Biology unit 1 ccea gcse double award science
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
what is a control experiment
the control experiment is given everything it needs including the substance being tested for to compare to the experiment
what does sodium hydroxide and soda lime do
remove carbon dioxide from the air
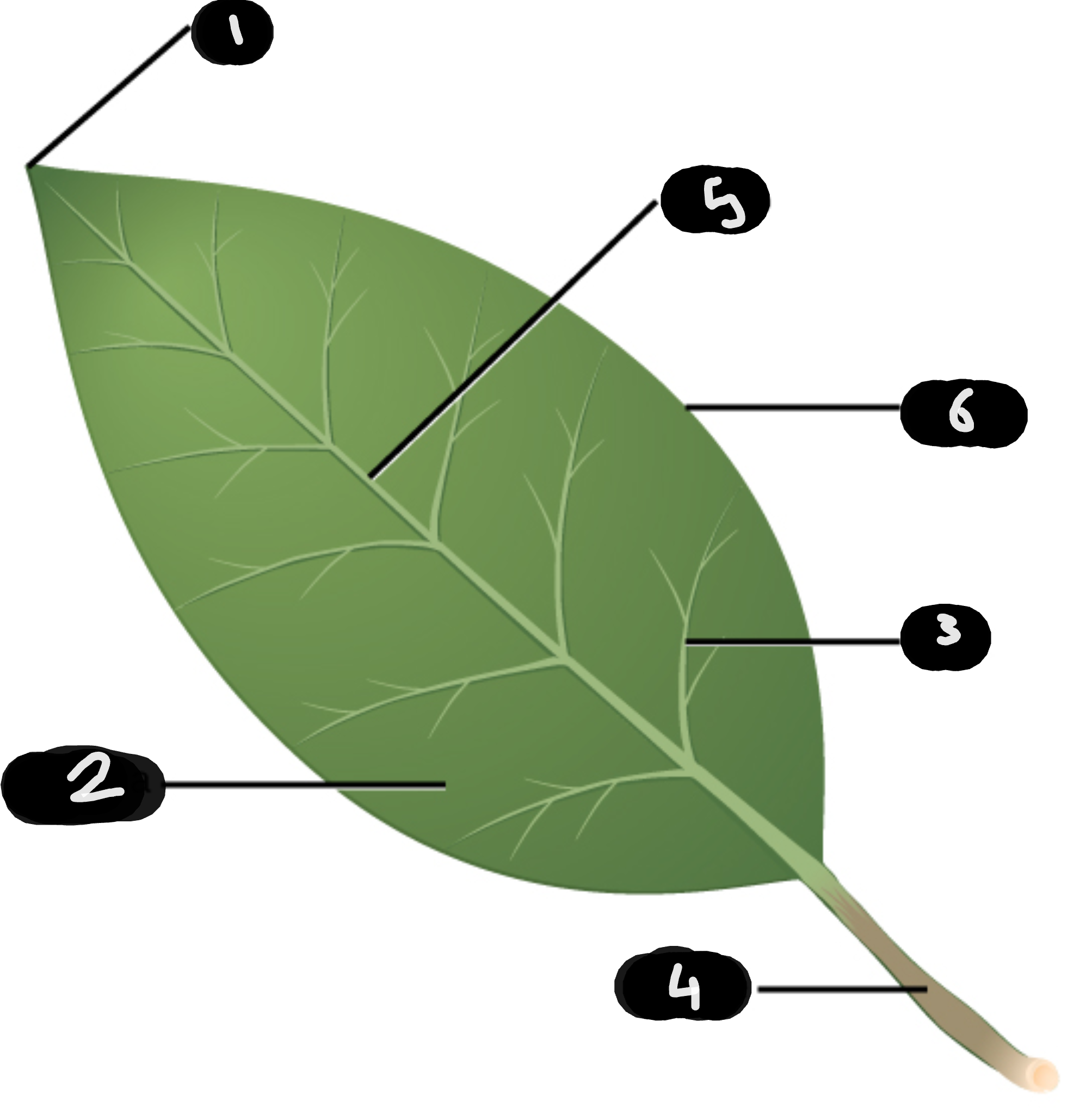
name number 1
tip
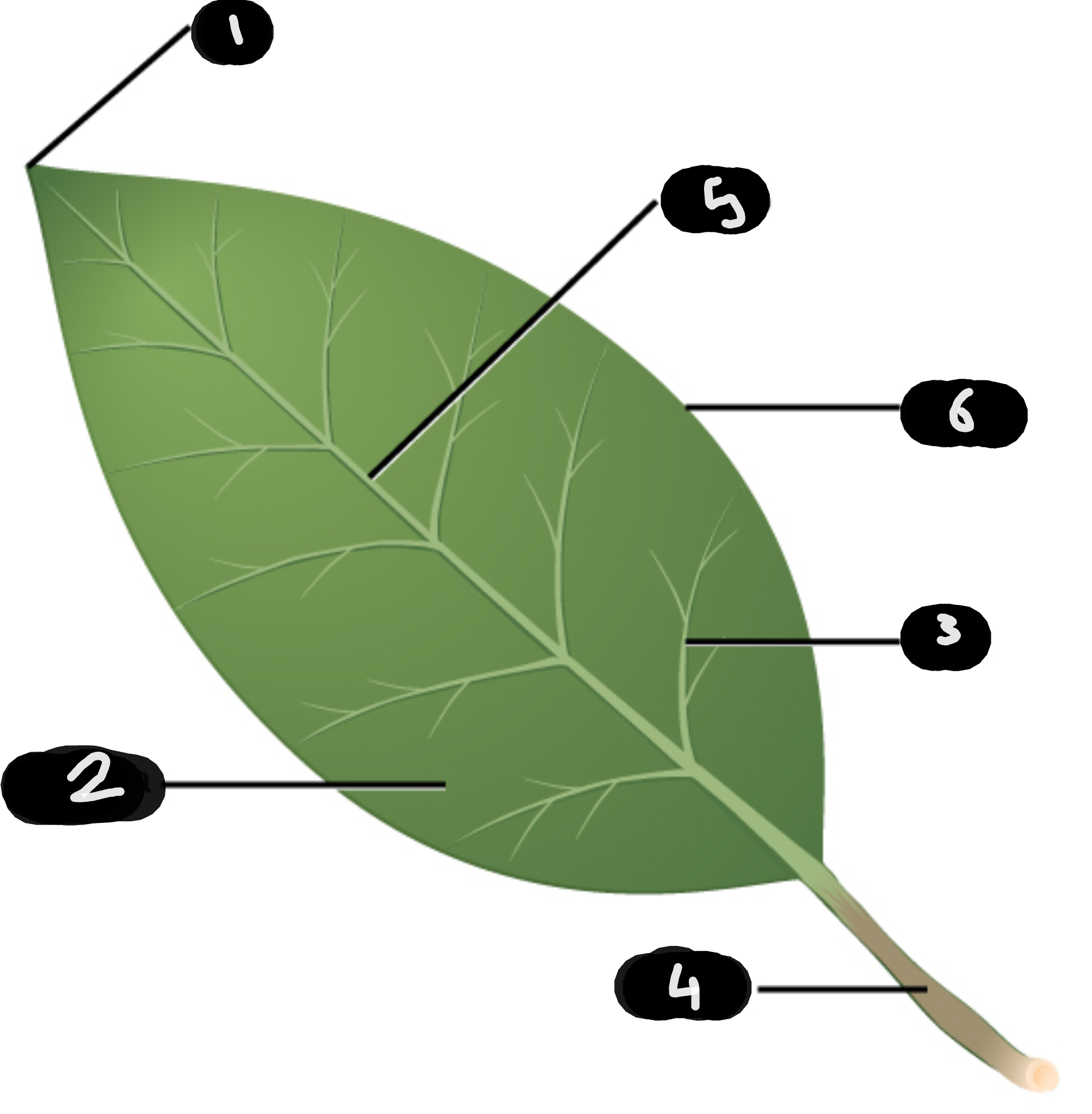
name number 2
lamina
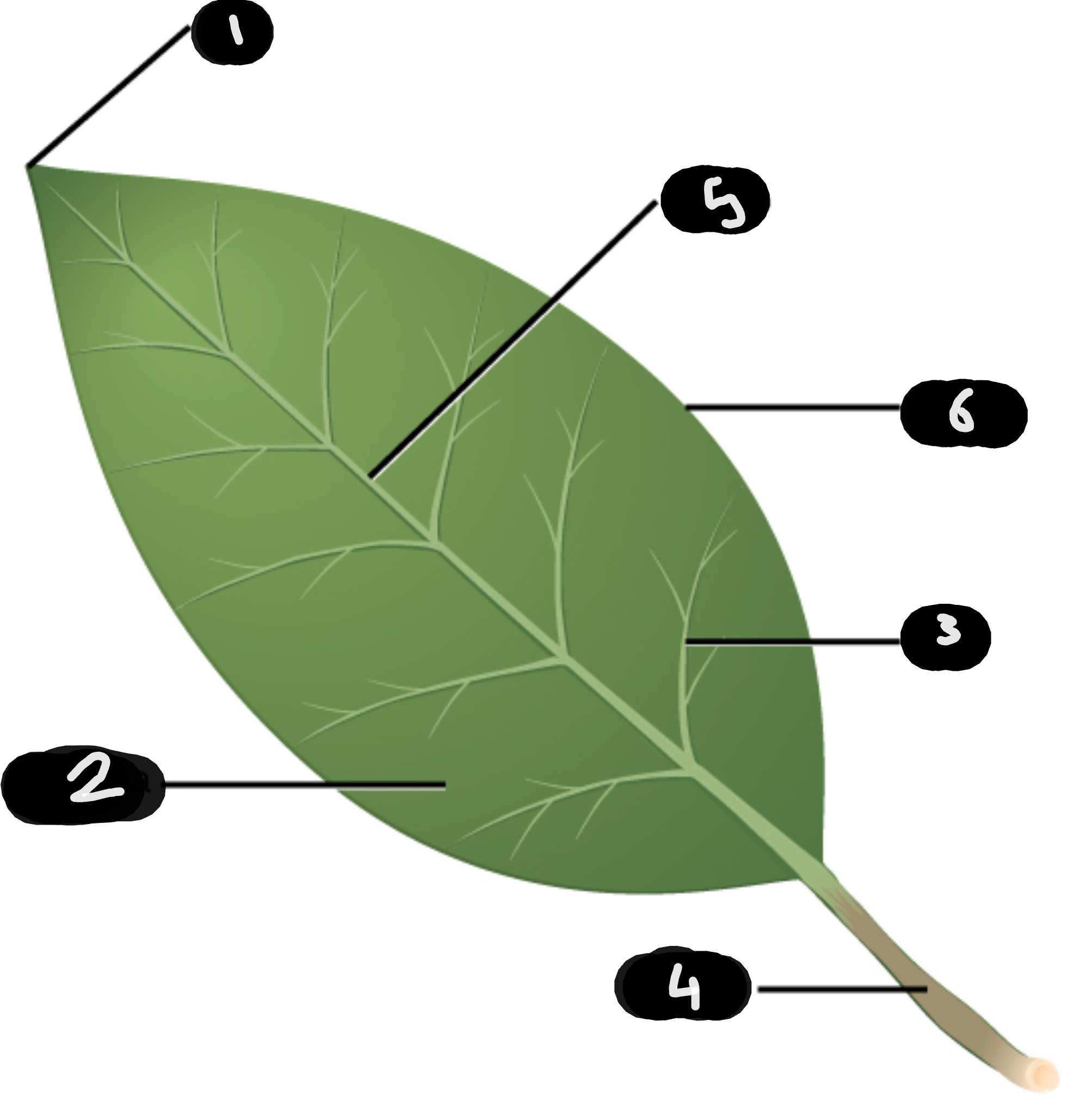
name number 3
vein
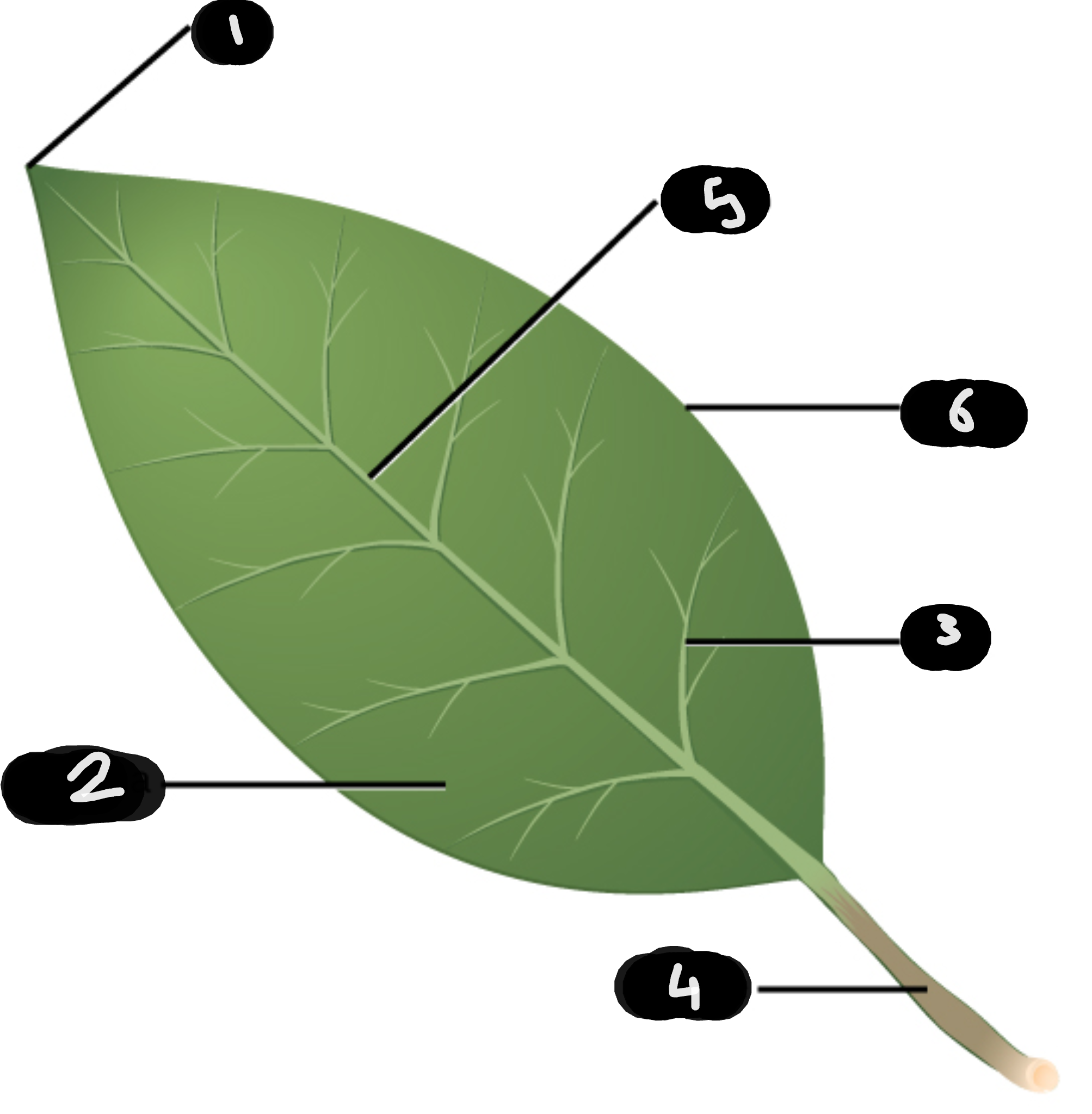
name number 4
petiole
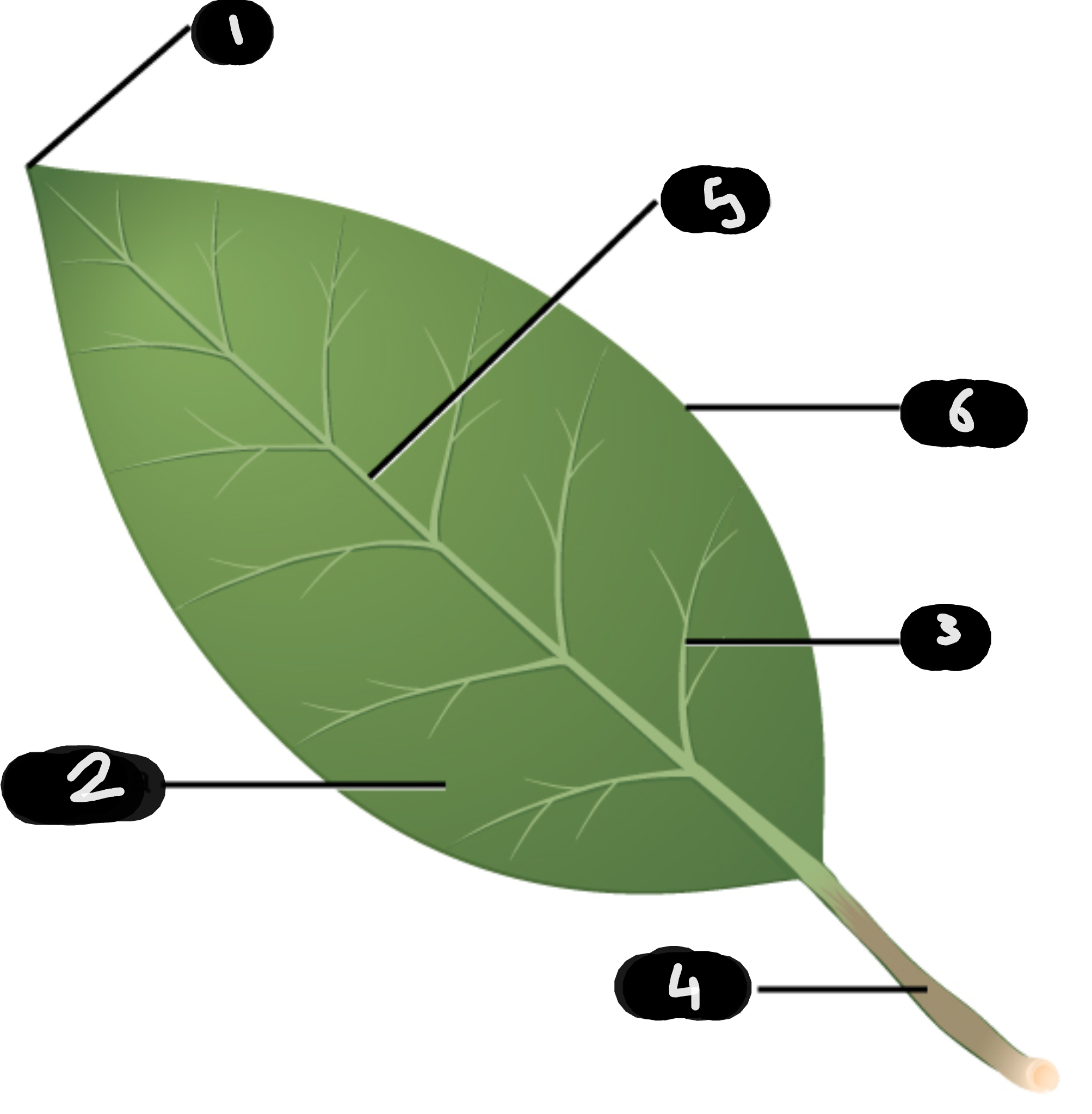
name number 5
midrib
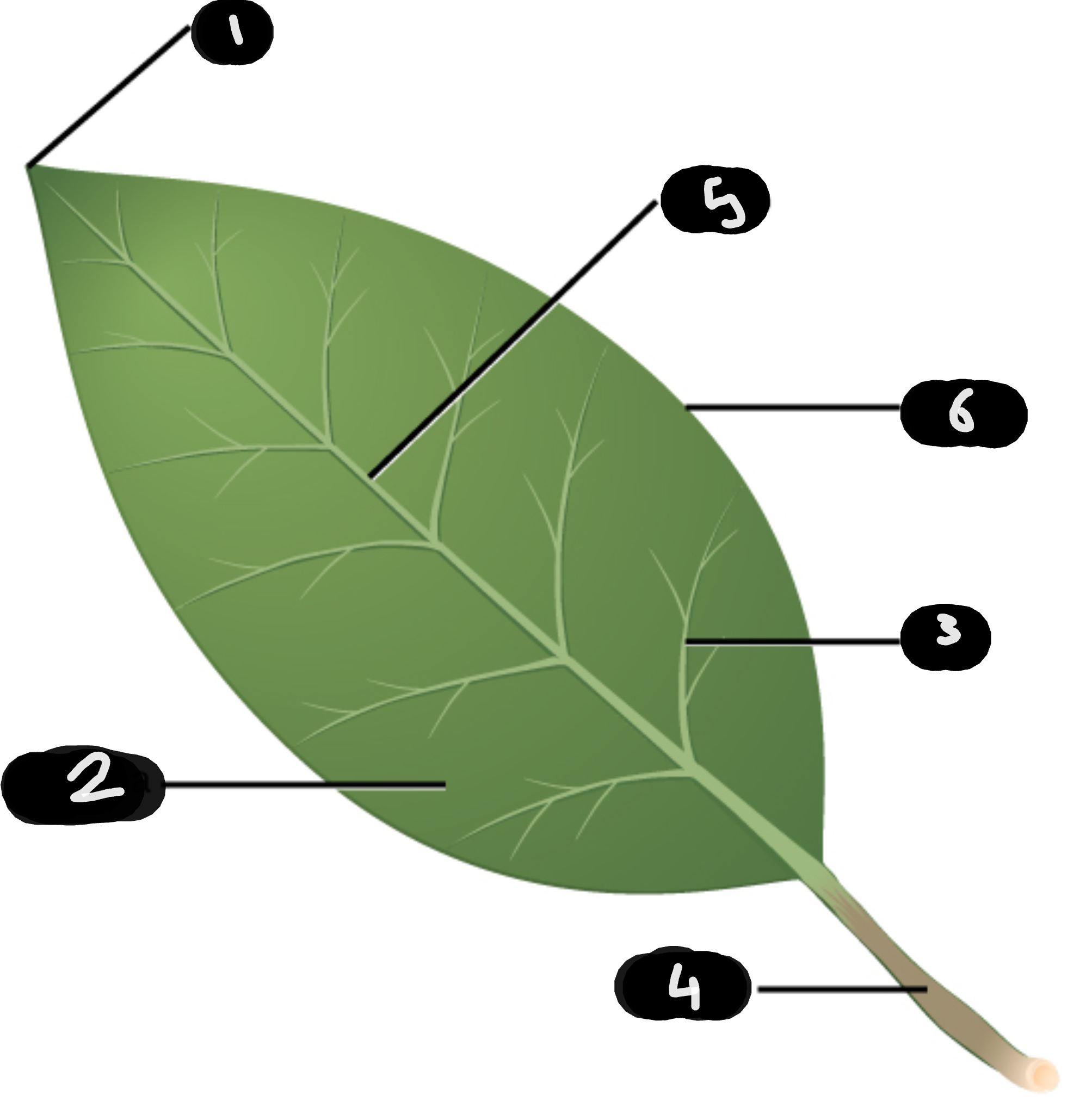
name number 6
margin
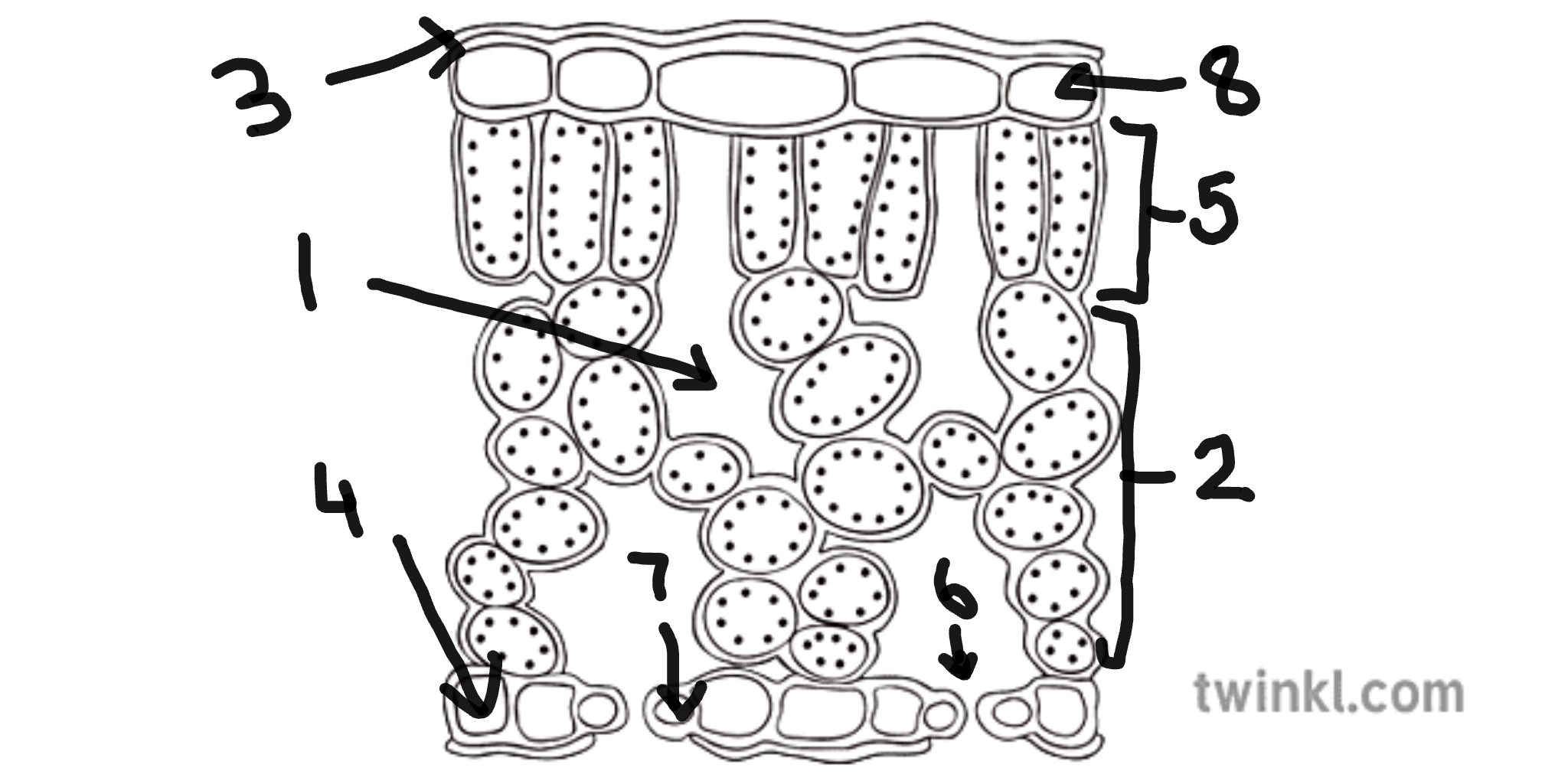
name number 1
sub-stomatal air space
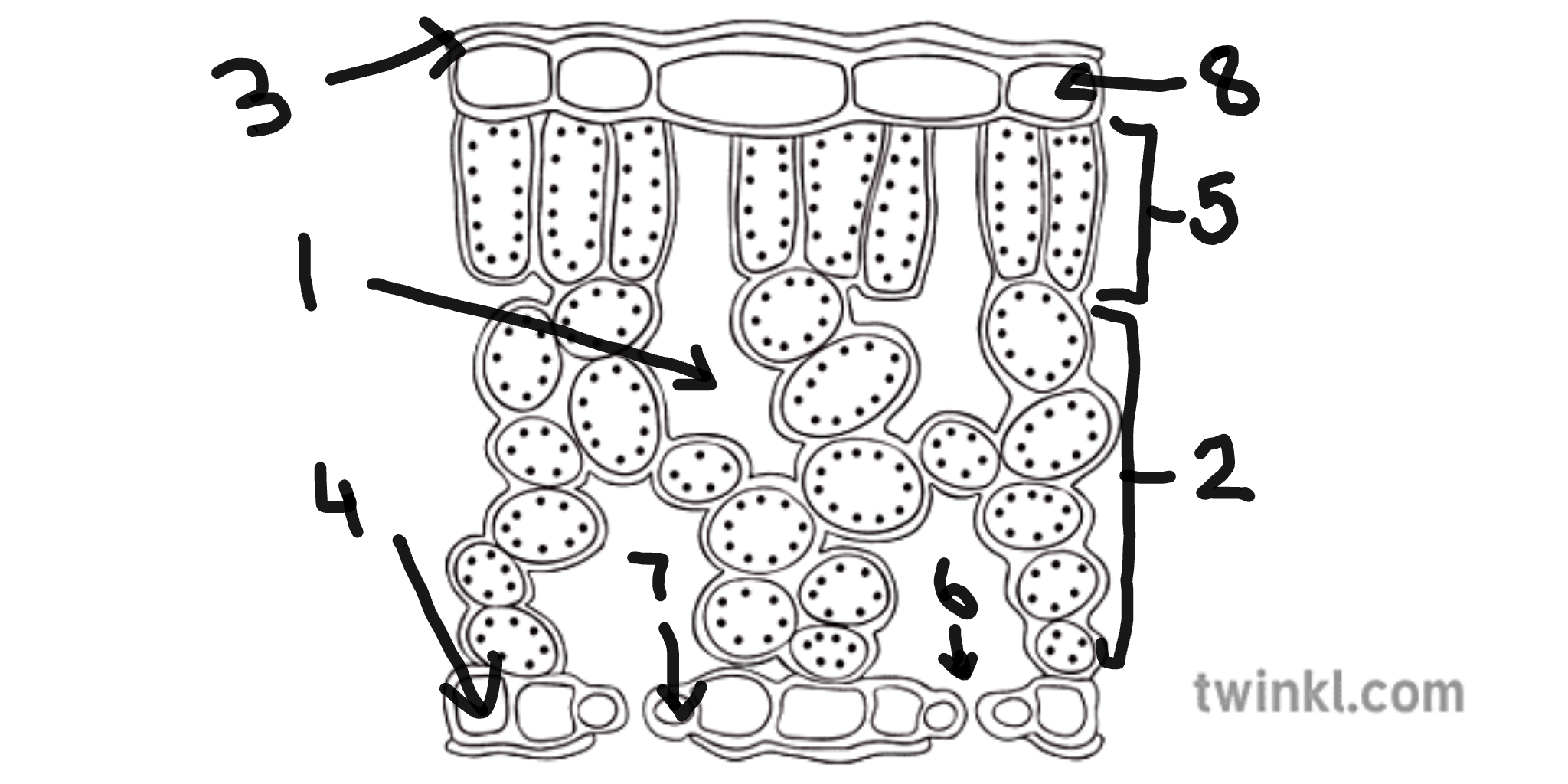
name number 2
spongy mesophyll cells
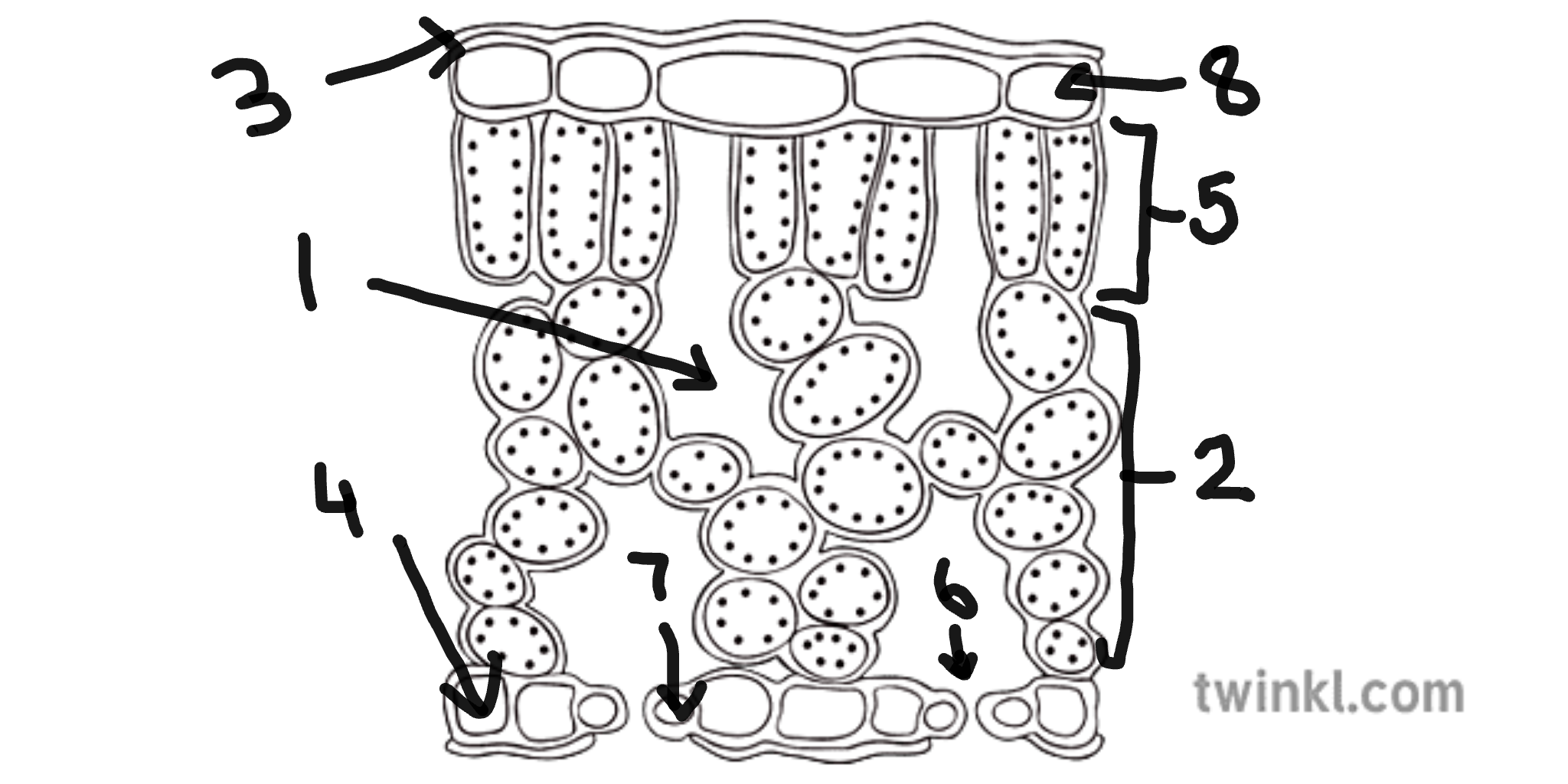
name number 3
cuticle
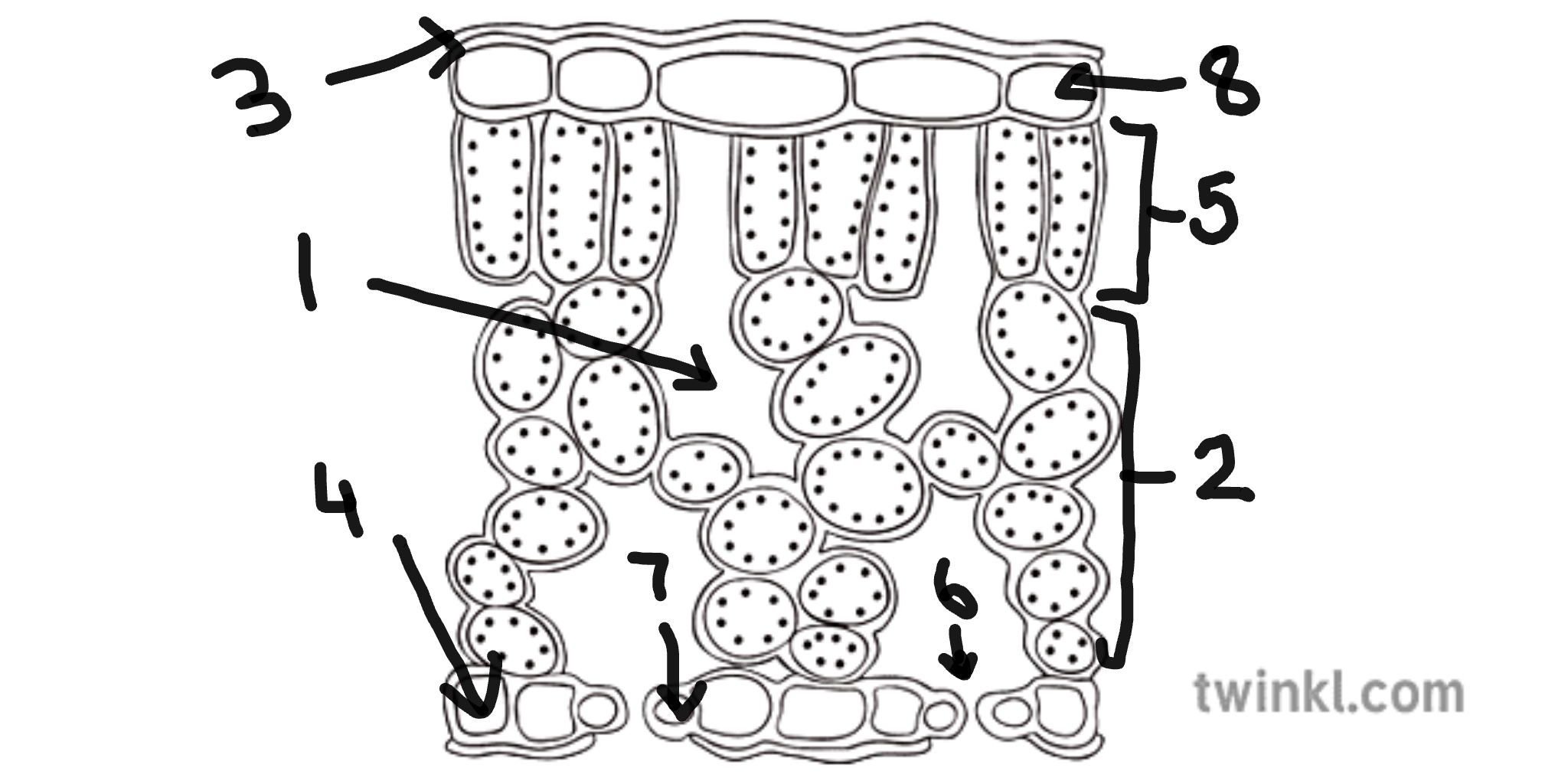
