Communicable diseases
1/100
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
virus
fungi
protoctista
suggest how the immune system causes damage to the nervous system in autoimmune diseases (2)
immune system recognises antigens on neurones as foreign
produces antibodies against the neurones
OR phagocytes break down the neurones
Attachment proteins on surface to attach to host cells
or to breakdown products when cell wall is attacked (1)
stimulates release of signal molecules (1)
signal molecules turn on certain genes to trigger response (1)
3 plant responses to infection
synthesis of callose and lignin
synthesis of defensive chemicals to alert nearby cells
synthesis of defensive chemicals to attack the pathogen
structure of callose
beta glucose
1-3 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
1. callose deposited between cell wall and cell membrane of cells adjacent to infected cell to create a thick barrier for pathogen to penetrate through
2. blocks sieve plate of phloem to seal off infected area
3. blocks plasmodesmata between infected and nearby cells
inserts genetic material into DNA of host cell
viral genetic material is replicated
new viruses burst out of host cell and kill the host
bark
cell wall
stomatal closure
insecticides
antibacterial compounds
antifungal compounds
anti-oomycetes
general toxins
how do bacteria infect an organism (2)
produce toxins
which poison or damage host cells
what are the 3 ways in which toxins can affect an organism
breakdown cell membranes
inactivate enzymes
interfere with genetic material so host cells cannot divide
how do fungi infect an organism
digest and destroy living cells by releasing extracellular enzymes from their hyphae
bacterial meningitis
ring rot (potatoes and tomatoes)
influenza
tobacco mosaic virus
potato/tomato late blight
ringworm (cattle)
athlete’s foot (humans)
skin to skin contact
through breaks in skin
from animal bite
sharing needles
taking in contaminated food and drink
droplets in air
vectors
what is a fomite
inanimate object which can carry pathogens
e.g. clothes, bedding
poor nutrition
compromised immune system
poor healthcare and infrastructure
climate change
culture
vectors
water
animals
humans
poor nutrition
climate change
planting succeptible plants
damp warm conditions is favourable for pathogens
rotate crops
strict hygiene practises
control insect vectors
plant variety of susceptible plants
mucous membraines
blood clotting
wound repair
phagocytosis
inflammation
expulsive reflexes
acid in stomach
secretes sebum (oily substance) to inhibit growth of pathogens
how do mucous membranes act as non-specific defence against pathogens
produce mucus which trap pathogens
contain lysosomes and phagocytes to destroy pathogens
