Carbonyls
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Differentiate kinetic and thermodynamic enolates in terms of:
Double bond substitution.
Thermodynamic stability.
Rate of reaction.
What reagents to use to make either.
Kinetic enolates:
Less substituted double bond.
Less thermodynamically stable.
Faster to form due to less steric hinderance.
Selectively made by using a strong, bulky base at low temperature.
Thermodynamic enolates:
More substituted double bond.
More thermodynamically stable.
Slower to form due to more steric hinderance.
Selectively made by using small bases at non-low temperatures.
If you wanted to make an E-enolate from a carbonyl-containing molecule, how would you do proceed?

If you wanted to make an Z-enolate from a carbonyl-containing molecule, how would you do so?
What is one functional group that will force the molecule to reject being a E-enolate? Why?
Amides due to steric strain.

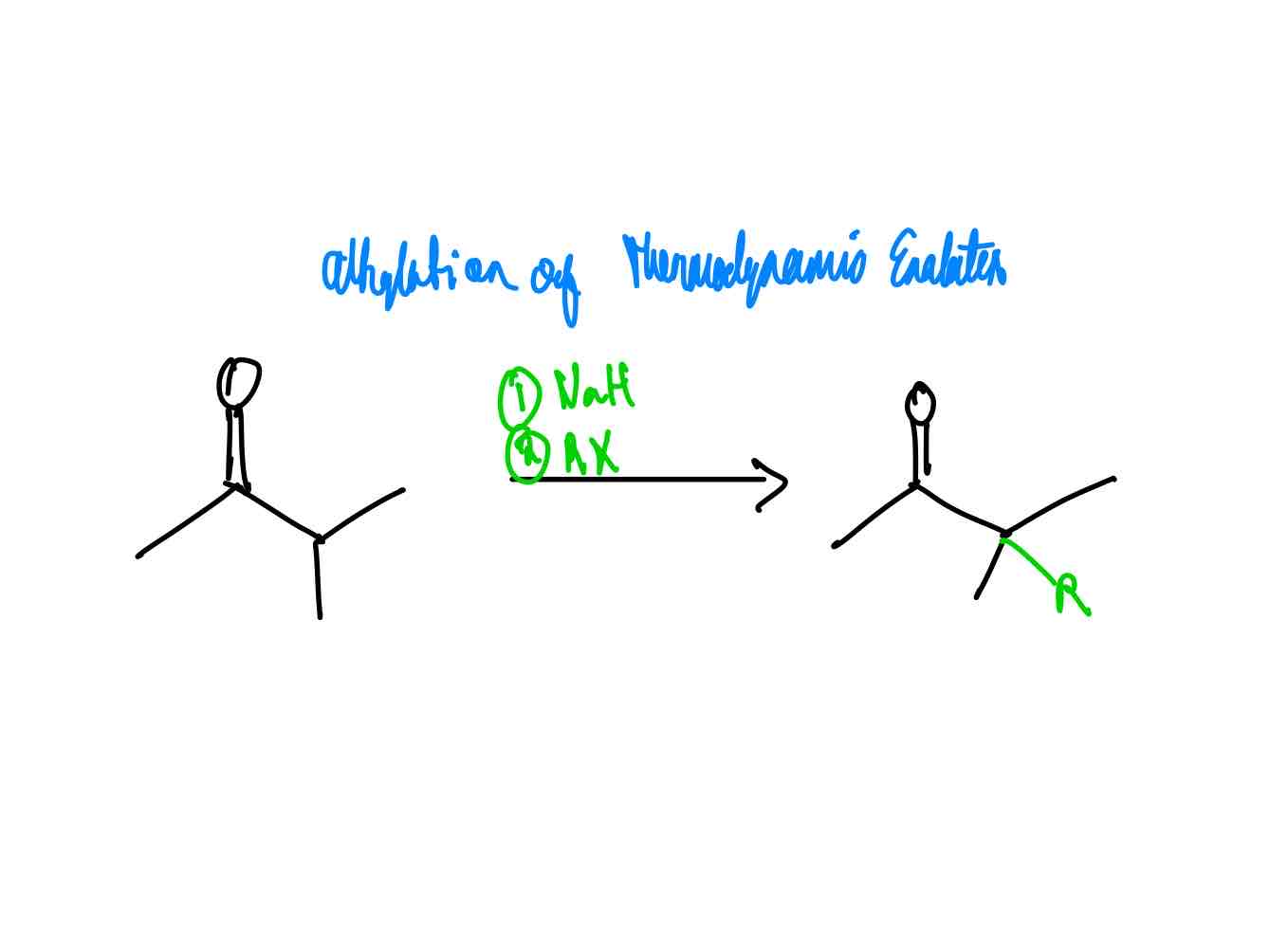
If you wanted to alkylate the α position of a carbonyl compound, how would you alkylate it via the thermodynamic enolate?
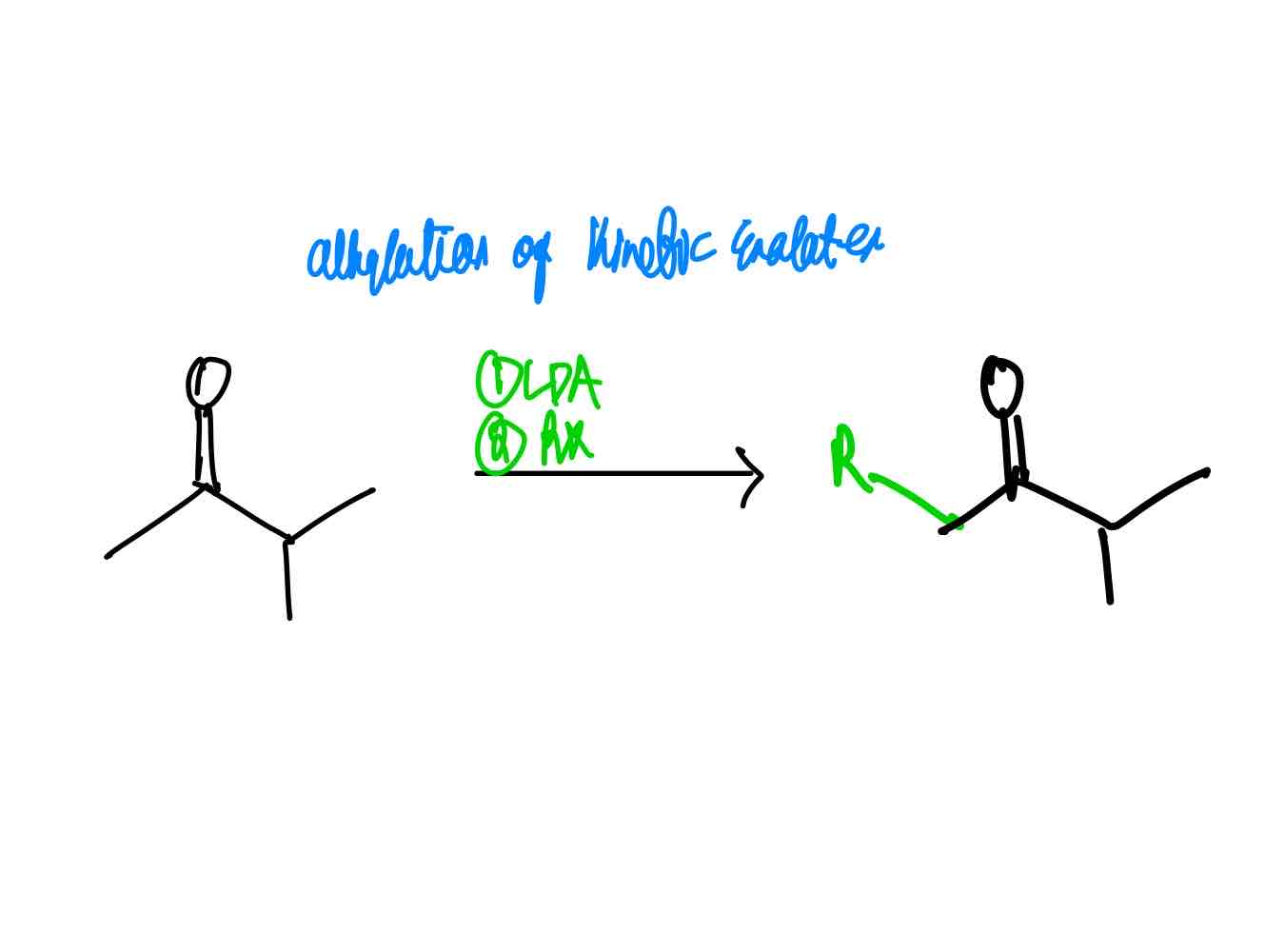
If you wanted to alkylate the α position of a carbonyl compound, how would you alkylate it via the kinetic enolate?
