flow but be unprofitable as cash could be sourced from bank loans, gained from the sale of fixed assets or obtained from shareholders funds
cash flow forecast definition
future predictions of a firm’s cash inflows and outflows over a given time period
cash flow forecast first columns
opening balance
total cash inflow
total cash outflow
net cash flow
closing balance
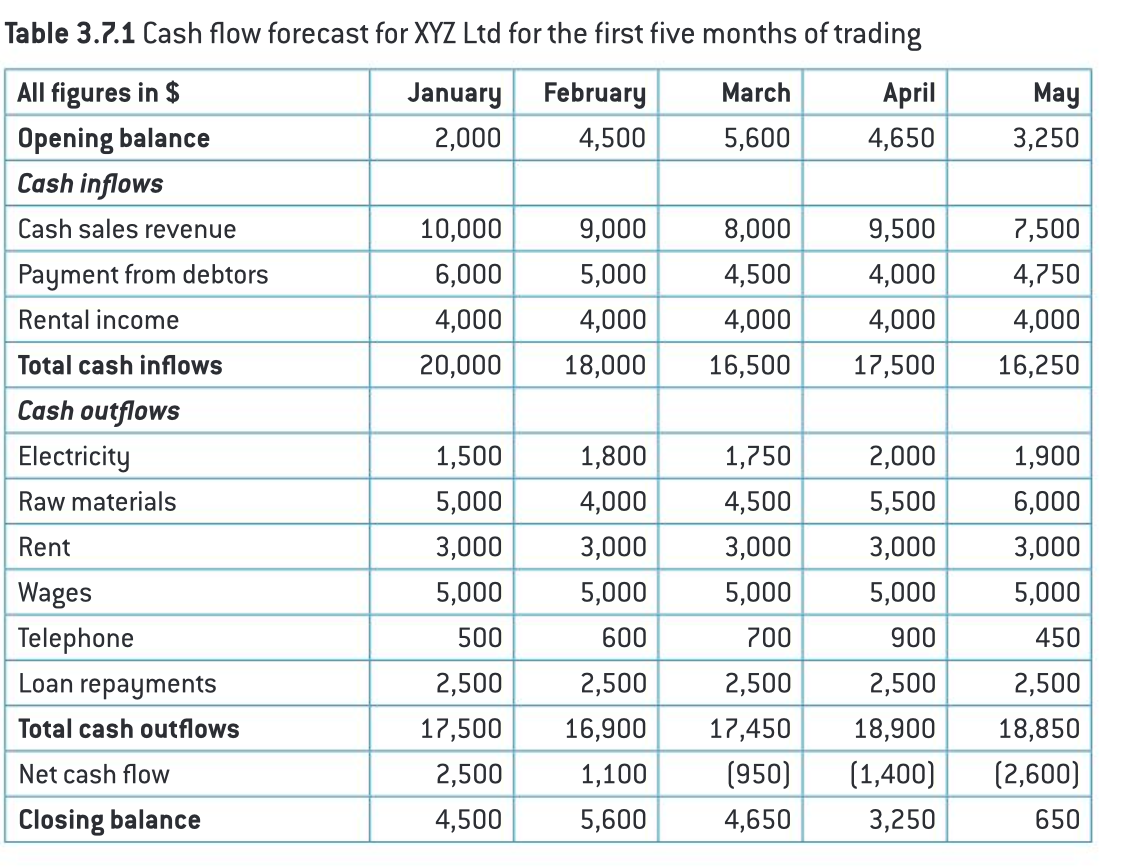
closing balance calculation
= opening balance + net cash flow
advantages of using a cash flow forecast
see where unnecessary costs can be cut
set goals and targets for future
useful to structure budgets
can determine risks
warning of cash shortages
disadvantages of using a cash flow forecast
may be inaccurate, cannot predict unexpected changes in economy e.g. pandemic, bankruptcy
competitor may join the market
poor market research can lead to false sales forecasting
may have demotivated employees
ways to improve cash inflows
insist on customers paying with cash
offer discounts to encourage debtors to pay early
diversify its product offering
ways to reduce cash outflows
negotiate with suppliers or creditors to delay payment
→ however, it is time consuming
purchase of fixed assets can be delayed
→ however, this may lead to decreased efficiency
decrease specific expenses e.g. advertising costs
→ however, this may lower future demand
source cheaper supplies
→ however, the quality of products may be worse
relationship between investment, profit and cash flow investment
start up → has high investment, no profit and negative cash flow
growing firm → still has high investment, low profit and positive but low cash flow
established firm → minimal investment, high profit and positive cash flow
additional finance resources to improve cash flow
sales of assets
bank overdrafts
sale and leaseback
grants and subsidies
three methods of investment appraisal
payback period, average rate of return and net present value
payback period definition
estimates the length of time required for an investment project to pay back its initial cost from its net cash flows
payback period calculation
= initial investment cost/annual cash flow from investment
advantages of using payback period
simple and fast to calculate
useful for rapidly changing industries e.g. technology
helps firms with cash flow problems
disadvantages of using payback period
ignores the profitability of an investment
could be effected by unexpected external changes in demand
payback period calculation month
= extra cash inflow required / annual cash flow in year when investment is covered x 12 months
average rate of return (ARR) definition
