upright tilt testing
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
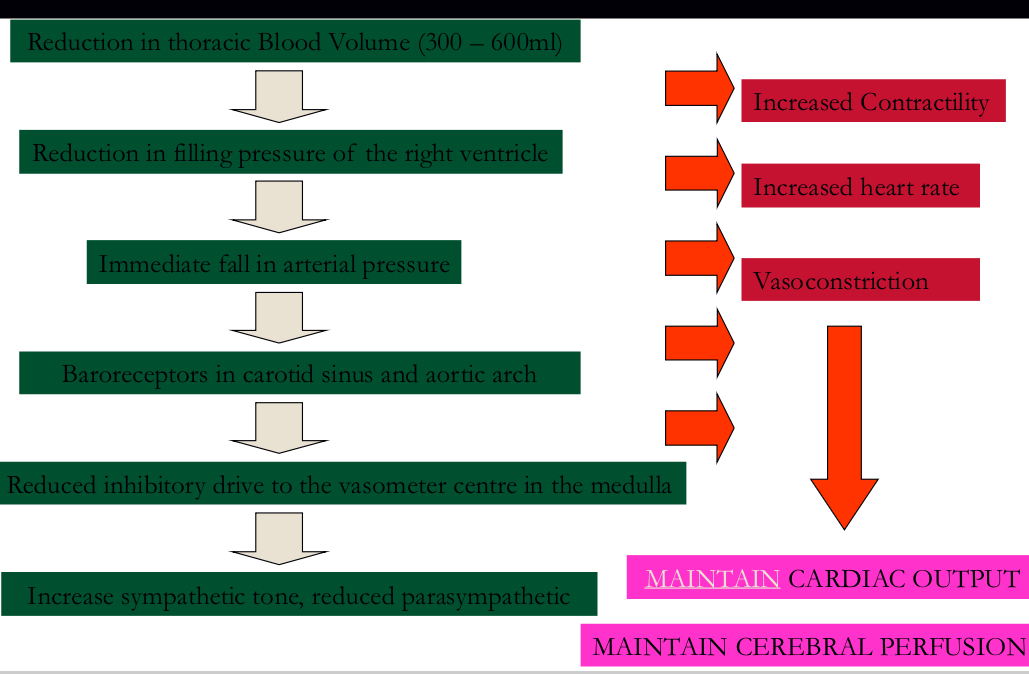
What’s the normal response?
In the heart,
Contractility is increased
HR increases
Vasoconstriction
Maintain cardiac output
Reduction in thoracic Blood Volume (300 – 600ml)
Reduction in filling pressure of the right ventricle
Immediate fall in arterial pressure
Baroreceptors in carotid sinus and aortic arch
Reduced inhibitory drive to the vasometer Canter in the medulla
Increase sympathetic tone, reduce parasympathetic
Maintain cerebral perfusion
Causes of syncope
Irregularities of heart rate and rhythm
◦ Brady arrhythmias
◦ Varying degrees of heart block
◦ Tachy arrhythmias
◦ Brugada Syndrome / Long QT, ARVC
Cardiac lesions which obstruct blood flow
◦ Aortic stenosis
◦ HOCM
◦ Pulmonary stenosis
Reflex-mediated vasomotor instability syndromes
◦ Reflex mechanisms with inappropriate vasodilatation and/or bradycardia
Differential diagnosis - TIAs, epileptic seizures, hypoglycaemia
Highly age dependent
5 main categories of syncope
Neurally mediated
e.g. vasovagal, carotid sinus, situational
Orthostatic hypotension
e.g. drug induced, ANS failure
Cardiac arrhythmia
Structural cardio-pulmonary
e.g. HOCM
Non syncopal
e.g. metabolic
What tests can assess syncope?
ECG
Echo
Ambulatory ECG, loop recorders
Tilt table test
EP Study
What are the three stages of Neurocardiogenic Syncope?
BP and HR increase due to sympathetic tone
Abrupt hypotension and bradycardia with symptoms resulting in syncope
(Rapid) recovery
Causes of neurocardiogenic syncope
Provoked : -
Prolonged standing
Vigorous exercise in warm environment
Fear
Emotional distress
Severe pain
Blood loss
Patient symptoms and signs (neurocardiogrnic syncope)
Weakness
Diaphoresis
Light headedness
Headache
Nausea
signs are
Facial pallor
Yawning
Pupils dilate
Nervousness
POTS
What is it?
What happens?
Symptoms?
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia
Syndrome (POTS)
It is orthostatic intolerance, primarily affects young women
Insufficient vasoconstriction with increased sympathetic cardiac activation
Marked increase in heart rate with no change in blood pressure
Symptoms:
light-headedness, confusion, syncope - occur on standing