Physics 30 - Unit C: Chapter 13.3
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
13.3 - Reflection
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Specular
regular reflection
clear reflection in water

Diffuse
irregular reflection
blurry reflection in water
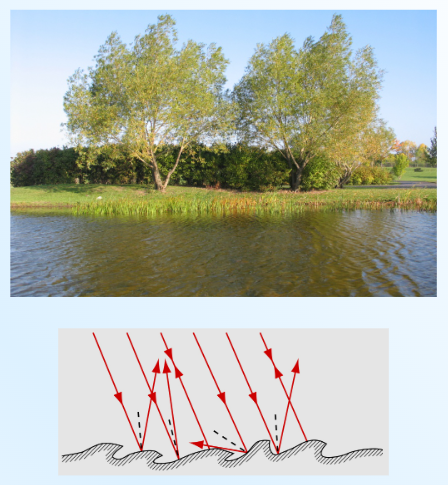
The Law of Reflection
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence and is in the same plane.
*angles are always measured towards the normal*
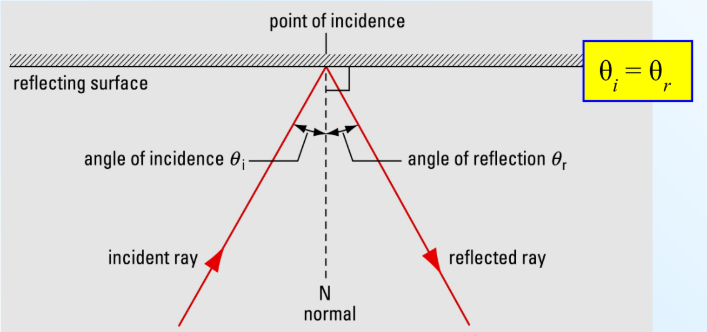
Image Formation in a Plane Mirror
Our brains perceive that light rays travel in straight lines
Extending the reflected rays in a straight line, they appear to come from a point that is behind the mirror.
These dashed lines represent virtual rays of light, and they form a virtual image.
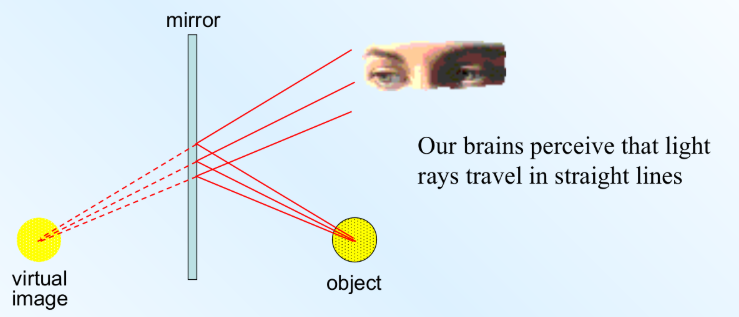
Characteristics of an Image in a Plane Mirror
same size as object
vertically upright
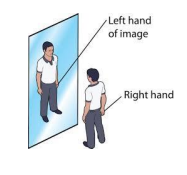
but laterally inverted (flipped!)
virtual image
image is located same distance from the mirror as the object
Where can a Real Image be formed at?
A real image can be formed on a diffusely reflecting surface, such as a movie screen.

