Hazards, Disaster, Earthquakes and Volcanic Hazards
5.0(6)
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/179
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
1
New cards
HAZARDS (1)
Potentially damaging physical events, phenomena, or human activities that may cause injury, loss of life, damage to property, social and economic disruption, or environmental degradation (UNISDR, 2007)
2
New cards
HAZARDS (2)
A dangerous (natural) phenomenon, substance, human activity or condition that may cause loss of life, injury or other health impacts, property damage, loss of livelihood and services, social and economic disruption, or environmental damage (RA No. 10121)
3
New cards
HAZARDS (3)
Potential or existing condition that may cause harm to people or damage to property or the environment (Australian Natural Disasters Organization)
4
New cards
**TYPES OF HAZARDS (According to Origin)**
Natural, or Anthropogenic Origin
5
New cards
GEOLOGIC Hazards
Natural earth processes or phenomena
(Ex: Tsunami, earthquakes, volcanic eruption)
(Ex: Tsunami, earthquakes, volcanic eruption)
6
New cards
BIOLOGICAL Hazards
Ex: Plague, epidemics
7
New cards
EXTRATERRESTRIAL Hazards
Ex: Meteorites, asteroids, space satellites
8
New cards
HYDRO-METEOROLOGICAL Hazards
Ex: Combination of meteorological and hydrological hazards
9
New cards
HYDROLOGICAL Hazards
Ex: flash floods, storm surges, rain-induced landslides
10
New cards
METEOROLOGICAL Hazards
Ex: High winds, high seas, storm surges
11
New cards
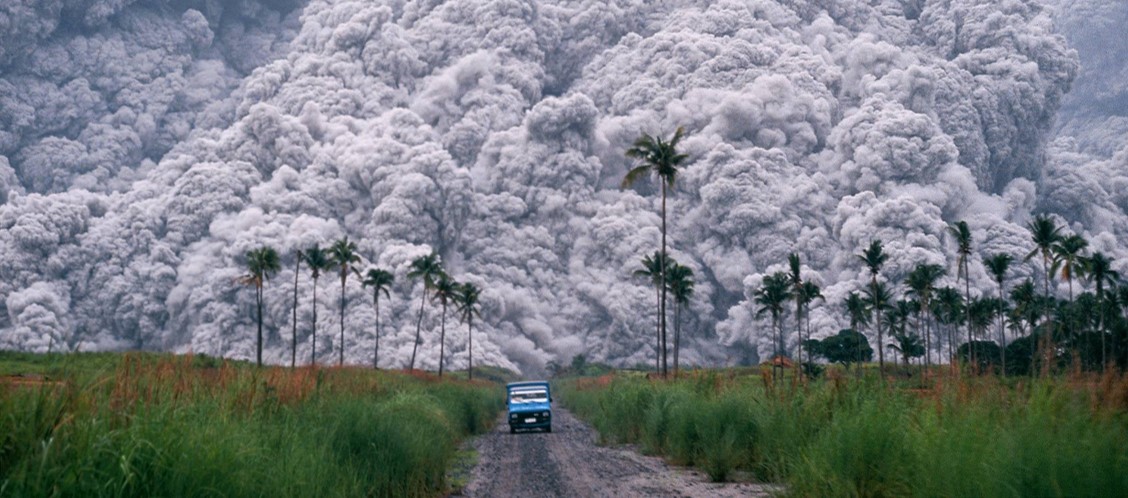

1991 Pinatubo Eruption
Geological Hazard
12
New cards
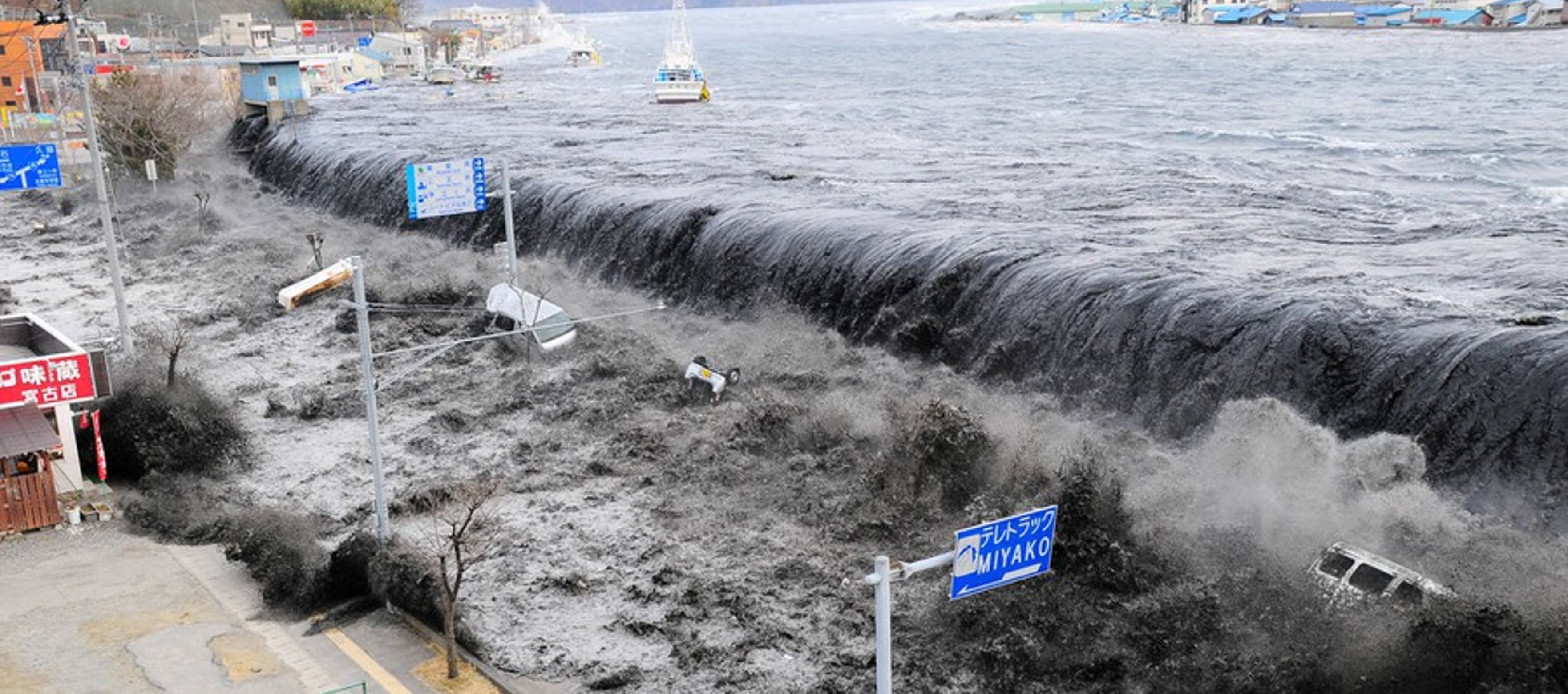

2011 Japan Tsunami
Geological & Hydrological Hazard
13
New cards
Covid 19
Biological Hazard
14
New cards
2013 Typhoon Yolanda
Hydrometeorological Hazard
15
New cards
Jakarta flash flood
Hydrological Hazard
16
New cards
2013 Russia Meteorite Impact
Meteorological Hazard
17
New cards
Zika Virus - induces Birth Defects
Biological Hazard
18
New cards
Hazards of Natural Origin
Geologic, Biological, Extraterrestrial, Hydro-meteorological, Hydrological, Meteorological Hazard
19
New cards
Hazards of Anthropogenic Origin
Technological, Environmental, and Socio-Economic, Political, and Security Hazard
20
New cards
**TECHNOLOGICAL HAZARD**
Little or no warning to precede the incident. Originate from industrial accidents, dangerous procedures, infrastructure failures, or certain human activities. May cause loss of life or injury, property damage, social and economic disruption, or environmental degradation
21
New cards
**ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARD**
Pose a threat from the surrounding environment. Encompassing the broad spectrum of acute and chronic effects of industrial, agricultural, and naturally occurring microorganisms, chemicals and radiation in our soil, water, air, food, and wastes
22
New cards
**SOCIO-ECONIMIC, POLITICAL, AND SECURITY HAZARD**
Caused by criminal and human violence. Pose a threat to the security of a great number of people. Motivated perhaps by political or economic reasons
23
New cards
**Adsorb**
Di totally naabosrb parang naattract or nagaacumalate lang; vicinity of the body
24
New cards
**Absorb**
Napupunta sa loob
25
New cards
**Acute**
short, minor
26
New cards
**Chronic**
long-term, major
27
New cards
MIINAMATA DISEASE
* miinamata river, dumped mercury by one of the companies, tap water ng mga tao yon
* post-war
* neurological disease caused by severe mercury poisoning.