name number 4
lower epidermis cells
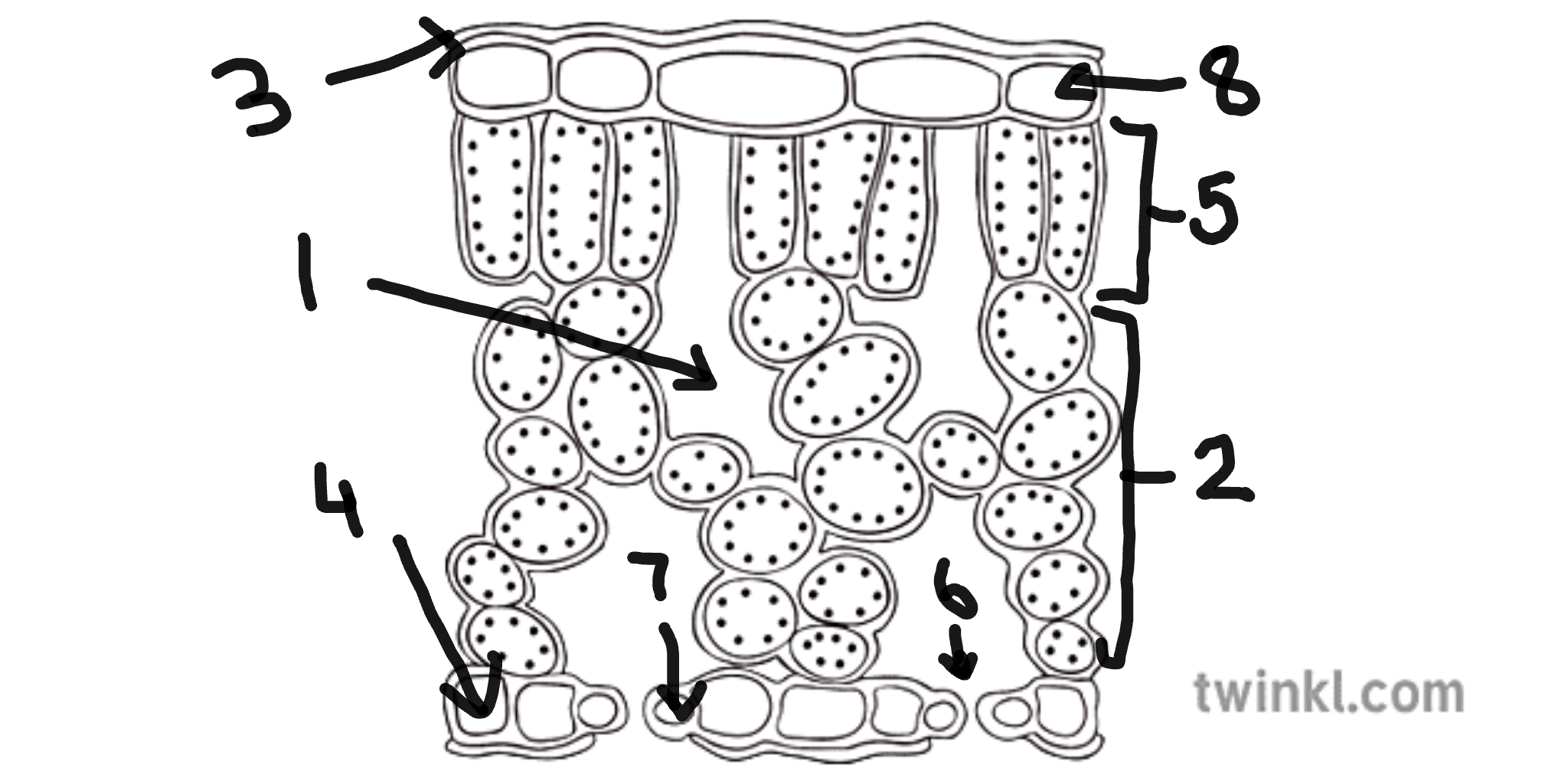
name number 5
palisade mesophyll cells
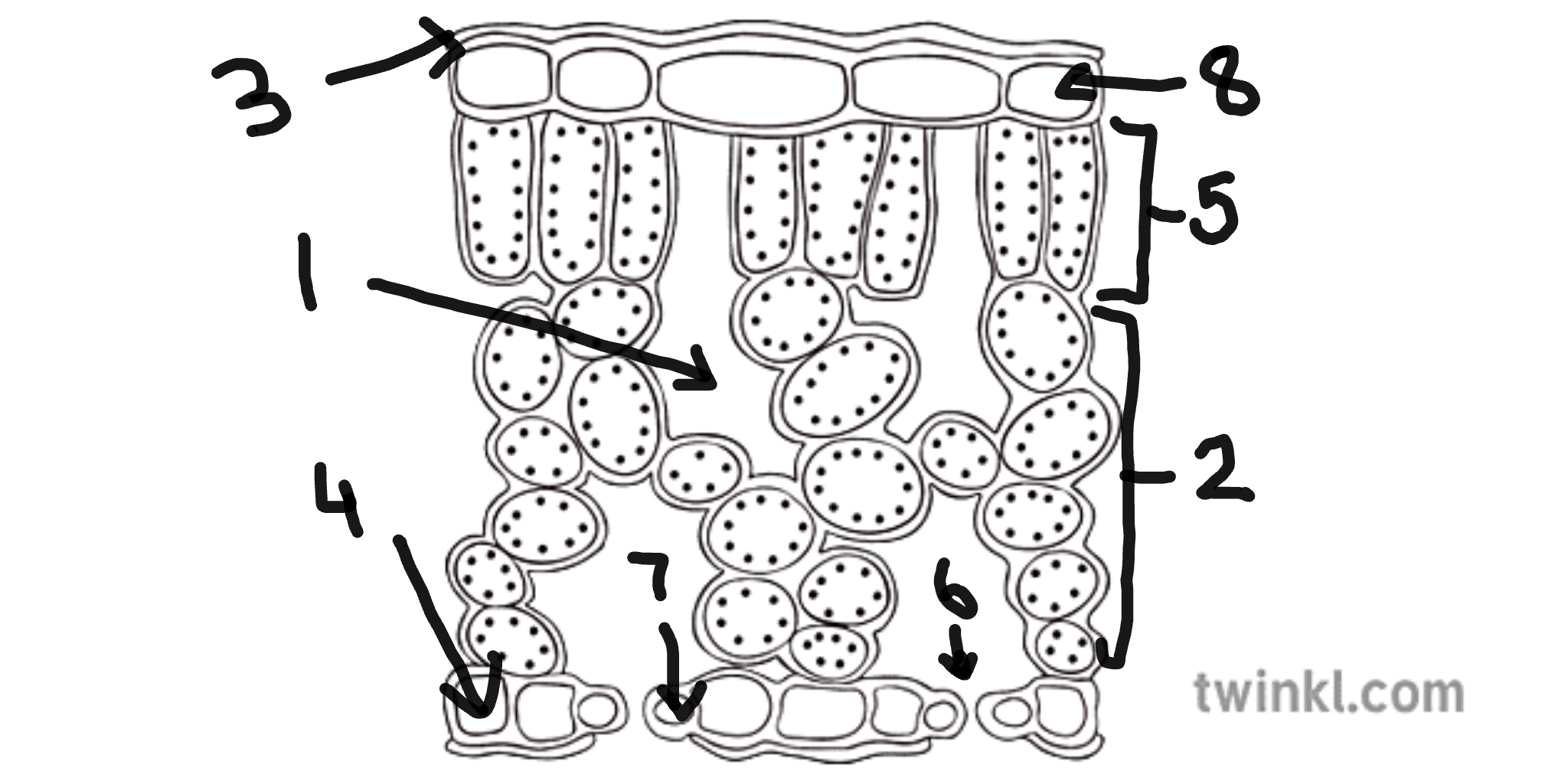
name number 6
stomata
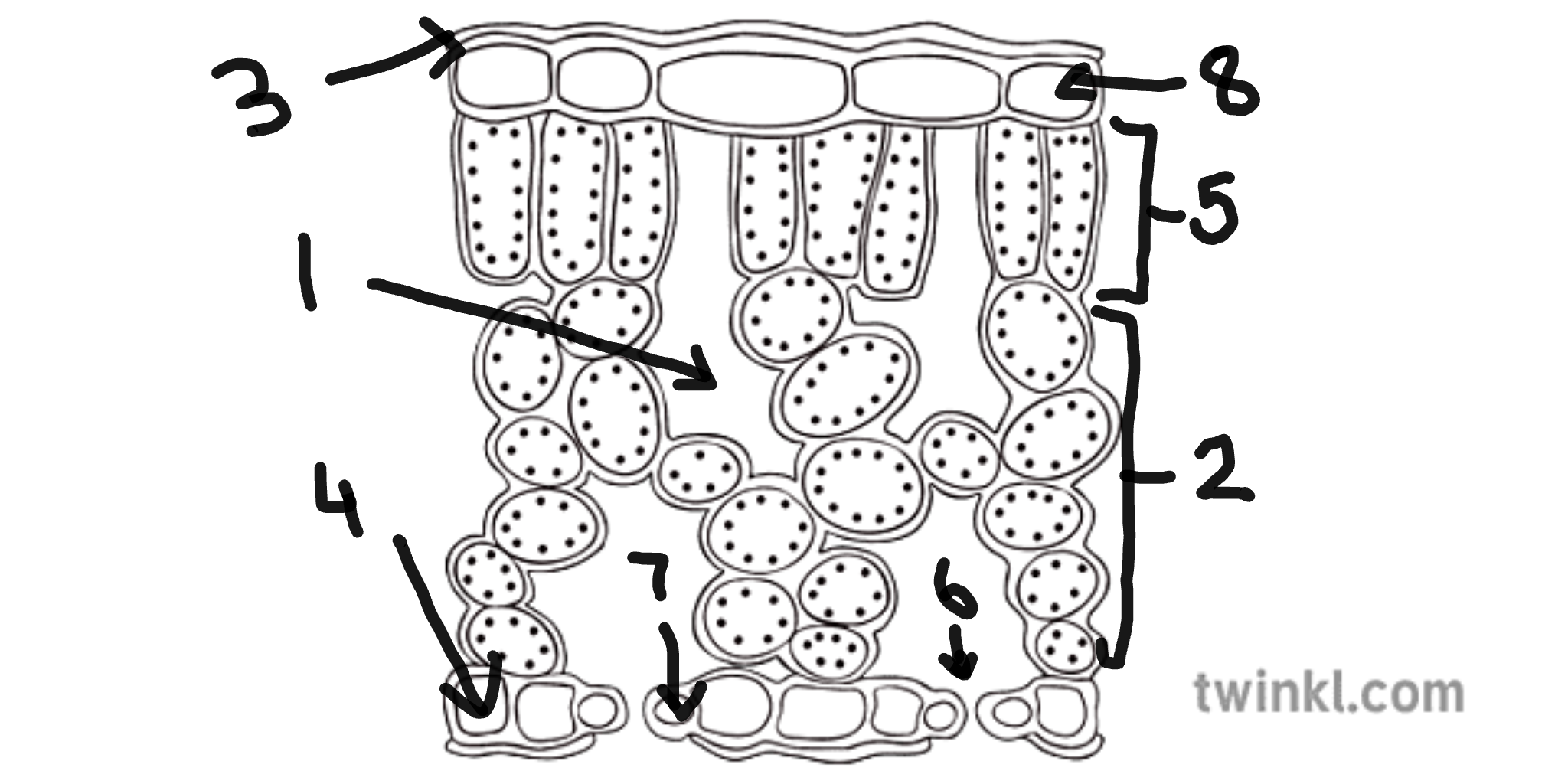
name number 7
guard cells
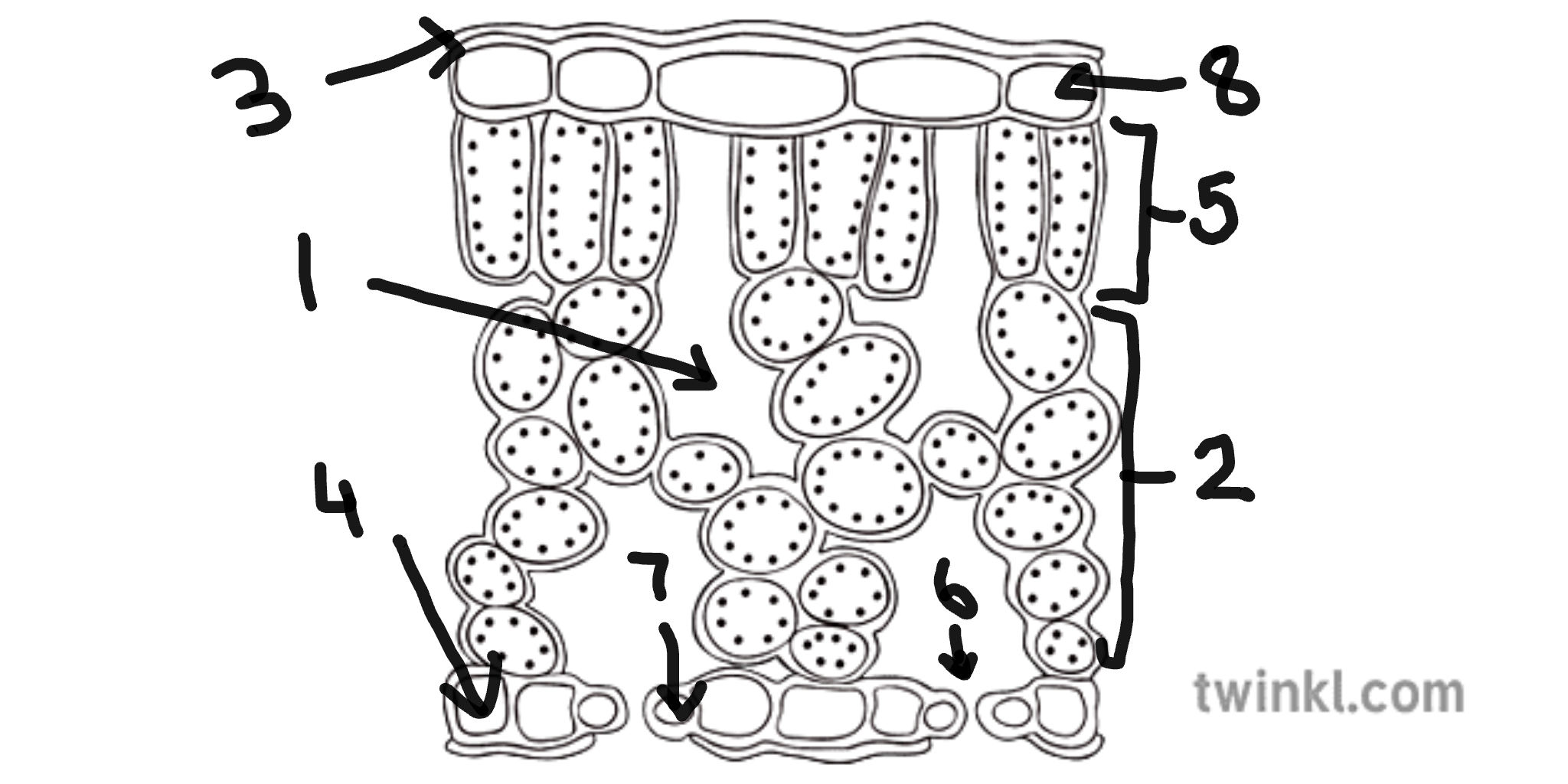
name number 8
upper epidermis cells
what is it called when the rate of resp and photo are equal and when does it happen
compensation point at dawn and dusk
where does respiration occur
mitochondria
what are carbs broken down into
simple sugars and complex sugars
chemicals used to test for starch
iodine
colour change for starch
yellow/brown to blue/black
chemicals used to test for reducing sugars
blue benedict's solution
colour change for reducing sugars
blue to green to yellow to orange to brick red precipitate
chemicals used to test for protein
blue copper sulfate solution and sodium hydroxide solution
colour change for protein
blue to purple/lilac
colour change for fats
