Physiology Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
1
New cards
Olfactory nerve (1)
sense of SMELL
2
New cards
Optic nerve (2)
transmitting VISUAL information
3
New cards
Oculomotor nerve (3)
moves the eyeball
4
New cards
Trochlear nerve (4)
innervates the eyelid muscle
5
New cards
Trigeminal nerve (5)
main sensory nerve of the face
6
New cards
Abducens nerve (6)
controls the lateral rectus muscle
7
New cards
Facial nerve (7)
innervates the muscles of facial expression
8
New cards
Vestibulocochlear nerve (8)
hearing and balance
9
New cards
Glossopharyngeal nerve (9)
swallowing, speech, and saliva
10
New cards
Vagus nerve (10)
innervates thoracic and abdominal organs
11
New cards
Accessory nerve (11)
innervates the shoulder muscles
12
New cards
Hypoglossal nerve (12)
supplies the tongue and is important for chewing and speech
13
New cards
Soma/cell body
The part of the neuron that interprets the signal
14
New cards
Nucleus
Stores the genetic material and is the “brain” of the neuron
15
New cards
Axon Hillock
Connects the axon to the cell body
16
New cards
Axon
Sends signals through neurotransmitters
17
New cards
Myelin Sheath
An insulating layer around nerves that is made up of lipids and fats, these conduct impulses faster than axons without it
18
New cards
Dendrites
The part of the neuron that receives a signal
19
New cards
Terminals
They are located at the end of the axon
20
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
The gaps in between the myelin sheaths
21
New cards
Role of Na+
The ion that rushes into the cell, making it more positive (depolarization)
22
New cards
Role of K+
The ion that flows out during repolarization in attempt to rebalance the charges
23
New cards
Role of Na/K pump
Maintains the resting potential
24
New cards
Role of ATP
The energy used to rebalance the ions (resting potential) and is the energy needed to start the Na/K pump
25
New cards
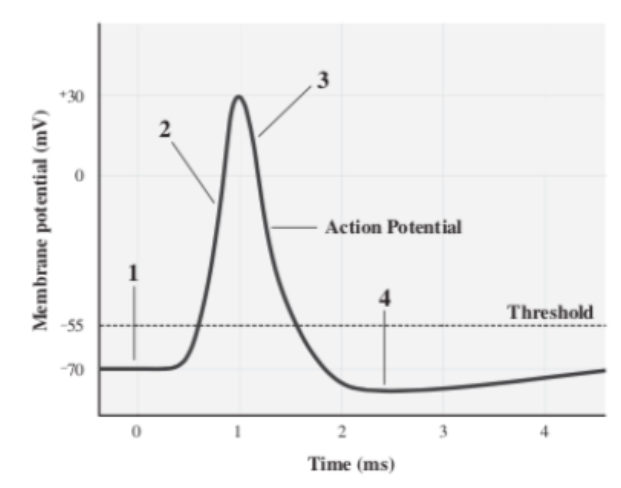
Polarization
