Echo quiz 1
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
What is automaticity?
Property of cardiac cells that generates spontaneous action potentials to create electrical impulses
How is the electrical impulse created in the body?
By moving electrolytes across cell walls via a sodium-potassium pump
What is Phase 0 of the action potential curve (APC)?
Depolarization
Open sodium channels produce sodium influx
Inside of cell = POSITIVE
Outside of cell = NEGATIVE
What is Phase 1 of the action potential curve (APC)?
Closed sodium channels reduce sodium influx
Open potassium channels produce potassium influx
Inside of cell = LESS POSITIVE
Outside of cell = NEGATIVE
What is Phase 2 of the action potential curve (APC)?
Sodium influx is completely stopped
Calcium influx begins via slow channels
What is Phase 3 of the action potential curve (APC)?
Repolarization or recovery - cell returning to ready state
Open potassium channels cause potassium to leave cell
Inside of cell = NEGATIVE
Outside of cell = POSITIVE
What is Phase 4 of the action potential curve (APC)?
Refractory
Open channels cause sodium to leave cell
Open channels cause potassium influx
What determines the degree of contraction during an action potential?
Amount of calcium
What is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
Molecule that supplies energy for action potential to take place
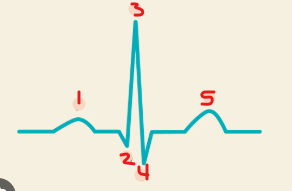
Identify this image.
P wave
Q wave
R wave
S wave
T wave
How are the EKG and action potential waveforms related?
P wave: Atrial depolarization
Hidden QRS wave: Atrial repolarization
QRS: Ventricular depolarization
T wave: Ventricular repolarization
Blood flows from areas of ___ pressure to areas of ___ pressure.
High; Low
Where is HIGH pressure located in the heart?
Left side
Where is LOW pressure located in the heart?
Right side
(T/F) Each ventricle expels the SAME VOLUME of blood per beat.
True
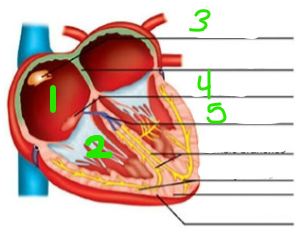
Identify this image.
RA
RV
SA node
AV node
Bundle of HIS
What is the average resting heart rate?
75 bpm
How long does each cardiac cycle take?
0.8 seconds
What is the role of the right and left atrium during systole?
Atrial contraction forces blood into ventricles
What is the role of the right and left atrium during diastole?
Atrial relaxation allows blood to fill ventricles
What is the role of the AV valves during systole?
Valves close to prevent backflow of blood into atria
What is the role of the AV valves during diastole?
Valves open to allow blood to flow from atria to ventricles
What is the role of the right and left ventricle during systole?
Ventricular contraction pushes AV valves closed
What is the role of the right and left ventricle during diastole?
Ventricle relaxation allows blood to fill ventricles
What is the role of the semilunar valves during systole?
Valves open so blood can enter great vessels
What is the role of the semilunar valves during diastole?
Valves close to prevent backflow of blood into ventricles
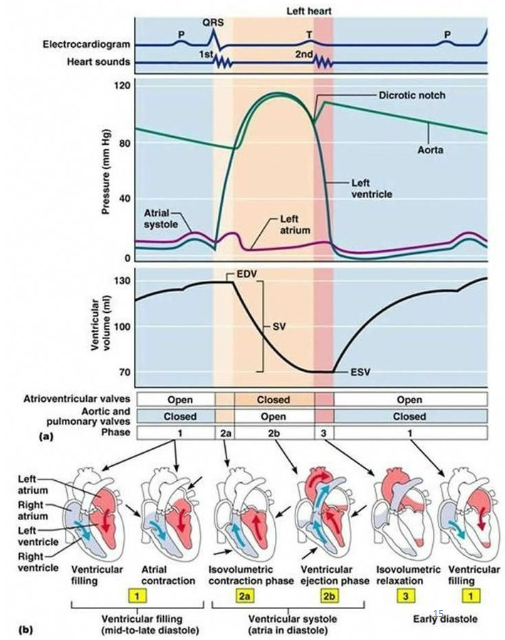
How are the EKG and phases of cardiac cycle waveforms related?
