6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds (incomplete)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are arenes?
aromatic hydrocarbons containing one or more benzene rings
What is the relationship between aromatic and aliphatic compounds?
they are mutually exclusive
What is the molecular formula of a benzene ring?
C6H6
What is the skeletal formula of a benzene ring?
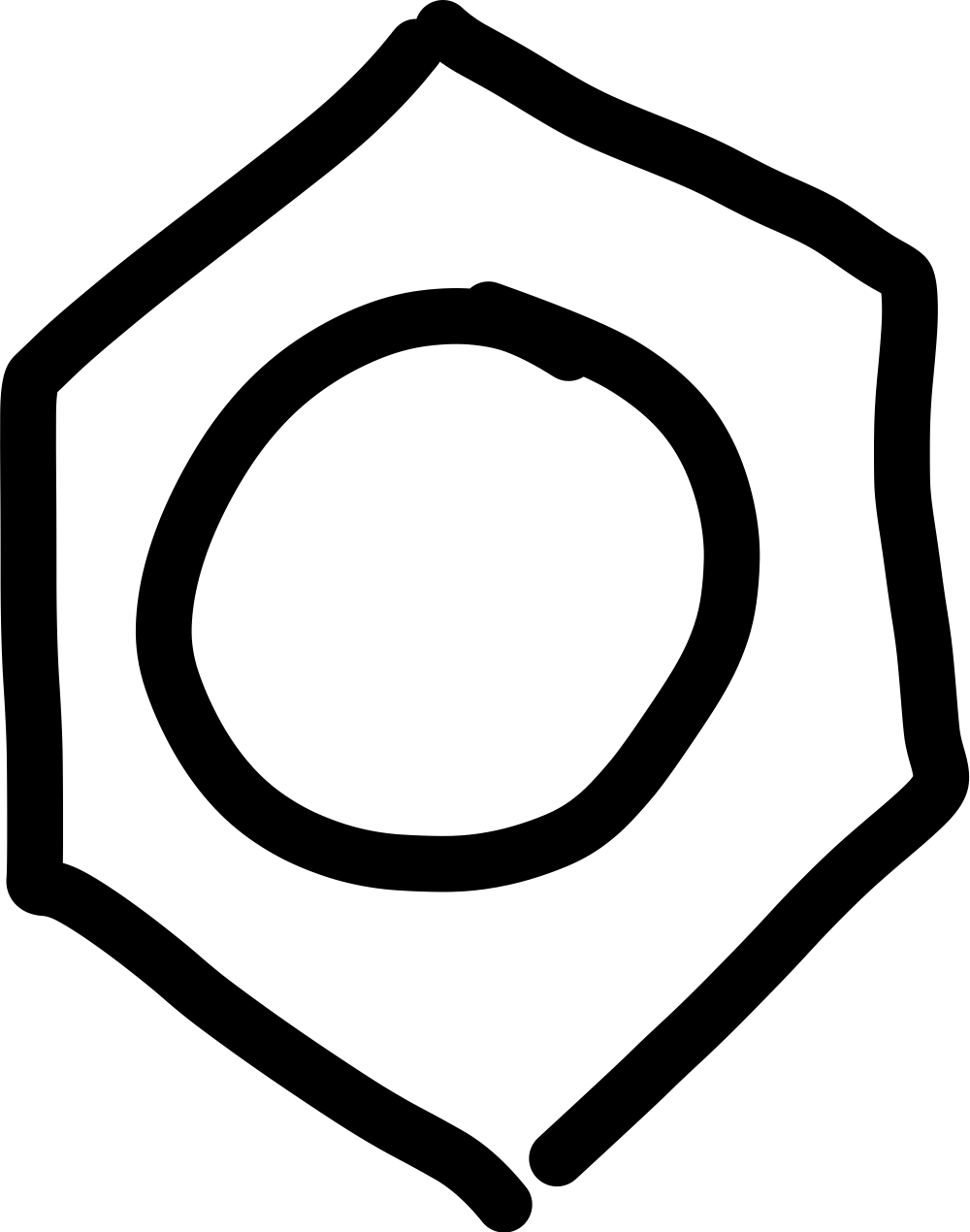
What is the displayed formula of a benzene ring?