clear to white emulsion
nucleus
the control centre of the cell
chromosomes
found inside the nucleus and contain genetic information
cytoplasm
the main part of the cell where chemical reactions take place
mitochondria
where respiration takes place
cell membrane
a selectively permeable membrane that forms a boundary to the cell and controls what enters and the leaves the cell
nuclear membrane
surrounds the nucleus
cellulose cell wall
a rigid structure immediately outside the cell membrane that provides support
large permanent vacuole
contains cell sap and when full pushes the cell membrane against the cell wall making the cell rigid and providing support
chloroplasts
contain chlorophyll which traps light and helps the plant make food during photosynthesis
bacteria
microscopic single-celled organisms
total magnification
magnifying power of eyepiece lens x magnifying power of objective lens
light
passes through the specimen and into the lens forming an image
focusing knob
raises and lowers the stage for focusing and allows a clear image
low power objective lens
allows a wide field of view to be seen but not in lots of detail and allows you to find what your looking for
high power objective lens
allows you to focus on a small field of view in lots of detail
stage
holds the slide
eyepiece lens
where you look through and magnifies the image along with the objective lens and allows you to see the image close up
what do onion cells look like
a brick wall
non-cellulose cell wall
a cell wall not composed of cellulose found in bacterial cells
plasmids
small rings of dna
multi-celled organisms
specialised tissues, organs and organ systems improve exchange with the environment, transport substances and communicate between cells
specialised tissues
similar cells grouped together are called a tissue
organs
structures made of several types of tissue that carry out a particular function
organ systems
