biology - topic 3: organism level systems
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What does CNS stand for?
Central Nervous System
What does the CNS consist of?
The brain and the spinal chord.
What is the process of the CNS helping to coordinate a response?
Receptor cells convert a stimulus into an electrical impulse.
The electrical impulses travels along the sensory neurons to the CNS.
Information is processed and a response is coordinated, resulting in an electrical impulse being sent along the motor neuron to the effector.
The effector (glands which secrete hormones or muscles that contract) carry out the response.
What is a reflex arc?
A subconscious response to a dangerous stimuli, for example a hot surface or a bee sting.
What is the process of coordinating a reflex arc response?
The receptor cells detect a stimulus.
Impulses are sent along the sensory neuron to the CNS, where it is passed to the relay neuron.
Impulses are sent along the motor neuron.
The impulse reaches the effector which results in an appropriate response — for example contraction of the biceps to move your hand away from a hot surface.
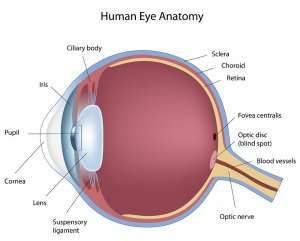
What are the parts of the eye and their functions?
Cornea: Refracts the light onto the retina.
Iris: Controls how much light enters the eye.
Pupil: Allows light through the eye.
Lens: Focuses the light onto the retina.
Retina: Converts light to electrical signals which are transmitted to the brain.
Optic nerve: Carries impulses from the eye to the brain.
Ciliary muscles: Adjusts the shape of the lens so that the refraction of light increase or decreases.
Suspensory ligaments: Slackens or stretches as the ciliary muscles contract or relax, to adjust the thickness of the lens.
What will the pupil do in dim/bright light?
In dim light, the pupil will dilate so more light enters the eye and focuses on the retina.
In bright light, the pupil will get smaller, restricting as much light from entering the eye.
What happens to the eye when you focus on a distant object?
Your ciliary muscles relax and your suspensory ligaments tighten.
What happens to the eye when you focus on a close-up object?
Your ciliary muscles contract causing your suspensory ligaments relax.
How is myopia and hyperopia treated?
Myopia: Short-sightedness, lens focuses image in front of the retina, treated with a concave lens.
Hyperopia: Long-sightedness, lens focuses image behind the retina, treated with a convex lens.
What is the structure of the brain and their functions?
Cerebellum: Coordinates balance and movement.
Cerebrum: Responsible for intelligence, personality, memory, and language.
Medulla: Controls heart-rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate.
Hypothalamus: Maintains homeostasis in the body.
Pituitary Gland: A gland that secretes hormones into the blood.
What are two limitations of studying the brain?
Unethical since the patient might not be in the right state of mind to make an informed decision to take part in the study.
There is a considerable amount we still need to learn about the brain, so surgery for an investigative study is dangerous.
What is a hormone?
A chemical messenger (secreted by endocrine glands into the bloodstream).
What are adrenaline and thyroxine, and what are they responsible for?
Adrenaline:
Produced by adrenal glands.
A hormone responsible for ‘fight or flight’ response for survival — increases heart rate, breathing rate, dilates pupils, makes hairs stand up, etc.
Thyroxine:
Produced by the thyroid gland.
A hormone responsible for the control of metabolic rate (therefore responsible for growth).
Example of negative feedback: when thyroxine levels are low, the hypothalamus produces the hormone TRH and the pituitary produces TSH (thyroxine stimulating hormone), which causes the thyroid to produce thyroxine.
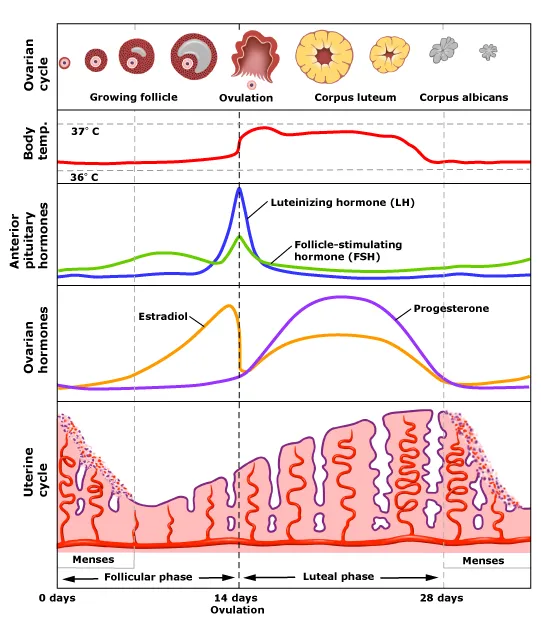
What are the four hormones that are responsible during the menstrual cycle, what do they do, and where are they produced?
FSH: Pituitary gland — Matures the egg.
Oestrogen: Ovaries — Thickens the uterus.
LH: Pituitary gland — Stimulates the release of the egg.
Progesterone: Ovaries (yellow body) — Inhibits the release of LH and FSH.
What are the 2 hormonal methods of contraception?
The pill (99%+) and contraceptive implants (99%+).
What are the 3 non-hormonal methods of contraception?
Physical barriers e.g. condoms (99%+ and protect from STISs), vasectomy (almost 100%), and IUD/the coil (99%+).
What 2 hormones are mainly used to treat fertility issues?
FSH and LH because they stimulate the maturation of the egg.
What is an alternative treatment for fertility?
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF).
Plants need hormones to coordinate ___.
Growth.
What is the growth plant hormone called?