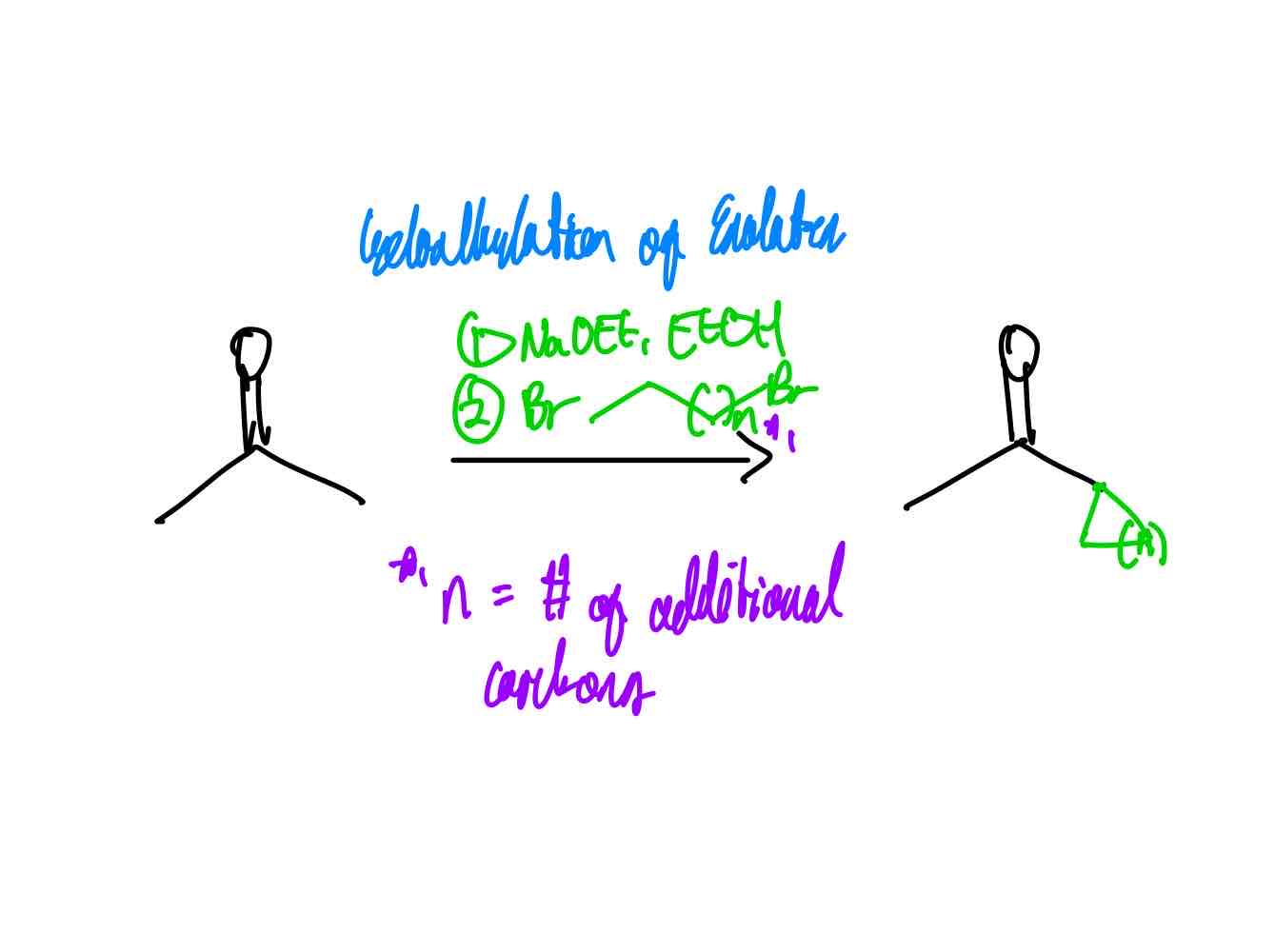
If you wanted to cycloalkylate a carbonyl compound at the α position, how would you proceed?
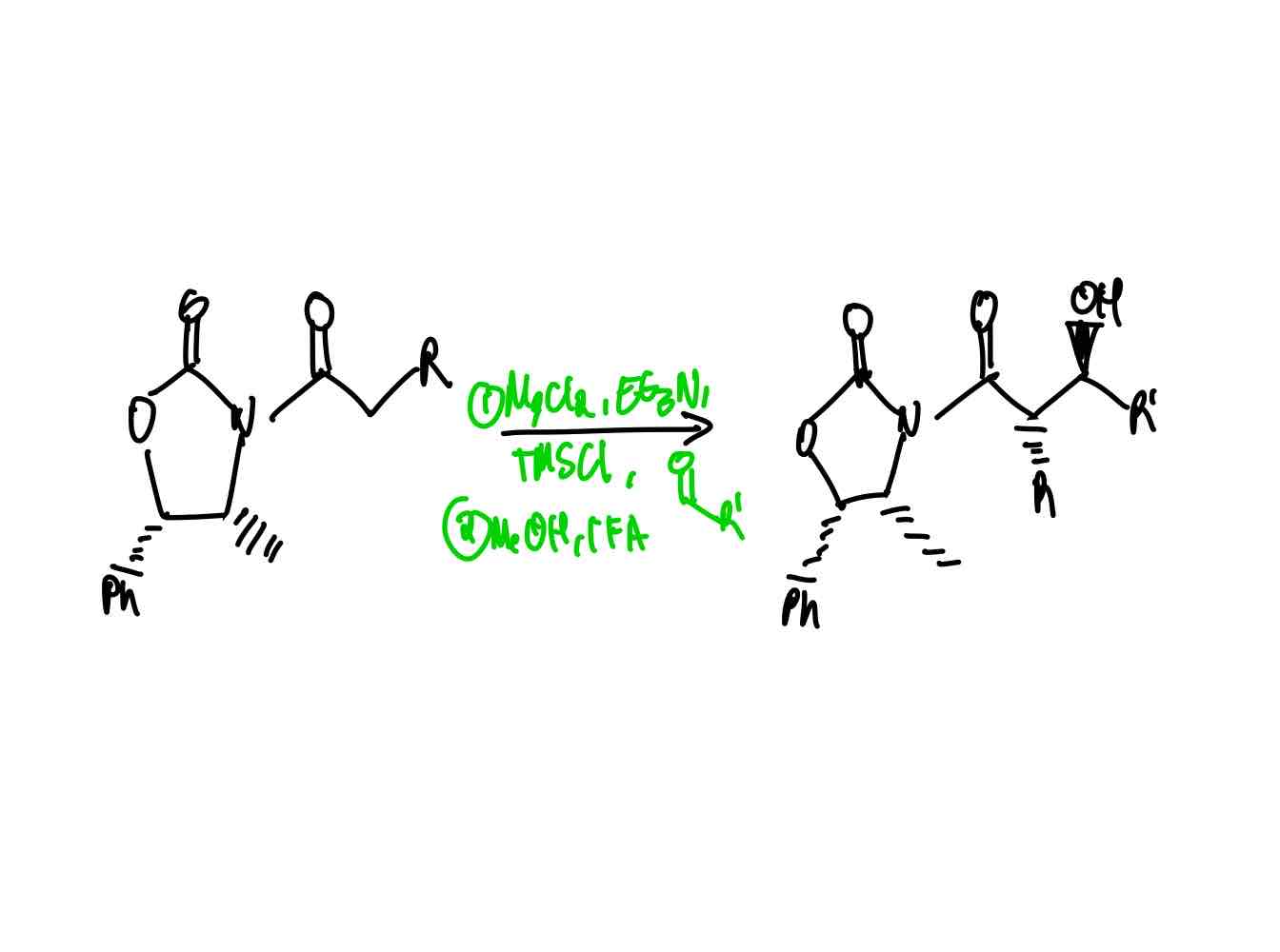
When you are about to make a chiral centre via alkylation of the α position, how can you ensure the desired stereochemistry?
Evans auxiliary groups.