organs that operate together to carry out a particular function that are grouped together
function of the digestive system
breaking down of larger food molecules into simple soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the blood
function of nervous system
responding to stimuli and making responses
function of reproductive system
production of young
function of circulatory system
transports materials around the body and helps to protect the body against infection and maintain body temperature
function of excretory system
allows toxic waste products to be removed from the body
function of skeletal system
supports and protects the body and allows it move
function of respiratory system
allows gas exchange
functions of roots
to anchor plant in soil and to absorb water and minerals from the soil
functions of the stem
to provide support and to transport water minerals and food
functions of leaves
to make food by photosynthesis
functions of the flower
to reproduce
adaptions to respiratory surfaces in humans
large surface area, good blood supply, thin permeable walls, moist walls
is respiration exothermic or endothermic
exothermic
what do living organisms use energy for
growth, repair, reproduction, heat production, movement and active transport
chemical equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 > 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy
word equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast
glucose > carbon dioxide + alcohol + small amount of energy
word equation for anaerobic respiration in mammalian muscles
glucose > lactate + small amount of energy
what are fats broken down into
fatty acids and glycerol
what are proteins broken down into
amino acids
equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H20 > C6H1206 + 6O2
WHAT COLOUR DOES HYDROGEN CARBONATE INDICATOR CHANGE IN HIGH CO2
yellow
WHAT COLOUR DOES HYDROGEN CARBONATE INDICATOR CHANGE IN LOW CO2