vomiting and diorrhoea remove any pathogens in the gut
heat
swelling
pain
what is the function of histamines in the inflammatory response (4)
vasodilation to cause redness and localised heat to kill pathogens
make walls of blood vessels more leaky so more tissue fluid forms to cause swelling and pain
what is the function of edema (2)
provide nutrients and immune cells to site of infection
helpts to dilute and remove pathogens from the area
what is the function of cytokines in the non specific immune response (4)
act as signalling molecules to attract phagocytes to site of infection
regulate the intensity and duration of the inflammatory response
increase body temperature
stimulate specific immune system
differences in structure between neutrophils and macrophages
neutrophil has lobed nucleus to squeeze through narrow gaps - macrophage has round nucleus as it stays in blood
1. phagocyte detects antigens on pathogen
2. engulfs pathogen and encloses it in a vacuole to form a phagosome
3. lysosomes move and fuse with the phagosome to form a phagolysosome
4. enzymes from lysosome digest and destroy the pathogens
what are the main stages of phagocytosis in macrophages
phagocyte detects antigens on pathogen
engulfs pathogen and encloses it in a vacuole to form a phagosome
lysosomes move and fuse with the phagosome to form a phagolysosome
enzymes from lysosome digest and destroy the pathogens
antigen from pathogen is combined with glycoprotein MHC in the cytoplasm
MHC/antigen complex is displayed on the macrophages’ cell membrane
macrophage becomes an antigen presenting cell to stimulate other phagocytes
what is the function of opsonins in the non specific immune system (3)
non-specific proteins which bind to antigens on pathogen
tag them so they are more easily recognised by phagocytes
phagocytes have receptors to bind to common opsonins
main steps of the coagulation cascade
thromboplastin released by platelets
thromboplastin and Ca2+ ions convert the precursor prothrombin into thrombin
thrombin acts as an enzyme and converts fibronigen into fibrin
fibrin forms a mesh which traps red blood cells forming the clot
tissue fluid
epithelial surfaces
what causes fevers
cytokines signal to hypothallamus to raise body temperature
specific immune system works faster at higher temperatures
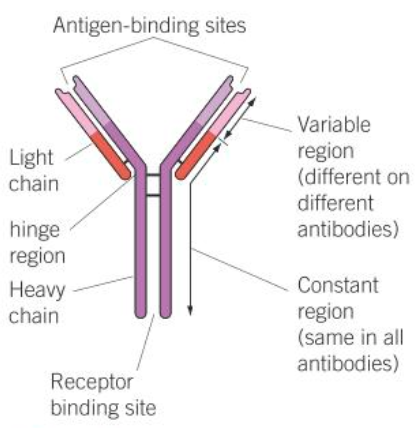
binding site made of different amino acids called the variable region
constant region where white blood cells bind to antibody
hinge region for flexiblity
1. agglutination - act as agglutanins to clump together pathogens to make it easier to be engulfed by one phagocyte
2. opsonisation - act as opsonins to make it easier for the phagocytes to detect and engulf the pathogens
