BCH Week 1 - Lec 1 - Biomolecules
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
what are the two main types of bonding patterns
covalent bonds and non-covalent bonds
covalent bonds
atoms share electrons in covalent bonding
biomolecules are held together through these bonds
non-covalent bonds
bonds not involving electron sharing
i.e. hydrogen bonds (Van der Waals), ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions
polarity of covalent bonds - what determines this
covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar
polar - unequal e- sharing which creates ± dipoles
non-polar - equal e- sharing
if the difference in electronegativity between the atoms is >0.5, the atom with the higher EN attracts more e-s
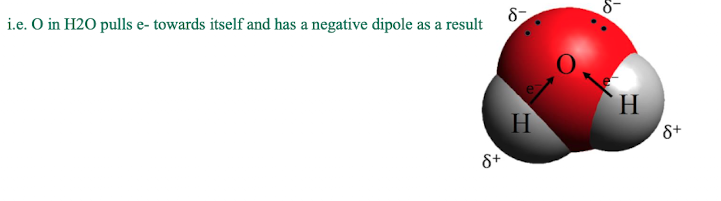
what are ionic bonds (aka electrostatic interactions)?
attractions between oppositely charged molecules
i.e. Na+ and Cl-
what are hydrogen bonds?
dipole-dipole interactions between a partially positive hydrogen atom (covalently bonded to electronegative N, O, or F) and another electronegative atom with a lone pair
what are hydrophobic interactions?
the exclusion of non-polar (like oil) substances from water (which is polar)
non-polar molecules will aggregate together
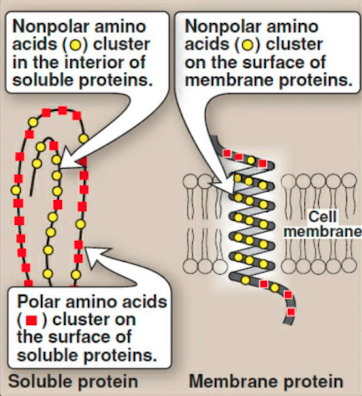
what is the cell membrane like?
the phospholipid bilayer makes up cell membranes
membranes have a hydrophobic interior due to the hydrophobic tails
extracellular and intracellular surfaces of the bilayer are hydrophilic
can hydrophilic, hydrophobic, and charged molecules pass through the bilayer structure easily?
no, therefore, cells need transporters to support the movement of molecules that struggle to pass through the lipid bilayer
what are functional groups?
functional groups are formed by atoms found in organic molecules, they have predictable non-covalent bonding patterns based on their polarities
what group is this?
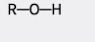
hydroxyl group
what group is this?
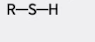
sulfhydryl group
what group is this?
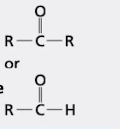
carbonyl group
ketone on top (COR)
aldehyde on bottom (COH)
what group is this?
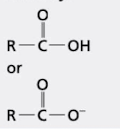
carboxyl group
what group is this?
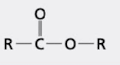
ester group
what group is this?
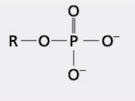
phosphoryl group
what group is this?
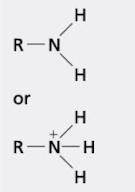
amino group
what group is this?
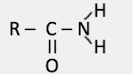
amido group aka amide
what group is this?
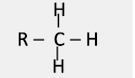
methyl group
what group is this?
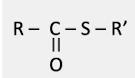
thioester group
what functional groups can participate in H bonding
hydroxyl
carboxyl (uncharged)
amino (uncharged)
amido (uncharged)
what functional groups participate in ionic bonds?
carboxyl (RCO²-)
phosphoryl (–PO4²-)
amino (RNH³+)
what functional groups participate in hydrophobic interactions?
methyl
Why do you think the addition or removal of a phosphoryl group can completely change the function of the molecule?
The addition or removal of a phosphoryl group dramatically changes a molecule’s charge and conformation due to the highly EN O atoms, altering its interactions and switching enzyme activity on or off.
why does the cleavage of phosphate from ATP release energy?
ATP hydrolysis releases energy because the products are more stable than ATP due to reduced electrostatic repulsion, increased resonance stabilization, and improved hydration.
what are monosaccharides, what atoms do they contain?