P wave: Atrial systole and mid-to-late ventricular diastole
QRS wave: Atrial diastole and ventricular systole
T wave: Early ventricular diastole
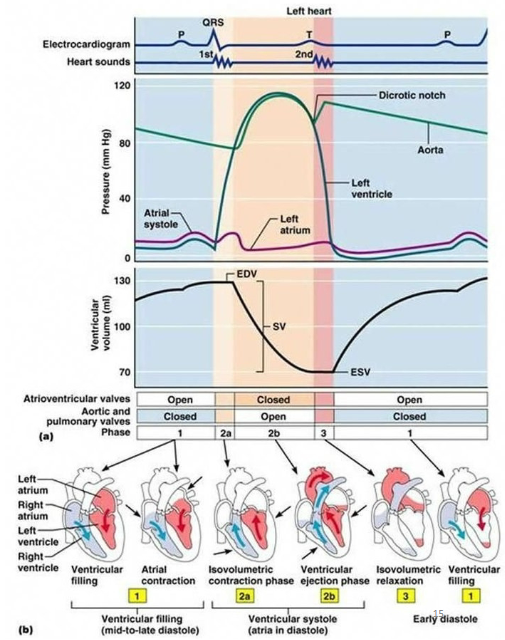
How are the EKG and pressure curve waveforms related?
P wave: Ventricular filling or when ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure (brief moment all valves closed)
QRS: Isovolumetric contraction or when volume is constant and ventricular pressure increases (brief moment all valves closed)
T wave #1: Ventricular ejection or when ventricular pressure surpasses great vessel pressure and blood is ejected from heart
T wave #2: Isovolumetric relaxation or when volume is constant and ventricular pressure decreases (brief moment all valves closed)
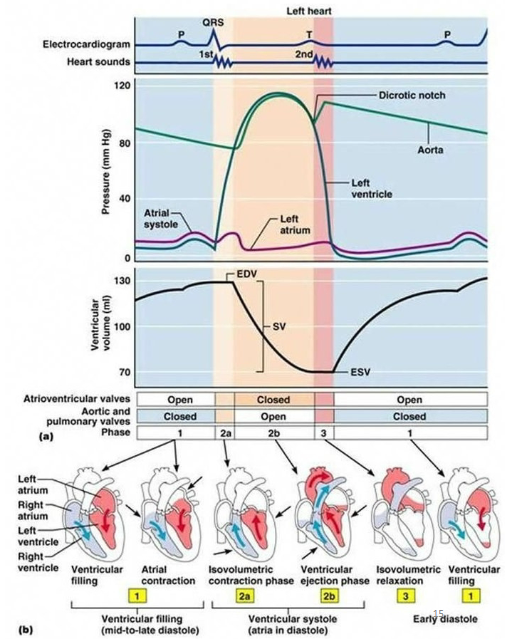
What are the phases of ventricular filling?
Rapid ventricular filling
Diastasis or when flow slows due to equal AV pressures
Slow filling (atrial kick/contraction) or when SA node sends impulse causing atrial contraction
What is end diastolic volume (EDV)?
When small traces of blood (120 mL) are left in each ventricle after ventricular diastole
What is end systolic volume (ESV)?
When small traces of blood (50 mL) are left in each ventricle after systole
What is stroke volume (SV)?
Amount of blood ejected per beat
What is the average stroke volume (SV)?
70 mL
What is the formula for stroke volume (SV)?
SV = EDV - ESV
What is preload?
Stretch of heart before it contracts due to blood filling ventricles
What is the Frank-Starling law?
Describes how preload is related to force of contraction
Example: High preload from high volume of blood filling ventricles during diastole = Strong contraction during systole
What is contractility?
Forcefulness of contraction
What is afterload?
Amount of pressure that must be exceeded for ventricular contraction to occur that is dependent on systemic and pulmonic vascular resistance
What is cardiac output (CO)?
