ACCT 212 Exam 2
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
process operating
mass production of similar products in a flow of sequential processes.
process costing system
measures costs per equivalent unit at period-end. Each process has a separate WIP inventory account.
conversion costs
direct + Applied factory overhead
equivalent units
number of whole units that could have been. started and compelted given the costs incurred. Compute separately for dircet materials and conversion costs.
weigthed average
combines units and costs across two periods in computing EUP
Weighterd average computations
EUP= Equivalent units completed and transferred out + Equivalent units in ending work in process
Cost per EUP (WA)
costs of beg. WIP + Costs added this period / Equivalent units of production
FIFO
based on current-period production activity
FIFO Computations
EUP = Equivalent units to complete beg. WIP + Units started and completed + Equivalent units in ending WIP
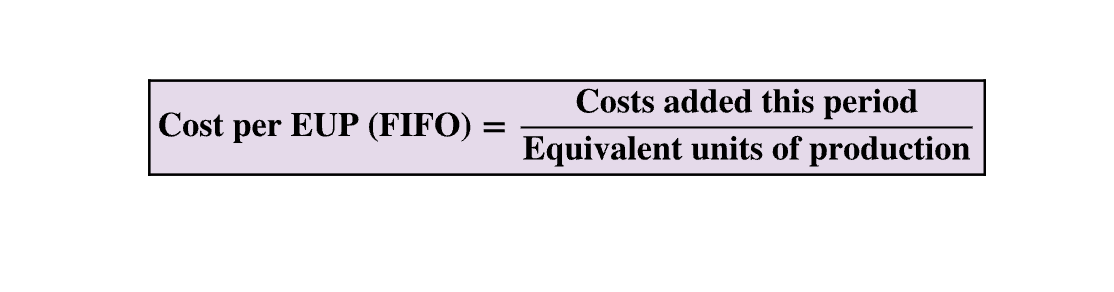
FIFO Comp.
Cost per EUP (FIFO) = Costs added this period / equivalent units of production
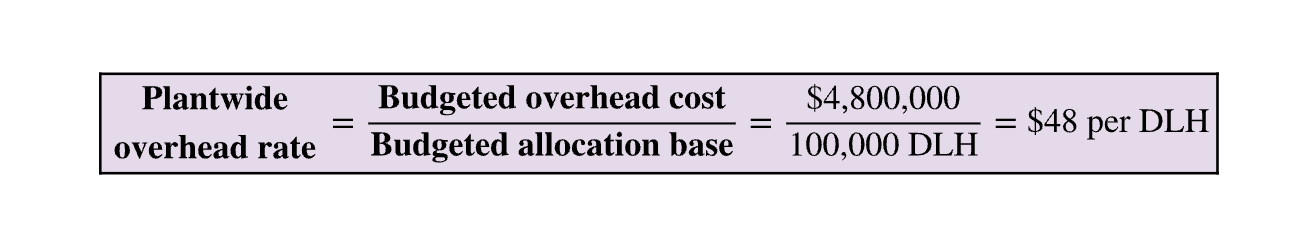
Plantwide rate method
use one overhead rate
Plantwide Overhead Rate
Allocating Overhead using plantwide rate

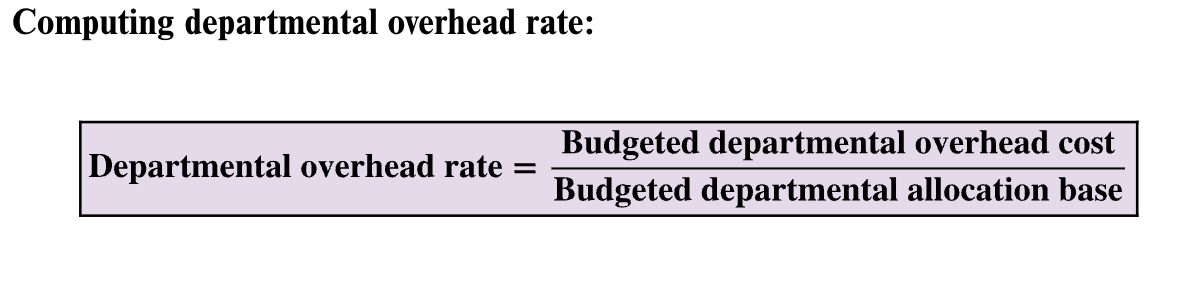
Department rate method
use a different overhead rate for each department
Activity cost pool
group of costs related to same activity
three steps to activity-based costing
identify the activities and their budget overhead rate
compute an overhead activity rate for each activity
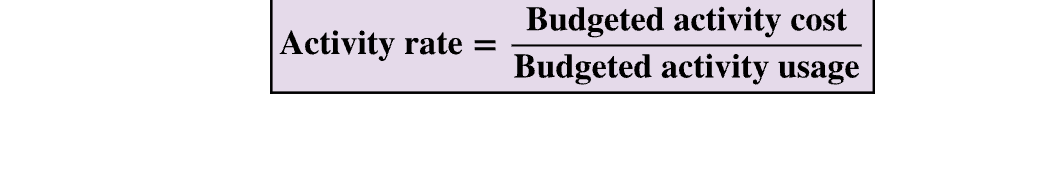
Allocate overhead cost to cost objects (products)