monosaccharides are the monomers of carbohydrates
they contain carbon atoms and water (H2O)
carbohydrate composition and general naming
carbs have a minimum of 3 Cs and each has a hydroxy group except one, which is either an aldehyde or a ketone
general naming of carbs is based on the number of Cs and whether it is an aldehyde or ketone
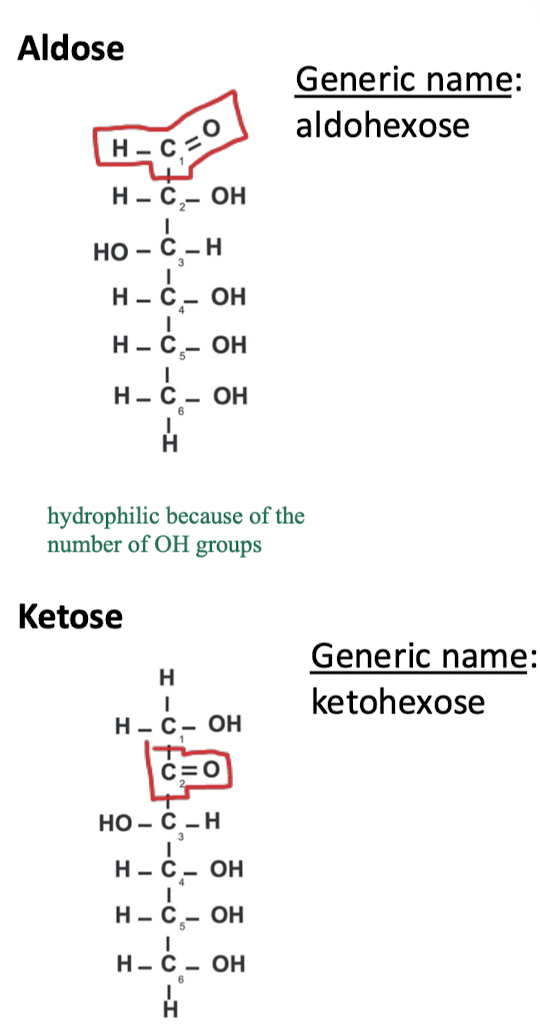
are monosaccharides linear or cyclic?
they can exist as linear that can be converted to cyclic
this is because linear carbs react in solution as certain C positions (i.e. aldehydes at C5) to form a ring structure
aldohexose → glucose
ketohexose → fructose
what type of carbs make up dietary carbs? what foods contain these carbs?
dietary carbs are polymers of hexose monosaccharides
specifically, glucose, fructose, galactose
Starches & grains → glucose
Fruits & sweeteners → fructose
Dairy → galactose
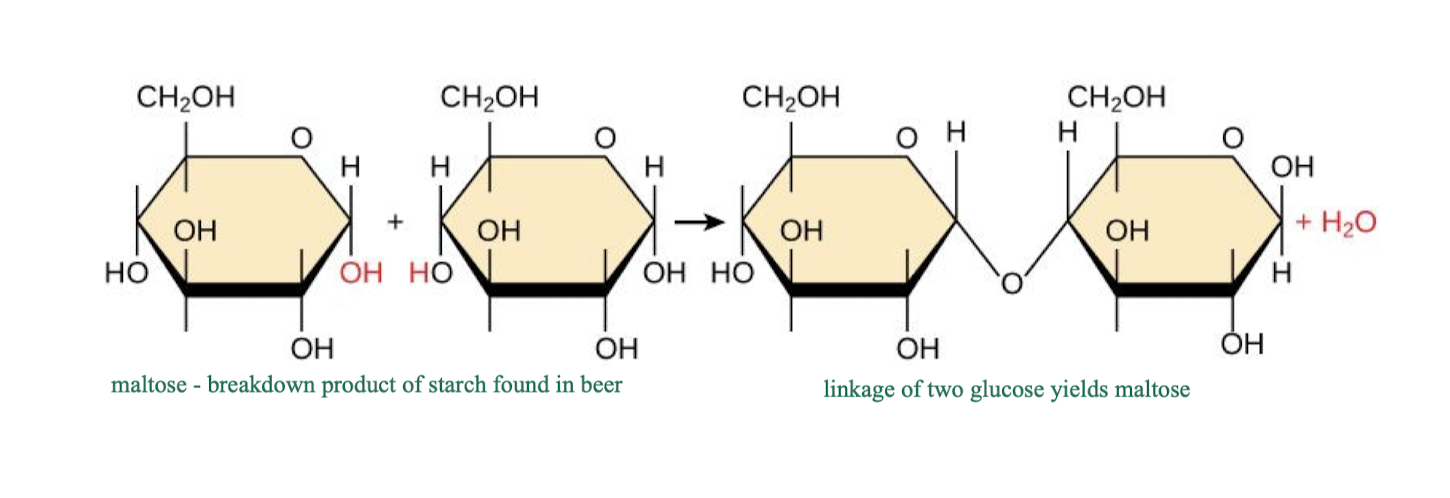
how do monosaccharides bond to one another?
via glycosidic bonds to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
very strong binding
glucose + glucose = maltose
fatty acid key functions in the body
fatty acids are a main lipid category
they provide fuel for cells, have structural functions (phospholipids), are used in recognition (glycolipids), etc.
dietary sources of lipids
nuts, cheese, oil, fast food, etc.
