12-06: Geometric Vectors
Vectors
- Scalar: a quantity that @@describes magnitude or size only@@ (with or without units) @@but does not include direction@@
- Magnitude, no direction
- Magnitude: a number/numerical value is associated
- e.g. mass (2 kg), speed (2 km/hr)
- Vector: a @@quantity that has both magnitude and direction@@
- Magnitude and direction
- Direction: where it is going
- e.g. velocity (2 km/hr west)
Vectors can be represented as:

The magnitude of a vector is designated using absolute value brackets

A vector’s direction can be expressed using many different methods
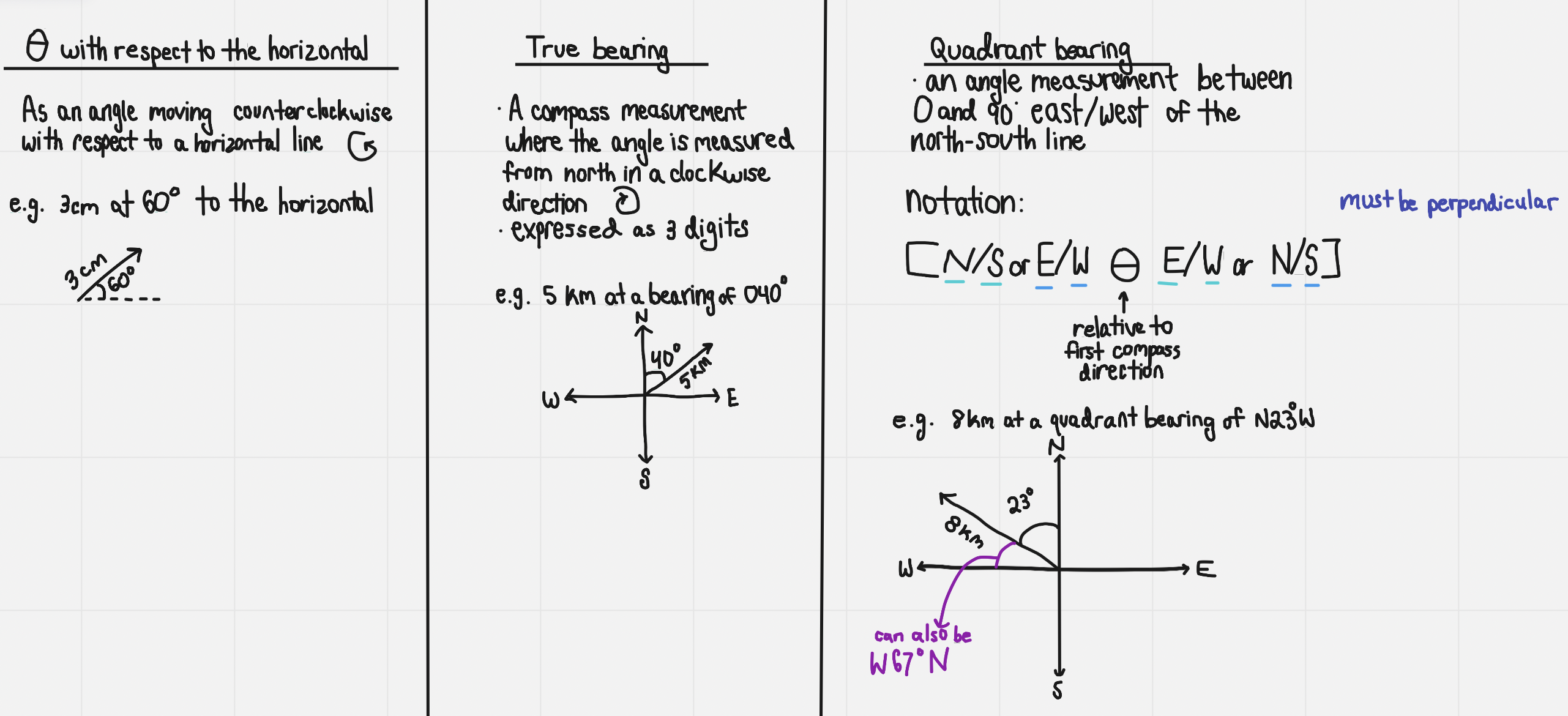
