Ovaries: Functional Cysts
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What type of cysts result from the NORMAL function of the ovary?
Functional cysts
What type of cysts are the MOST COMMON cause of ovarian ENLARGEMENT in YOUNG women?
Functional cysts
List the different types of functional cysts.
Follicular
Corpus luteum
Hemorrhagic
Theca-lutein cysts
Regarding a functional cysts, what is sometimes administered to SUPRESS a cyst?
Hormonal therapy
What type of cysts measure LESS than 5 cm and REGRESS during subsequent menstrual cycle?
Functional cysts
For fucntional cysts, a follow-up sonographic exam in ___ weeks usually documents change in size. Why don’t you want to do it at the 4 week mark?
6 weeks; its in the same cycle, so you wouldn’t be able to accurately notice a change in size
What type of functional cysts forms when the DOMINANT follicle does NOT ovulate and remains acitve through immature?
Follicular cysts
Are follicular cysts usally unilateral or bilateral?
Unilateral
What are the symptoms for a follicular cyst?
Usually asymtomatic, but there could be:
Dull adnexal pressure and pain
Abnormall ovarian function
Torsion of the ovarys results in serve pain
What are the measurements for follicular cysts?
They usally measure less than 2 cm; has a range of 1-8 cm, but can grow up to 20 cm in diameter
What type of cysts can spontaneously regress and are frequently detected incidentally on sonographic exams?
Follicular cysts
How would you generally describe the sonographic appearence of follicular cysts?
Thin-walled
Translucent watery fluid
May project above or within surface of the ovary
Treatment for follicular cysts.
They usually regress on their own, but surgical intervention or surgery may be needed if they grow to large.
What is a sonographic finding for follicular cysts?
Simple cysts
What AGE of women would you see get follicular cysts?
Women of REPRODUCTIVE age
What type of functional cysts results from FAILURE of resorption or excess bleeding into the corpus luteum?
Corpus luteum cysts
What type of functional cysts results from hemorrhage within persistently mature corpus luteum?
Corpus luteum cysts
Are corpus luteum cysts usually unilateral or bilateral?
Unilateral
What are corpus luteum cysts filled with?
Blood and cystic fluid
What are the measurements for corpus luteum cysts?
Usually 4 cm (less than) but can be 1-10 cm in size
What type of functional cysts are prone to hemorrhage and rupture?
Corpus luteum cysts
Corpus luteum cysts may accompany what?
Intrauterine pregnancy (IUP)
List the risk factors to corpus luteum cysts.
Intrauterine pregnancy
Hormonal imbalance
Endometriosis
Pelvic infections
PCOS
What are the symptoms of corpus luteum cysts?
Irregular menstural cycle
Pain
Mimics ectopic pregnancy
Rupture
What type of functional cyst is a “cystic” type of lesion and may have INTERNAL echoes secondary to hemorrhage and INCREASED color doppler?
Corpus luteum
With a corpus luteum cyst, how does a hemorrhage cause it to look?
It appears as a COMPLEX mass with CENTRAL blood clot and echogenic sepatations.
True or False
A corpus luteum cysts may exhibit posterior enhancement, depending on internal content.
True
A ___-velocity waveform is present with a corpus luteum cyst.
Low
What type of functional cysts will you see a peripheral rim of color around the wall (“ring of fire”)
Corpus luteum cyst
Treatment for corpus luteum cyst.
They do NOT require treatment because they usually resolve on their own within a few weeks to months; however, surgery is nedded if it does become large and cause server pain.
What type of functional cysts are a fluid-filled sac on the ovary that contains blood?
Hemorrhagic cysts
Internal HEMORRHAGE may occur in follicular cysts or MORE commonly in ________ _________ cysts.
Corpus luteum cysts
A sonographic image of a hemorrhagic cyst are dependent on what?
The amount of hemorrhage
Clot formation
Time passed since hemorrhage
ACUTE hemorrhagic cyst usually is __________ (echogenicity). What may it mimic?
Hyperechoic; solid mass
Describe the wall of a hemorrhagic cyst.
SMOOTH posterior wall with posterior enhancement, which indicates its CYSTIC components.
As a hemorrhagic cyst AGES, what happens?
The INTERNAL pattern becomes more COMPLEX.
Hemorrhagic cysts may have diffuse ____-level echoes, but are MORE commonly seen in ______________.
Low; endometriomas
With a hemorrhagic cyst the clotted blood become MORE ________ and may show a _______ level.
Echogenic; fluid
What could help confirm the diagnosis of a RUPTURED or LEAKING hemorrhagic cyst?
Echogenic free intraperitoneal fluid in the cul-de-sac
True or False
Hemorrhagic cysts usually go away on their own, but may require pain medication, hormonal therapy, or surgery/follow-up if it gets to large and the symptoms its causing.
True
List the risk factors for hemorrhagic cysts.
History of ovarian cysts
Fertility drugs
Pregnancy
Hormonal imbalances
PCOS
Symptoms for hemorrhagic cysts.
Acute (sudden) onset of pelvic pain
A RUPTURE or LEAKING hemorrhagic cyst may mimic a what?
