Newton's First Law of Motion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Natural Motion
Every object in the universe has a proper place determined bya combination of four elements:
Any object not in its proper place will strive to get there.
Examples:
Stones fall.
Puffs of smoke rise.
Straight up or straight down for all things on Earth
Beyond Earth, motion is circular. Example: The Sun and Moon continually circle Earth
Violent Motion
Produced by external pushes or pulls on objects
Example: Wind imposes motion on ships.
Applying forces to objects
Galileo’s concept of Inertia
Galileo demolished Aristotle's assertions in the 15 00s. Galileo's discovery:
Objects of different weight fall to the ground at the same rate in the absence of air resistance.
A moving object needs no force to keep it moving in the absence of friction.
Just before Newton, Galileo died in 1642
Newton was born in the same year
Galileo is the father of scientific thinking
Force
is a push or a pull
Inertia
is a property of matter to resist changes in motion.
depends on the amount of matter in an object (its mass)
Balls rolling on downward-sloping planes pick up speed.
Balls rolling on upward-sloping planes lose speed.
SO a ball on a horizontal plane maintains its speed indefinitely.
If the ball comes to rest, it is not due to its nature, But due to friction
Newton’s first law of motion
Every object continues in a state of rest or at uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a non zero net force
The key word in this law is continues:
An object continues to do whatever it happens to be doing unless a force is exerted upon it.
If it is at rest, it continues in a state of rest.
If an object is moving, it continues to move without turning or changing its speed.
vector quantity
a quantity whose description requires both Magnitude (how much) and direction(which way)
can be represented by arrows drawn to scale, (this quantity is) called vectors
length of arrow represents magnitude and arrowhead shows direction
Examples: force, velocity, acceleration
Net force
Net force is the combination of all forces that act on an object.
Example Two 5-N pulls in the same direction produce a 10-N pull (net force of 10 N). If the pair of 5-N pulls are in opposite directions, the net force is zero.
Applied force
The first object is pulled to the right by two forces of 5 newtons each. The net force is 10 newtons to the right.
The second object is pulled left with 5 newtons and pulled right with 5 newtons. The net force is 0 newtons.
vector quantity 2
has magnitude and direction.
is represented by an arrow.
Example: velocity, force, acceleration
Scalar Quantity
has magnitude but not direction.
Example: mass, volume, speed
resultant force
The sum of two or more vectors
For vectors in the same direction, add arithmetically.
For vectors in opposite directions, subtract arithmetically.
Two vectors that don't act in the same or opposite direction: use parallelogram rule.
Two vectors at right angles to each other use pythagorean theorem
The equilibrium rule
A string holding up a bag of flour
Two forces act on the bag of flour:
Tension force in string acts upward.
Force due to gravity acts downward.
Both are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
When added, they cancel to zero.
So, the bag of flour remains at rest.
The equilibrium rule: the vector sum of forces acting on a nonaccelerating object equals zero
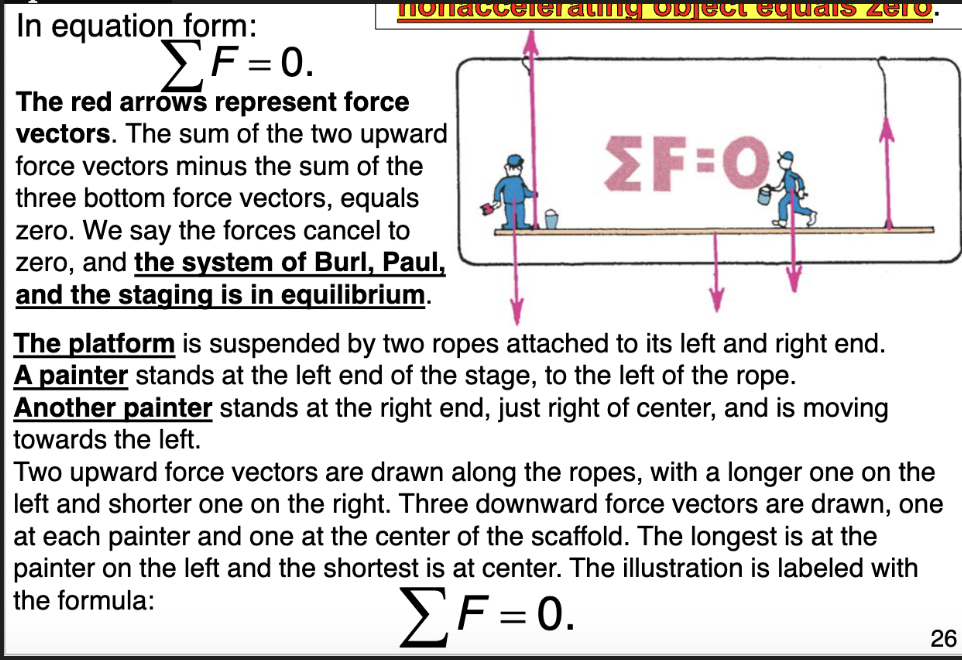
Support Force
Support force (normal force) is an upward force on an object that is opposite to the force of gravity.