how do you differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
saturated - the hydrocarbon chains in saturated fatty acids are linked by single bonds, giving them a higher melting point because they can pack better together
unsaturated - cis double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain create a kink in the molecule, making the section very hydrophobic, and the double bonds decrease the melting point of the fatty acids
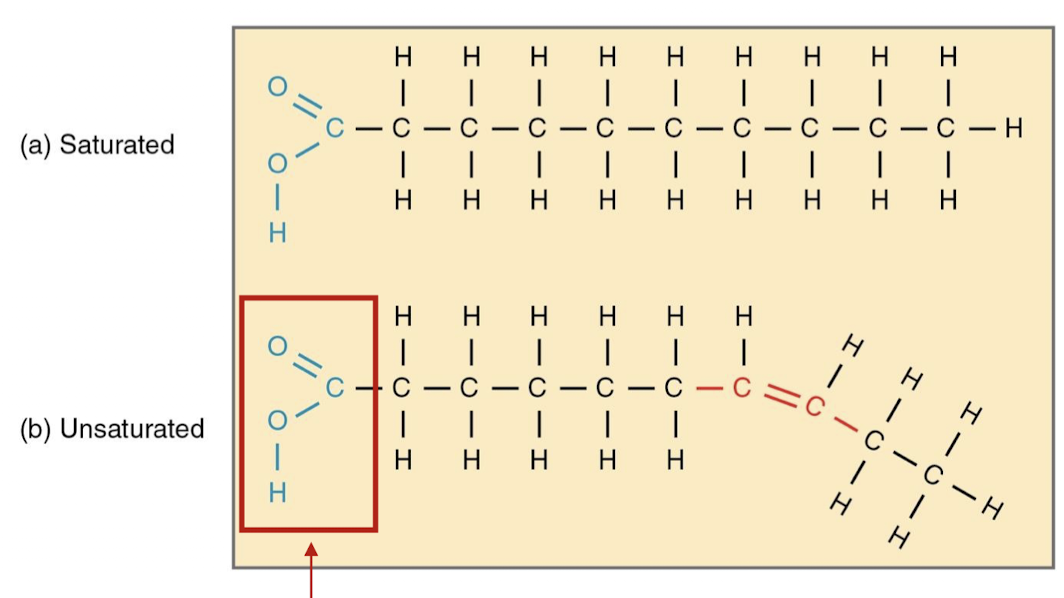
what type of functional groups do fatty acids have at the end?
carboxyl
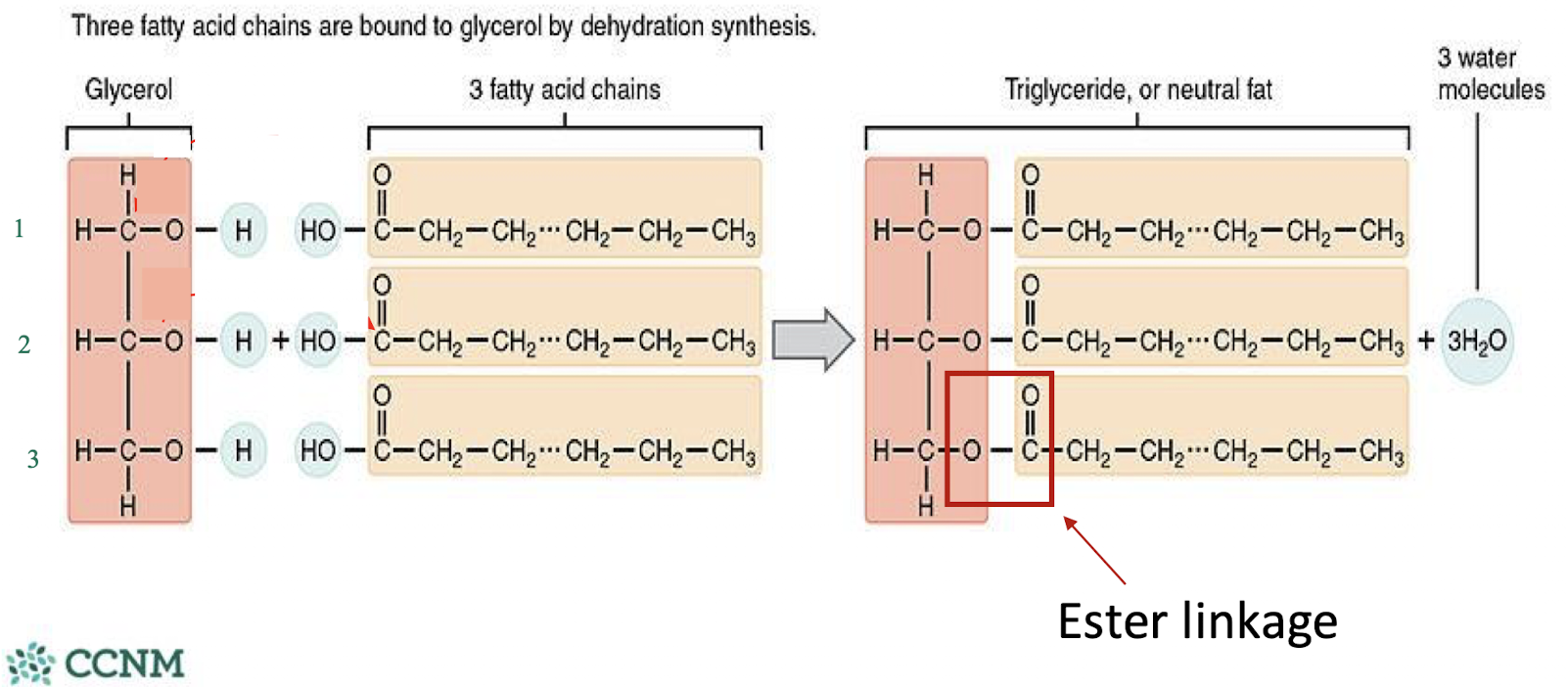
what do fatty acids link themselves to and how? what is the attachment pattern usually like?
fatty acids attach to a glycerol backbone via ester linkages (very strong)
they create mono, di, or tri-glycerides - this is how we store fatty acids in our body
the first fatty acid attached is usually saturated, second is usually unsaturated, and third can be either or
fatty acids are stored in adipocytes and when oxidized, release a considerable amount of ATP
what are amino acids and what are some functions?