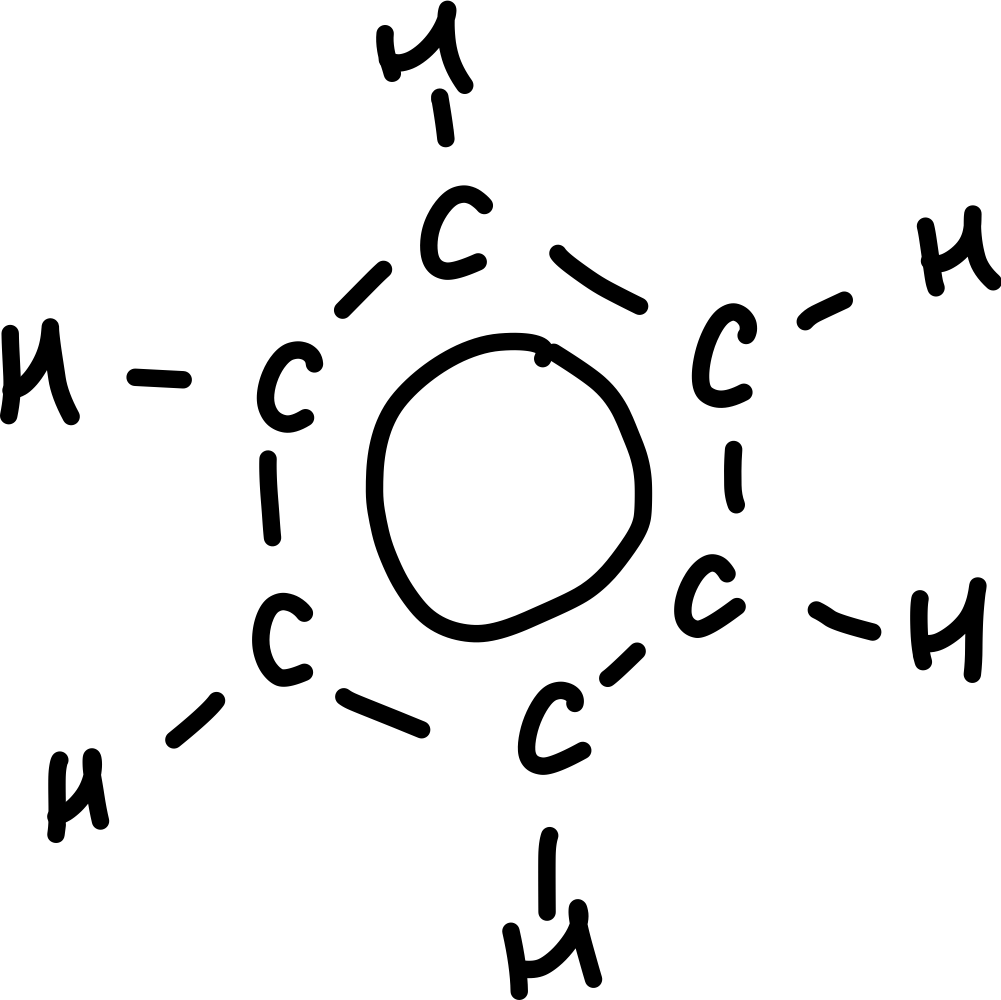
How are benzene rings with a halogen group named?
halo-benzene
How are benzene rings with an alkyl group named?
alkyl-benzene
How are alcohols with a benzene ring named?
phenyl-alcohol
How are benzene with a ketone group named?
phenyl-ketone
What is a nitro group?
-NO2
How are arenes with a nitro group named?
nitrobenzene
How are arenes with a halogen and alkyl group named?
halo-alkyl-benzene
How is an arene with a carboxylic acid named?
benzoic acid
What is an amine group?
-NH2
How are arenes with an amine group named?
phenylamine
How are are arenes with an OH group named?
phenol
When is the phenyl-prefix used when naming arenes?
when the benzene ring is attached to a alkyl group with 7 or more carbons or that contains a functional group
When is the benzene suffix used when naming arenes?
attached to an alkyl group woth less than 7 carbons or directly attached to a group
What are the exceptions when naming arenes?
phenol
benzoic acid
benzaldehyde
phenylamine
What is the name of C6H4OHNO2?
2-nitro-phenol
Who suggested that the structure of benzene is the same as triene?
Kekule von Stradonitz
What is the Kekule structure of benzene?
triene
Give 3 pieces of evidence that suggest the Kekule structure of benzene is incorrect?
resistance to reacting with bromine
bond lengths
enthalpy change of hydrogenation
Does benzene decolourise bromine at room temperature?
no
Why doesn’t benzene react with bromine?
it doesnt contain C=C bonds
How can the bond lengths of benzene be found?
xray diffraction analysis
Describe the bond lengths in benzene?
all C-C bond lengths are the same
the C-C bond length is between that of C-C and C=C length
What do the bond lengths of benzene suggest?
benzene does not consist of alternating, isolated C-C and C=C bonds
Compare the enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of benzene and the hydrogenation of triene?
the enthalpy change for hydrogenation of benzene is less exothermic than predicted
What does the enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of benzene suggest?
benzene does not contain 3 C=C bonds and is more stable than expected
Compare the stability of benzene and triene
benzene is more stable
What is the theoretical enthalpy change for hydrogenation of triene?
-360
What is the enthalpy change for benzene?
-208
What is the correct structure of benzene?
the delocalised structure
Describe the delocalised structure of benzene
cyclic molecule
shape around each C molecule is trigonal planar (120)
sigma bonds between each carbon atom
a pi system above and below the plane of carbon rings that consists of 6 delocalised electrons
What is the shape and around each C atom of benzene?
trigonal planar, 120
What bonds exist between the C atoms and CH atoms?
sigma bond
How are sigma bonds formed?
single overlap of orbitals directly between the nuclei of C atoms
How is rge pi system of a benzene ring formed?
formed by the sideways double overlap of p orbitals on each c atom on the carbon ring
How many delocalised electrons does the benzene pi system consist of?
6
Describe the delocalised electrons in the benzene system?
they are mobile across all 6 carbon atoms on the benzene ring
What are the similarities between the pi bond in cyclohexene and the pi system in benzene
pi bond formed in the same way
pi bond above and below the plane
What are the differences between the pi bond in cyclohexene and the pi system in benzene
pi system made up of 6 delocalised electrons while pi bond made up of 2
pi system - electrons are delocalised, pi bond- electrons are localised