Example: A book on a table compresses atoms in the table, and the compressed atoms produce the support force.
understanding support force
When you push down on a spring, the spring pushes back up on you.
Similarly, when a book pushes down on a table, the table pushes back up on the book.
equilibrium
a state of no change with no net force acting
static equilibrium
Example: hockey puck at rest on slippery ice
dynamic equilibrium
example: hocky puck sliding on slippery ice
equilibrium test
whether something undergoes change in motion
Example: A crate at rest is in static equilibrium (no change in motion)
Example: When pushed ,at a steady speed, it is in dynamic equilibrium (no change in motion)
The moving Earth
Copernicus proposed that Earth was moving cirulating the sun
this idea was refuted by people
Example: If Earth moved, how could a bird swoop (jump/dive) from a branch to catch a worm?
Solution: As it swoops, due to inertia, it continues to move sideways at the speed of Earth along with the tree, worm, etc.
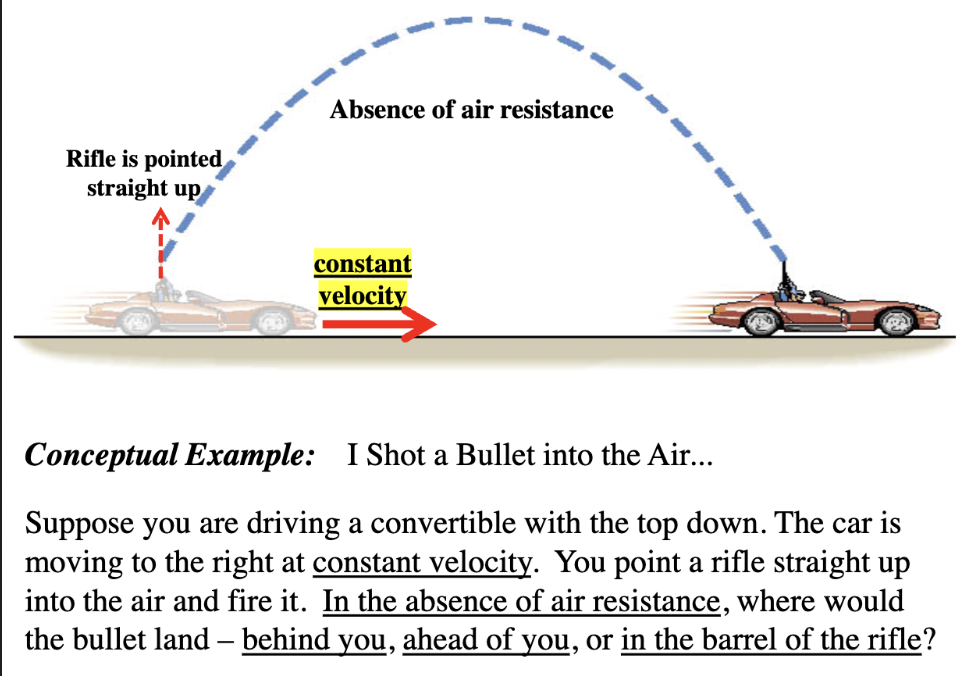
conceptual example