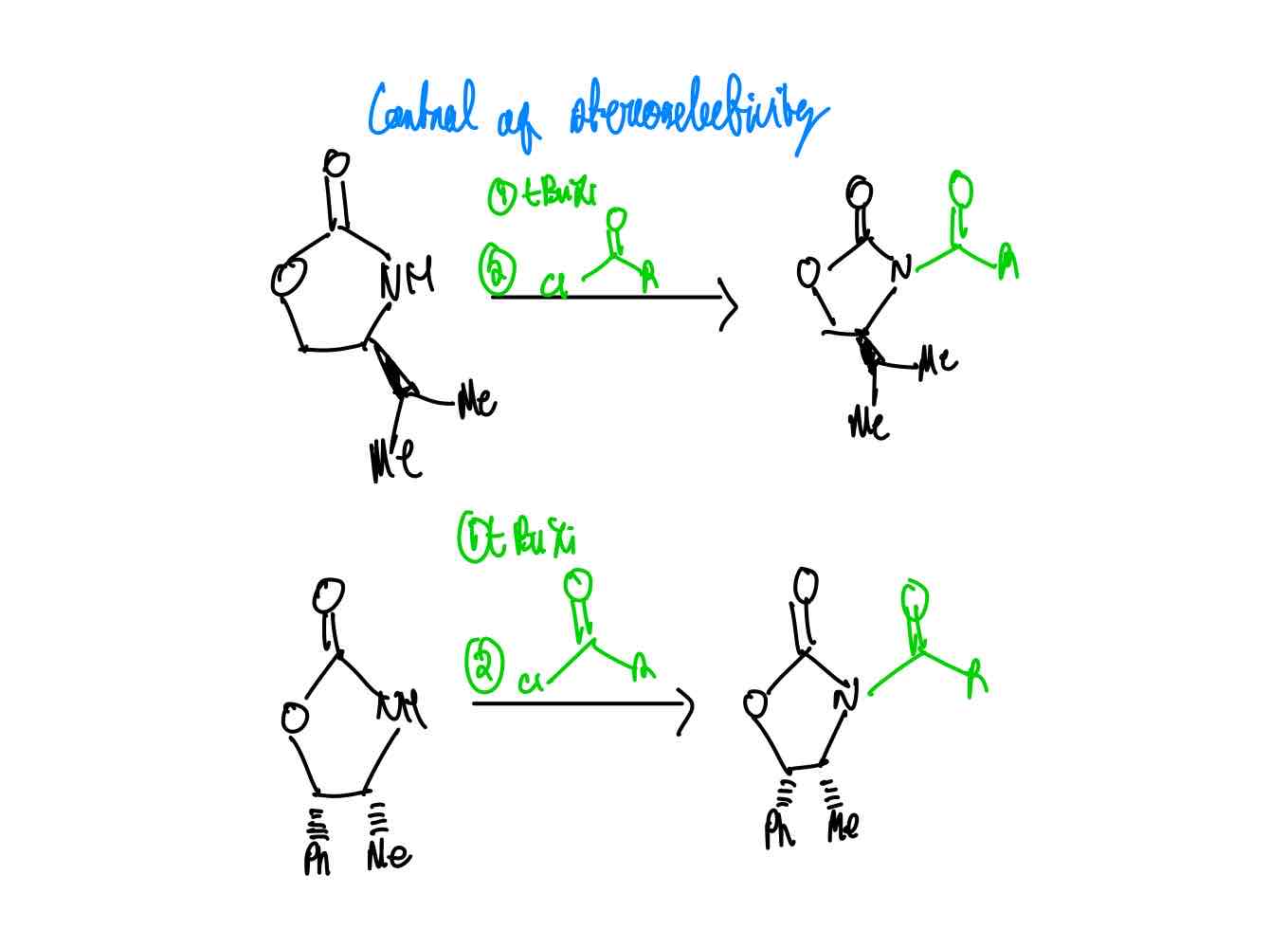
What are the two famous Evans auxiliary groups that assists you in ensuring the desired stereochemistry of a chiral centre? How do you load each auxiliary?
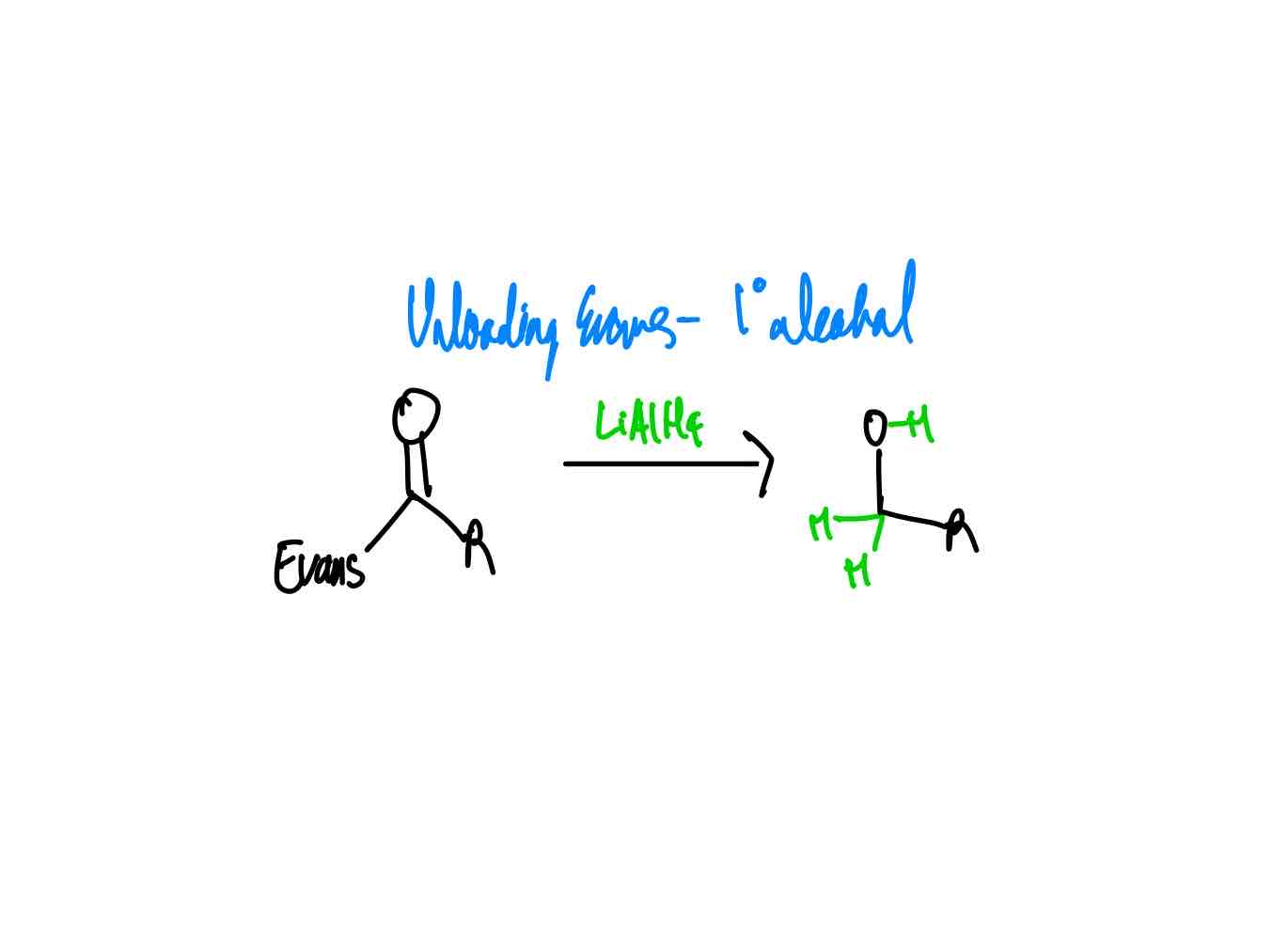
After you have done your alkylation with its correct stereochemistry, how do you remove your auxiliary to get a primary alcohol?
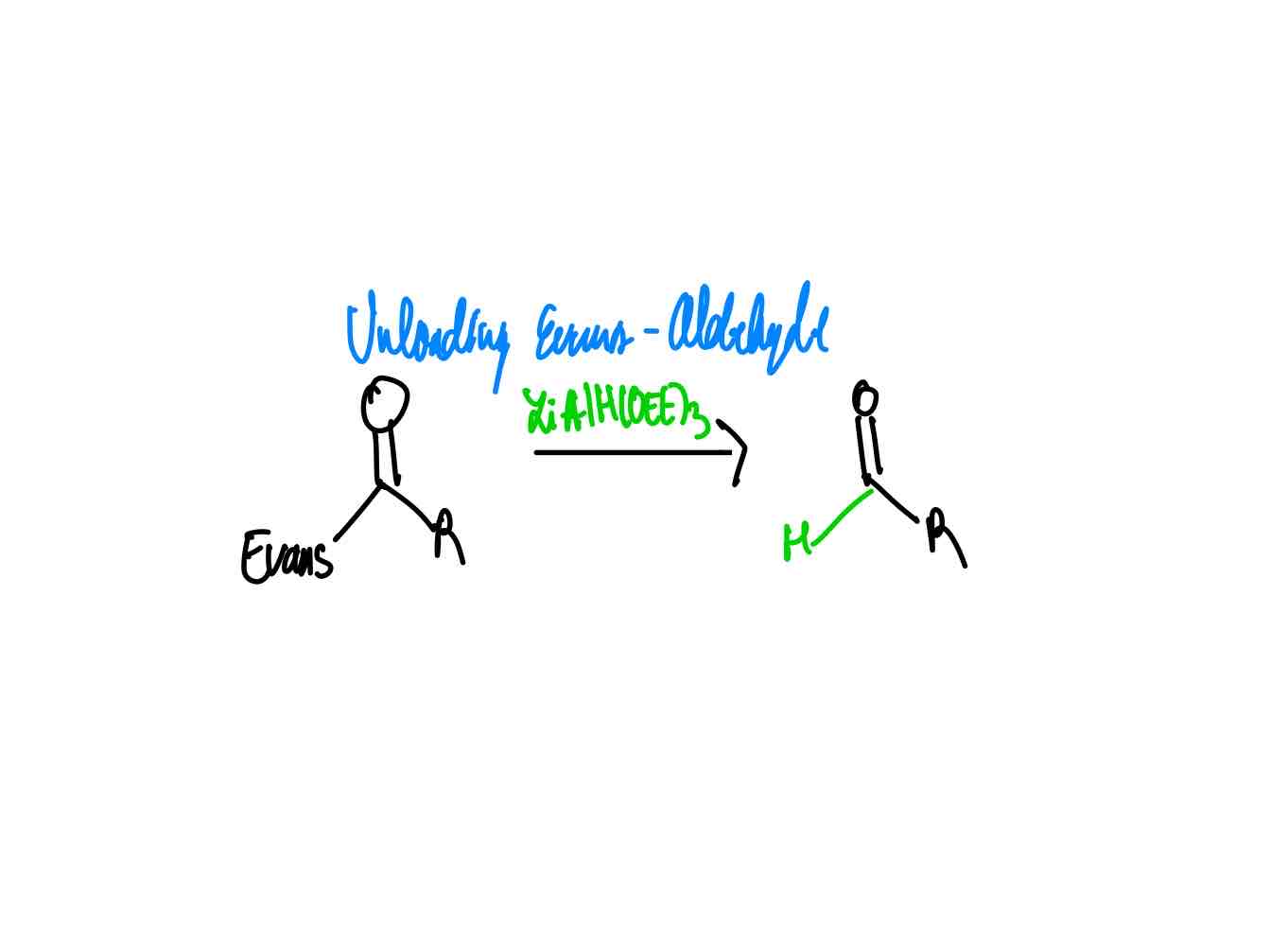
After you have done your alkylation with its correct stereochemistry, how do you remove your auxiliary to get an aldehyde?