Amount of blood pumped out of heart in one minute that is determined by stroke volume and heart rate
What is the normal value for cardiac output (CO)?
4 - 8 L/min
What is the equation for cardiac output (CO)?
CO = SV x HR
(T/F) Echo is the only way to determine cardiac pressure.
False; Only way to determine cardiac pressures is by heart catheterization
What is the normal range of right heart pressures?
Right atrial pressure (RAP): 0-6 mmHg
Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP): 15-25 mmHg
Right ventricular diastolic pressure (RVDP): 8-15 mmHg
Pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP): 15-25 mmHg
Pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (PADP): 8-15 mmHg
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP): 6-12 mmHg
What is the normal range of left heart pressures?
Right atrial pressure (LAP): 8-12 mmHg
Left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP): 90-140 mmHg
Left ventricular diastolic pressure (LVDP): 10-16 mmHg
Aorta systolic pressure (ASP): 90-140 mmHg
Aorta diastolic pressure (ADP): 60-90 mmHg
What is blood pressure?
Amount of blood exerted by blood on walls of vessel that is generated by
ventricular contractions
What is normal blood pressure?
120/80
What blood pressure values constitute for an emergency?
Hypertension: Over 180/120
Hypotension: Under 90/60 with symptoms
What is auscultation?
Listening to sounds from heart, lungs, or other organs with a stethoscope
What are the parts of a stethoscope that can be placed on the patient?
Diaphragm: Transmits higher frequency sounds
Bell: Transmits lower frequency sounds
What are the normal heart sounds and what do they indicate?
S1 “lub”: Closure of AV valves
S2 “dub”: Closure of semilunar valves
What is a heart murmur?
Blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through heart valves or near heart
How many chambers does the heart have?
4
(T/F) The thickness of muscular walls varies depending on the chamber.
True
What is the normal heart rate?
60-100 contractions per minute
Where is the heart located?
Posterior to sternum within middle mediastinum
What angle does the heart lie at?
45 degrees towards left side between third and fifth intercostal space
What is the apex of the heart?
Cone or bottom of heart that consists of tip of left ventricle and rests on diaphragm below seventh rib
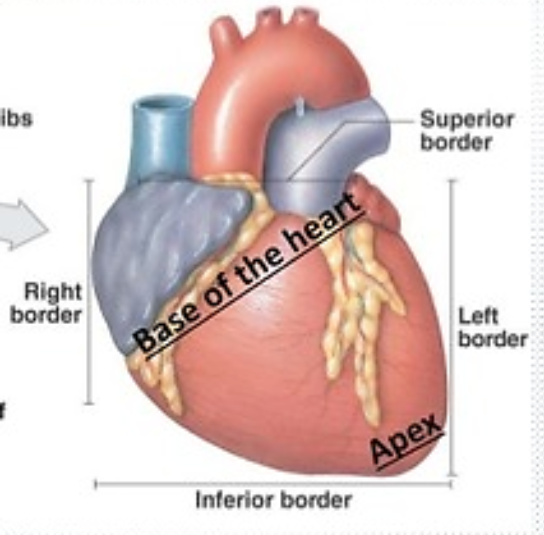
What is the base of the heart?
Top of heart that consists of atria and great vessels
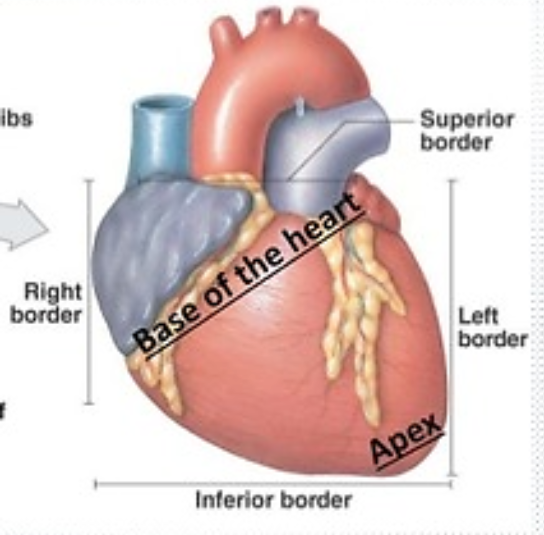
What are the great vessels?