Auxin.
Why do plants grow towards the light?
Positive phototropism:
The plant is exposed to light on one side.
Auxin moves to the shaded side of the shoot and stimulates cells to grow here.
This means the shoot bends towards the light and photosynthesis can occur at a faster rate.
Note: if auxin is equal on both sides it’ll grow straight in that direction.
Shoots show ___ ______ and roots show ___ ______.
Shoots show negative gravitropism and roots show positive gravitropism.
What is another use of auxins?
Weed killers.
Rooting powders (reduce risks of fungal infections).
Promotes growth in tissue growth.
What are gibberellins and ethene?
Gibberellins: A plant hormone important for seed germination.
Ethene: A hormone that is involved in the ripening of fruits.
What is the definition of homeostasis?
The maintenance of a constant internal environment.
What happens to your body when your temperature gets too low or high?
If it becomes to high:
Sweating.
Vasodilation (more blood flows closer to the skin).
If it becomes too low:
Hairs stand on ends.
Skeletal muscles contract — shivering.
Vasoconstriction (more blood doesn’t flow closer to the skin).
What does your body do when glucose levels are too high in the blood?
Your pancreas secretes the hormone insulin.
Insulin binds to cell in target organs (muscles and liver).
This causes glucose to move from the blood into the muscle cells for respiration. Excess glucose is converted to glycogen which is stored in the liver.
Glucose concentration is therefore reduced.
What does your body do when glucose levels are too low in the blood?
Pancreas produces the hormone glucagon.
Glucagon binds to the liver cells, causing the glycogen to be broken down into glucose.
Glucose is released into the blood, increasing the blood glucose concentration.
What is a negative feedback loop?
When something increases/decreases, it’s level is stabilised back to ‘normal’.
What is type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1: The pancreas can not produce enough insulin. Treated with insulin injections at mealtime.
Type 2: The body no longer responds to insulin. Treated with diets, increasing exercise, and losing weight.
What will happen in your body when water concentration of your blood increases?
Water will move into your cells, causing them to expand and eventually burst.
What will happen in your body when water concentration of your blood decreases?
Excess water will leave the cells, causing shrinking.
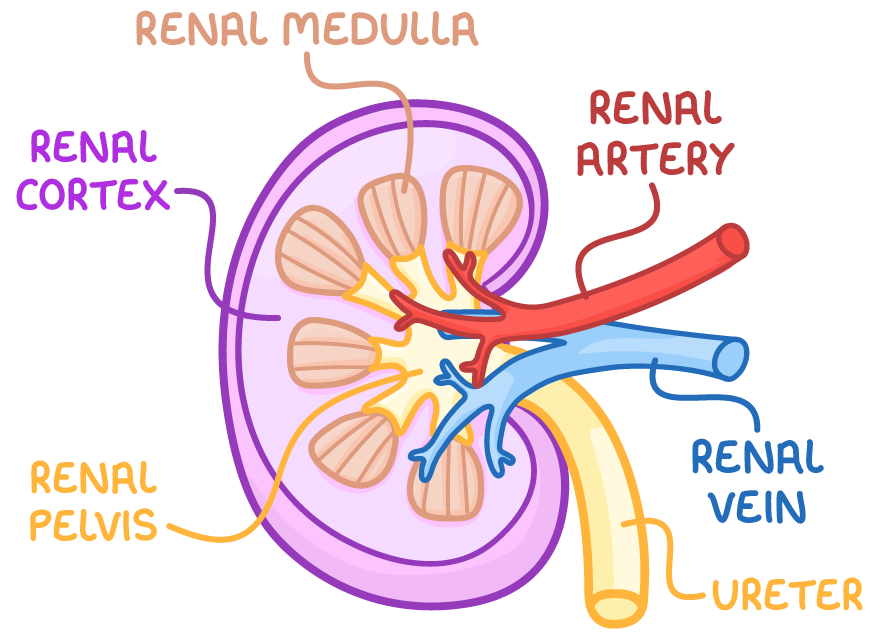
What is the function of the kidneys?
To filter out waste products (e.g. urea) and selectively re-absorb useful substances (e.g. glucose and water).
What are the parts of the kidney?
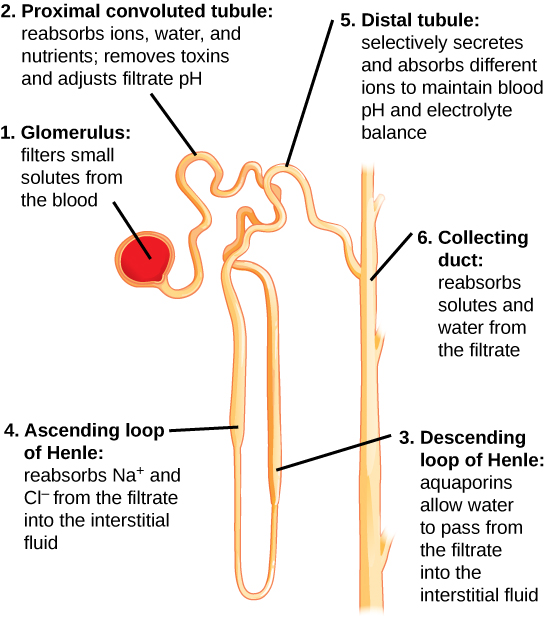
What is a nephron?
The functional unit of the kidney.
What happens at the different parts of the nephron?
What is ADH?
A hormone involved in the loss of water as urine. It’s released by the pituitary gland when a receptor in the brain detects that the blood is too concentrated.