Topic 3.9 - Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is a carboxylic acid?
Functional group?
-COOH (C=O and C-OH)
How do you name
carboxylic acids?
-oic acid
Are carboxylic acids soluble
in water? Why? What
influences their solubility
Yes. Acid group can form hydrogen bonds with
water molecules
What are the intermolecular
forces in carboxylic acids?
Hydrogen bonds in solid state - very strong.
What are esters (what are
they formed from)?
Functional group, general
formula?
Formed from carboxylic acids and alcohols.
RCOOR’ (C=O, C-O-C)
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoic acid
with propan-1-ol
CH 3 COOH + CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH → CH 3 COOCH 2 CH 2 CH 3 + H 2 O
How do you name esters?
Start with the group that has replaced the
hydrogen, then acid part e.g. propyl (from
alcohol) ethanoate (from carboxylic acid).
What characteristic physical
properties do esters have?
Volatile, pleasant fruity smells e.g. apple, pear
drops
What are some uses of
esters?
Flavourings, perfumes (both for longer chains),
solvents (short chains), plasticisers.
What are some common
natural esters?
Fats and oils
In what way is the
carboxylic acid group
polarised? (Diagram)
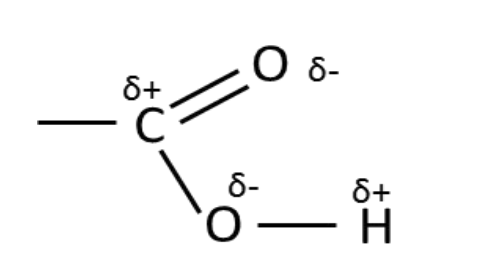
Write an equation for the
equilibrium formed by a
ethanoic acid in solution
CH 3
COOH (aq) ⇌ CH 3
COO - (aq) + H + (aq)
What happens to the
negative charge on the
ethanoate ion in terms of
electrons?
Electrons delocalise so the negative charge is
shared across the whole of the carboxylate group
How could you distinguish
carboxylic acids from other
-OH containing
compounds?
Add NaHCO 3 , acids will produce sodium
salt, water and carbon dioxide.
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoic acid
with NaOH
CH 3
COOH + NaOH → H 2
O + CH 3
COO -
Na +
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoic acid
with Na 2 CO 3 .
2CH 3 COOH + Na 2 CO 3 → 2CH 3 COO -
Na + + H 2 O + CO2
What catalyst is needed for
the formation of esters from
alcohols and carboxylic
acids?
Concentrated strong acid e.g. H 2 SO 4
What catalyst is needed for
the hydrolysis of esters?
Dilute strong acid e.g. H 2 SO 4
What is an alternative
method of hydrolysis?
Base hydrolysis
What are the advantages of
base hydrolysis?
Reaction goes to completion due to neutralisation
by base - more product in the mixture than acid
catalysed hydrolysis.
Which alcohol forms the
esters that make up animal
and vegetable oils?
Glycerol / propane-1,2,3-triol
What is the difference
between oil and fat?
Oils are liquid at room temperature, fats are
solids; fats are usually saturated, oils are not
What are the products of
hydrolysing fats and oils?
Propane-1,2,3-triol and sodium salts of the acids
that make up the ester (hydrolysed with NaOH)
What are the uses of these
products
(Propane-1,2,3-triol and
sodium salts)?
Soaps and cleaning products
What does the long
hydrocarbon chain of the
carboxylate ion do?
Mixes with grease
What does the COO - group
do?
Mixes with water
How does the carboxylate ion
with a long carbon chain
make a good cleaning agent?
Means that grease can be removed from
water
What is the systematic
name of glycerol?
propane-1,2,3-triol
What are some common
uses of glycerol?
Used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations e.g. to
stop creams drying out
Solvent in many medicines, present in toothpaste
Solvent in food industry e.g. food colourings
Plasticising various materials like sheets and gaskets,
cellophane and paper
How do you make biodiesel
(general equation and
conditions)?
NaOH catalyst, 60 o
C
Lipids (fats/oils - esters) + 3CH 3
OH → 3 methyl
esters + glycerol
What does
transesterification mean?
Converting one type of ester to another
What kind of crops is
biodiesel made from?
Rapeseed oil or soybean oil
How is the reaction mixture
of biodiesel purified and
separated?
Settling tank or centrifuge; remove remainder
with water. Add acid to neutralise excess alkali
catalyst. Solid soap is formed - easy to remove
What is a problem with
producing biodiesel?
Crops that could be used to make food are being
used to make fuel - are the resources being best
used?
What are carboxylic acid
derivatives?
Molecules that have the acyl group as part of
their structure, formed from carboxylic acids
Name two acid derivatives
and give their functional
groups
Acyl chlorides: RCOCl
Acid anhydrides: RCOOCR / (RCO) 2 O
Draw the mechanism for the
acylation of a nucleophile by
an acid derivative.