Parallel Vectors
Parallel vectors: have the same or opposite direction, but not necessarily the same magnitude
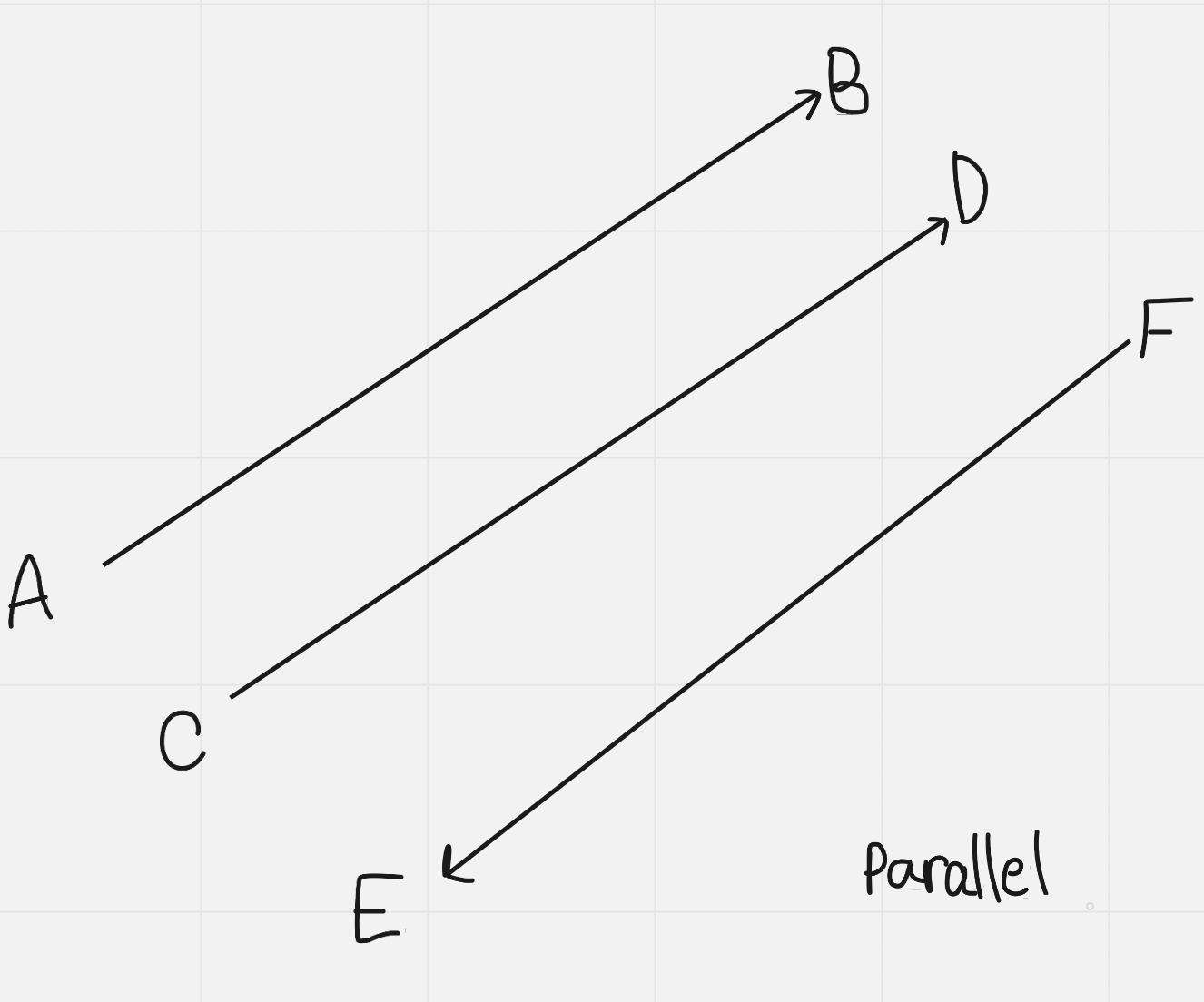 Equivalent vectors: have the same magnitude and the same direction
Equivalent vectors: have the same magnitude and the same direction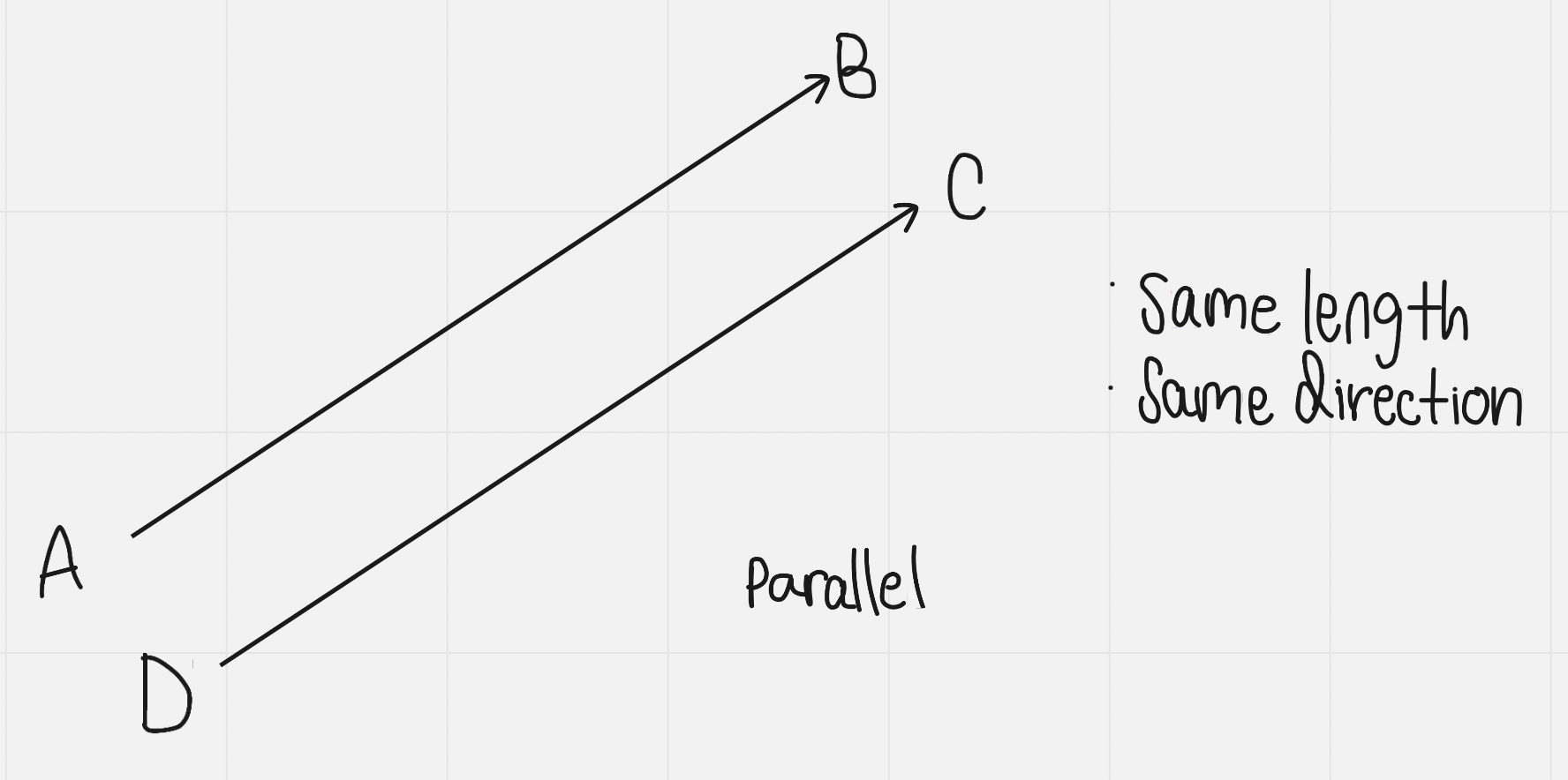 Opposite vectors: have the same magnitude but opposite direction
Opposite vectors: have the same magnitude but opposite direction
Multiplying a vector by a negative means that the direction gets flipped (or you could also say that its origin point gets flipped)

Addition & Subtraction of Vectors