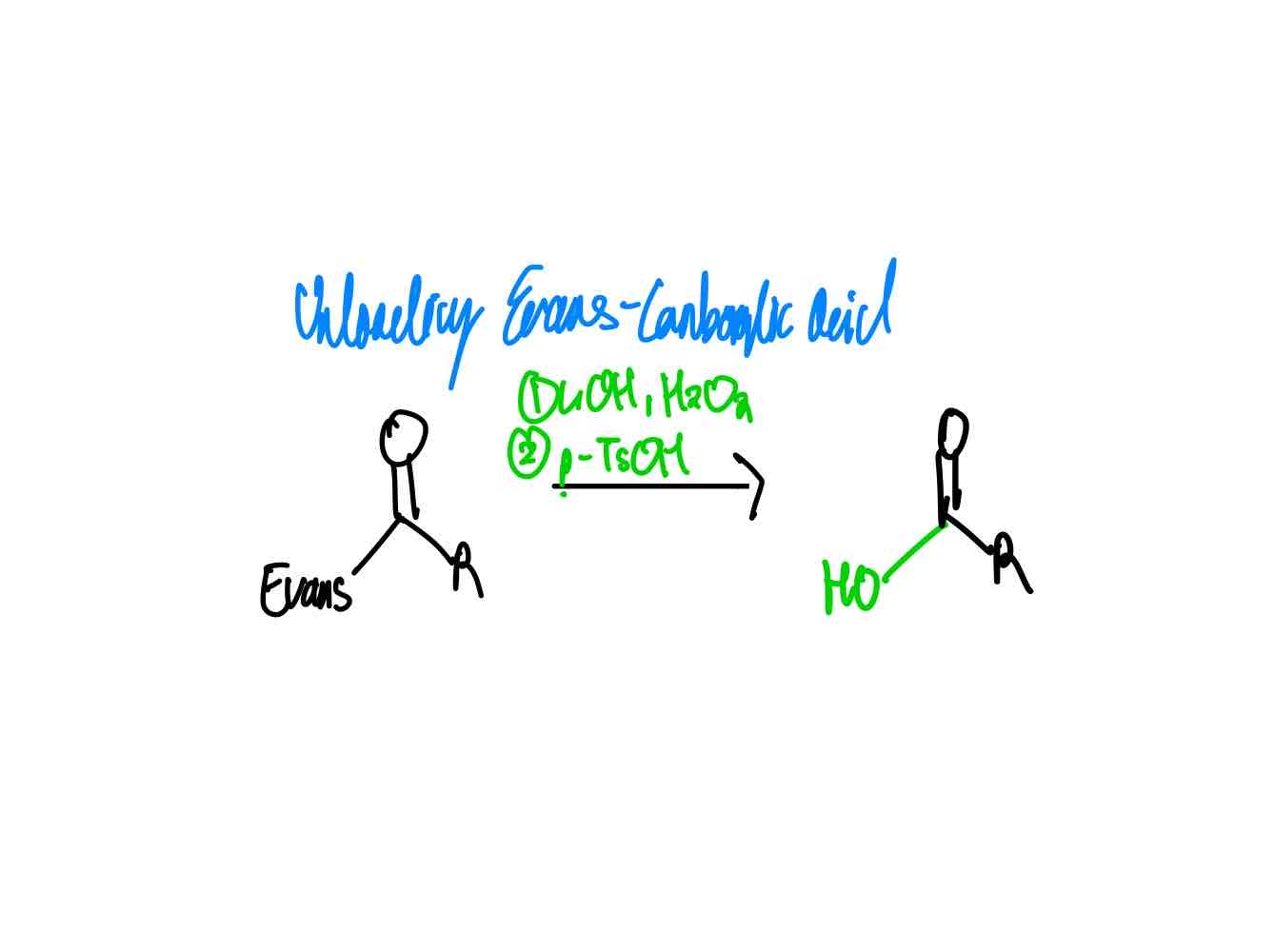
After you have done your alkylation with its correct stereochemistry, how do you remove your auxiliary to get a carboxylic acid?
After you have done your alkylation with its correct stereochemistry, how do you remove your auxiliary to get an alcohol and protect the hydroxy in one reaction?