purple
WHAT COLOUR DOES HYDROGEN CARBONATE INDICATOR CHANGE IN normal CO2
red
how are leaves adapted to absorb light
large surface area, thin transparent cuticle, chloroplasts
how are leaves adapted for gas exchange
intercellular air space, stomata
what is a receptor
part of the body that is affected by and stimulated by a stimulus
what is a co-ordinator
links the receptors and the effectors
what is the effector
the parts of the body that produce a response to the stimulus
what is a stimulus
a detectable change in the internal or external environment that causes a reaction in an organ or cell
what does cns stand for
central nervous system
what does the cns do
controls and coordinates the response between the receptors and effectors
what are the nerves that branch out to the side of the cns called
peripheral nervous system
what are nerve impulses
small electrical charges
what is a sensory neurone
carry nerve impulses from receptor to cns
what is a motor neurone
carry nerve impulses from cns to effector causing a response
what is an association neurone
receive nerve impulses from sensory neurone and carry them to the motor neurone inside the cns
what is a synapse
the small gap where 2 neurones meet and acts as a junction
what is a voluntary action
involves conscious thought and is done deliberately
what are reflex actions
they do not involve conscious thought and are automatic responses that follow a stimulus
what is a reflex arc
the pathway that the impulses travel by
what are hormones
chemicals produced by special glands that release them into the blood
what is homeostasis
the maintenance of the constant state in response to changes outside and inside the body
roles of homeostasis
controlling blood glucose concentration and osmoregulation
what is osmoregulation
controlling the water content of the body
where does insulin act
liver
where is insulin produced
pancreas