fixed costs
costs that do not change in total as volume changes
variable costs
costs that change proportionately with volume
mixed costs
costs that include both fixed and variable components
step-wise costs
costs with step pattern, but fixed in each relevant range
relevant change
normal operating range; neither near zero nor maximum capacity
cost equation
fixed costs +(Variable cost per unit * unites produced)
High-Low
estimates cost equation using highest and lowest volumes

Regression
Statistical method using all data. Likely more accurate.
contribution margin per unit

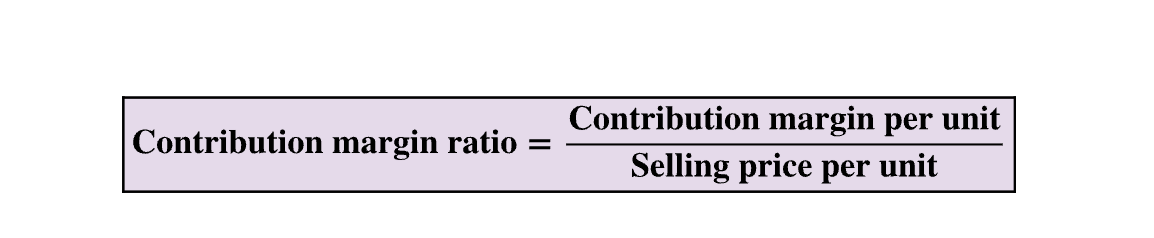
Contribution Margin Ratio
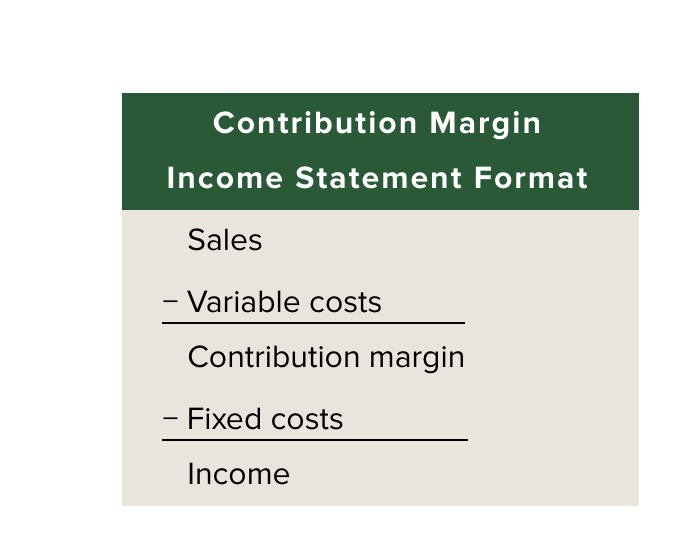
Contribution Margin Income Statement Format
Contribution Margin Income Statement (at Break Even)