amino acids are the building blocks of proteins in the body
some functions
enzymes - each have their respective locations, descriptive names
transporters - deliver materials across PM of cells
i.e. albumin - found in plasma binds to fatty acids and delivers to cells to use as a fuel source
lipoproteins - transport lipid material (LDL, HDL, VODL)
many other functions in cells and body
what are some dietary sources of protein?
nuts
lentils
beans
cheese
tofu
meat
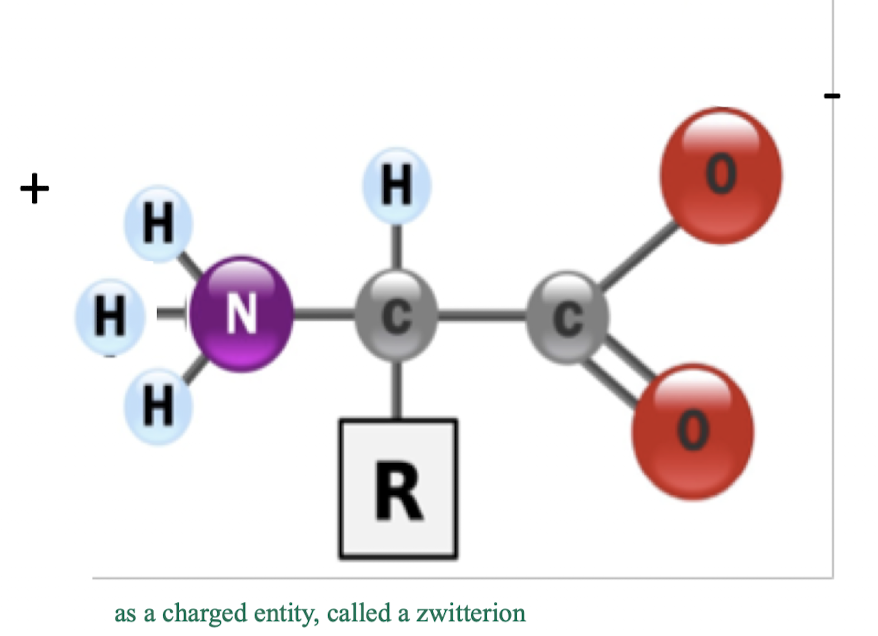
general structure of amino acids
a central carbon that holds: an amino group + R group + carboxyl group
the R group varies based on the specific amino acid