* A congenital form of the disease can also affect fetuses in the womb and may cause cerebral palsy.
* Signs and symptoms include ataxia, numbness in the hands and feet, general muscle weakness, loss of peripheral vision, and damage to hearing and speech. In extreme cases, insanity, paralysis, coma, and death follow within weeks of the onset of symptoms.
* post-war
* neurological disease caused by severe mercury poisoning.
* A congenital form of the disease can also affect fetuses in the womb and may cause cerebral palsy.
* Signs and symptoms include ataxia, numbness in the hands and feet, general muscle weakness, loss of peripheral vision, and damage to hearing and speech. In extreme cases, insanity, paralysis, coma, and death follow within weeks of the onset of symptoms.
28
New cards
MARAWI SIEGE
**Socio-Economic, Political, and Security Hazard**
29
New cards
**TYPES OF HAZARDS (According to Onset)**
Sudden and Slow Onset
30
New cards
Sudden Onset
* Little or no warning
* Minimal time to prepare
* (Ex: Tsunami, Earthquakes)
* Minimal time to prepare
* (Ex: Tsunami, Earthquakes)
31
New cards
Slow Onset
* Slow to develop (Ex: Drought, Civil Strife)
32
New cards
Stages of Slow Onset
Situation develops > Emergency > Disaster
33
New cards
**EFFECTS OF HAZARDS**
* Primary Effect
* Secondary Effect
* Tertiary Effect
* Secondary Effect
* Tertiary Effect
34
New cards
**PRIMARY EFFECT**
Result of the process itself (Ex: Collapse of building during an earthquake, landslide, or hurricane
Water damage during flood)
Water damage during flood)
35
New cards
**SECONDARY EFFECT**
Caused by the primary effect (Ex: Fires due to earthquakes, Flooding caused by a landslide into a lake or river)
36
New cards
**TERTIARY EFFECT**
Long term effects that are set off as a result of a primary event (Ex: Loss of habitat caused by a flood, Crop failure due to volcanic eruption)
37
New cards
Destruction of houses due to tsunami
Primary
38
New cards
Fires after 2011 Japan Tsunami
Secondary
39
New cards
Injury, loss of life, habitat and livelihood
Tertiary
40
New cards
**HAZARD ANALYSIS**
Identification, study, and monitoring of any hazard to determine its potential, origin, characteristics, and behavior (UNISDR, 2007)
Its purpose is to:
* Provide descriptions of the hazards
* Help in setting priorities corresponding to the need for protection
* Assist in designing the appropriate DRRM system, plan, programs, and services.
Its purpose is to:
* Provide descriptions of the hazards
* Help in setting priorities corresponding to the need for protection
* Assist in designing the appropriate DRRM system, plan, programs, and services.
41
New cards
**COMMUNITY HAZARDS AND DISASTER HISTORY CONSTRUCTION**
* Existing hazards and the disasters that the community experienced are identified.
* Uses records of past hazard events in the community
* Uses records of past hazard events in the community
42
New cards
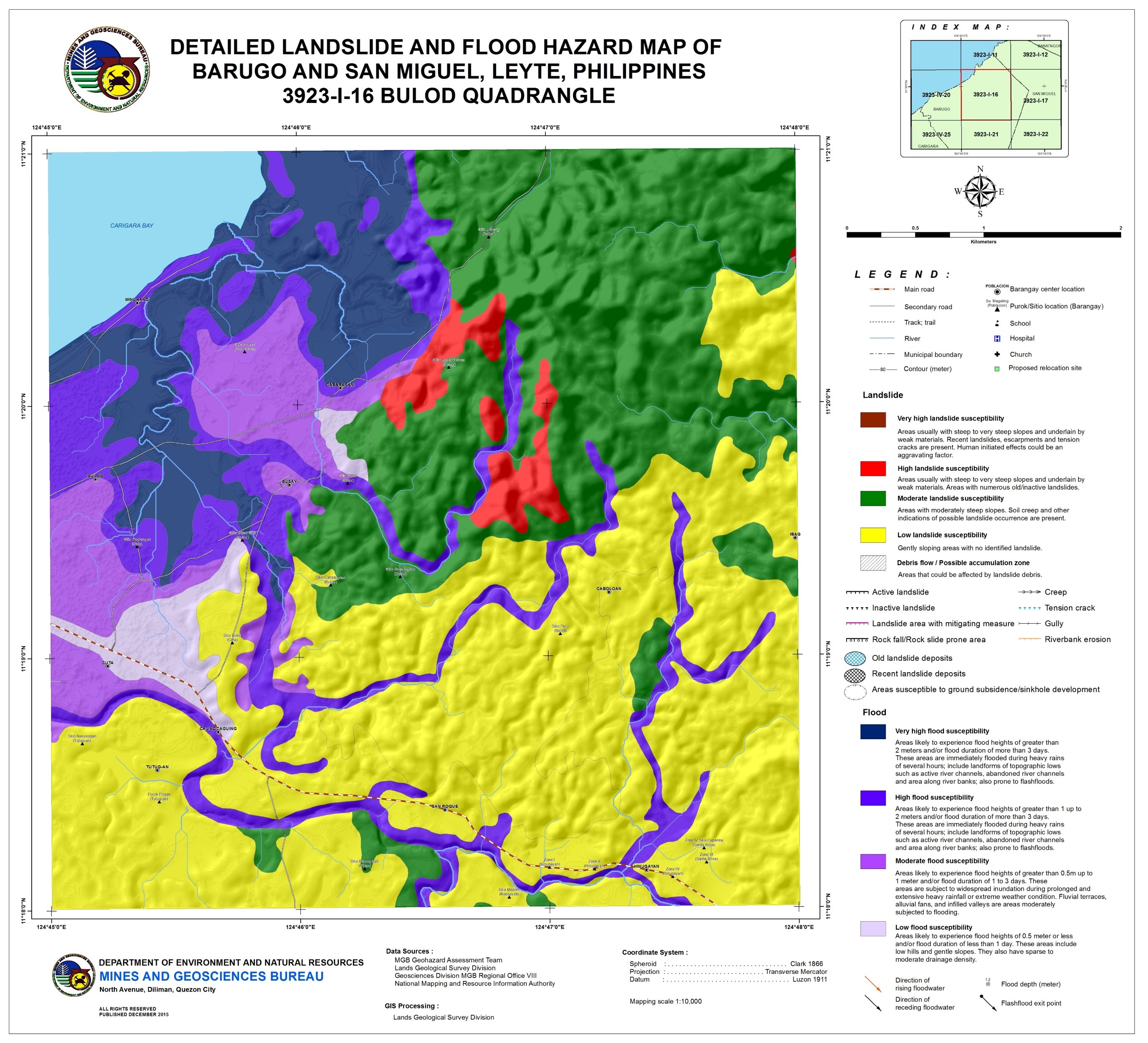
**HAZARD AND VULNERABILITY MAPPING**
Areas in the community that are vulnerable to a specific hazard are identified and then located in the map.