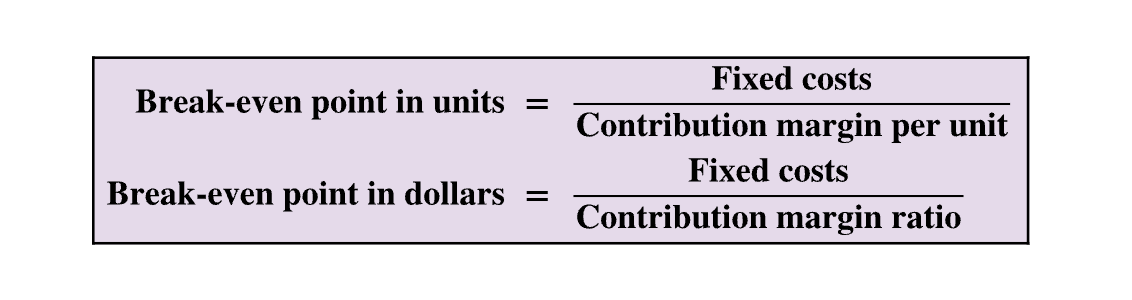
break-even point in units and in dollars
Margin of Safety
amount that sales can drop before company incurs a loss
Margin of Safety
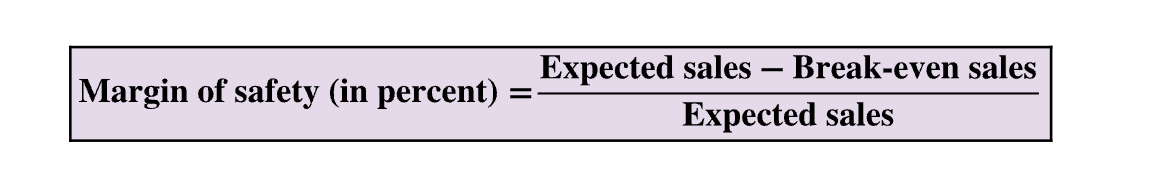
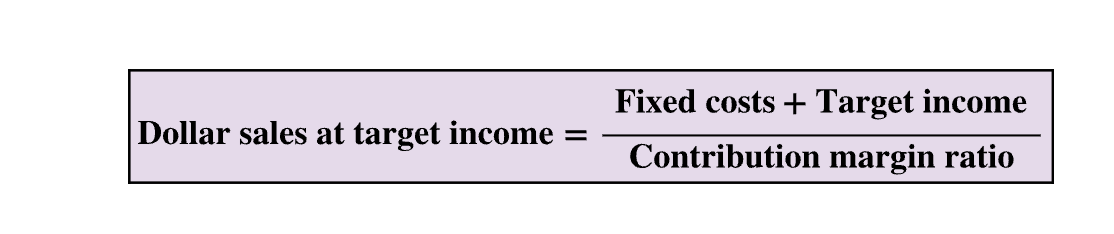
Dollar Sales for a target income
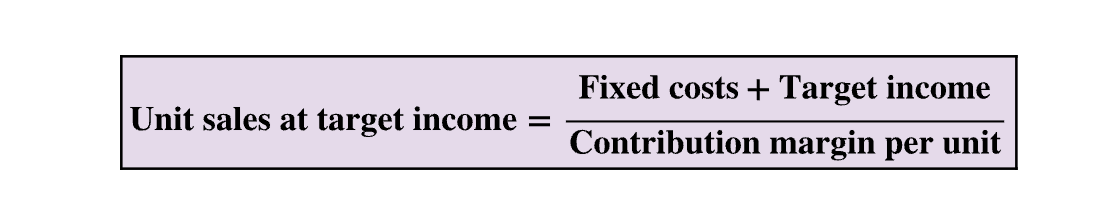
Unit sale for a target income
Business strategy and break-even

sales mix
proportion of sales volumes for various products or services
weighted average contribution margin

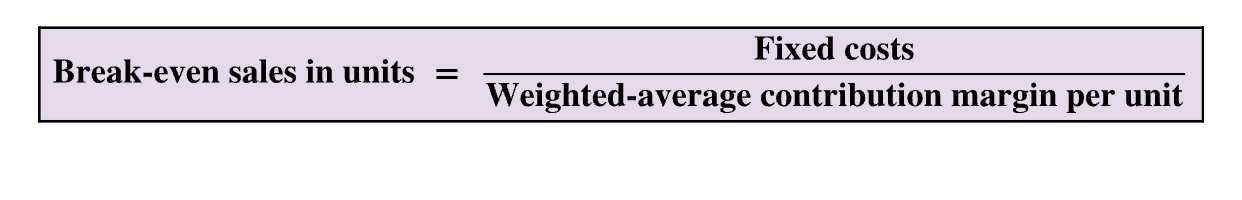
Break-even in sales units
Degree of operating leverage (DOL)