No ions move through voltage-gated channels (1)
26
New cards
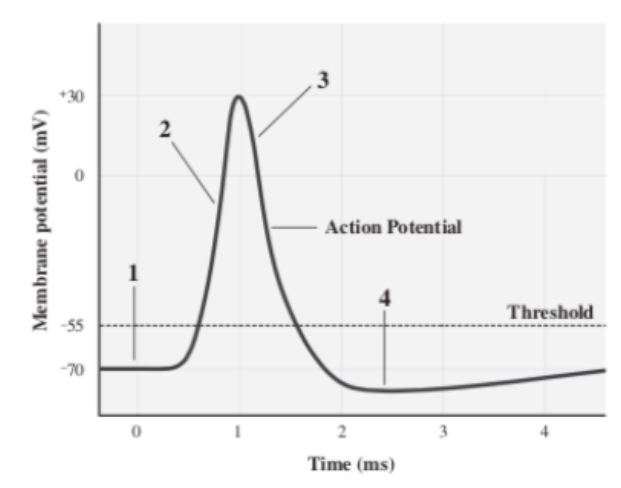
Depolarization
The stage at which the mV of a neuron is increasing because Na+ is flowing into the cell (2)
27
New cards
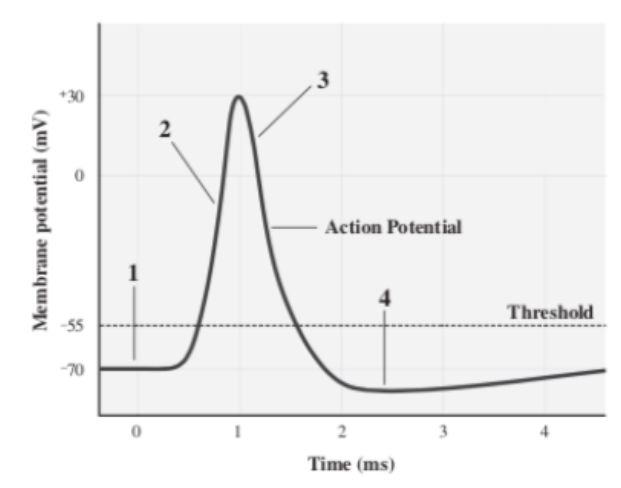
Repolarization
The stage at which the mV of a neuron is decreasing because K+ is flowing out of the cell (3)
28
New cards
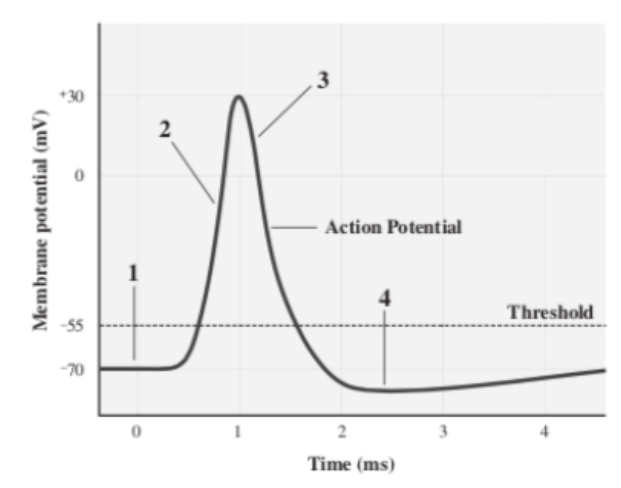
Hyperpolarization
Caused by K+ continuing to leave the cell, eventually bringing it back to its resting state(4)
29
New cards
Somatic
Voluntary branch of the nervous system
30
New cards
Autonomic
Involuntary branch of the nervous system
31
New cards
Sympathetic
Fight or flight response
32
New cards
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest response
33
New cards
Afferent
Nerves that travel from PNS to CNS
34
New cards
Efferent
Transmits from CNS out to the rest of the body
35
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord/Column
36
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Nerves
37
New cards
Oligodendrocytes produce
MULTIPLE myelin sheaths in the CNS
38
New cards
Schwann Cells produce
ONE myelin sheath in the PNS
39
New cards
Brain Stem
Responsible for basic life support
40
New cards
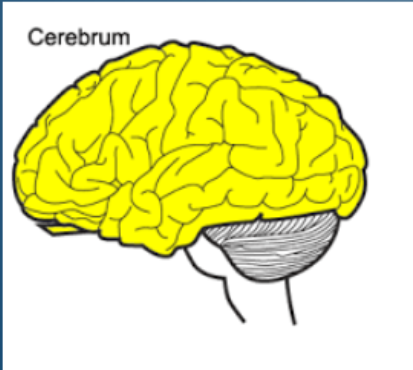
Cerebrum
Controls higher brain functions, including sensory perception, storing memory, reasoning, and determining intelligence
41
New cards
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for conscious, voluntary thought and attention, processing and making decisions, personality and language (primary motor cortex)
42
New cards
Parietal Lobe
The part of the brain that processes hearing and touch and relays it to the frontal lobe (primary sensory cortex)
43
New cards
Temporal Lobe
The part of the brain that stores memory and processes emotion
44
New cards
Occipital Lobe
The part of the brain that processes vision
45
New cards
Hippocampus
Holds our short-term memory (AKA brain’s librarian)