43
New cards
Hazard and Vulnerability Map
44
New cards
**FACTOR ANALYSIS**
Describes the characteristics of the hazard in terms of the following (Heijmans and Victoria, 2001):
* Frequency
* Duration
* Speed of Onset
* Intensity
* Probability
* Forewarning
* Manageability
* Frequency
* Duration
* Speed of Onset
* Intensity
* Probability
* Forewarning
* Manageability
45
New cards
DISASTER (1)
Disaster is a serious disruption of the functioning of a society, causing widespread human, material, or environmental losses which exceed the availability of the affected society to cope using only its own resources (RA No. 10121; UN DMTP, 1992).
46
New cards
DISASTER (2)
“An event, natural or man-made, sudden or progressive, which impacts with such severity that the affected community has to respond by taking exceptional measures” (Carter, 1991).
47
New cards
DISASTER (3)
“An event which deprives people of life, property or livelihood and which taxes the resources of the survivors beyond their collective capacity to cope” (OFDA)
48
New cards
**DISASTER IN THE PHILIPPINES**
In the PDRRM or Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act 2010, which adopted the definition of UNISDR:
\
“A dangerous phenomenon, substance, human activity, or conditions that may cause loss of life, injury or other health impacts, property damage, loss of livelihood and services, social and economic disruption, or environmental damage.”
\
“A dangerous phenomenon, substance, human activity, or conditions that may cause loss of life, injury or other health impacts, property damage, loss of livelihood and services, social and economic disruption, or environmental damage.”
49
New cards
VULNERABILITY
The extent to which a community’s structure, services, or environment are likely to be damaged or disrupted by the impact of hazard.
50
New cards
EXPOSURE
The number of people, property, systems, or other elements present in hazardous areas that are thereby subject to potential losses (UNISDR, 2011b).
51
New cards
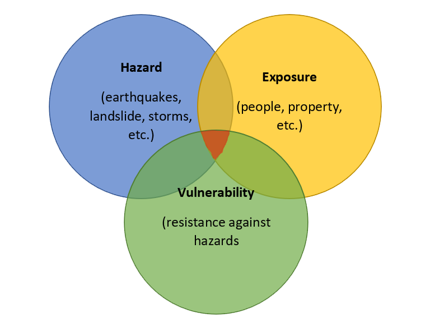
**Disaster Risk**
A disaster caused by a hazard (typhoon, flood, storm surge, earthquake, tsunami, volcanic eruption, landslide, etc.) and its impact on the vulnerability of structures, population, economy, etc.
As such, one can summarize that there is **no risk** if there are **no people to be affected**.
As such, one can summarize that there is **no risk** if there are **no people to be affected**.
52
New cards
**Disaster Risk Formula**
*Disaster Risk = Hazard x Vulnerability x Exposure*
53
New cards
Disaster Prediction
A catastrophic natural event is unlikely to be stopped. As such, the best way is to predict the event and to avoid it as soon as possible.
It is impossible to predict exactly the occurrence of such event, as such, predictable cycles in natural events are used.
It is impossible to predict exactly the occurrence of such event, as such, predictable cycles in natural events are used.
54
New cards
Cyclic Event
These are events that occur at predictable intervals.
\
Most recurring natural events are not truly cyclic due to many factors that affect its behavior.
\
Most events appear to be at random and at unpredictable intervals.
\
Most recurring natural events are not truly cyclic due to many factors that affect its behavior.
\
Most events appear to be at random and at unpredictable intervals.
55
New cards
Forecasting
Scientists cannot predict exactly when an event will occur.
\
Instead they forecast based on experience and studies about the change that a hazardous event will occur in a region within a few decades.
\
Instead they forecast based on experience and studies about the change that a hazardous event will occur in a region within a few decades.
56
New cards
Recurrence Interval
To do forecasting, scientists applies the idea that
*“The past is the key to the future”*
\
These intervals relate to the probability that a natural event of a particular size or magnitude will happen within a certain period of time or within a certain frequency.
*“The past is the key to the future”*
\
These intervals relate to the probability that a natural event of a particular size or magnitude will happen within a certain period of time or within a certain frequency.
