EXAM 3- KHAN - ANTIFUNGALS
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
2 major classes of fungal infections?
superficial fungal infections
invasive fungal infections
What are the antifungal drug classes?
Inhibitors of fungal membrane stability
Polyenes
Amphotericin B
Nystatin
Inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis
Flucytosine
Inhibitors of ergosterol synthesis
Azoles
Allylamines
Inhibitors of fungal wall synthesis
Echinocandins
Inhibitor of fungal mitosis
Griseofulvin
What are the structural features of Amphotericin B?
Is this drug soluble or insoluble in water
has many double bonds—> INSOLUBLE IN WATER
has large macrolide lactone ring (a cyclic ester)
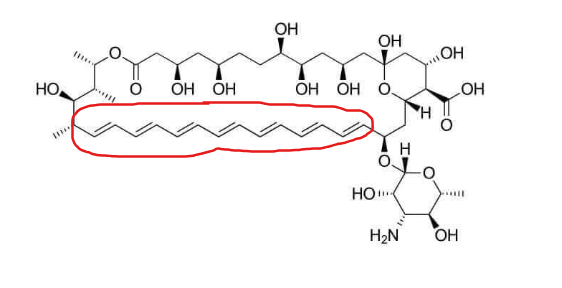
What is the composition of conventional Amphotericin B?
Amphotericin B complexed with deoxycholate
What are the advantages of using liposomal preparation for Amphotericin B?
LESS NEPHROTOXIC than conventional preparation
less infusion related rxns
What’s the difference in cell walls between fungi and mammals?
fungi—> uses ergosterol in membrane
fxn: structural support, ion transport, enzyme activity
mammals—> use cholesterol in membrane, NO ERGO
MOA of inhibitors of fungal membrane stability like Amphotericin B and Nystatin?
binds to ergosterol of fungal membrane
destroys integrity of membrane—> forms pores/channels
increase in permeability—> cell contents leak= cell death
Is Amphotericin B selective or non-selective towards fungal cells?
selective towards fungal cells, no ergo in mammal cells
Answer the following about the PK of Amphotericin B:
absorption?
distribution?
excretion?
A- poor oral, only IV route
D- long t 1/2 , no CNS pen.
E- kidneys, slow
Main ADRs with Amphotericin B?
infusion related reactions (fever, shakes, chills, hypotension, tachypnea)
nephrotoxicity
How do you manage infusion-related rxns associated with Amphotericin B?
decrease rate of drug admin
use of opioids, NSAIDs, or hydrocortisone to decrease rxns
Amphotericin B causes nephrotoxicity.
what is the mechanism behind this?
what electrolytes are altered?
which agents should not be co-administered?
mechanism: vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles, renal ischemia
electrolytes: hypoKALEMIA, hypoMAGNESEMIA
agents to avoid/caution: other nephrotoxic agents (NSAIDs, aminoglycosides), hypokalemic agents (loop diuretic)
What’s the oral bioavailability of nystatin?
poor—> topical product only
What antifungal has an allyl amine group? IDENTIFY IT!!!!!!
Terfinabine
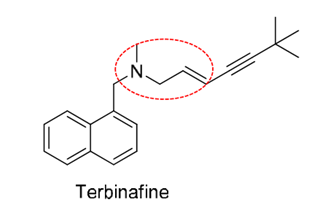
MOA of terfinabine?
inhibits ergosterol synthesis
inhibits squalene epoxidase
responsible for squalene to squalene epoxide
squalene accumulation= toxic to fungal cells
How is the selectivity of Terfinabine?
selective towards fungal cell!!
only inhibits mammal squalene epoxidase at high conc
IDENTIFY SQUALENE EPOXIDE:
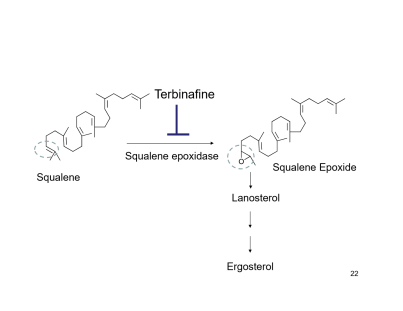
NOTE HOW THE SQUALENE EPOXIDE HAS AN -O- group
Answer the following about the PK of Terfinabine:
Absorption?
bound?
excretion?
A- PO or topical, well absorbed PO, bioavailability decreased due to 1st pass effect
99% protein bound—> accumulates in skin, nails, fat
E- kidney
Terfinabine INHIBITS CYP____.
Terfinabine INHIBITS CYP2D6..
List the names of the azole antifungals:
Fluconazole
Itraconazole
Posaconazole
Voriconazole
Isavuconazonium
Clotrimazole
Miconazole
Ketoconazole
What is the ONLY azole antifungal that contains a THIAZOLE?
(note: TRIAZOLE AND THIAZOLE not the same thing)
Isavuconazonium
What azole antifungals contain an IMIDAZOLE?
Ketoconazole
Clotrimazole
Miconazole
What azole antifungals contain an TRIAZOLE?
(note: TRIAZOLE AND THIAZOLE not the same thing)
Fluconazole
Itraconazole
Posaconazole
Voriconazole
Be able to IDENTIFY a Imidazole and triazole group!!!!
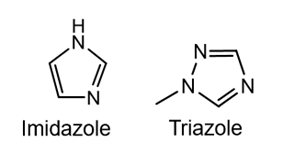
Tip: notice how a TRIazole has 3 nitrogens!!!!!!!!