When you add 2 or more vectors, you are finding a single vector called the ^^resultant^^
- Think of adding vectors as finding a shortcut, it accomplishes the same thing that the original vectors did when applied one after the other
Adding Vectors
2 methods to adding vectors:
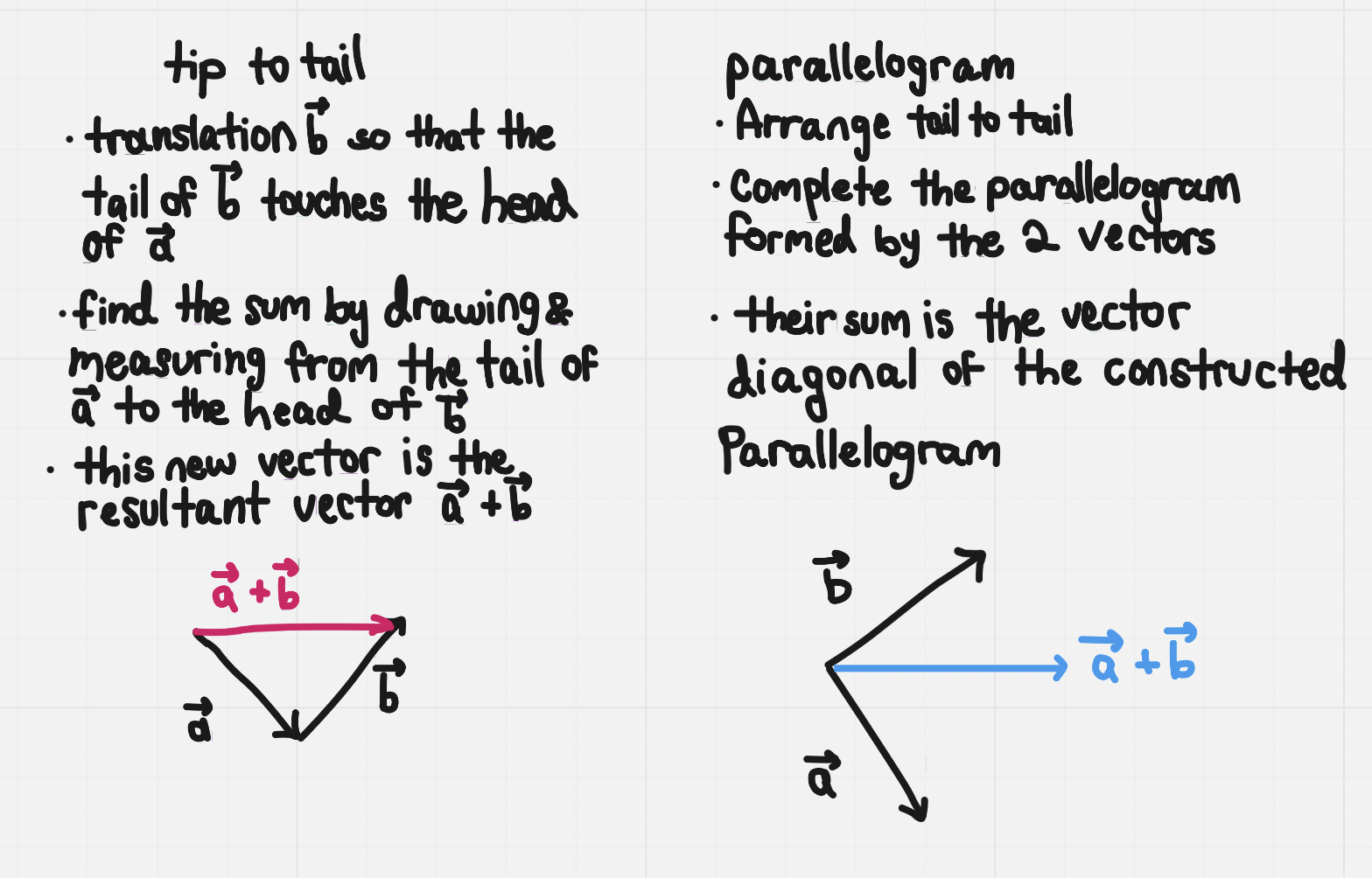
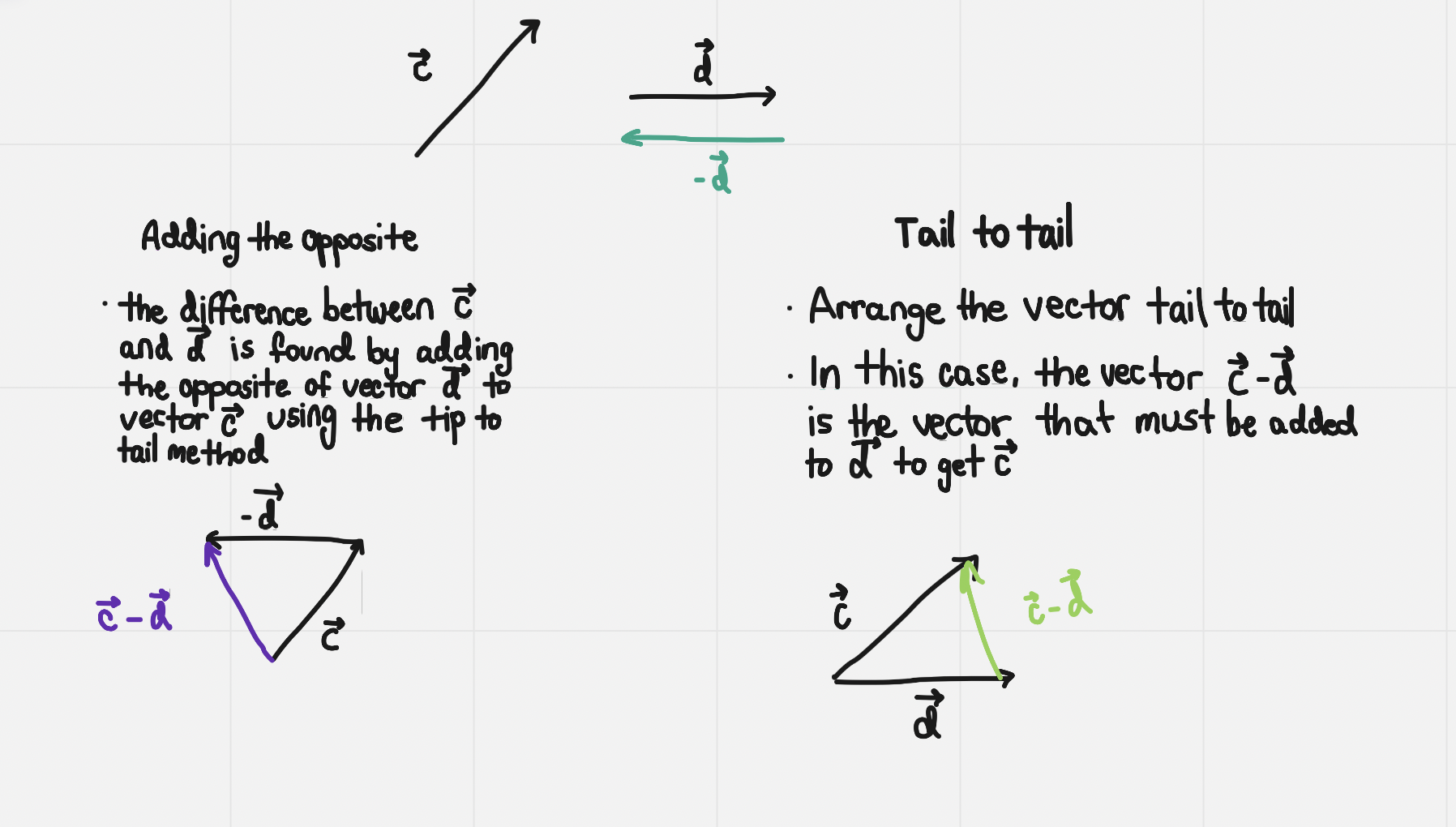
Subtracting Vectors
- To subtract c-d, add the opposite of d to c
2 methods to subtracting vectors:
 Parallel vectors:
Parallel vectors:
If ^^2 vectors are parallel and acting in the same direction^^, the ^^overall magnitude^^ is equal to: the ^^sum of the individual vectors^^ (use simple addition)