Using DOL to predict Income from sales
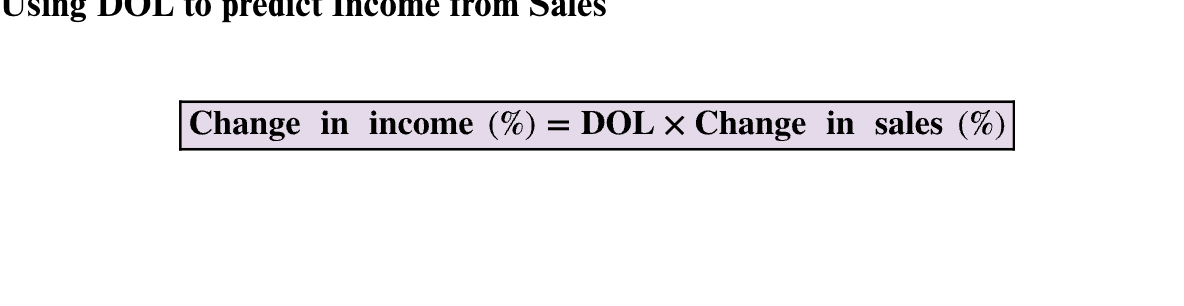
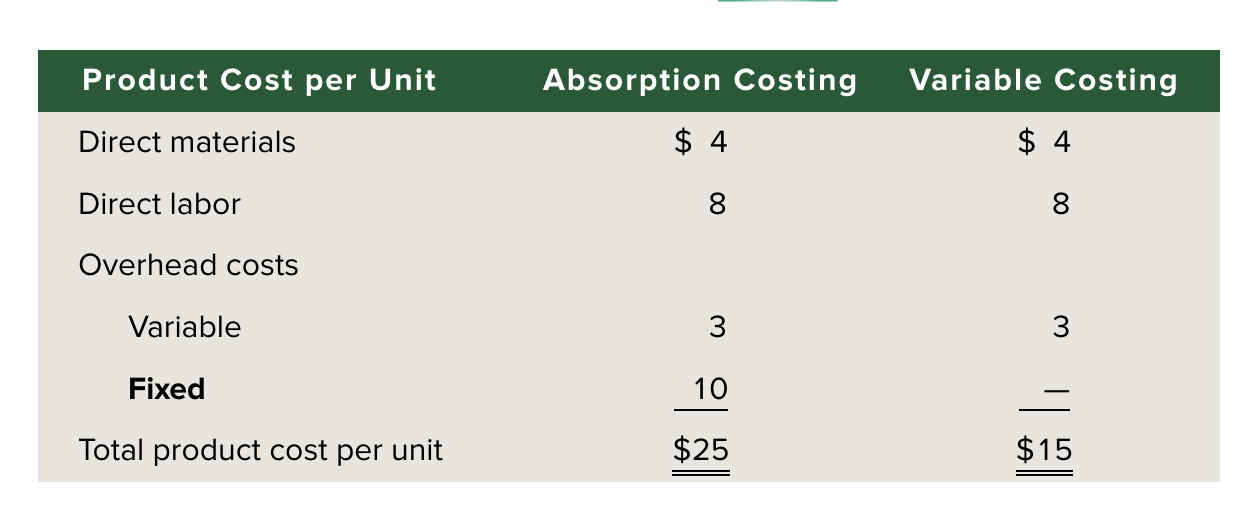
Absorption Costing
Fixed overhead is in product costs
Variable costing
fixed overhead is in period expenses
Absorption and Variable Costing
General Rule
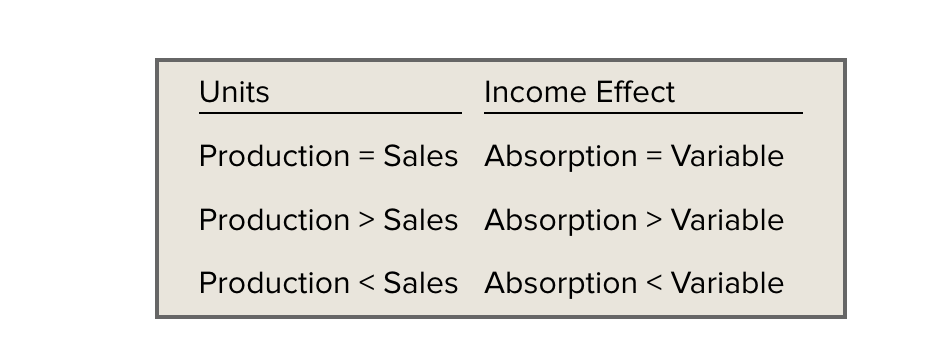
when inventory levels change: Absorption costing income = variable costing income
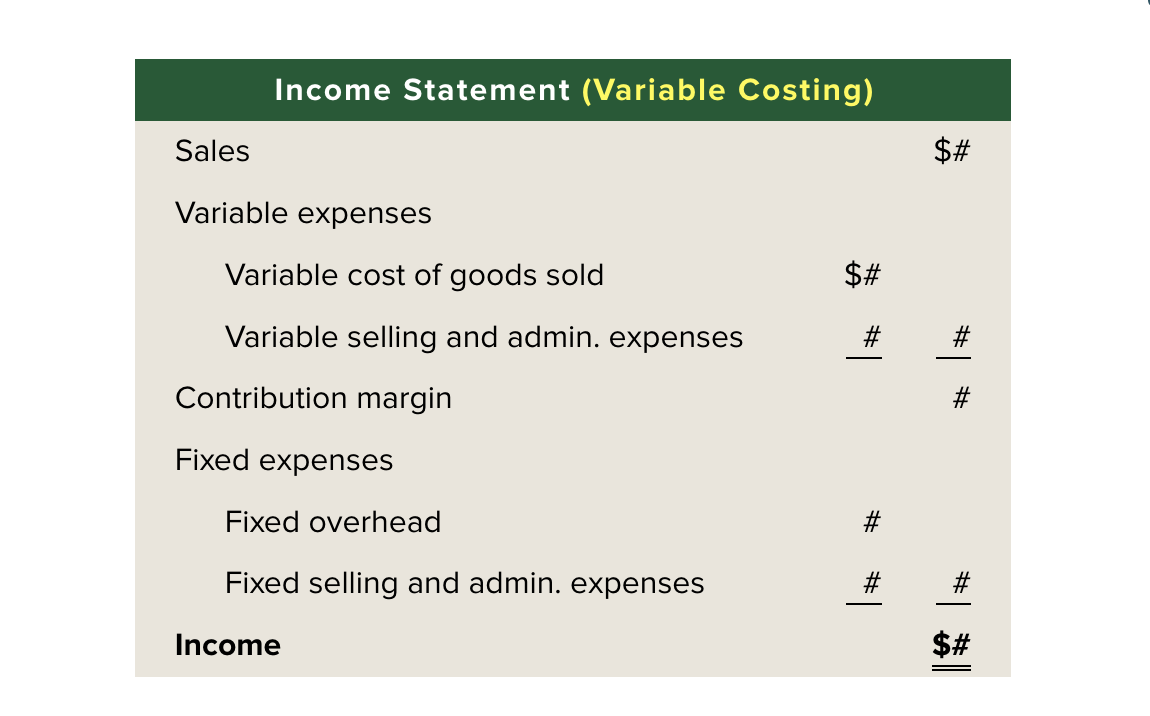
Income Statement Absorption Costing