57
New cards
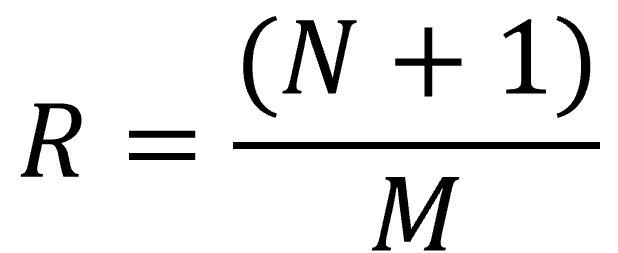
Recurrence Interval Formula
To estimate such interval, we rank each event according to their magnitude from 1 to *n,* then one can get the Recurrence Interval (R) for a given annual maximum by using the formula:
\
\
Where
R – Recurrence Interval
N – Number of data
M – Rank
\
\
Where
R – Recurrence Interval
N – Number of data
M – Rank
58
New cards
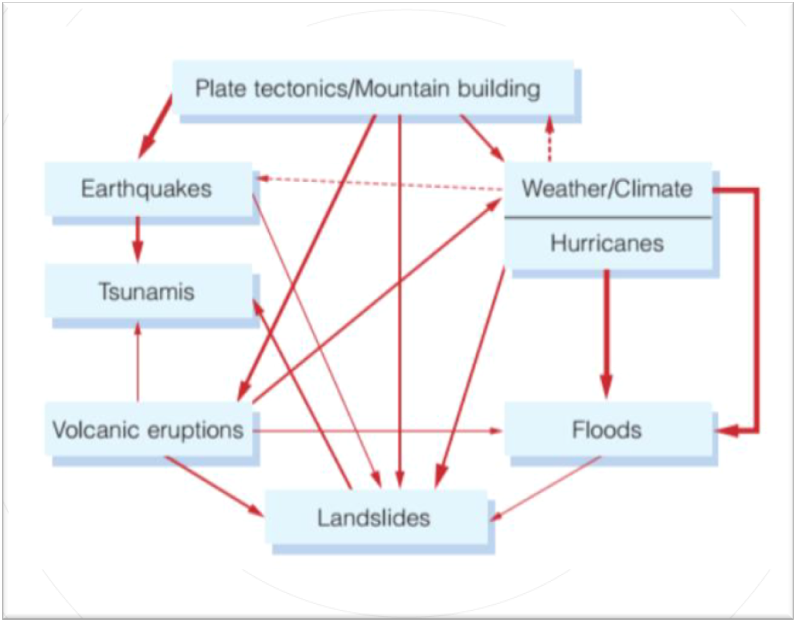
Relationship among events
Some events are directly related to others.
\
For example, a tsunami could be caused by an earthquake or an underwater landslide.
\
For example, a tsunami could be caused by an earthquake or an underwater landslide.
59
New cards
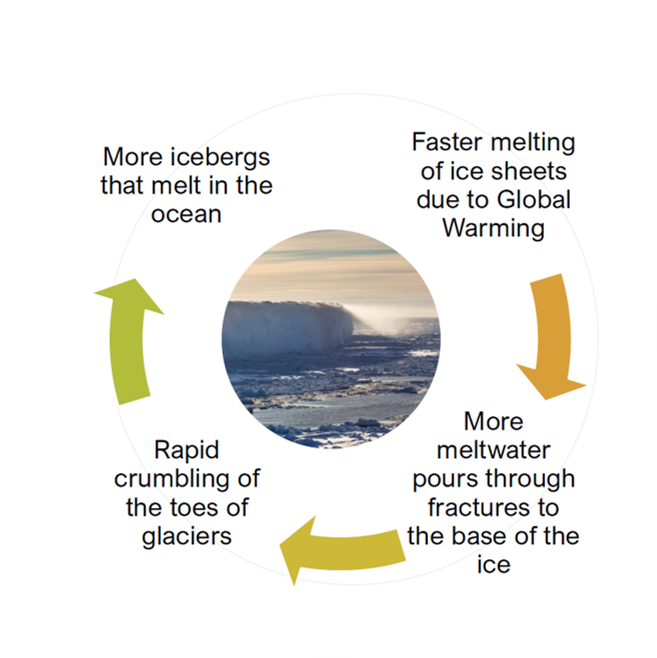
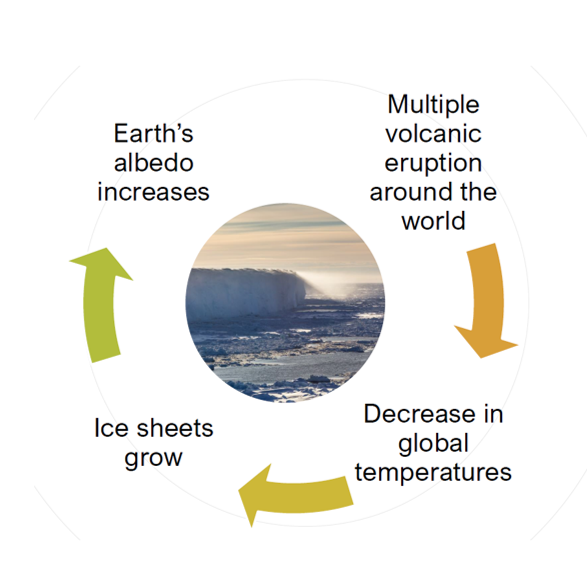
Feedback Effect
Some processes result in more rapid changes, called **feedback effect**.
60
New cards
Precursor Events
Some major natural events are preceded by a series of smaller **precursor events**.
\
These events could be used as a warning of an impending disaster.
\
These events could be used as a warning of an impending disaster.
61
New cards
Mitigating Hazards
Refers to the efforts to prepare for a disaster and reduce its damage.
\
Includes:
Engineering solution
Government Policies
Public Education
\
Includes:
Engineering solution
Government Policies
Public Education
62
New cards
**SOFT Mitigation SOLUTIONS**
* Zoning to prevent buildings in hazardous areas
* Strict building codes to minimize damage.
* Strict building codes to minimize damage.
63
New cards
**HARD Mitigation SOLUTIONS**
* Riprap along coasts
* Spur dikes
* Spur dikes
64
New cards
**LAND-USE PLANNING**
In order to reduce losses from natural disasters:
* Find where they occur
* Restrict development in that area
\
For example
* Prevent development near faults
* Limit development on floodplains
* Find where they occur
* Restrict development in that area
\
For example
* Prevent development near faults
* Limit development on floodplains
65
New cards
**INSURANCE**
These are designed to help with recovery after a disaster.
\
Lessens the financial impact of disaster.
\
Lessens the financial impact of disaster.
66
New cards
**Earthquake**
A weak to violent shaking of the ground due to sudden movement of rock material below the surface.
67
New cards
Earthquakes Types
Tectonic and Volcanic
68
New cards
**Tectonic**
Sudden movement along faults and plate boundaries
69
New cards
**Volcanic**
Due to rising lava or magma beneath active volcanoes
70
New cards
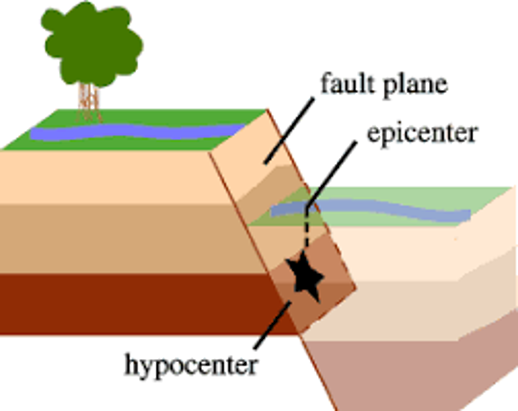
Parts of an Earthquake
Hypocenter/Focus, Epicenter
71
New cards
Hypocenter/Focus
Also known as **focus**. Point inside the Earth where the earthquake originated.