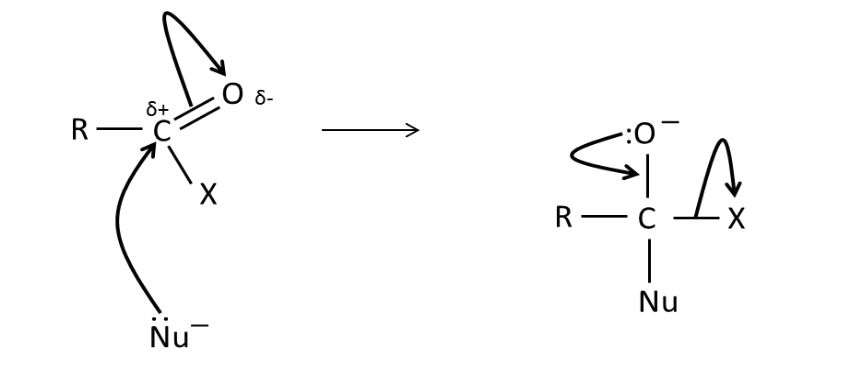
Which factors determine
how readily the acylation of
a nucleophile by an acid
derivative occurs? (3)
Magnitude of the delta + charge on the carbonyl carbon,
which depends on the electronegativity of the atom/group
being substituted.
How easily the atom/group being substituted is lost
How good the nucleophile is (how readily it will donate
electrons)
What effect do the Cl and O
atoms in acyl chlorides/acid
anhydrides have on the
partial charge of the
carbonyl carbon?
Increase the partial + charge by attracting
electrons; this means that they react more readily
with nucleophiles
Are acyl chlorides or acid
anhydrides more reactive?
Acyl chlorides
What is the name of the
mechanism by which acyl
chlorides and acid anhydrides
acylate nucleophiles?
Addition-elimination
If the nucleophile is
ammonia for the acylation of
acyl chlorides or acid
anhydrides, what are the
products of the reaction?
An amide
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and ammonia
CH 3 COCl + 2NH 3 → CH 3 CONH 2 +
NH 4 Cl
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and ammonia
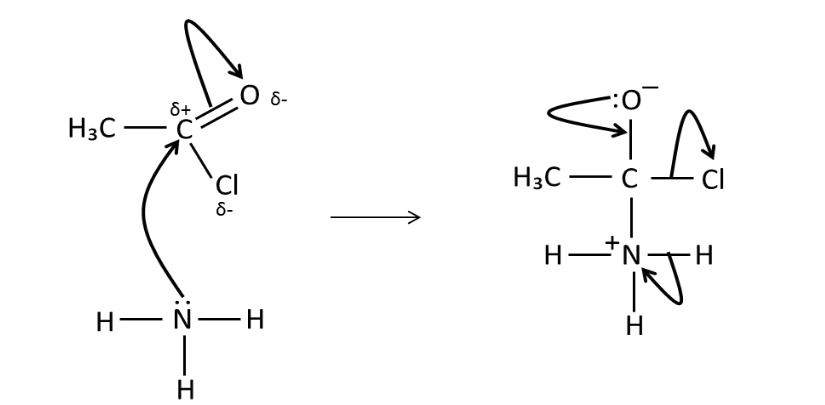
If the nucleophile is a
primary amine, what are the
products of the acylation of
acyl chlorides or acid
anhydrides?
N-substituted amide
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and methylamine
CH 3 COCl + CH 3 NH 2 → CH 3 CONHCH 3 + CH 3 NH 3 Cl
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and methylamine.
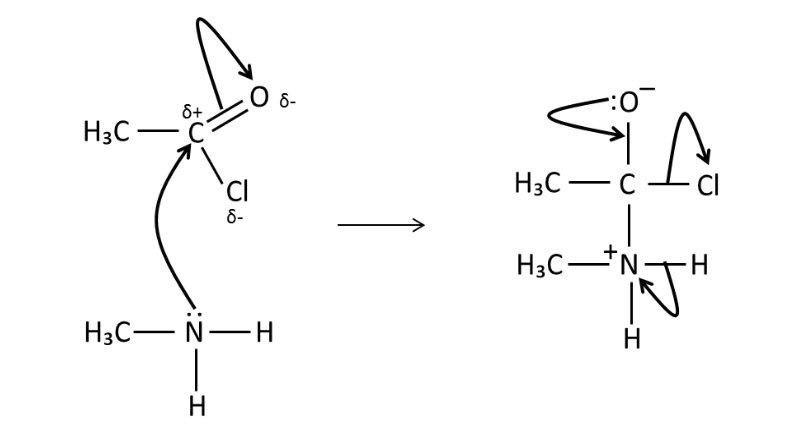
If the nucleophile is an
alcohol, what are the
products of the acylation of
acyl chlorides or acid
anhydrides?