If %%2 vectors are parallel but acting in opposite directions,%% the %%overall magnitude%% is equal to: the %%difference of the two individual vectors%% (use simple subtraction)
Zero vector: when two opposite vectors are added together, the resultant has zero magnitude and no specific direction. Written as
 Properties of Vector Addition
Properties of Vector Addition

Multiplying a Vector by a Scalar
We can multiply a vector by a number k to produce a new scalar multiple of the vector
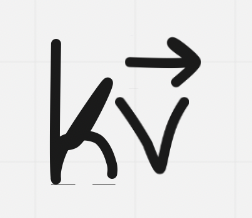
k is used as multiplication and is called a scalar, it can be any real number
%%Multiplying a vector by a scalar k can impact the vector’s magnitude & direction%%
Rules:
If %%k>0,%% then (vector) kv has the %%same directio%%n as (vector) v
If ^^k<0^^, then (vector) kv has the ^^opposite direction^^ as (vector) v
If 0<|k|<1, then the vector is decreased in magnitude, shortened
If ==|k| > 1, then the vector is increased in magnitude==, lengthened
If @@k=0, then the result is a zero vector@@
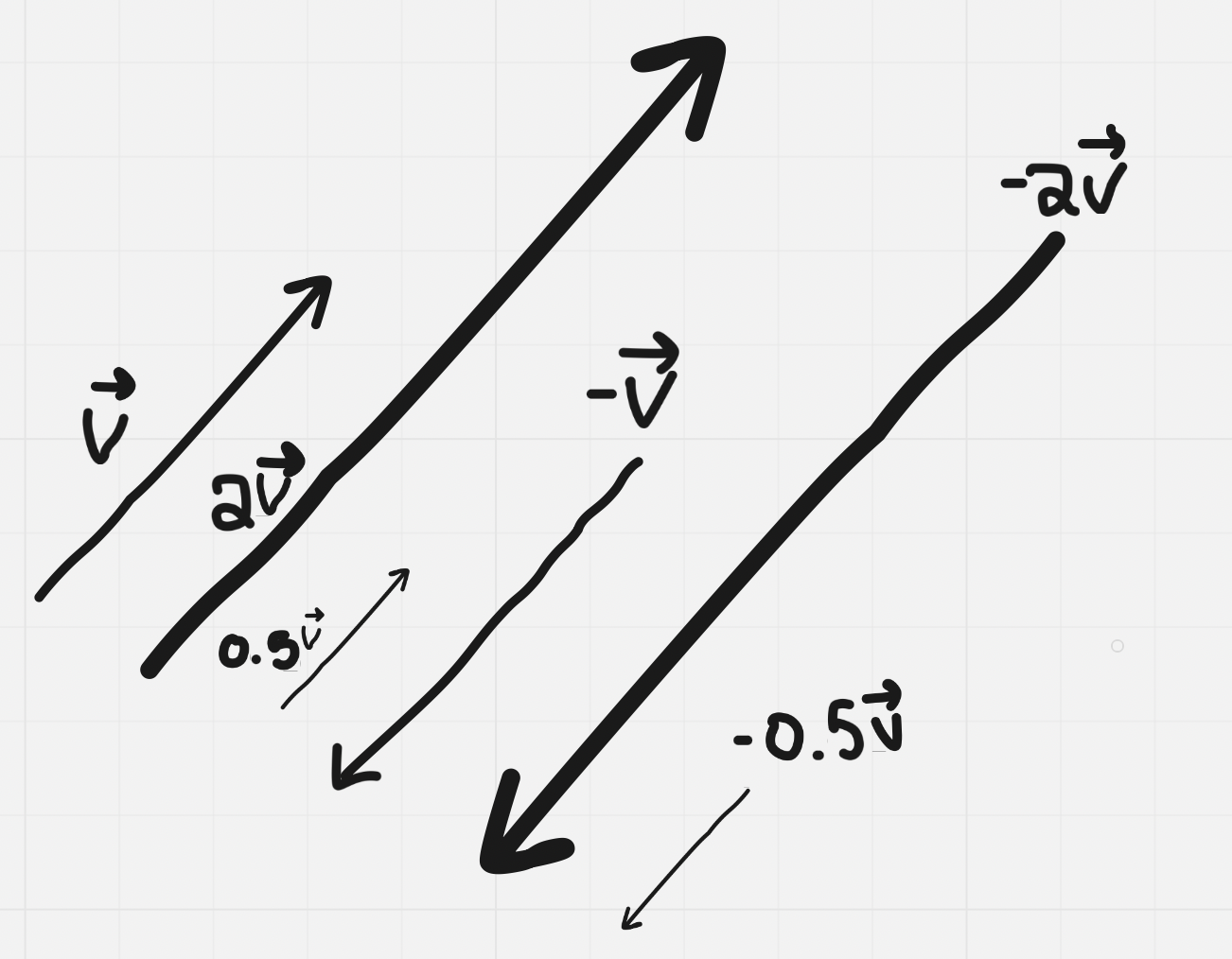 Vectors that are scalar multiples are parallel and are said to be colinear. They form a straight line when arranged tip to tip