72
New cards
Epicenter
The point on the surface of the earth directly above the focus.
73
New cards
Causes of Earthquakes
Plate Tectonics, Elastic Rebound Theory
74
New cards
**PLATE TECTONICS**
The plates tend to move in a continual slow motion, and cause interaction with its neighboring plates causing stress on margins.
75
New cards
Plates
___ are large slabs of the Earth’s lithosphere which rides on a partially hot molten layer of the upper mantle or asthenosphere.
76
New cards
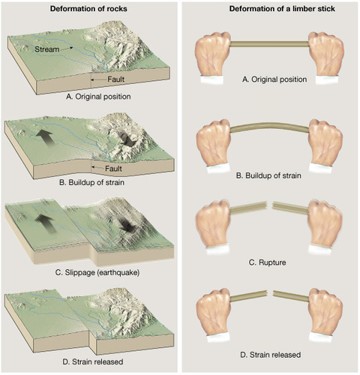
**Elastic Rebound Theory**
Explains that most earthquakes are produced by the rapid release of energy stored in rocks that had been subjected to great stress.
\
Upon exceeding the rock strength, it suddenly ruptures, causing vibrations of an earthquake
\
Upon exceeding the rock strength, it suddenly ruptures, causing vibrations of an earthquake
77
New cards
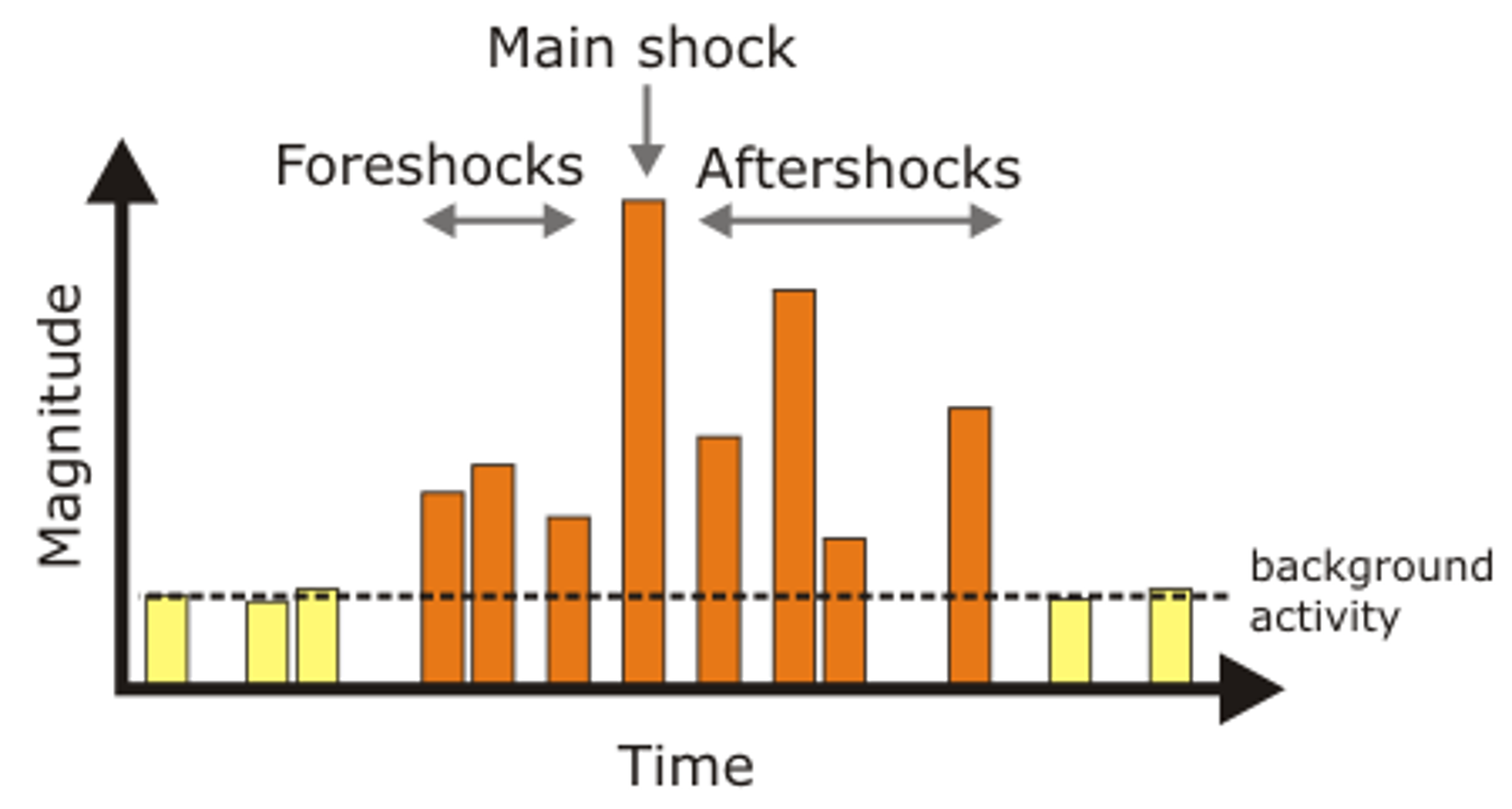
Stages of an Earthquake
Foreshocks, Main Shock, Aftershocks
78
New cards
**MAIN SHOCK**
Major Earthquake
79
New cards
**FORESHOCK**
Possibly results from the development of the smaller cracks in the vicinity of what will be the major rupture
80
New cards
**AFTERSHOCK**
Occurs in days or months following a large earthquake.
Occurs due to readjustment of the crust after the slip from the mainshock.
Occurs due to readjustment of the crust after the slip from the mainshock.
81
New cards
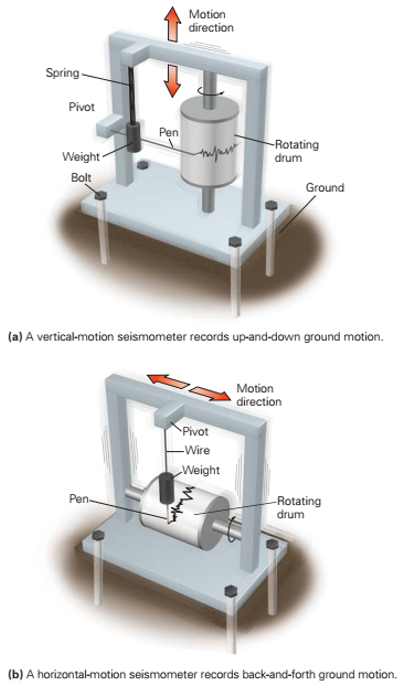
**Seismometer**
An instrument that measures the ground motion of an earthquake.