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy, so it’s critical to know if the patient has POSITIVE pregnancy test
What are the LARGEST functional cysts and they are BENIGN, fluid-filled cysts that develop on the ovaries?
Theca-Lutein cysts
What may theca-lutein cysts undergo?
Torsion
Hemorrhage
Rupture
Are theca-lutein cysts bilateral or unilateral? Are they loculated or multiloculated?
Bilateral; multiloculated
What are theca-lutein cysts associated with?
HIGH levels of human chrionic gondotropin (hCG)
Theca-Lutein cysts are most FREQUENTLY seen in what?
**Think of a percentage.
30% of patients with gestational trophoblastic disease
List some risk factors for theca-lutein cysts.
Pregnancy
Infertility drugs (Pergonal)
Multiple gestations
Symptoms for theca-lutein cysts.
Nausea and vomiting
Ovarian enlargement
Pelvic pain
Why do theca-lutein cyst usally go away on their own? When may someone with these types of cyst need surgery?
Because they are BENIGN and if they become very LARGE.
A women of REPRODUCTIVE age has been on Fertility drugs for a few months and as NOT shown any symptoms up until recently. She has been sent in to do a pelvic exam due to some pressure and pain in her ADNEXAL area. When you scan her this is what you see. It measures about 4 cm in diameter. What pathology could this be? How would you describe it?
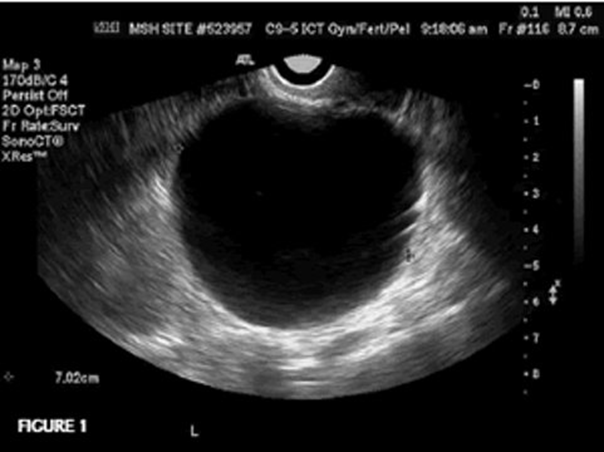
Follicular cyst
Unilateral, thin-walled, anechoic structure projecting within the ovary.
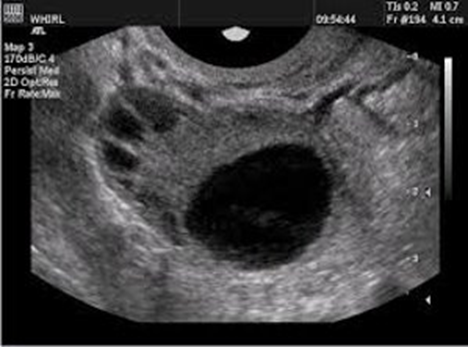
A 35 year-old women has went in to get a pelvic exam done because she has been experiencing some pain and has irregular menstrual cycle. She has history of hormonal imbalance, pelvic infections, and PCOS. She mentions that she has had these when she was PREGNANT (IUP) 4 years ago. She has had a previous ultrasound done 6 weeks ago and shows a structure measuring LESS than 4 cm in diameter. When you scan it, it is 6 cm. What pathology could this be? How would you describe it?
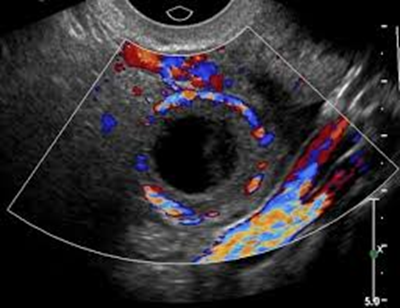
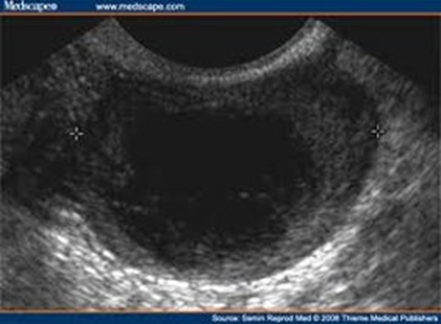
Corpus luteum cyst
Unilateral, cystic lesion, with internal echoes. Has the “ring of fire sign”
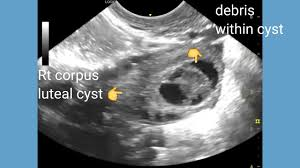
Other than the debris seen within the corpus luteum cyst. What do you also notice?
The internal echogenic region demonstrates a CENTRAL blood clot
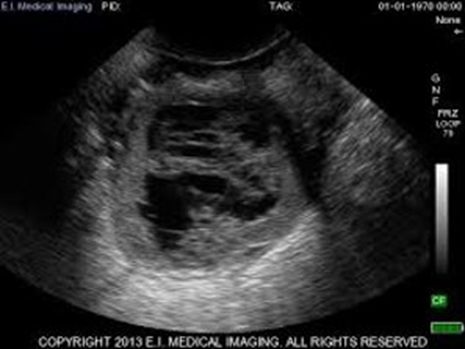
A 31-year-old women has come through the ER due to ACUTE onset of pelvic pain. You do a brief patient interview with her and learn that she has hormonal imbalances, PCOS, has been on fertility drugs and has a history of ovarian cysts. You scan her and see this. What could be the possible diagnosis? How would you describe it sonographically?
