Ap Human Geo Unit 4
5.0(2)Studied by 53 people
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:15 PM on 12/5/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
1
New cards
**relict (relic) boundary**
boundary that no longer exists as an international border, but remnants of its existence remain
2
New cards
**nation**
people who think of themselves as one based on a sense of shared culture and history and who desire political autonomy
3
New cards
**nation-state**
a state with a single nation (very few exist)
4
New cards
**stateless nation**
a nation who do not have their own independent state
5
New cards
**multi-national state**
a state with two or more nations (includes *most* states)
6
New cards
**multi-state nation**
a nation living across states
7
New cards
**autonomous region**
an area which governs itself, but is not an independent country
8
New cards
**semi-autonomous region**
an area that can govern itself in certain areas, but does not have complete power to govern. Ex: Native American reservations
9
New cards
**sovereignty**
final authority over a territory and the right to defend territorial integrity against incursion
10
New cards
**colonialism**
rule by an autonomous power over a subordinate people and place that creates unequal cultural and economic relations
11
New cards
**imperialism**
the drive toward creation and expansion of an empire and then once established, its perpetuation
12
New cards
**self-determination**
the process by which a country determines its own statehood and forms its own allegiances and government
13
New cards
**independence movements**
an area that believes that it should be its own country
14
New cards
**political power**
expressed geographically as control over people, land, and resources
15
New cards
**government**
political system with governing authority
16
New cards
**authoritarian government**
gov’t with a strong central power, no constitutional accountability, no individual freedoms e.g.absolute monarchy(Saudi Arabia), dictatorship (North Korea), fascism (Germany)
17
New cards
**democracy**
government where power resides with the majority (Ancient Greece)
18
New cards
**republic**
government where power resides in a body of citizens entitled to vote and is exercised by elected representatives responsible to them and governing according to law (U.S., Germany, France)
19
New cards
**democratization**
the process of moving from a non-democracy (authoritarian rule, colonial rule) to a democratic system
20
New cards
**neocolonialism**
form of indirect control through the use of economic/political pressures to control or influence other countries, especially former colonies in which they continue to be exploited
21
New cards
**shatterbelt**
region endangered by local conflicts within the state or between countries in the area, as well as the involvement of opposing great powers outside the region
22
New cards
**choke points**
geographical feature (sea OR land) that has significant strategic importance. Ex: Panama Canal
23
New cards
**human territoriality**
the connection of people, their culture, and their economic systems to the land creating a desire for ownership over a defined space
24
New cards
**boundary**
line that determines the limit of state jurisdiction that is a vertical plane that cuts through the subsoil and extends into the airspace above and often coincides with cultural, national or economic divisions
25
New cards
**boundary definition**
phase in which the boundary is negotiated and legally described
26
New cards
**boundary** **delimitation**
phase in which the boundary is drawn on the map
27
New cards
**boundary** **demarcation**
phase in which markers are placed on the ground (signs, walls, fences)
28
New cards
**boundary** **administration**
phase in which the boundary is maintained
29
New cards
**boundary dispute**
disagreement over the location of a boundary/movement across the boundary (migration/smuggling) and can cause conflict
30
New cards
**irredentism**
when a state wants to annex territory whose population is ethnically similar
31
New cards
**antecedent boundary**
boundary in the natural landscape that existed before the cultural landscape emerged and stayed in place as people moved in
32
New cards
**subsequent boundary**
boundary that evolves as the cultural landscape of an area takes shape and changes as cultural landscape changes
33
New cards
**superimposed boundary**
boundary that is drawn by powerful outsiders (e.g. colonizers) and ignores existing cultural groups
34
New cards
**geometric boundary**
boundary that follows a straight line or arc
35
New cards
**Berlin Conference**
a meeting (1884-1885) between European nations to divide Africa among them for colonization with the intent of preventing conflict over the process
36
New cards
**colonization in Africa**
from the 17th to 19th centuries, large parts of Africa were divided according to which pieces of land belonged to which European colonizer and *not* by the existing patterns of different tribal people/ethnicities living on the land
37
New cards
**de-colonization in Africa**
the superimposed boundaries of Africa remained in place after independence, which has led to much of the current conflict and lack of ability to establish effective leadership
38
New cards
**demilitarized zone (DMZ)**
a buffer zone created by treaties/agreements between two or more military powers that falls on either side of the actual boundary