82
New cards
2 Seimometer configurations
Vertical- and Horizontal- motion seismometer
83
New cards
**Vertical-motion seismometer**
Records up-and-down ground motion
84
New cards
**Horizontal-motion seismometer**
Records back-and-forth ground motion
85
New cards
**Intensity**
The effect or consequence of an earthquake’s ground shaking at a locality on the Earth’s surface.
86
New cards
**Magnitude**
A number that characterizes the relative size of an earthquake. It is based on measurement of the maximum motion recorded by a seismograph.
87
New cards
Magnitude Scales
* Richter magnitude or local magnitude (ML)
* Surface-wave magnitude (MS)
* Body-wave magnitude (Mb)
* Moment magnitude (Mw)
* Surface-wave magnitude (MS)
* Body-wave magnitude (Mb)
* Moment magnitude (Mw)
88
New cards
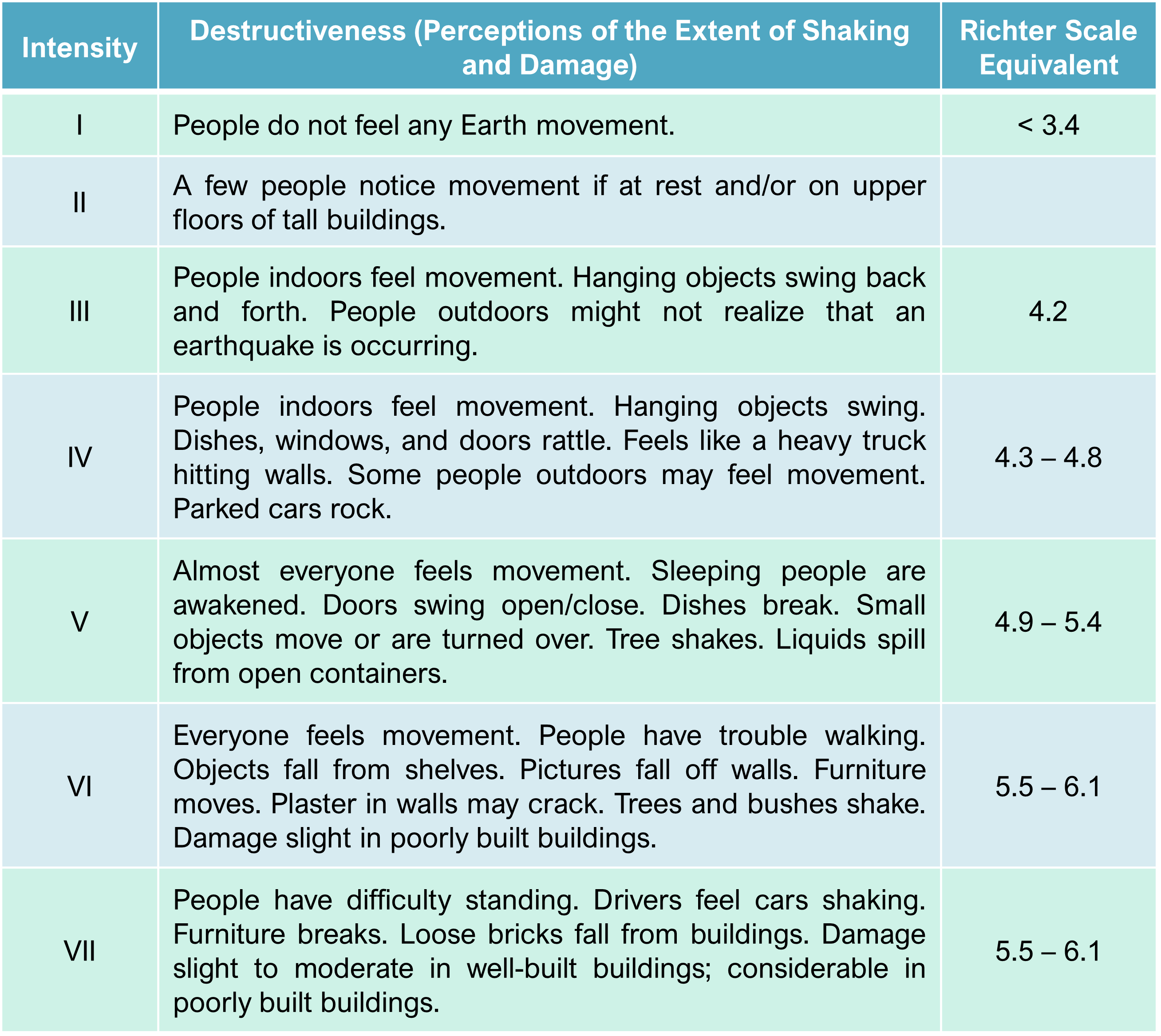
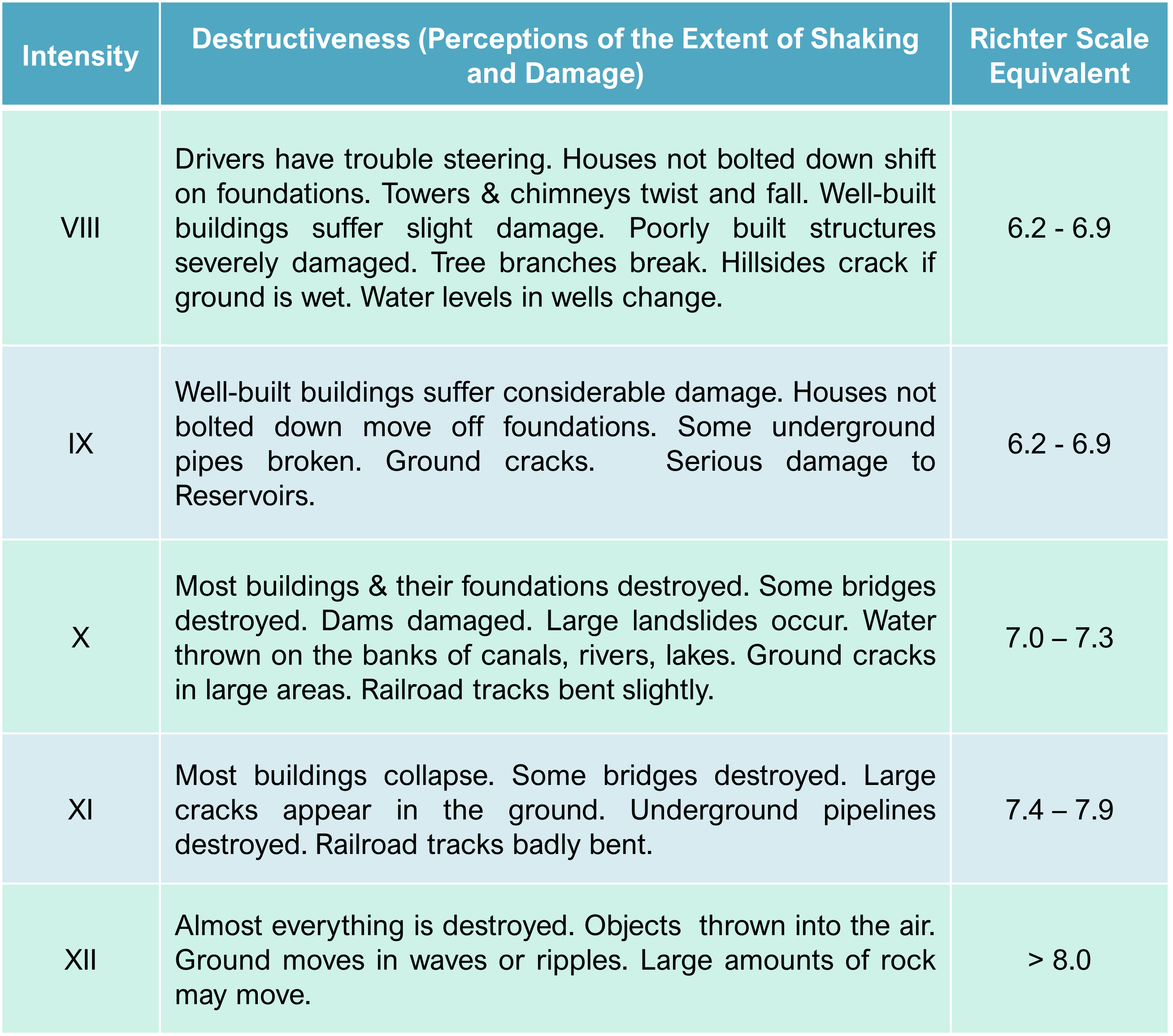
**Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale**
In 1902, an Italian scientist named **Giuseppe Mercalli** devised a scale for defining intensity by systematically assessing the damage that the earthquake caused.