Vectors that are scalar multiples are parallel and are said to be colinear. They form a straight line when arranged tip to tip
Vector properties for scalar multiples
Distributive property
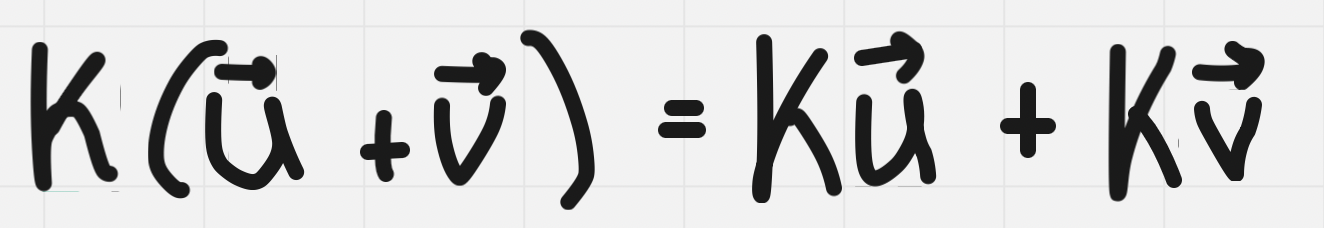
Associate property

Identity property

Applications of Vector Addition
| RULE | FORMULA | WHEN TO USE |
|---|---|---|
| Pythagorean | a² + b² = c² | Right triangles, when given 2 sides and looking for a 3rd side |
| SOH CAH TOA | sinϴ = opp/hyp, cosϴ = adj/hyp, tanϴ=opp/adj | Right triangles, given an angle and a side & finding a side or 2 sides given and finding an angle |