what amino acids are polar? and what non-covalent bonds do neutral polar amino acid R groups participate in?
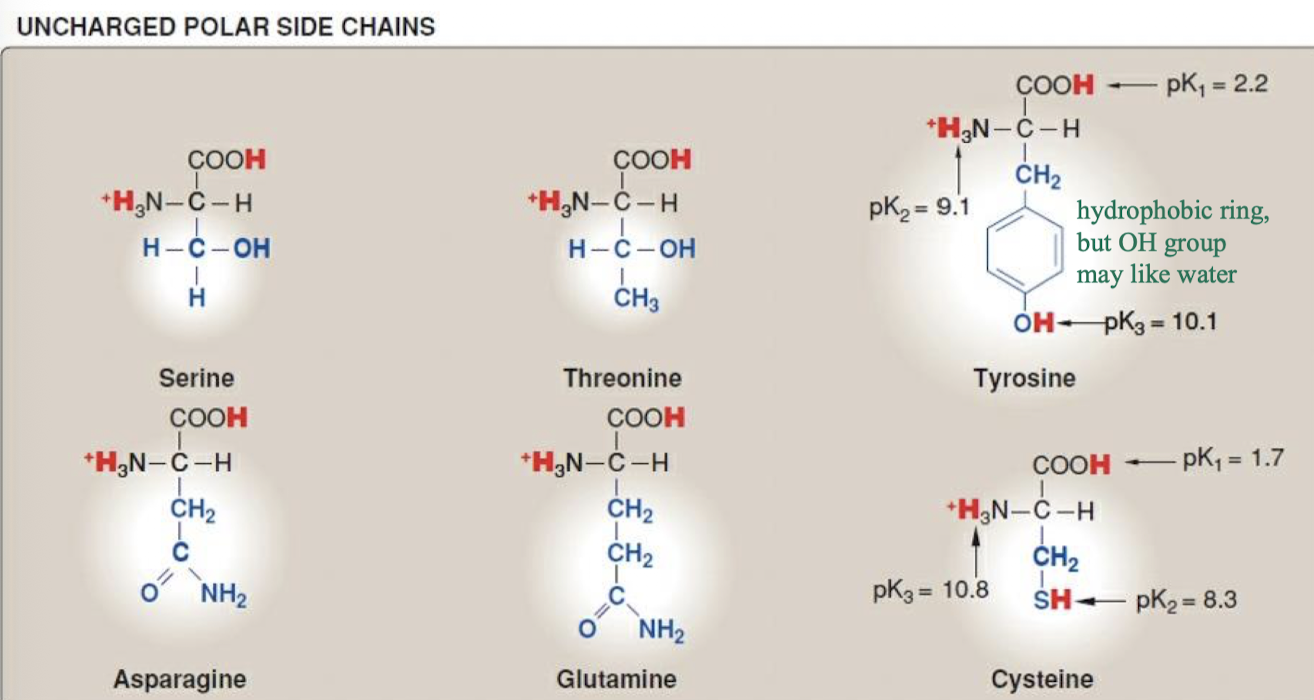
serine, threonine, tyrosine (np ring but OH group likes water), asparagine, glutamine, cysteine
they participate in hydrogen bonds
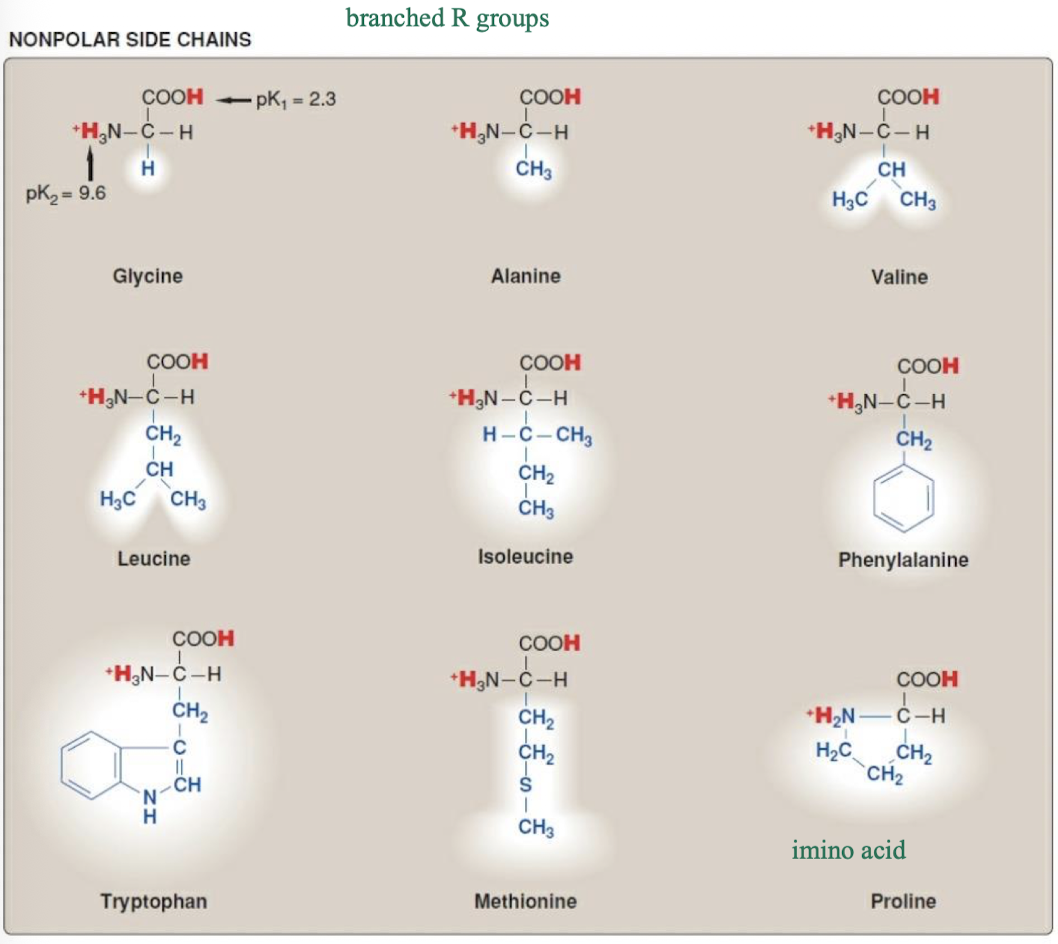
what amino acids are non-polar? and what non-covalent bonds do neutral non-polar amino acids participate in?
they participate in hydrophobic interactions
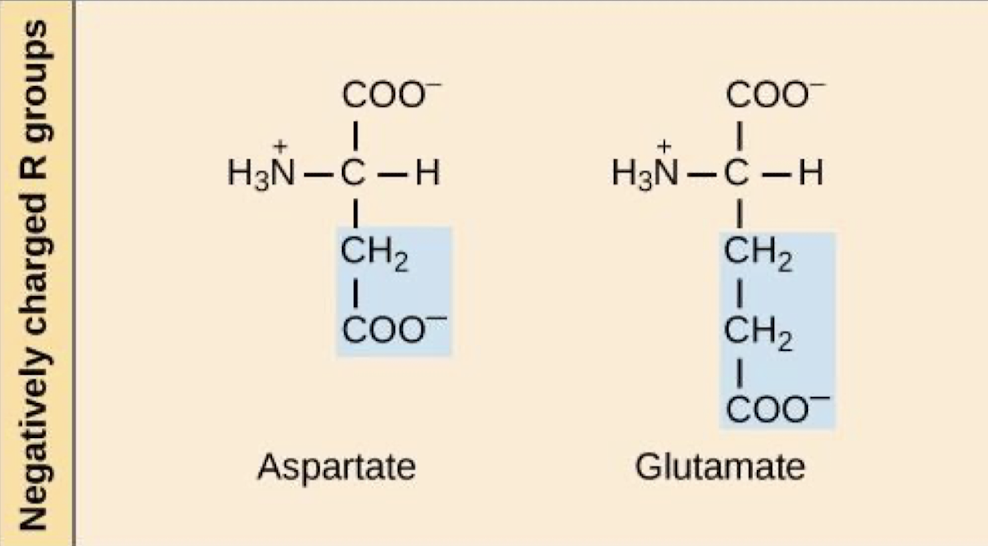
which amino acids are negatively charged? what are their characteristics and what type of bonding do they take part in?