Note that the specification of earthquake intensity depends on a **subjective assessment of damage**, and of the perception of shaking, not a direct measurement with an instrument.
Note that the specification of earthquake intensity depends on a **subjective assessment of damage**, and of the perception of shaking, not a direct measurement with an instrument.
89
New cards
**Richter Magnitude Scale**
•Developed by Charles Richter
•Based on the maximum amplitude of motion that would be recorded at a station about 100 km from the epicenter
•The original Richter scale works well only for shallow earthquakes that are close to the seismometer station – now called **local magnitude** (**ML**).
•Based on the maximum amplitude of motion that would be recorded at a station about 100 km from the epicenter
•The original Richter scale works well only for shallow earthquakes that are close to the seismometer station – now called **local magnitude** (**ML**).
90
New cards
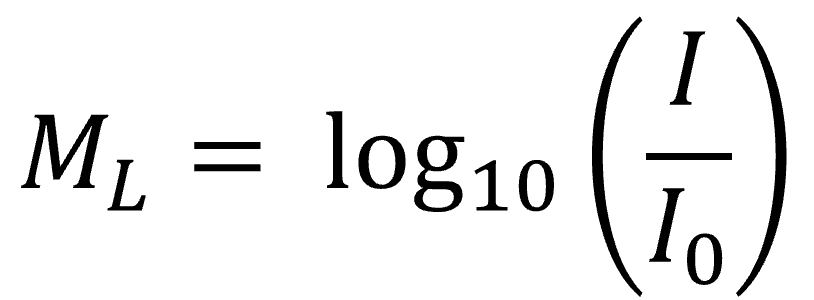
**Richter Magnitude Scale Formula**
Where **I** stands for the intensity of the earthquake and **I0** represents a zero-level earthquake the same distance from the epicenter.
91
New cards
Potential Earthquake Hazards
* Ground Shaking
* Ground Rupture
* Liquefaction
* Tsunami
* Earthquake-induced Landslide
* Ground Rupture
* Liquefaction
* Tsunami
* Earthquake-induced Landslide
92
New cards
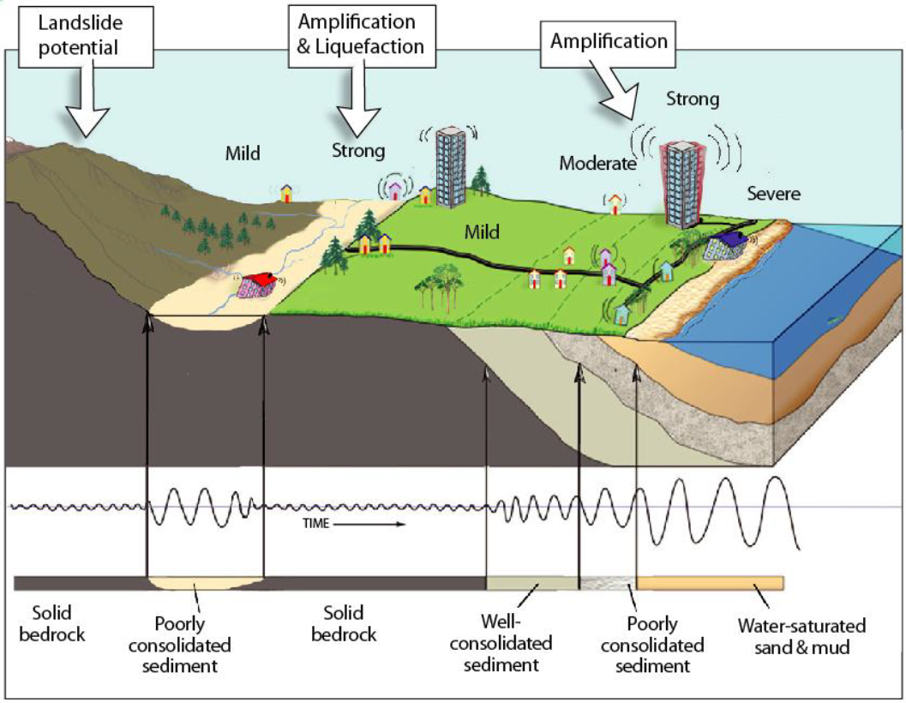
**Ground Shaking**
It is the disruptive up-down and sideways movement or motion experienced during an earthquake, and is responsible for the collapse of structures.
93
New cards
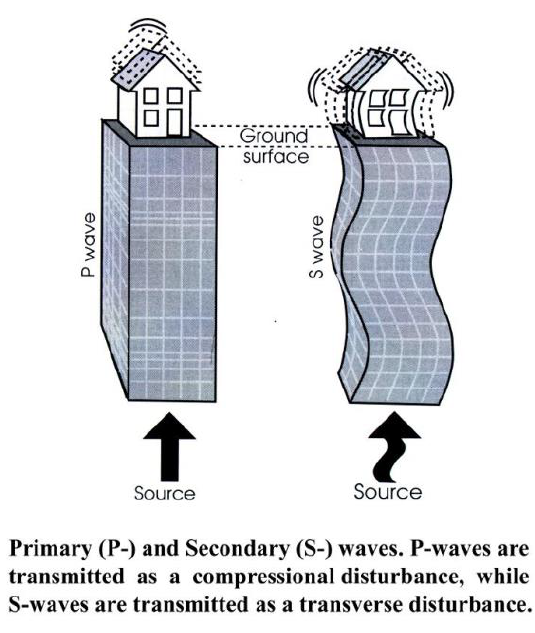
Motions of Ground Shaking
Up and Down, and Sideways
94
New cards
**Up and down**
First felt by people near the epicenter; not felt by people far from epicenter.
