chapter 20: the electron transport chain
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
negative, donate
a strong reductant has a ____________ potential and will _________ electrons
positive, accept
a strong oxidant has a _____________ potential and will __________ electrons
delta E naught prime (E'°)
standard reduction potential under standard biological conditions (pH 7, 25 C, 1M concentration, and 1 atm pressure); indicates how easily a molecule is reduced
delta E
the actual potential difference in a given reaction, not necessarily under standard conditions
reducing
strong _________ agent = donates electrons
oxidizing
strong _________ agent = readily accepts electrons
positive, negative
If ΔE'° is __________, the reaction is spontaneous (ΔG°' is __________)
negative, positive
If ΔE'° is __________, the reaction is nonspontaneous (ΔG°' is __________)
ubiquinone
what does Q stand for?
ubiquinol
What does QH2 stand for?
NADH-Q oxidoreductase (complex I)
accepts electrons from NADh, oxidizing it to NAD+, and transfer electrons to Q
pumps protons (H+) into intermembrane space
contains FMN and iron-sulfur clusters for electron transfer
Succinate-Q reductase (complex II)
transfers electrons from FADH2 to Q
does not pump electrons
contains FAD and Fe-S clusters for e- transfer
Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase (complex III)
transfers electrons from ubiquinone to cytochrome c
Contains cytochromes b and c₁ and Fe-S clusters
Pumps protons into the intermembrane space
cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV)
accepts electrons from cytochrome c and transfers them to O2, reducing it to H2O
pumps protons into intermembrane space
contains Cu centers that aid in electron transfer
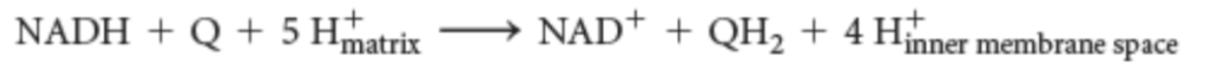
-
equation for NADH-Q oxidoreductase reaction
NADH, FMN, Fe-S, Q, Q2-, QH2
In complex I, electrons flow from _____ to ______ and then through a series of seven _____ clusters to _____, forming _____ —> _______
succinate dehydrogenase
oxidizes succinate into fumarate and generates FADH2, which is used in complex II
FADH2, 2, Fe-S, Q, QH2
In complex II, ______ transfers its ___ e- through a series of _____ clusters, where it is passed to ___ and reduced to ____
2, QH2, cytochrome c, cytochrome b, Q, Q-, 2 H+, intermembrane
in the first half of Q cycle, ___ electrons from ____ are transferred, one to __________ and the other passes through _____________ to reduce ___ into ___. this results in the release of _____ into ______________ space, contributing to the overall proton gradient
QH2, 2, cytochrome c, cytochrome b, Q-, QH2, 2 H+, matrix, 2 H+, intermembrane
in the second half of the Q cycle, a second _____ also gives up ___ e-, one to a second molecule of ___________ and the other passes through ________ to reduce ___ to _____. the second electron transfer results in the uptake of _____ from the _______. there is also an overall release of _____ into ___________ space, contributing to the overall proton gradient
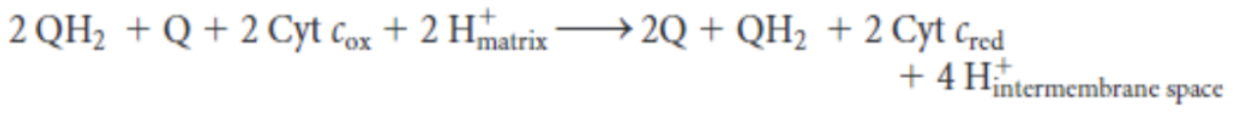
-
equation for Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase reaction
4, heme a, heme a3, Cu_B, heme a3, Cu_B, O2, peroxide, 2 H+, matrix, H+, 2 H2O
In complex IV, ___ reduced cytochrome molecules transfer electrons one by one through: ___ —> _____ —> _______. Reduced centers (______ and ______) bind to ____, leading to the formation of a _______ bridge. The additiion of _____ from the _______ cleaves the bridge. Addition of two more ____ leads to the release of _______.
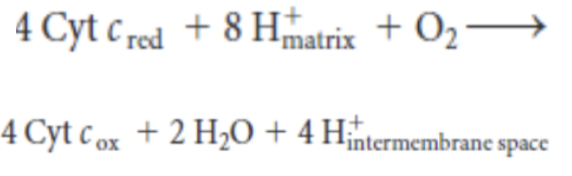
-
write the equation of the cytochrome c oxidase reaction
chemical protons
protons (H⁺) that are involved in the chemical reaction that reduces oxygen (O₂) to water (H₂O).
pumped protons
refer to protons (H⁺) that are actively transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space.