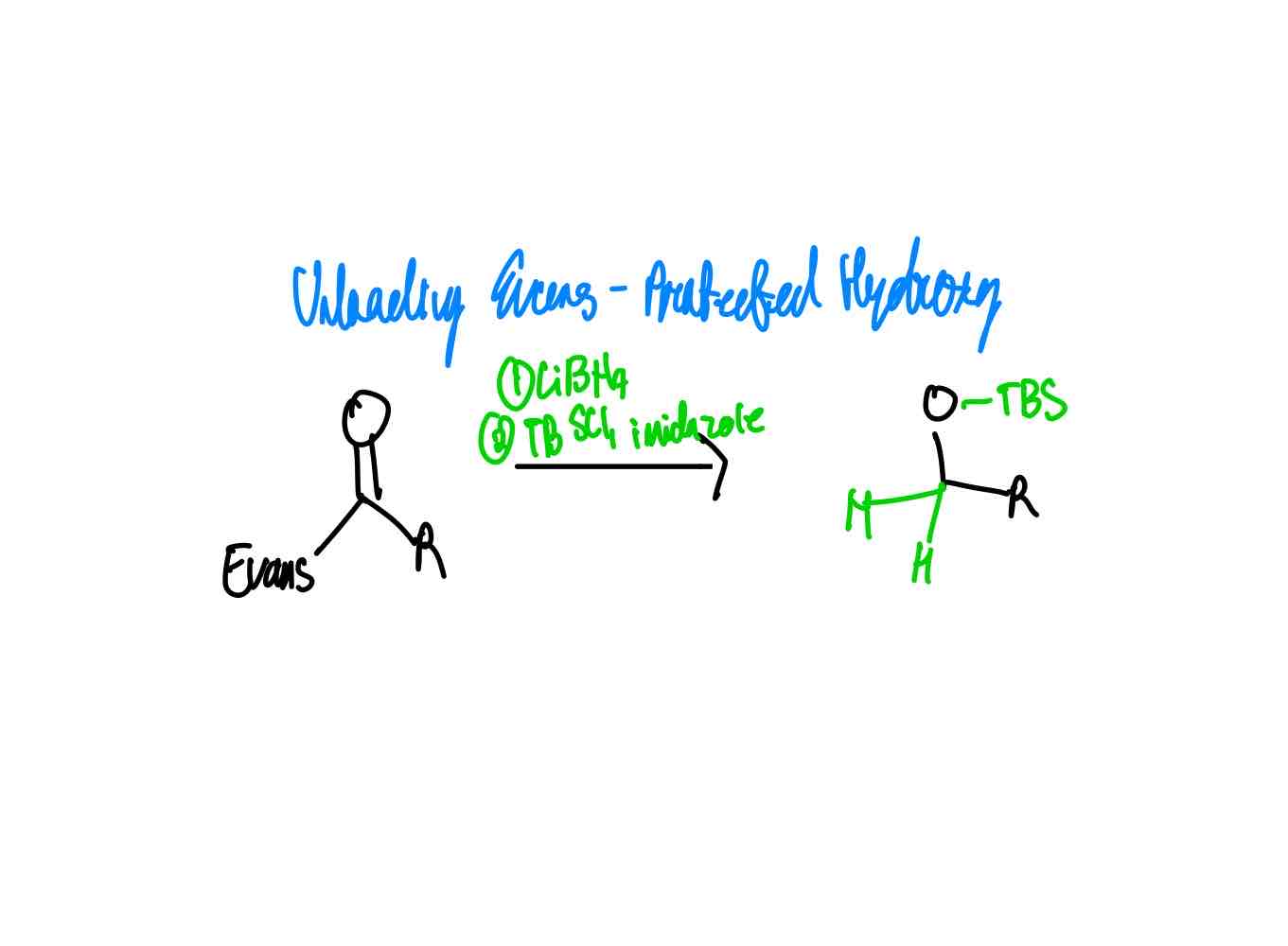
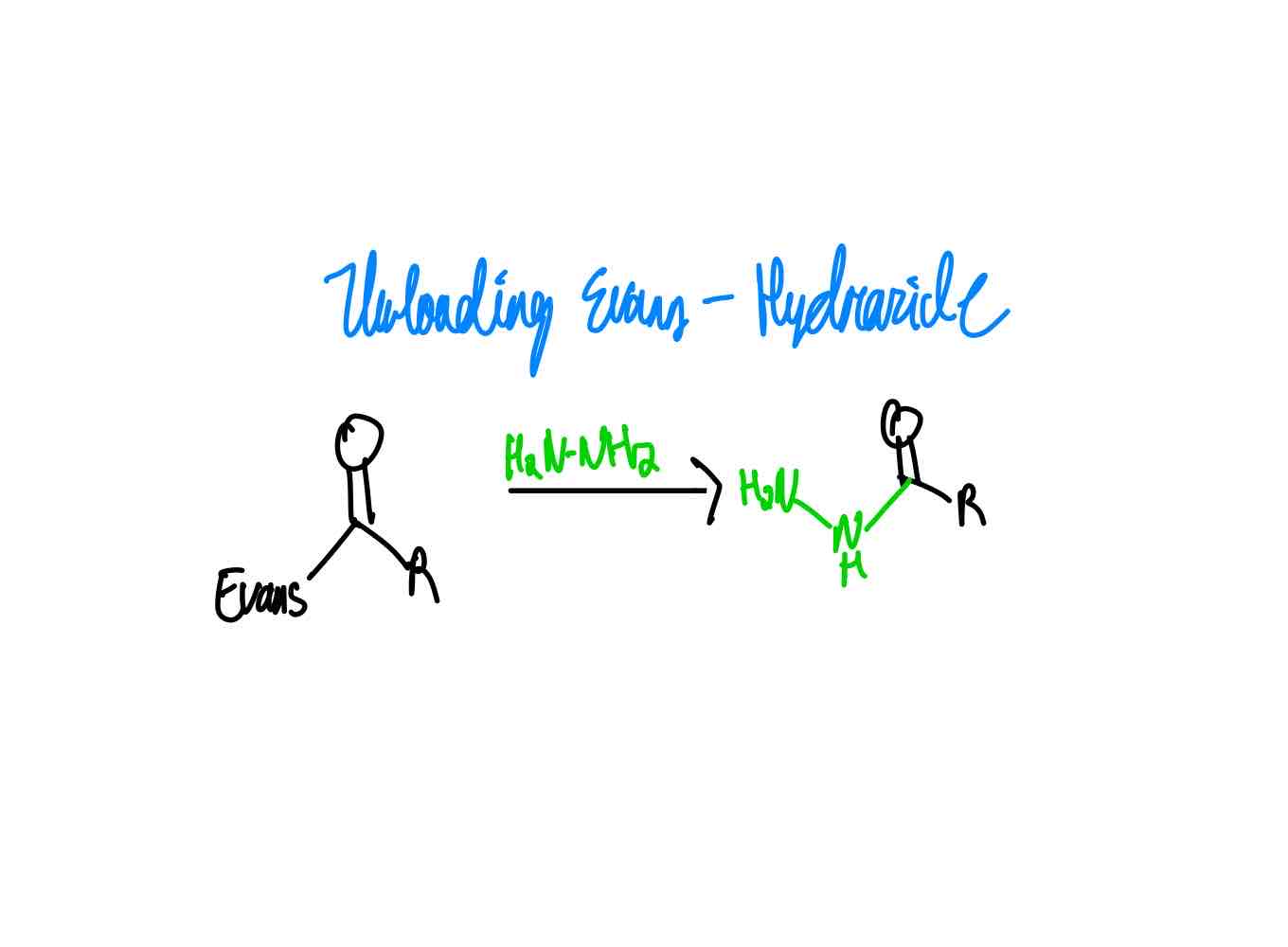
After you have done your alkylation with its correct stereochemistry, how do you remove your auxiliary to get a hydrazide?
If you wanted to install NH2 at the α position of an enolate, how would you proceed?
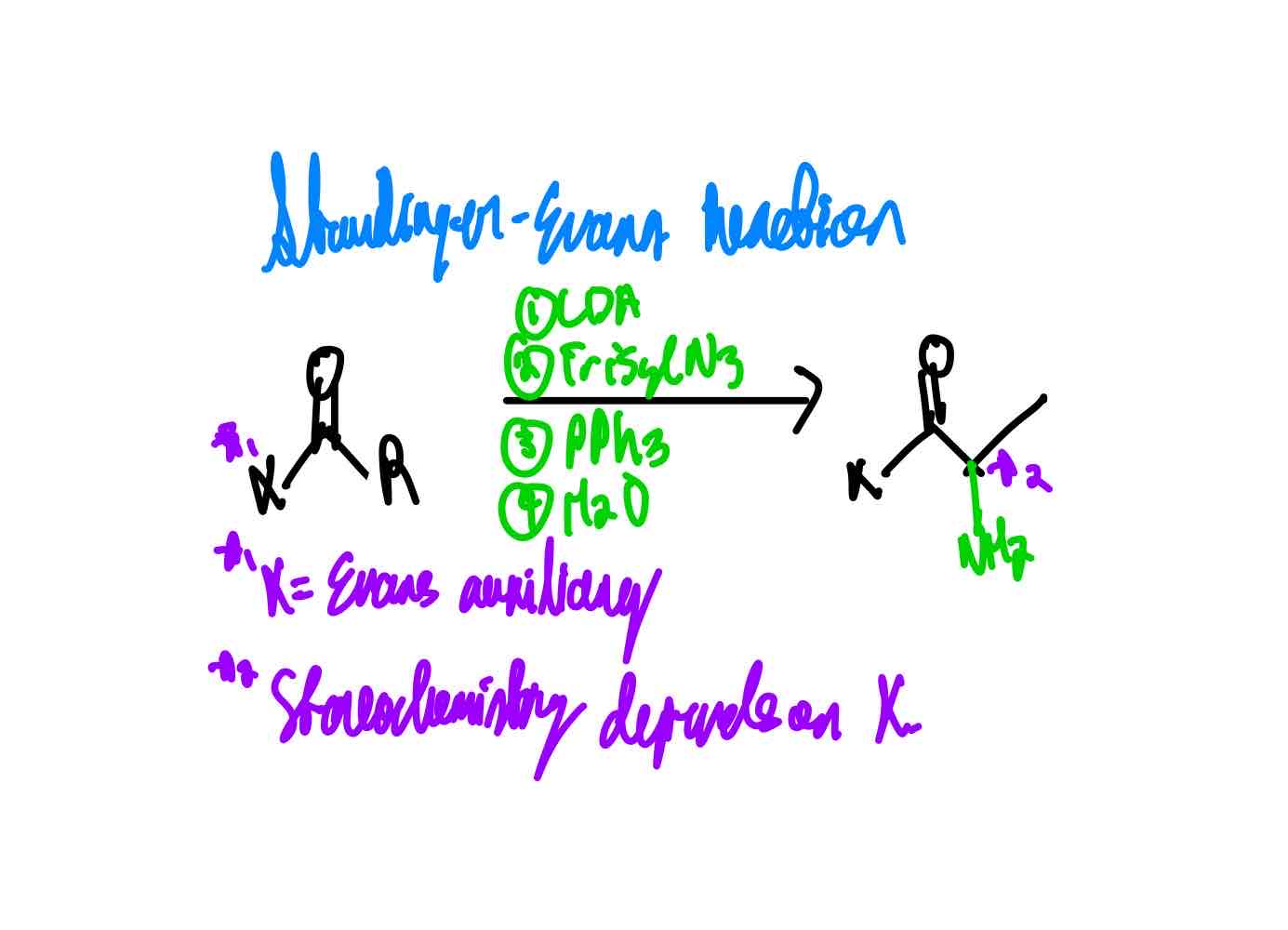