at a pH of 7, the acidic R groups of these amino acids are negatively charged
and they take part in ionic bonds (aka salt bridges)
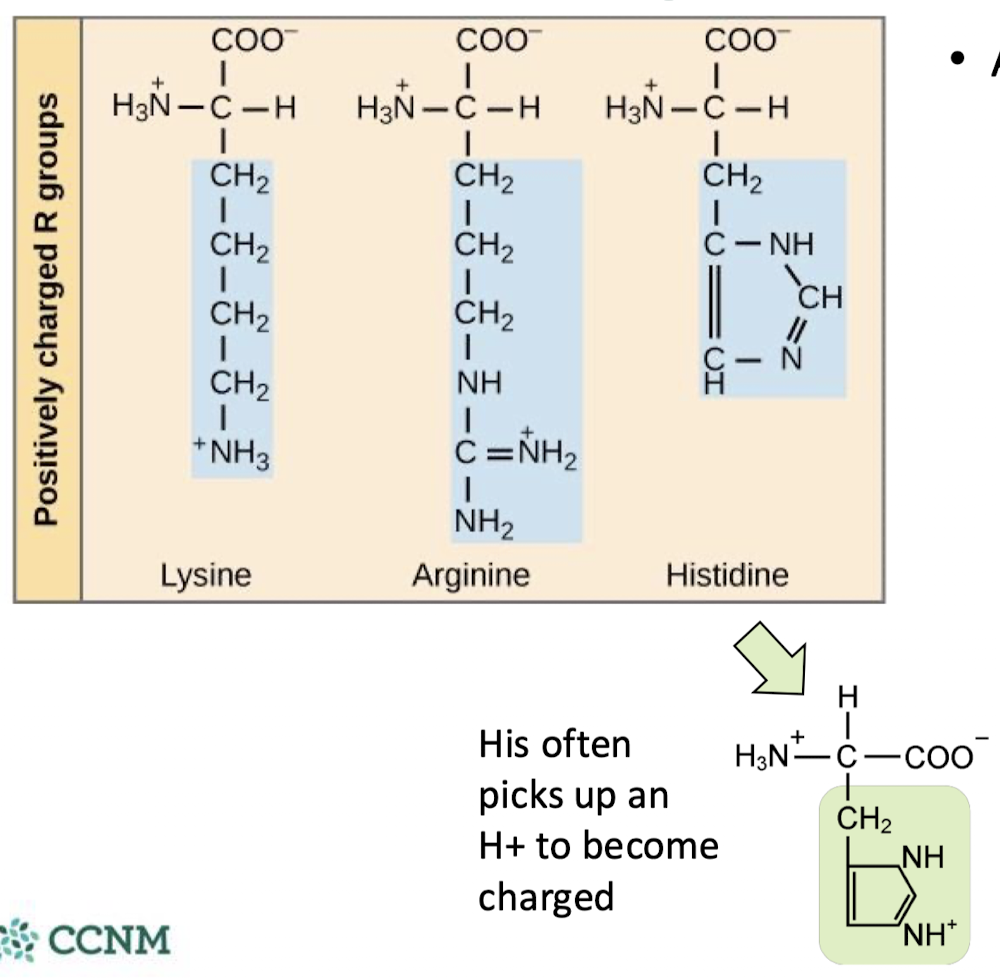
which amino acids are positively charged? what are their characteristics and what type of bonding do they take part in?
at a pH of 7, the basic R groups will be positively charged
they take part in ionic bonding (aka salt bridges)
what amino acids should we know for quiz 1 and test 1?
Cysteine
Glutamate
Aspartate
Asparagine
Glutamine
Proline
Methionine
Serine
Valine
Tryptophan
Glycine
Histidine
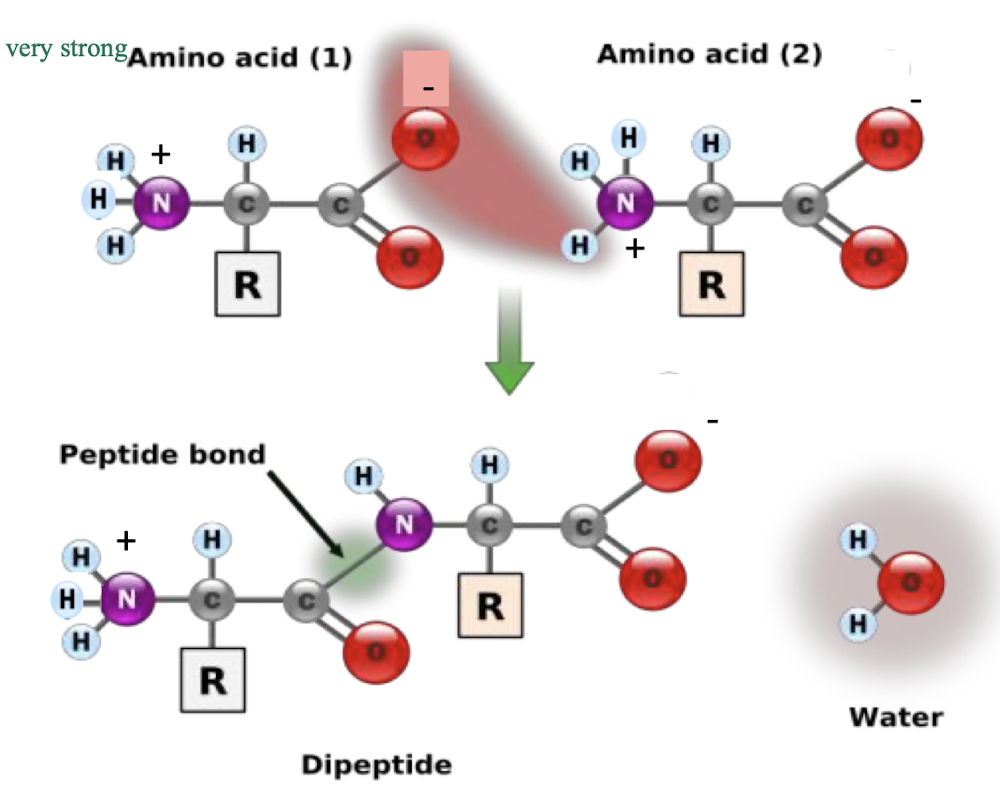
what bonds do amino acids form with one another?