Income Statement VR Costing
Setting target price

Analyzing special orders

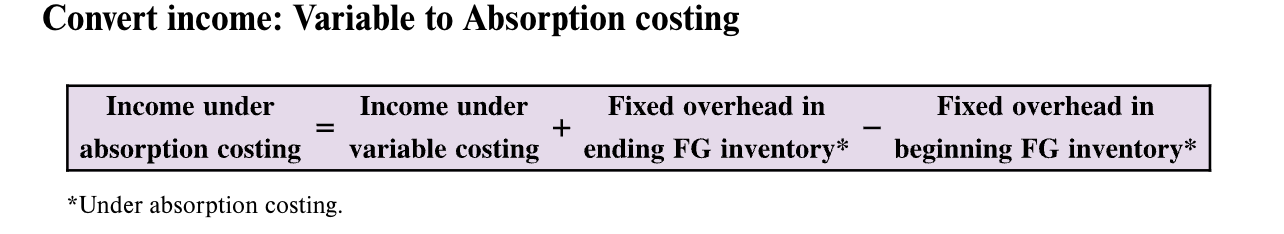
Convert Income: Variable to Absorption costing
Markup
Amount added to cost per unit in computing a selling price
Enviormental profit and loss (EP&)
A report in monetary terms of the impact on human welfare from an entity’s activities
Variable cost of goods sold
DM, DL, Variable overhead costs for units sold