95
New cards
**Sideways**
Felt after up and down by people near epicenter; first felt by people far from epicenter.
96
New cards
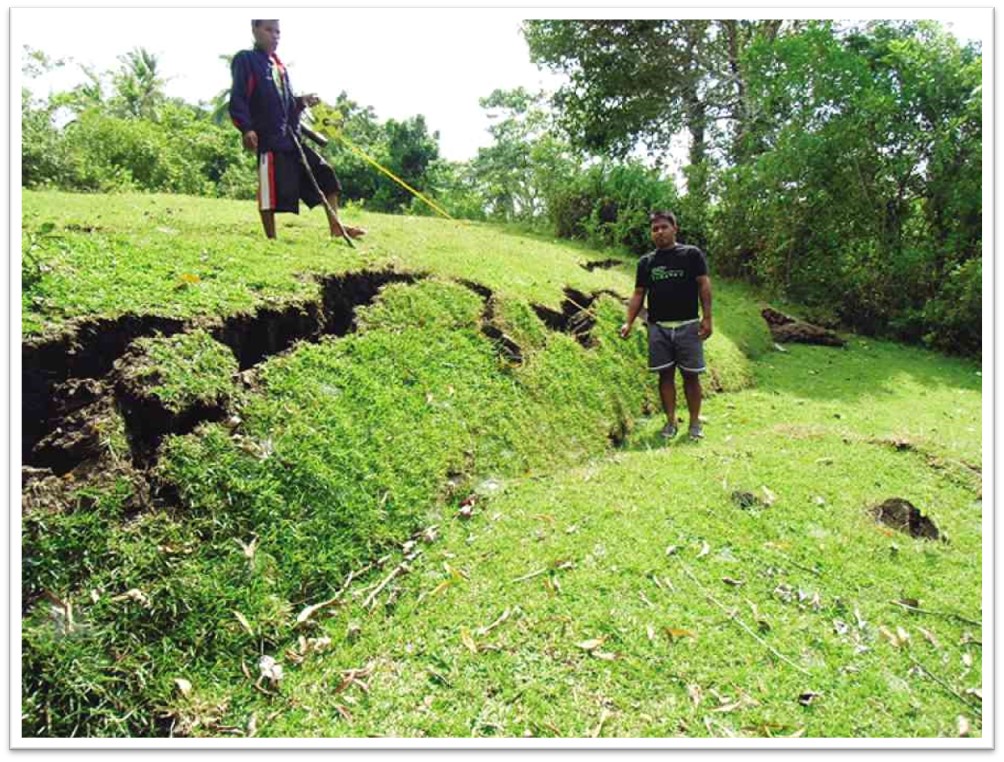

**Ground Rupture**
The displacement on the ground due to movement of a fault.
\
The structures that are only build across fault lines may experience collapse, whereas structures build adjacent to the fault may survive.
\
The structures that are only build across fault lines may experience collapse, whereas structures build adjacent to the fault may survive.
97
New cards
**Liquefaction**
Process where the unconsolidated sediments loose grain to grain contact during ground shaking, thus act almost liquid.
\
In some water-saturated sediments, the water may be expelled from the spaces between grains. The escaping water carries the sediment along as it rapidly flows to the surface as **sand boils** and **mud volcanoes**.
\
In some water-saturated sediments, the water may be expelled from the spaces between grains. The escaping water carries the sediment along as it rapidly flows to the surface as **sand boils** and **mud volcanoes**.
98
New cards
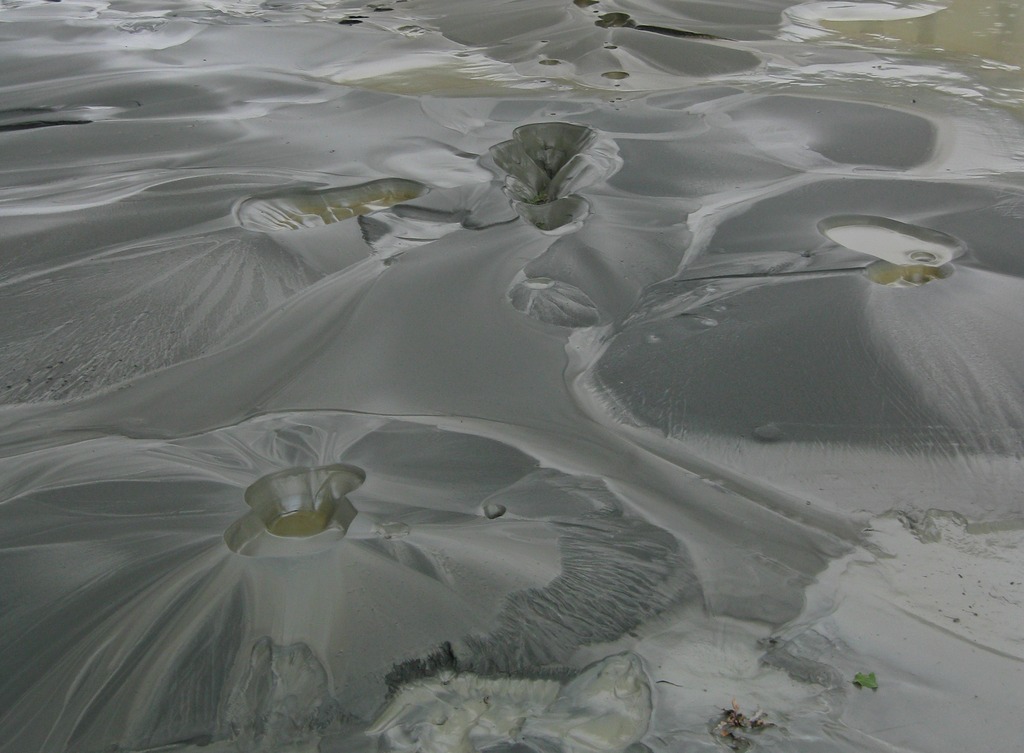
**Sand Boil**
___ or sand volcanoes occur when water under pressure wells up through a bed of sand. The water looks like it is boiling up from the bed of sand, hence the name. (Ex: Shinhua site, Taiwan)

99
New cards

**Tsunami**
Are giant ocean waves that rapidly travel across oceans.
\
These sea waves are formed due to the disturbance of the ocean floor by an earthquake or landsides.
\
These sea waves are formed due to the disturbance of the ocean floor by an earthquake or landsides.

100
New cards
**Earthquake-induced Landslide**
___ are failures in steep or hilly slopes triggered by ground shaking.
\
This is common in mountainous regions.
\
This is common in mountainous regions.