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
What makes up the superior border of the heart?
Right atrium
Left atrium
What makes up the inferior or diaphragmatic border of the heart?
Most of right ventricle
Small portion of left ventricle
What makes up the right border of the heart?
Right atrium
What makes up the left border of the heart?
Left ventricle
Small portion of left atrium
What makes up the anterior border of the heart?
Right ventricle
Small portion of right atrium
Small portion of left ventricle
What makes up the posterior (spine) border of the heart?
Left atrium
Left ventricle
What is the pericardium?
Thin sac that houses heart and roots of great vessels
What are the two layers of the pericardium?
Parietal
Visceral
What is located within the pericardial cavity?
10-20 mL of serous fluid used to lubricate for smooth contractions
What is the IV sulcus?
Part of cardiac skeleton that separates right ventricle and left ventricle externally
What is the AV sulcus?
Part of cardiac skeleton that separates left atrium and left ventricle externally
What is the coronary sulcus?
Part of cardiac skeleton that separates right atrium from right ventricle externally
What is the crux of the heart?
Posterior portion of heart where all 4 chambers meet
What is the function of the crux of the heart?
Determines dominance of heart by which coronary artery feeds which portion
How is dominance determined in the heart?
Right dominance is fed by right coronary artery
Left dominance is fed by left coronary artery
What is the epicardium or visceral layer of the heart?
Outermost layer composed of epithelial cells
What is the myocardial layer of the heart?
Middle layer composed of muscle fibers and cells that are responsible for contraction
What is the endocardial layer of the heart?
Innermost layer that is composed of simple squamous cells, lines inside of myocardium, and covers valves and tendons
What is the posterior portion of the right atrium?
Smooth walled portion where IVC and SVC enter heart and is derived from embryonic sinus venosus
What is the anterior portion of the right atrium?
Thin walled and trabeculated portion which is original embryonic right atrium
What is the crista terminalis?
Muscular ridge that internally separates two portions of right atrium
What is the sulcus terminalis?
Portion of heart that externally separates anterior and posterior portions of right atrium
What is the right atrial appendage or auricle?
Hollow, triangular shaped area located along free wall of right atrium that is lined by pectinate muscle
What is a Eustachian valve?
Normal variant in right atrium that presents as a functional valve in fetus that covers IVC
What is the Chiari Network?
Normal variant in right atrium that presents as a fine mobile fiber near IVC and often extends to crista terminalis
What is a prominent crista terminalis or terminal ridge?
Normal variant in right atrium that presents as a mass when prominent
What is the main function of the right ventricle?
Maintain pulmonary circulation by sending deoxygenated blood to lungs
What is the right ventricular inflow tract (RVIT)?
Part of right ventricle composed of tricuspid valve and its apparatus that contains trabeculated walls
What is the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) or infundibulum?
Part of right ventricle located below pulmonic valve that contains smooth walls
What are the inflow and outflow tracts of the right ventricle separated by?
Parietal band
Septal band
Moderator band
What is the moderator band?
Tissue that extends from anterior free wall of right ventricle to IVS and provides a quick path for conduction system to reach ventricular wall
Where is the moderator band best visualized?
A4C
What is the main function of the left atrium?
Receiving oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins
What is the anterior portion of the left atrium?
Thick left atrial appendage used to store blood
What is the posterior portion of the left atrium?
Smooth walled portion where pulmonary veins enter
What is the left atrial appendage?
Small finger-like outpouching of muscular wall of left atrium that moderates intravascular volume
(T/F) The left atrial appendage is typically seen transthoracically.
False; Left atrial appendage is most commonly seen through TEE
Where is the left atrial appendage visualized best?
PSAX basal
A4C
Why is it important to check for a clot in the left atrial appendage?
Left atrial appendage played role in TIA and stroke in those with atrial fibrillation
What is the main function of the left ventricle?
Pump oxygenated blood through aorta to rest of body
(T/F) The left ventricle is the main pumping chamber of the heart.
True