peptide bonds to be incorporated into proteins - very strong
H bonding between the negatively charged O on the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the H from the positively charged amino group on the other amino acid
the R groups of amino acids determine the overall shape of each protein
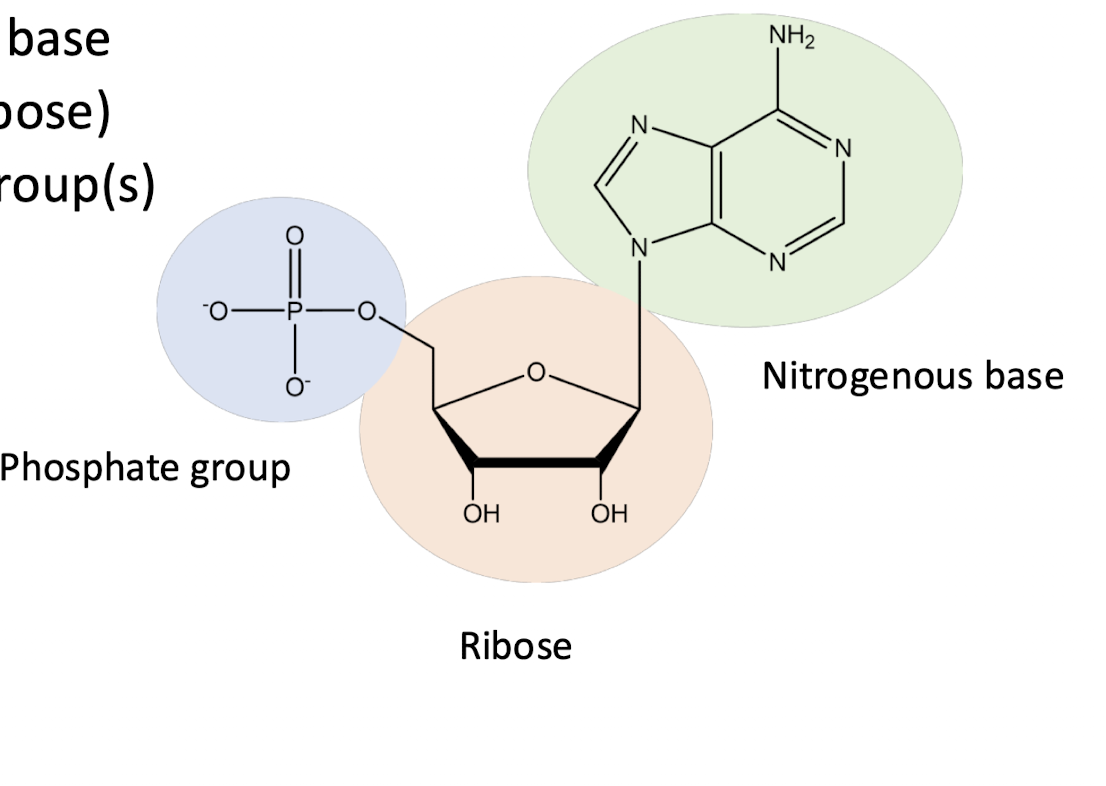
general nucleotide structure
nitrogenous base
5-C sugar (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA where one OH is not present)