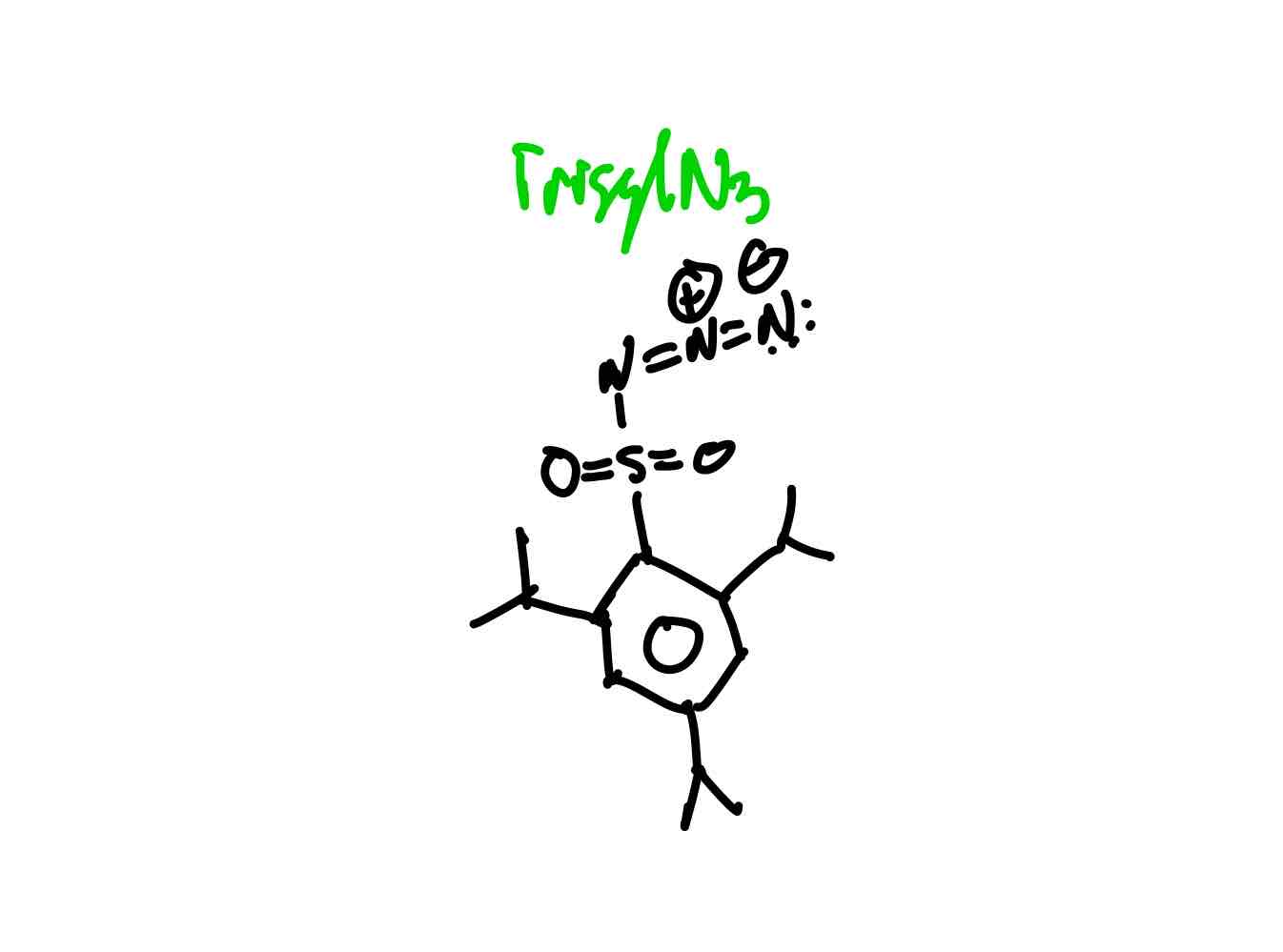
What does 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl (TrisylN3) look like?
If you wanted to install OH at the α position of an enolate, how would you proceed?
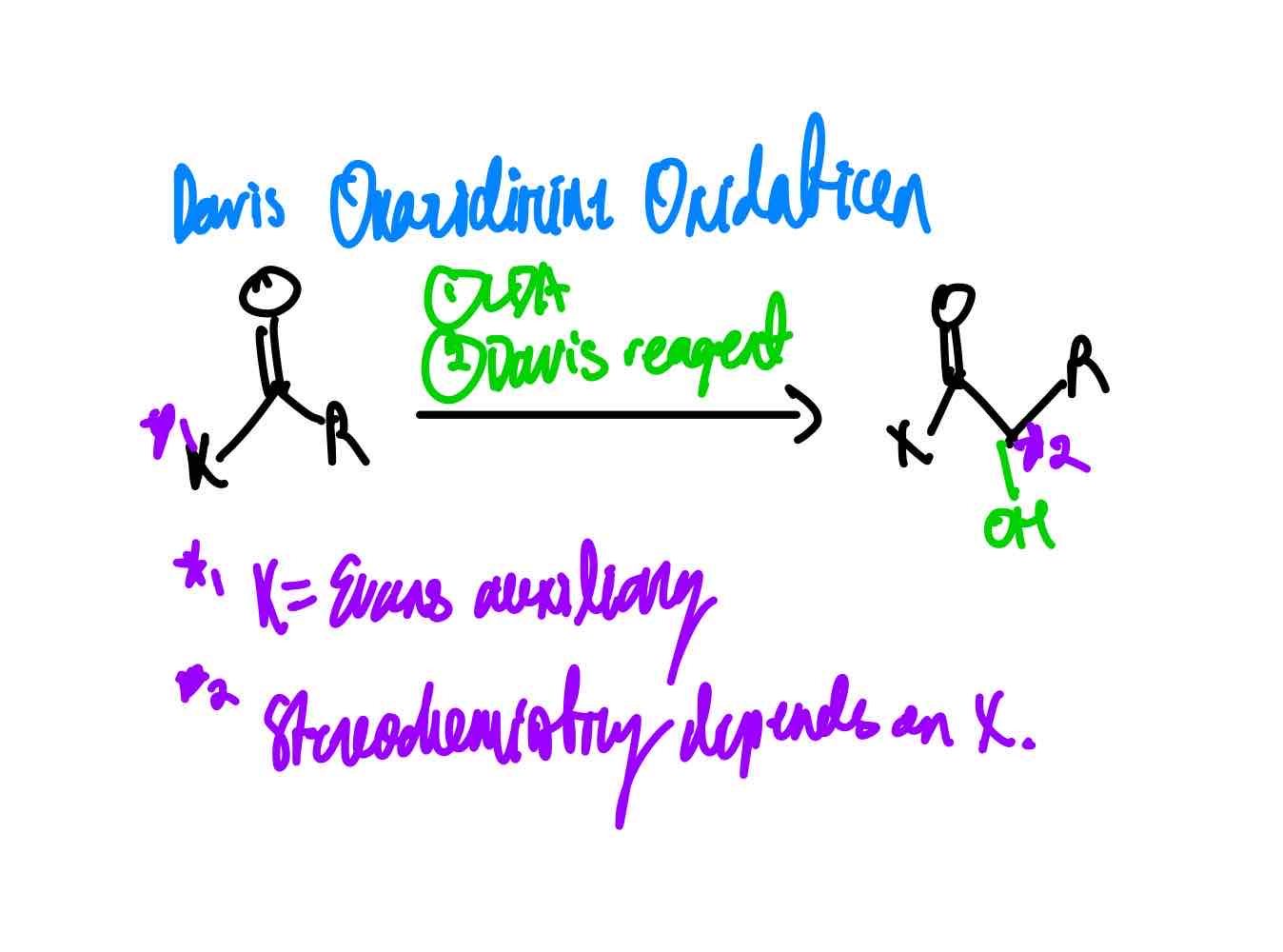
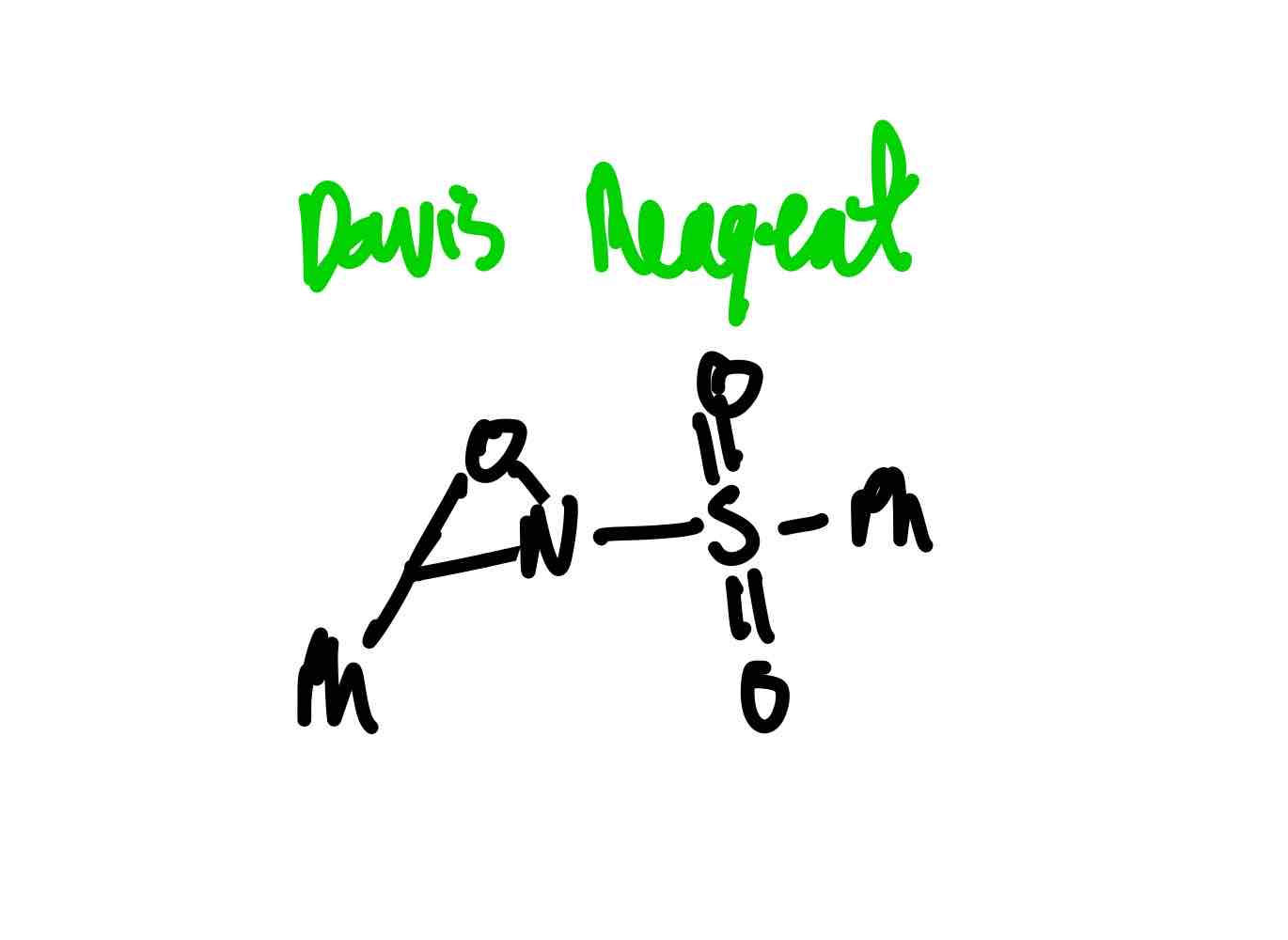
What does the Davis reagent look like?