| Sine law | a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC or sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c | Non right triangles, 2 sides and opp angle finding angle or given 2 angles opp side finding side |
| Cosine law | a² = b² + c² - 2bccosA or cosA = (b² + c² - a²)/2 | Non right triangles, given 2 sides and enclosed angle finding 3rd side or given all 3 sides and finding angle |
Resolution
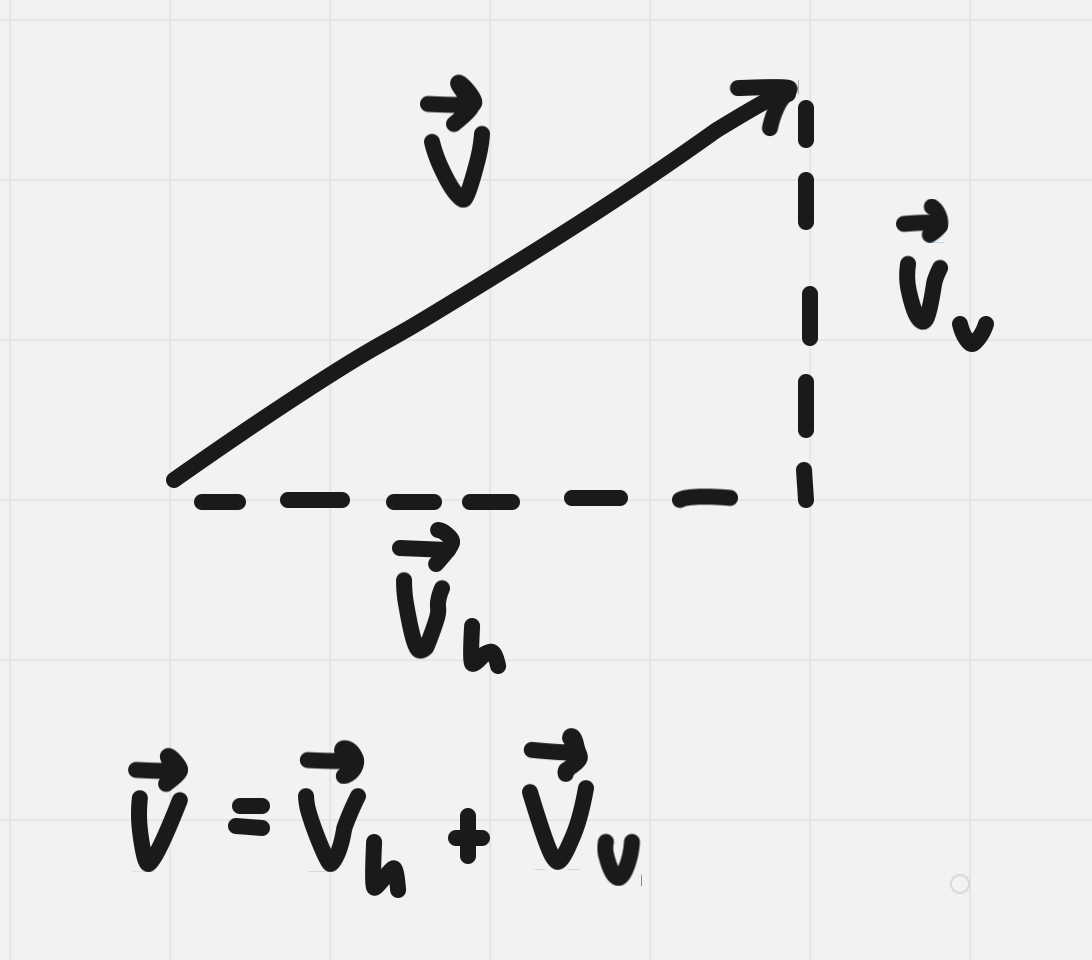
- @@Resolution: taking a single force and decomposing it into 2 components@@
- Most useful and important way to resolve a force vector occurs when this vector is resolved into 2 components that are at right angles to each other
- A vector can be resolved into 2 perpendicular vectors whose sum is the given vector
Rectangular components of vectors: 2 perpendicular vectors that are added to give a resultant
 Equilibrant vector: one that balances another vector/combination of vectors. Equal to the magnitude but opposite in direction to the resultant vector
Equilibrant vector: one that balances another vector/combination of vectors. Equal to the magnitude but opposite in direction to the resultant vector
- If the equilibrate is added to a given system of vectors, the sum of all vectors including the equilibrant is a zero vector