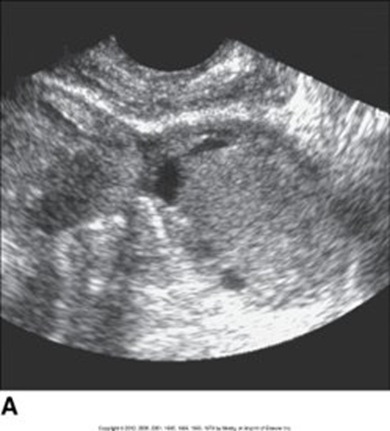
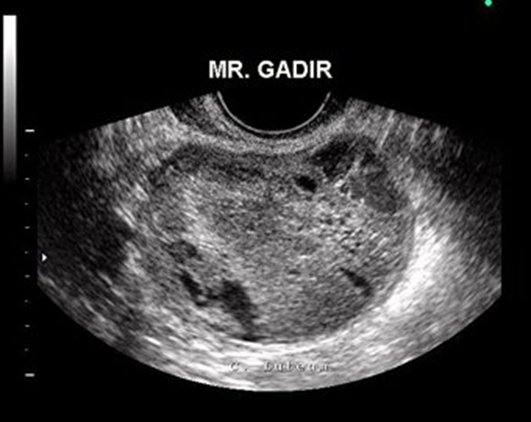
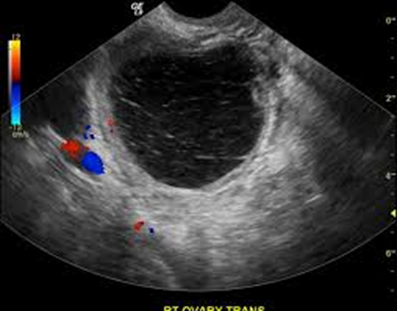
Hemorrhagic cysts
HYPERechoic with SMOOTH posterior wall and posterior enhancement due to its CYSTIC components
True or False (read the writing on the image)
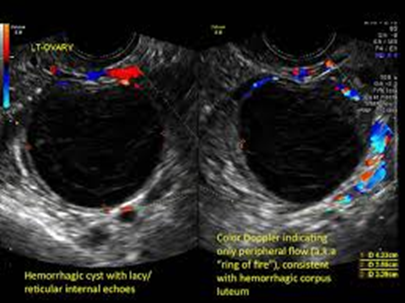
True
A PREGNANT women has a pelvic exam order because she has been experiencing some pelvic pain, nasuea and vomiting. She’s been pregnant MULTIPLE times and has a history of gestational trophoblastic disease. Her lab work also shows HIGH levels of hCG. When you scan her you notice how LARGE her ovaries are; the pathology is on BOTH ovaries and have MULTIloculated cysts. What could this pathology be?
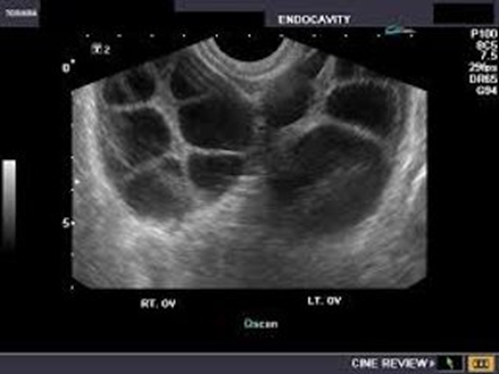
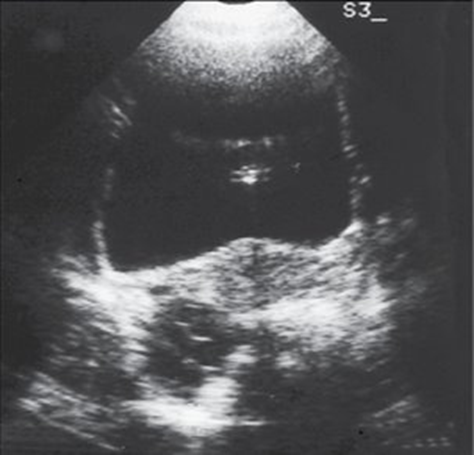
Theca-lutein cysts
What pathology is this?
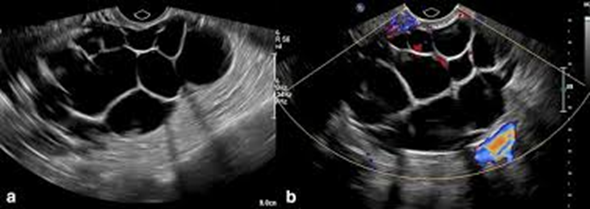
Theca-lutein cysts