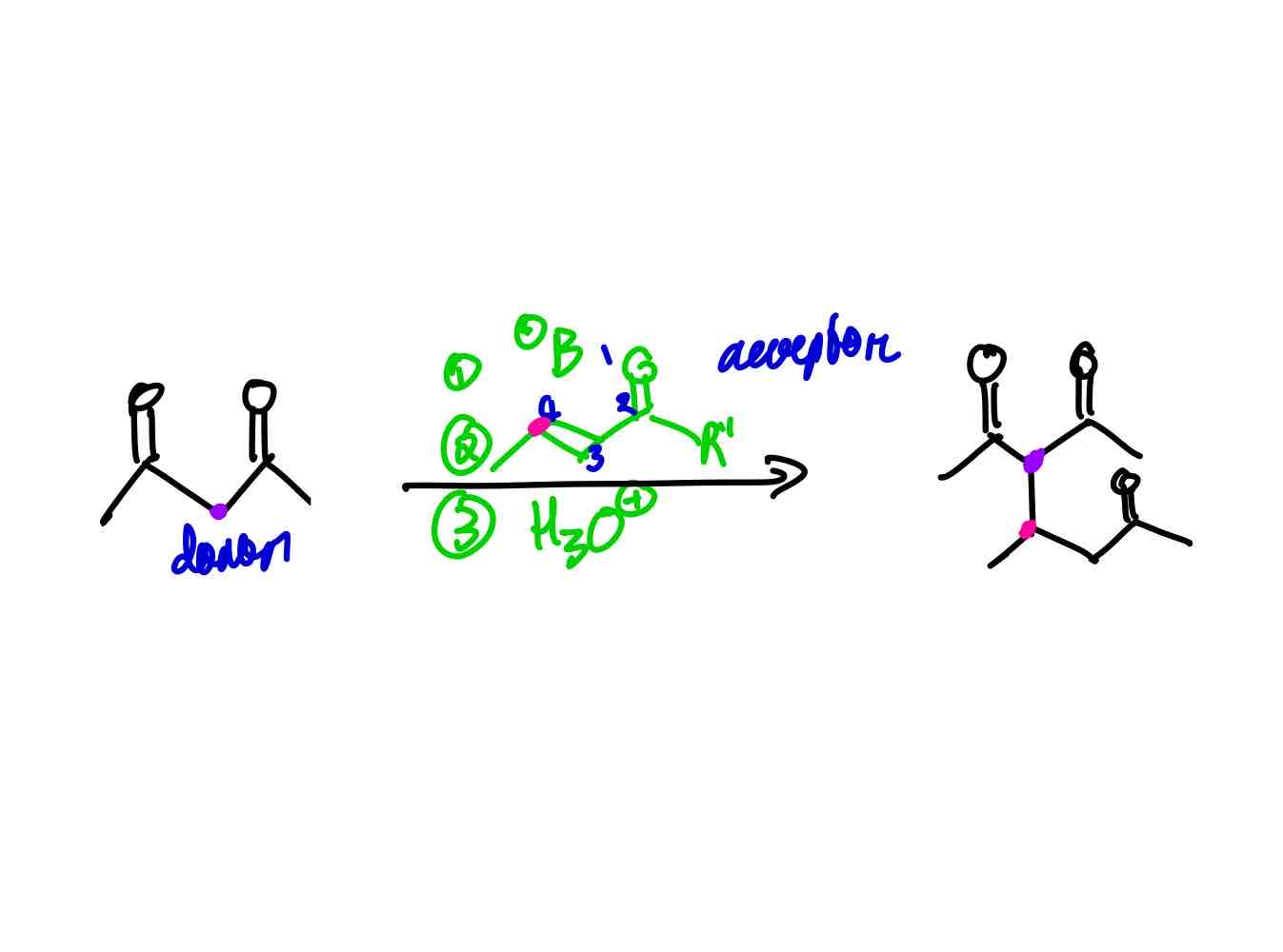
What is a Michael Donor? What is a Michael acceptor?
A Michael donor is a nucleophile that can donate electrons, typically a highly stabilized enolate or an anion (like Gilman’s reagent), while a Michael acceptor is an electrophile, often an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound that can accept electrons.
Give an example of how a Michael addition works.
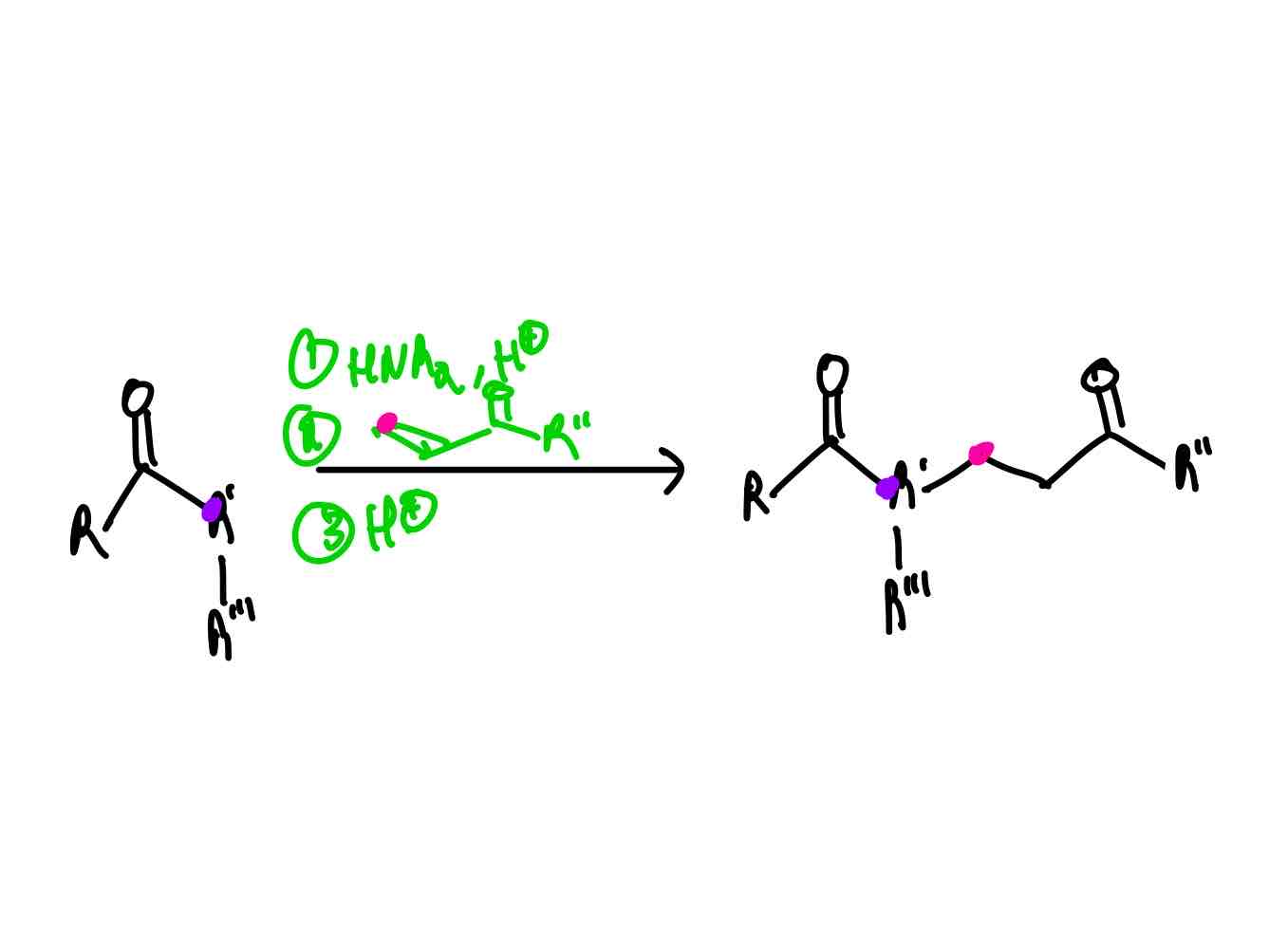
If you wanted to perform a Michael addition but you did not have a stabilized enolate, how would you perform this?