What is the MOA of azole antifungals?
(be able to identify which methyl group is normally removed)
Inhibits 14-a-demethylase CYP enzyme
Inhibits demethylation of Lanosterol to Ergosterol
Ergosterol analog formed lacks proper properties—> membrane leakage= cell death
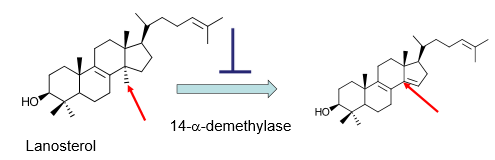
HOW do azoles inhibit the 14-a-demethylase enzyme?
N on azole antifungals forms a bond to the heme iron prevent 14-a-demthylase from normal action
What are the adverse effects of ketoconazole?
fatal hepatotoxicity
inhibits steroid biosynthesis
drug interactions
What are the resistance mechanism to azoles?
Mutations in gene coding for 14-a-demethylase
Increase azole efflux
Increased production of 14-a-demethylase
Answer the following about the PK of Fluconazole:
absorption?
tissue penetration?
excretion?
(idk how imp)
complete absorption from GIT
CSF penetration good
renal excretion
Describe each of the followings interactions with CYP enzymes:
Fluconazole
Voriconazole
Itraconazole
Posaconazole
Fluconazole- inhibits CYP3A4 (weak), CYP2C9 (STRONG)
Voriconazole- inhibits CYP3A4, 2C9, 2C19
Itraconazole- METABOLIZED by CYP3A4—> less d/i
Posaconazole- inhibits CYP3A4
What ADR is seen in Fluconazole, Voriconazole, Itraconazole, and Posaconazole?
QT prolongation (tip: these are all triazoles)
ADRs of Fluconazole:
GI, HA, dizzy
increased LFTs
QT PROLONGATION
ADRs of Voriconazole:
increased LFTs, SCr
QT prolongation
hallucinations
visual disturbances
ADRs of Itraconazole:
QT prolongation
Congestive HF
C/I in pts. with ventricular dysfunction or CHF
ADRs of Posaconazole:
increased LFTs
QT prolongation
How is POSACONAZOLE METABOLIZED?
UDP-glucuronidation (tip: UDP = Posaconazole)
How is Isavuconazium activated?
ester prodrug—> converted to isavuconazole by esterase
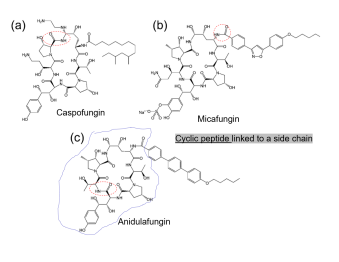
What drugs are Echinocandins?
Caspofungin (Cancidas)
Anidulafungin (Eraxis)
Micafungin (Mycamine)
MOA of Echinocandins:
Inhibits fungal cell wall synthesis
By inhibiting synthesis of beta(1-3) glucan
Component of cell wall (glucose homopolymers)
ADRs of Echinocandins:
Histamine mediated effects (rash, pruritic, facial swelling)
Increased LFTs
Electrolyte disturbances
Describe the PK of Echinocandins:
binding?
metabolism?
excretion
CNS penetration
CYPs?
(idk how imp)
protein binding 97%
metabolism—> peptide bond hydrolysis, N-acetylation
excretion—> biliary
minimal CNS penetration
not a CYP inducer/ any interactions with P-gp
ROA of Echinocandins?
IV
Describe the structure of Echinocandins:
cyclic peptide linked to a side chain
Describe the structure of Griseofulvin:
what functional groups?
benzofuran
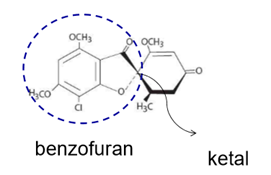
MOA of Griseofulvin:
mitotic inhibitor
binds to tubulin and microtubule-associated protein
disrupts assembly of mitotic spindle
What other effect is see by Griseofulvin besides its MOA?
Accumulates in keratin precursor cells
Prolonged association= new growth of skin, hair, nails
Answer the following about Griseofulvin:
absorption?
ADRs?
(idk how important)
PO, absorption increased with fatty meal
ADRs: HA, GI
What antifungal (that Khan talked about) is C/I in pregnancy?
Griseofulvin
Be able to Identify 5-flucytosine and 5-FU:
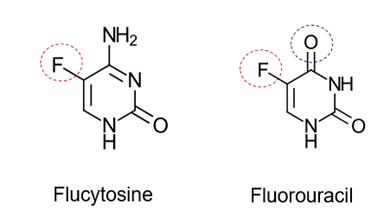
What is the function of cytosine permease?
cytosine permease—> cytosine transporter, takes up Flucytosine into fungal cell
What is the function of cytosine deaminase?
cytosine deaminase—> enzyme, inside fungal cells converts Flucytosine to 5-FU via deamination
What is the function of 5-fDUMP?
Inhibits thymidylate synthase= inhibits DNA synthesis
How does 5-FU acquire resistance?
Loss of cytosine permease for cytosine transport
Decreased activity of cytosine deamine
ADRs and BBW of Fluocytosine:
ADRs:
BMS (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia)
increased SCr and liver enzymes
BBW:
extreme caution in pts. with renal dysfunction
monitor hematologic, renal, and hepatic status