phosphate group
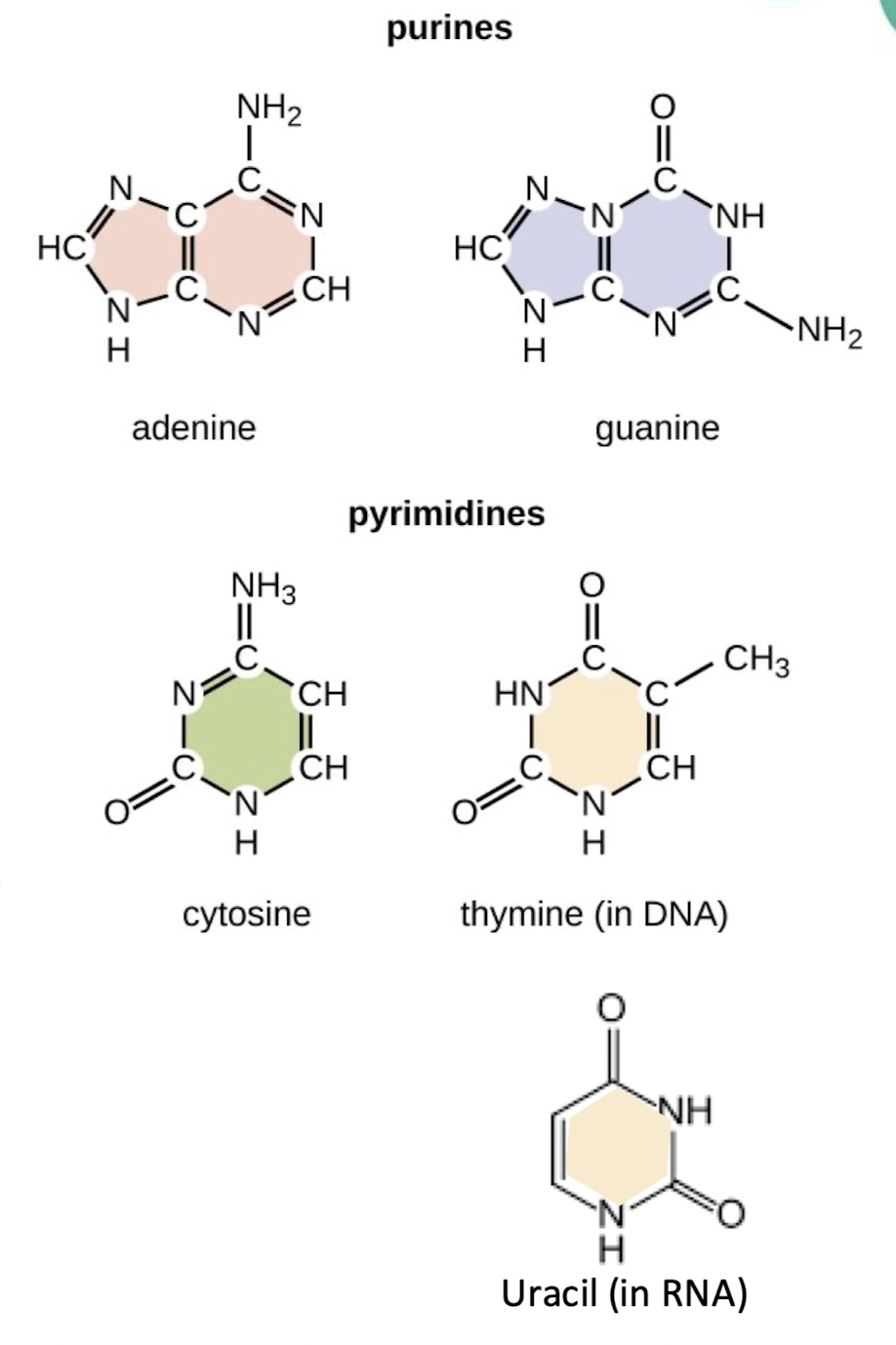
what are the two nitrogenous base types?
purines - double ring structure
include adenine and guanine
pyrimidines - single ring structure
thymine, uracil, cytosine
what are some examples of nucleotides in the body?
nucleic acid - DNA/RNA
various coenzymes - NAD+, NADP+
energy molecules - ATP, GTP
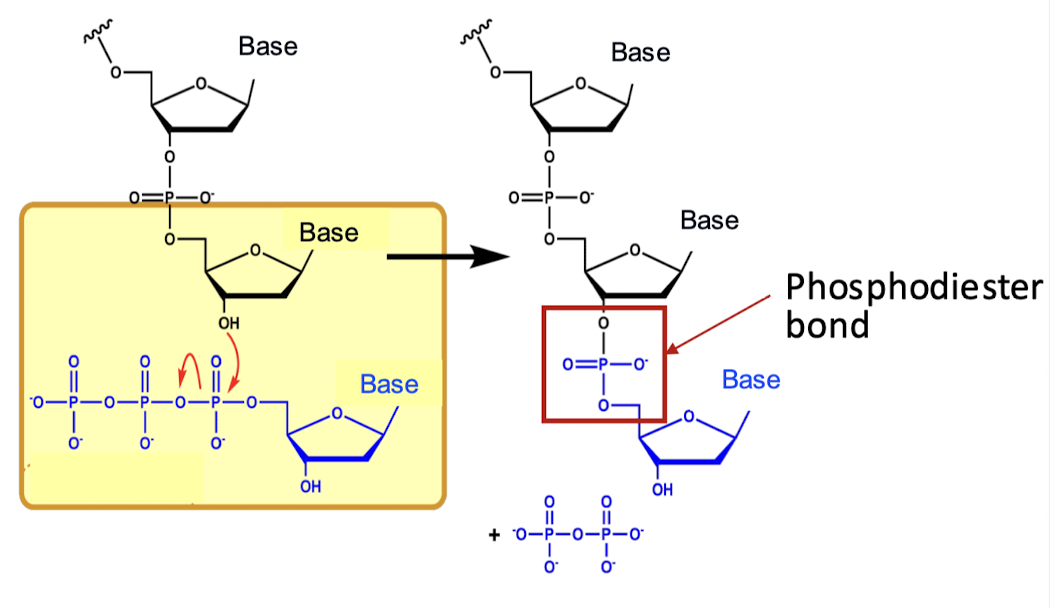
what bonding helps to synthesize nucleic acids from nucleotides?
phosphodiester bonds