46
New cards
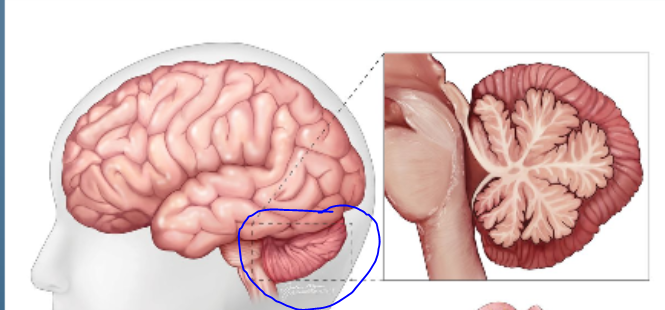
Cerebellum
The coordination center of the brain that is responsible for controlling movement and posture
47
New cards
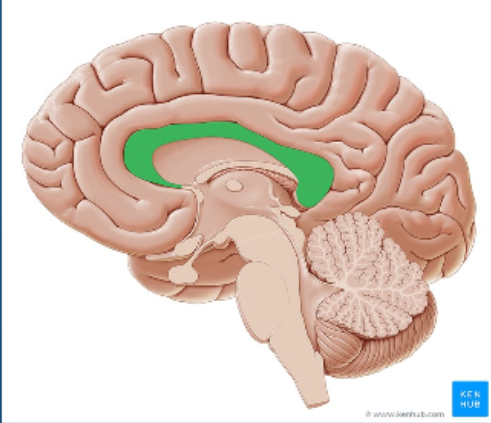
Corpus Callosum
The part of the brain that connects the two hemispheres
48
New cards
Thalamus
The brain’s “relay station” where most information from the outside world passes through
49
New cards
Hypothalamus
The part of the brain that controls the endocrine system
50
New cards
Epithalamus
Forms the pineal gland which secretes melatonin, and regulates the day/night cycle
51
New cards
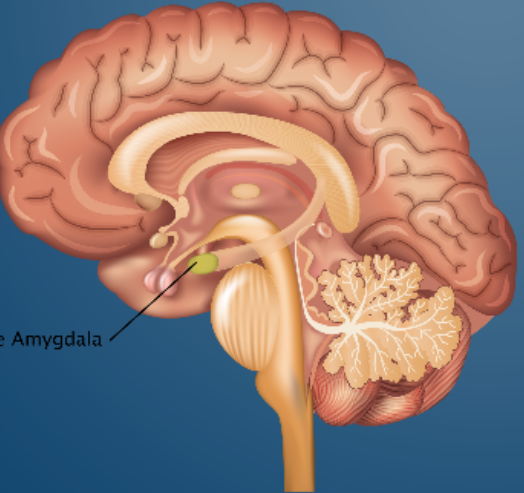
Amygdala
The part of the brain that processes stress and fear (primitive survival response center of the brain)
52
New cards
Ventricles
Cavities in the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid
53
New cards
Meninges
Outer membranes surrounding the brain
54
New cards
Dorsal Root Ganglion
How impulses from receptors in the PNS and relayed to the spinal cord (this also contains unipolar cell bodies of sensory neurons)
55
New cards
Reflex arc
The nerve pathway which makes a rapid, autonomic response to a stimulus possible
56
New cards
Receptor
Receives stimulation which sends an impulse (in the PNS)
57
New cards
Sensory Nerve
Afferent impulses travel up this to the spinal cord
58
New cards
Interneuron
They send efferent impulses down motor neurons to the effector muscles which causes an action to occur
59
New cards
Motor Nerve
Nerves that control muscle movement
60
New cards
Effector
The muscles/organs that respond to the information received by sensory reception
61
New cards
Dura mater
Thick outer layer that adheres to the inside of the skull
62
New cards
Arachnoid mater
Web-like middle layer spanning fissures of brain; arteries and veins run on top of it
63
New cards
Pia mater
The meninge that is microscopic
64
New cards
Resting membrane potential
\-70 mV
65
New cards
Threshold potential
\-55 mV