Magnification
same size
enlarged (larger)
diminished (smaller)
Image Characteristics
Magnification
Attitude
Position
Type
Attitude
Erect (upright)
Inverted (downright)
Position
displacement from mirror surface
Type
real
virtual
Image Formation in a Curved Mirror
a curved mirror can be formed from a hollow sphere
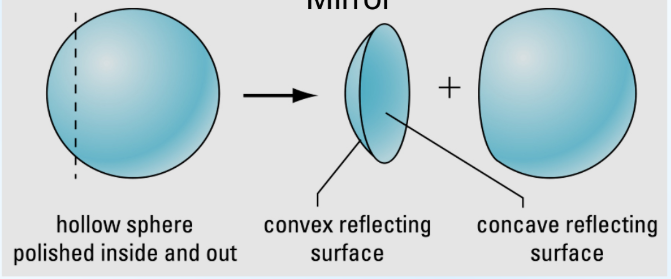
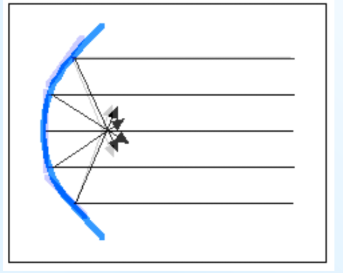
Concave Mirrors (Caved In)
Are converging mirrors because they cause reflected light rays to come together.
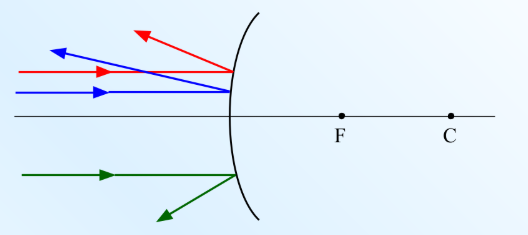
Convex Mirrors (Outwards)
Are diverging mirrors because they cause reflected rays to spread out.
light rays that are reflected diverge as if they come from a single point behind the mirror.
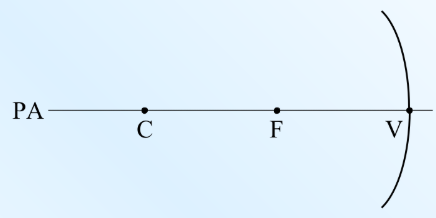
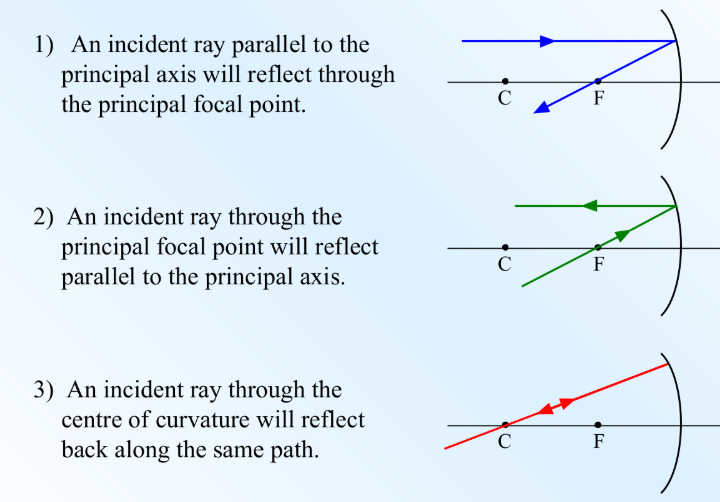
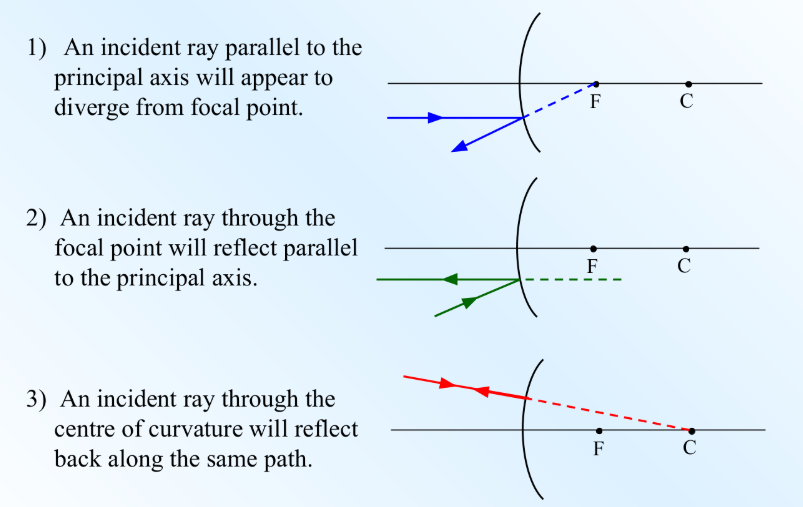
Terminology for Ray Diagrams
centre of curvature (C)
2 x focal length
radius of curvature (r)
2 x focal length
vertex (v)
principal axis (PA)
principal focal point (F)
inbetween (v) and (c)
focal length (f)
Drawing Ray Diagrams for Converging Mirrors
Drawing Ray Diagrams for Diverging Mirrors
Equations for Curved Mirrors

Sign Conventions for Use with the Mirror Equation
REAL objects and images = positive distances
VIRTUAL images = negative distances
ERECT objects and images = positive heights
INVERTED objects and images = negative heights
CONVERGING mirrors have a real focal point
focal length is positive
DIVERGING mirrors have a virtual focal point
focal length is negative
All real images (+di) = are inverted (-hi)
All virtual images (-di) = are erect (+hi)