What reagents would you use in order to create an aldol syn product with the α R group and hydroxy group on the back side?
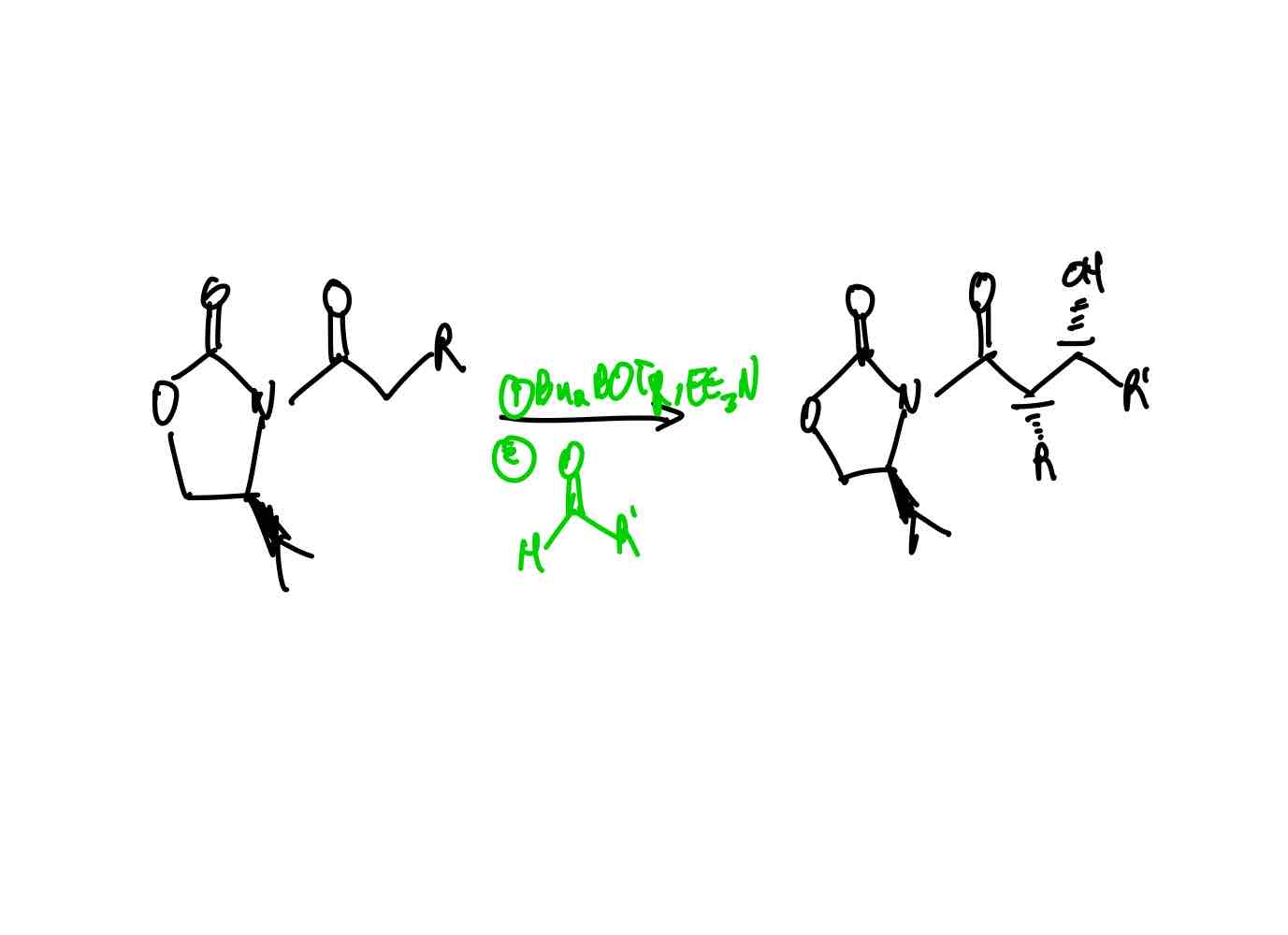
What reagents would you use in order to create an aldol syn product with the α R group and hydroxy group on the front side?

What reagents would you use in order to create an aldol anti product with the α R group on the front side and hydroxy group on the back side?
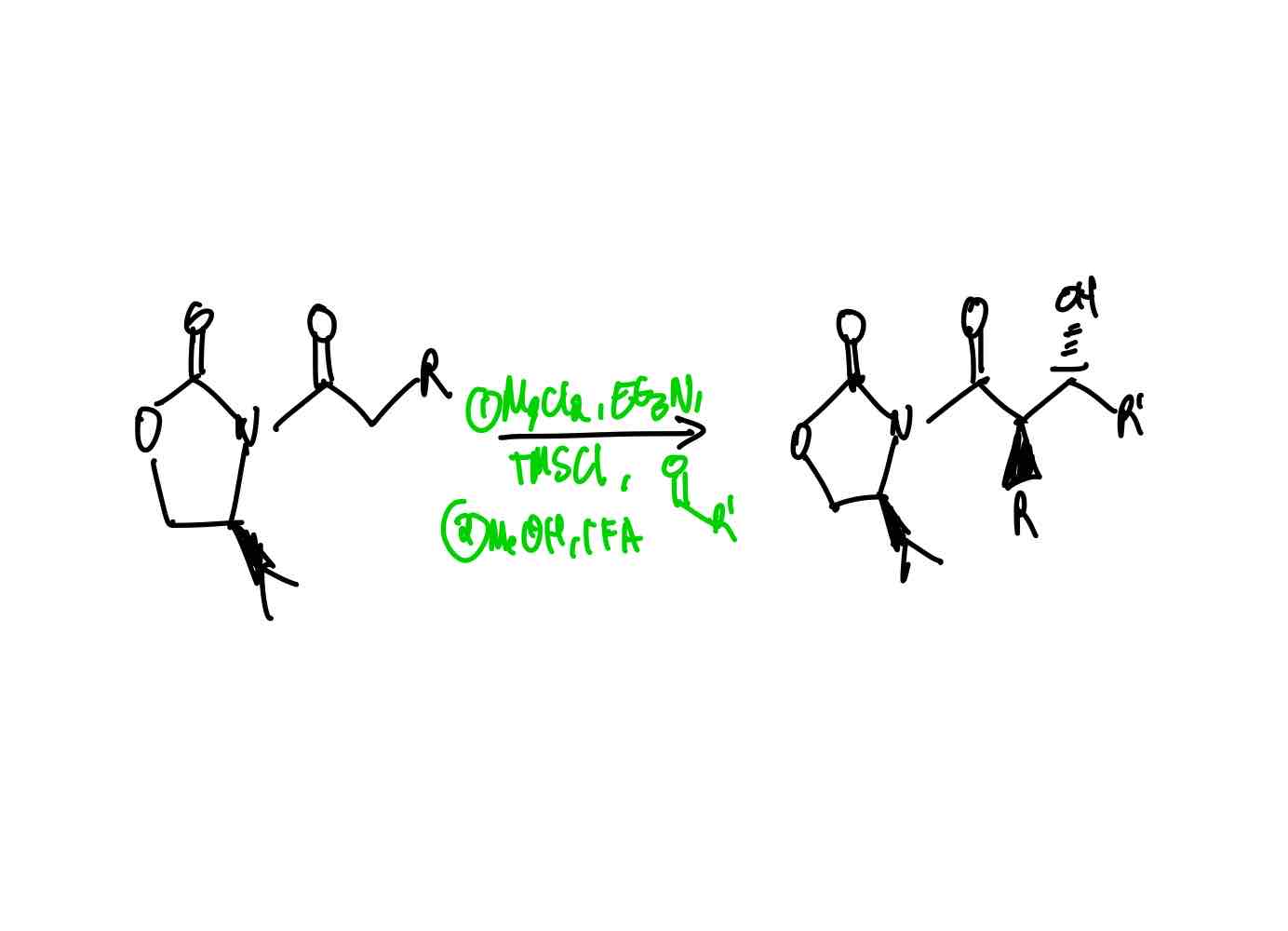
What reagents would you use in order to create an aldol anti product with the α R group on the back side and hydroxy group on the front side?