39
New cards
**international agreements**
establishment of formal commitments between countries on world related issues that can either encourage interactions (trade) or discourage disputes (resources)
40
New cards
**international sanctions**
policies or actions designed to induce states to change their behavior
41
New cards
**Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)**
established rights and responsibilities of states concerning ownership/use of oceans/seas and their resources as developed by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
42
New cards
**Territorial Sea**
zone of water adjacent to a state’s coast (12 miles) in which a state has sovereignty
43
New cards
**Contiguous Zone**
zone of water adjacent to Territorial Sea (24 miles) in which state can enforce customs, immigration, and sanitation laws
44
New cards
**Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)**
zone of water adjacent to Contiguous Zone (200 miles) in which a state has the Right to explore, exploit, conserve, and manage resources
45
New cards
**international waters (High Seas)**
ocean beyond the EEZ, in which all states have equal access
46
New cards
**median-line principle**
method used to divide the waters between states that do not have 400 miles between them
47
New cards
**voting district**
subdivision for electing members to a legislative body
48
New cards
**redistricting**
when voting districts are redrawn due to changes in population
49
New cards
**gerrymander**
redistricting that is unfair and gives an advantage to a particular political party by concentrating voting strength
50
New cards
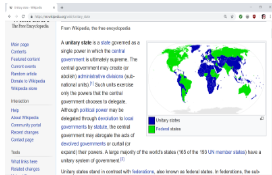
**unitary state**
state that is governed as a single unit with a central top down form of form of governance where local territories only have power that is granted by the central government e.g. U.K., France, Spain, China, Italy
51
New cards
**subnational political territorial unit**
region that is given greater autonomy from the central government
52
New cards
**devolution**
the transfer of decision-making power from a central government to a lower level
53
New cards
**CAUSES of devolution**
* ethnic separatism (religion, language, ethnicity)
* economic and social issues
* irredentism
* physical geography
* centrifugal forces
* terrorism
* ethnic cleansing
* economic and social issues
* irredentism
* physical geography
* centrifugal forces
* terrorism
* ethnic cleansing
54
New cards
**devolution occurs when…**
states fragment into subnational political territorial units
55
New cards
**supra-nationalism**
political and/or economic alliance of three or more states that is formed for mutual benefit to promote shared goals and resolve disputes, but can limit the economic or political actions of member states creating a challenge to state sovereignty
56
New cards
**United Nations**
union formed to promote international world peace and security after WWII, comprised of 6 principal organs that meet to decide on common issues and policies
57
New cards
**European Union**
economic alliance between European countries (1992) that established free trade and open borders and a common currency (Eurozone)
58
New cards
**North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)**
economic alliance to gradually eliminate tariffs and trade barriers between the U.S., Canada, Mexico
59
New cards
**African Union (AU)**
political, economic and social alliance aimed at promoting greater unity, cohesion, and efficiency of African states and reducing the strains of their colonial roots
60
New cards
**NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization**)
military alliance formed after WWII between the U.S., Canada and 26 European states to ensure mutual assistance in times of aggression
61
New cards
**ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)**
economic alliance aimed at improving development in Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Brunei
62
New cards
**Arctic Council**
alliance aimed at promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among Arctic states, Arctic indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on issues of sustainable development and Environmental protection in the Arctic members: U.S., Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia
63
New cards
**military alliance**
alliance between two or more states who agree on mutual protection and support in case of a crisis e.g. NATO formed to defend against threats by communist countries after WWII (**Cold War**: period of political and military tension between the USSR and Western states after WWII)
64
New cards
**trade agreement**
treaty between two or more states who agree on trade, tariffs, taxes, and often includes investment guarantees e.g. NAFTA formed to eliminate tariffs on trade between Canada, Mexico, and the U.S.
65
New cards
**economies of scale**
cost advantages gained by an increased level of production
66
New cards
**The Paris Agreement**
establishment of protocols dealing with greenhouse gas emissions by the United Nations
67
New cards
**political change**
advances in communication technology have facilitated devolution, supranationalism, and democratization
68
New cards
**centripetal forces**
forces within a state that promote unity and national stability (nationalism)
69
New cards
**centrifugal forces**
Forces within a state that destabilize or weaken it