Chemistry Investigation 3: Periodic Table for 9/12/24
People
Newlands
the first to arrange the elements into a periodic table with increasing order of atomic masses.
figured out that every eight elements had similar properties and called this the law of “octaves”.
Mendeleev (1860’s)
created element cards
sorted elements by how they reacted and then sorted them from lightest to heaviest
created a basic periodic table that left gaps for undiscovered elements
Ramsey (1894’s)
did not know there were shells because electrons had not yet been discovered
discovered Noble Gases
Moseley
discovered atomic numbers (from 20+ they were not accurate)
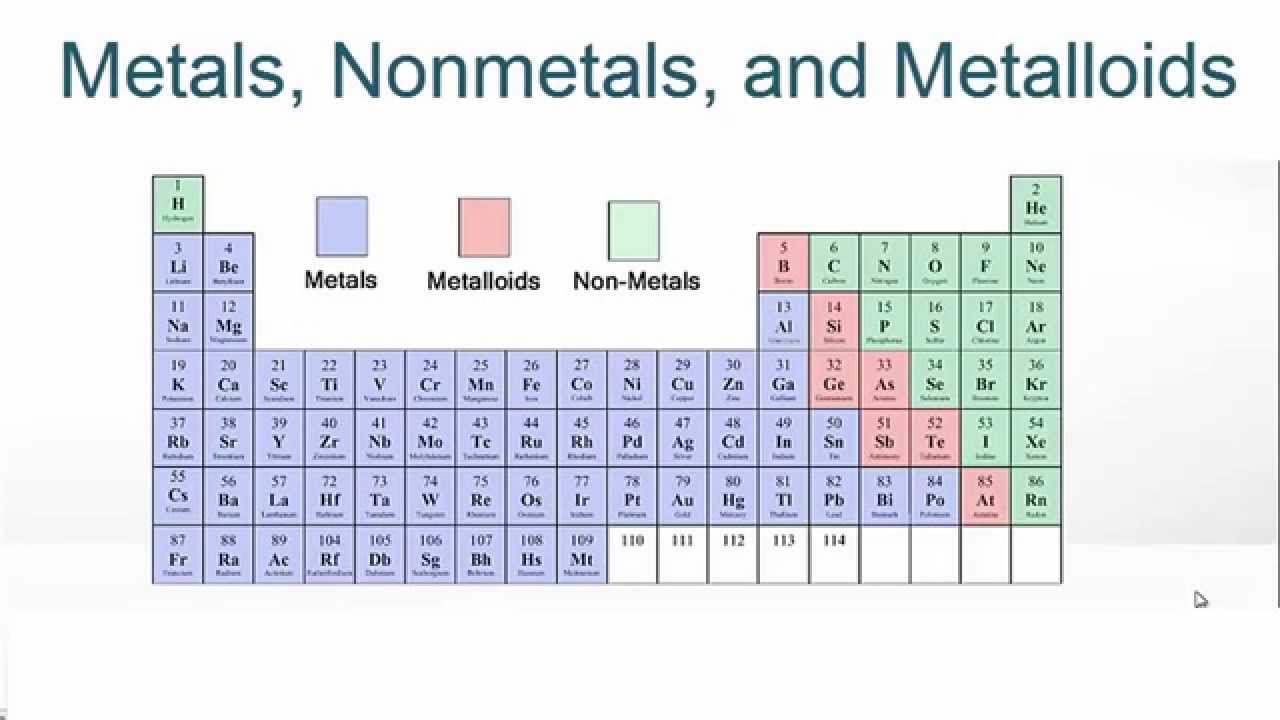
Silicon, Germanium, and Arsenic are the main metalloids
Element Types
Metals
Location
Everything on the left side of the table (except hydrogen)
Properties
Luster - Can be polished to make shine
Malleable - Can be shaped
Ductile - Can be stretched (into a wire)
Conductor - Electricity and heat can pass through it (conducts it)
Corrode - Reacts with elements in the atmosphere
Non-Metals
Location
Everything on right side of table is a non-metal
Properties
Dull - Not shiny
Brittle - Breaks easily
Poor Conductor - Electricity and heat cannot pass through it
Metalloids (Semi-Conductors)
Location
On the line (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, and At)
Properties
Has properties of metals and non-metals
Fact
Used in electronics
Periodic Table of Elements
Elements
Alkali Metals
Location
First row down - top is Hydrogen (H)
Properties
1 Electron in Outer Shell
Most reactive metals
Make a base in water
Alkaline Earth Metals
Location
Second row down - top is Beryllium (Be)
Properties
2 Electrons in Outer Shell
2nd most reactive metals
form an alkaline (base) solution when added to water
Transition Metals
Location
Big gap in middle of Alkaline Earth Metals and Boron family
Properties
1 or 2 Electrons in Outer Shell
Some are reactive (ex. iron and copper)
Some are not very reactive (ex. gold and platinum)
Rare Earth Metals
Location
Bottom part of periodic table
Halogens
Location
7 Electrons in the Outer Shell
Properties
Most reactive non-metals
Noble Gases
Location
Last row down - top is Helium (He)
Properties
Full outer shell
Most have 8 valence electrons (unsure ask)
Non-reacting under normal conditions similiar to old-time nobility and not being with the commoners
General
Coloumb’s Law
Describes forces between charges
If distance goes up force goes down
Atoms get bigger going across in a row because of Coloumbe’s attraction
Atomic Size
Row from top = shells
row from side = valence electrons
small elements on top
large elements on bottom
down = more valence electrons
up = less valence electrons
Ionization Energy
Lose electrons
+ Charge Ions
Low for metal; high non-metals
Electron Affinity
Gain electrons
- Charge Ions
High for metals; low non-metals
Atomic Properties
Metals are generally more reactive at the bottom of the table than the top (rows 1,2,3)
Non-Metals tend to be more reactive at the top of the table rather than the bottom (rows 4-8)
Period
Across a period from left to right, the elements become less metallic and more non-metallic in their properties and smaller to larger