3. neutralisation - inihibits ability of pathogens to invade host cells
4. detoxification - bind to toxins produced by pathogens to make them harmless
\
1. T helper cells
2. T regulator cells
3. T killer cells
4. T memory cells
\
stimulate B cells to produce more antibodies
binds to complimentary antigen on antigen presenting cell
releases interleukins
activate B cells, T killer cells, stimulate macrophages
what is the function of T killer cells
kill pathogens with specific antigens
kill any infected cells
how do T killer cells kill
produce chemical perforin
makes holes in the cell membrane of the pathogen
stop the immune response once the pathogen is dealt with
prevent autoimmune diseases
rapidly divide when a known pathogen’s antigen is detected
form clones of T killer cells
1. plasma cells
2. B memory cells
remember specific antigen
trigger secondary immune response rapidly if antigen is encountered again
T helper cells divide and stimulate: (clonal expansion)
* production of T memory cells
* production of T killer cells
* production of interleukins to stimulate B cells to divide
B cells divide rapidly (clonal expansion)
Differentiate into plasma cells and memory cells
Plasma cells release antibodies specific to that antigen into the blood
in secondary immune system no clonal selection is needed as the memory cells initiate clonal expansion rapidly as soon as the pathogen is detected
lupus
type 1 diabetes
what is artificial active immunity
when the immune system is stimulated to make antibodies by injecting it with a dead/inactive pathogen - vaccinesw
what is artificial passive immunity
when antibodies for a pathogen are injected into the body - gives temporary immunity
what are the steps of vaccination (4)
Pathogen is made safe and injected
antigen presentation/T helper cells bind to antigen
clonal selection, clonal expansion, and antibodies produced
memory cells produced for immunological memory
1. due to a random mutation, a small population of the bacteria are not affected by the antibiotic
2. the other bacteria are killed so there is less competition
3. the resistant bacteria are more likely to survive and reproduce
4. bacteria reproduce rapidly and all their daughters are resistant as well
5. soon majority of the bacteria population will be resistant
name of pathogen which carries malaria
plasmodium
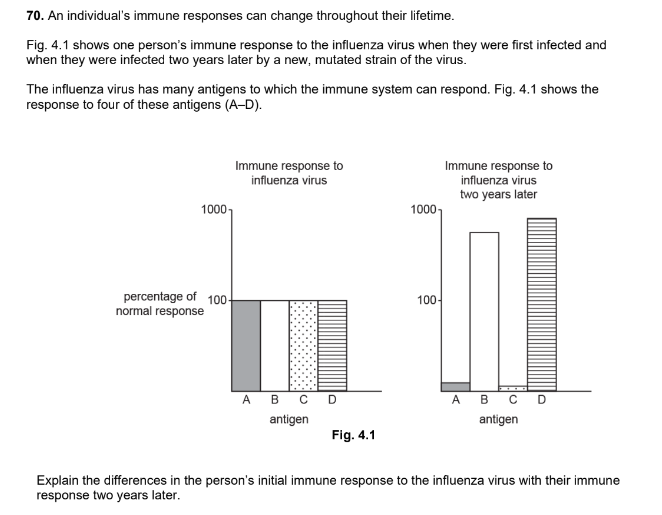
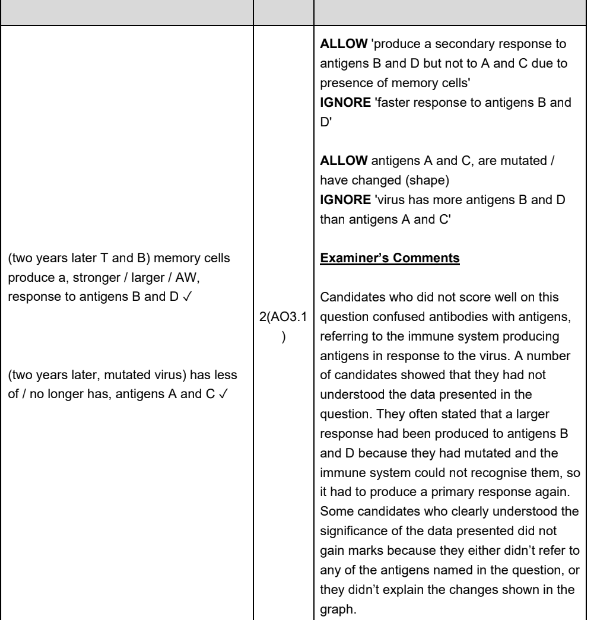
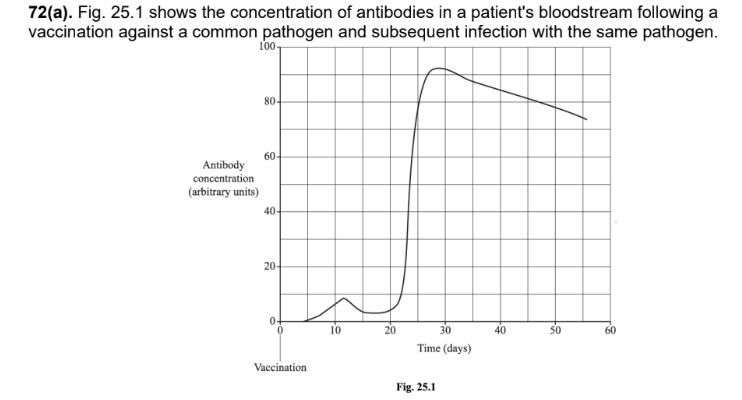
Explain why the response to the subsequent infection is much bigger than the response to vaccination (3 marks)
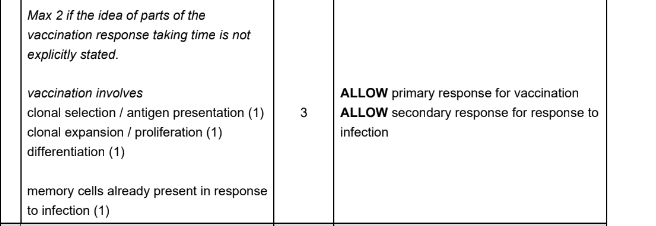
explain why vaccinations are an example of active immunity (2 marks)