An ester
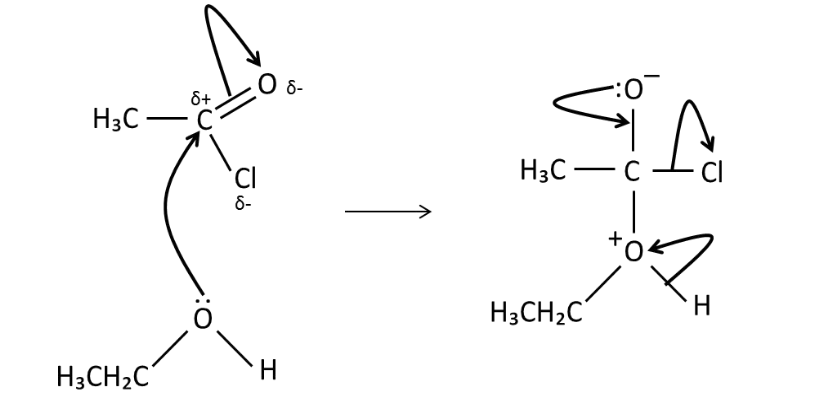
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and ethanol
CH 3 COCl + CH 3 CH 2 OH → CH 3 COOCH 2 CH 3 + HCl
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and ethanol
If the nucleophile is water,
what are the products of the
acylation of acyl chlorides or
acid anhydrides?
Carboxylic acid (hydrolyses ester
linkage)
What is the name of this
reaction (the acylation of
acyl chlorides/acid
anhydrides with water as a
nucleophile)?
hydrolysis
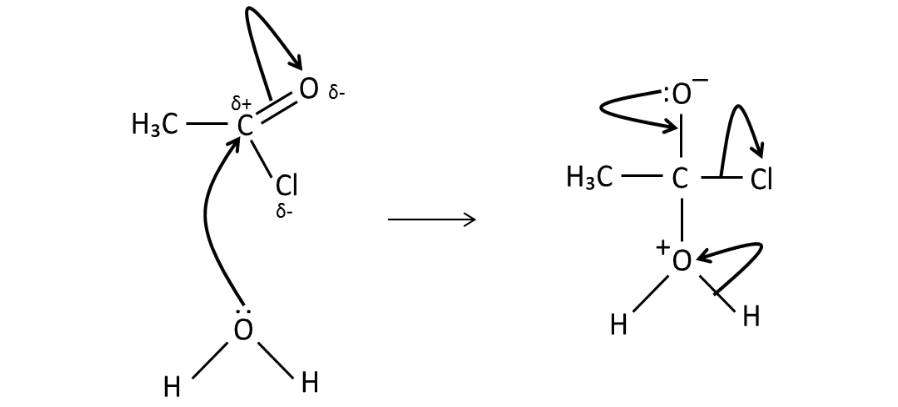
Write an equation for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and water.
CH 3 COCl + H 2 O → CH 3 COOH + HCl
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of ethanoyl chloride
and water.
What is a commercially
important acylation
reaction?
The manufacture of aspirin
What are the advantages of
using ethanoic anhydride as
an acylating agent over
ethanoyl chloride?
It is cheaper, less corrosive and does not react as readily with
water.
It is safer, as ethanoic acid is produced, rather than HCl,
which is corrosive.
What would you observe in
a melting point
determination if the sample
was not pure?
Sample melts over a large range (more than
3 o
C).
Sample’s melting point is below the accepted
value due to impurities disrupting structure
Why might the melting point
appear different to the true
value?
Temperature of the material in the machine might
be different to the temperature shown on the
thermometer - apparatus error.
When removing flue gases,
what are the issues?
Disposal of large amounts of CaSO 3 and CO 2 is
produced.
What conditions are needed
to form methyl esters from
an acid anhydride or acyl
chloride?
React with methanol and heat gently under reflux
When purifying by
recrystallisation, why is the
minimum volume of hot
solvent used?
So that a saturated solution is created, so that as
many crystals will fall out of solution as possible
when it is cooled
Why is the solution filtered
hot when purifying by
recrystallisation?
To remove insoluble impurities and ensure that
the crystals do not form in the filter paper
Why is the solution cooled
in an ice bath when
purifying by
recrystallisation?
To ensure that as many crystals as possible fall
out of solution - yield is higher
Why are the crystals
washed with cold water
when purifying by
recrystallisation?
To remove soluble impurities
How would you separate the
crystals from the reaction
mixture when purifying by
recrystallisation?
Filter under reduced pressure using a Buchner
funnel
Why might percentage yield
be below 100% (practical
reasons)?
Product is lost during filtration, drying and weighing - spills,
not all transferred from one piece of apparatus to the other
Product is left dissolved in the solution - some does not
crystallise. Some left on filter paper. Sample still wet