measures the annual net return of an investment as a percentage of its capital cost, assessing its profitability
average rate of return (ARR) calculation
= net returns per annum / capital cost = (total returns - capital cost) / years of usage / capital cost x 100
advantages of using average rate of return (ARR)
shows profitability of investment project
makes use of all the cash flows in a business, unlike the payback period
allows for easy comparisons with other competing projects to better allocate funds
disadvantages of using average rate of return (ARR)
forecasting errors are likely because of longer time period
doesn’t consider the timing of cash inflows
net present value definition
the difference in the sum of present values of future cash inflows and the original cost of investment
net present value calculation
= total present values - original cost of investment
advantages of using net present value
opportunity cost and time value is taken into consideration
all cash flows including their timing are included
disadvantages of using net present value
more complicated to calculate
may be affected by inaccurate interest or inflation rate predictions
figures may be overestimated due to changes in external environment
budget
a quantitative financial plan that estimates the revenue and expenditure over a specified future time period
the difference between cost and profit centres
cost centre:
a section of a business where costs are incurred and recorded
profit centre:
a section of a business where both costs and revenues are identified and recorded
→ profit centres allow comparisons to be made to judge the performance of a firm in various sectors
the roles of cost and profit centres
aiding decision-making
better accountability for poor performance
tracking problem areas
increasing motivation (providing incentives)
benchmarking (help find areas that are most or least efficient)
constructing a budget columns
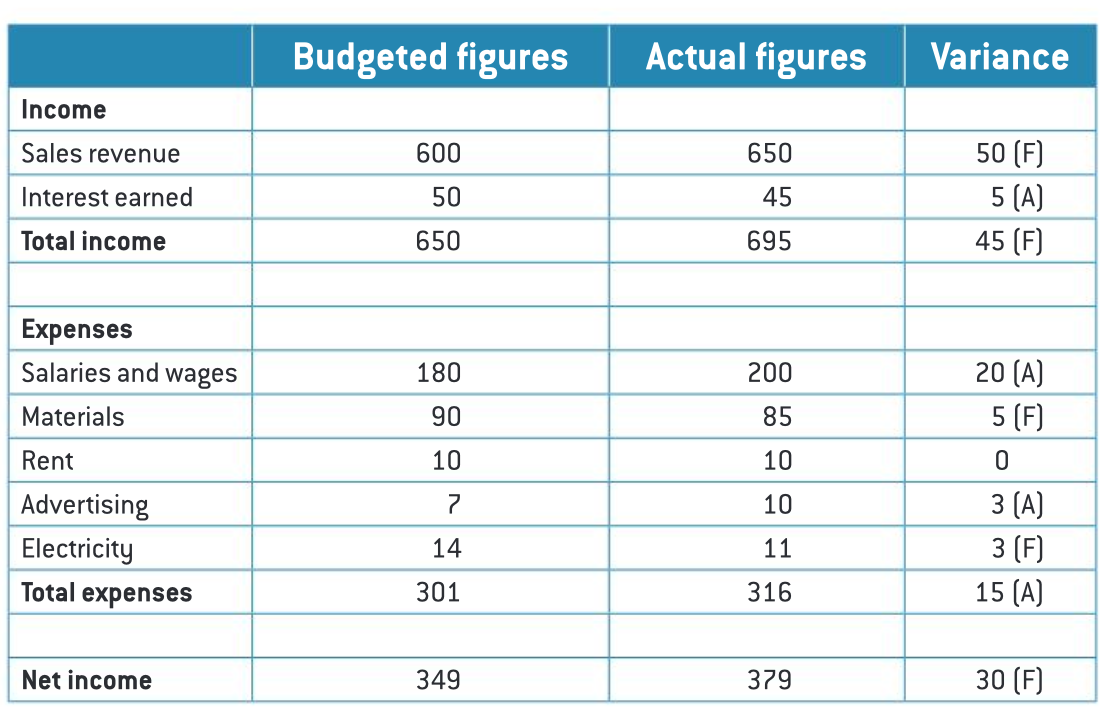
budgeted figures actual figures variance
income
total income
expenses
total expenses
net income
variance
the difference between the budgeted figure and the actual figure
favourable variance: when the difference between the budgeted and actual figure is financially beneficial to the firm
adverse variance: when the difference between the budgeted and actual figure is financially costly to the firm
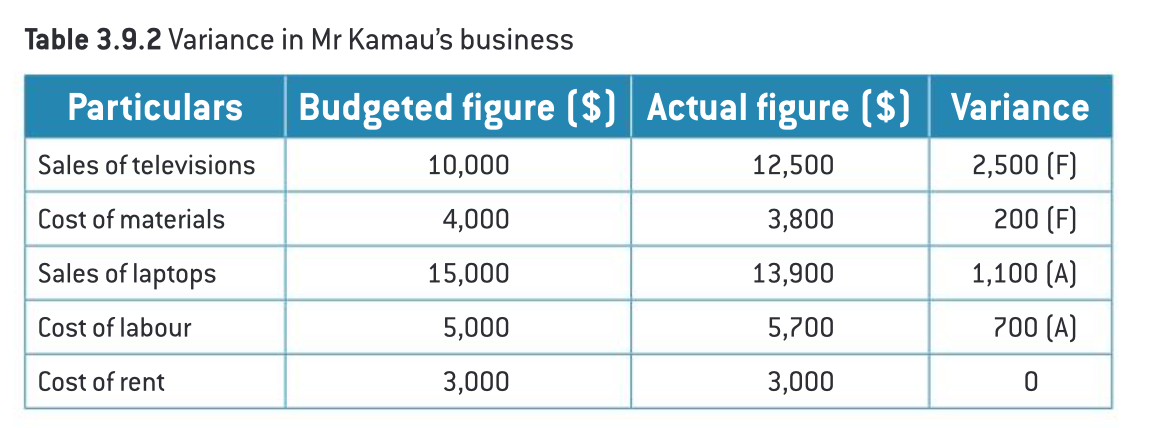
benefits of budgets and variances in decision making
better planning
better resource allocation
increasing motivation
improving coordination
better control revenue and expenditure
allows comparison between actual performance and budgeted performance
helps detect deviations
allows for the creation of SMART goals