The Axial Skeleton (Chapter 7)
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
how many bones are in the axial skeleton?
80 bones
how many bones does the skull consist of?
22 bones (not including the bones of the middle ears)
cranial bones
the 8 bones that form the cranial cavity to enclose and protect the brain
facial bones
14 bones that form the face
what are the two types of bones that make up the skull bones
cranial and facial
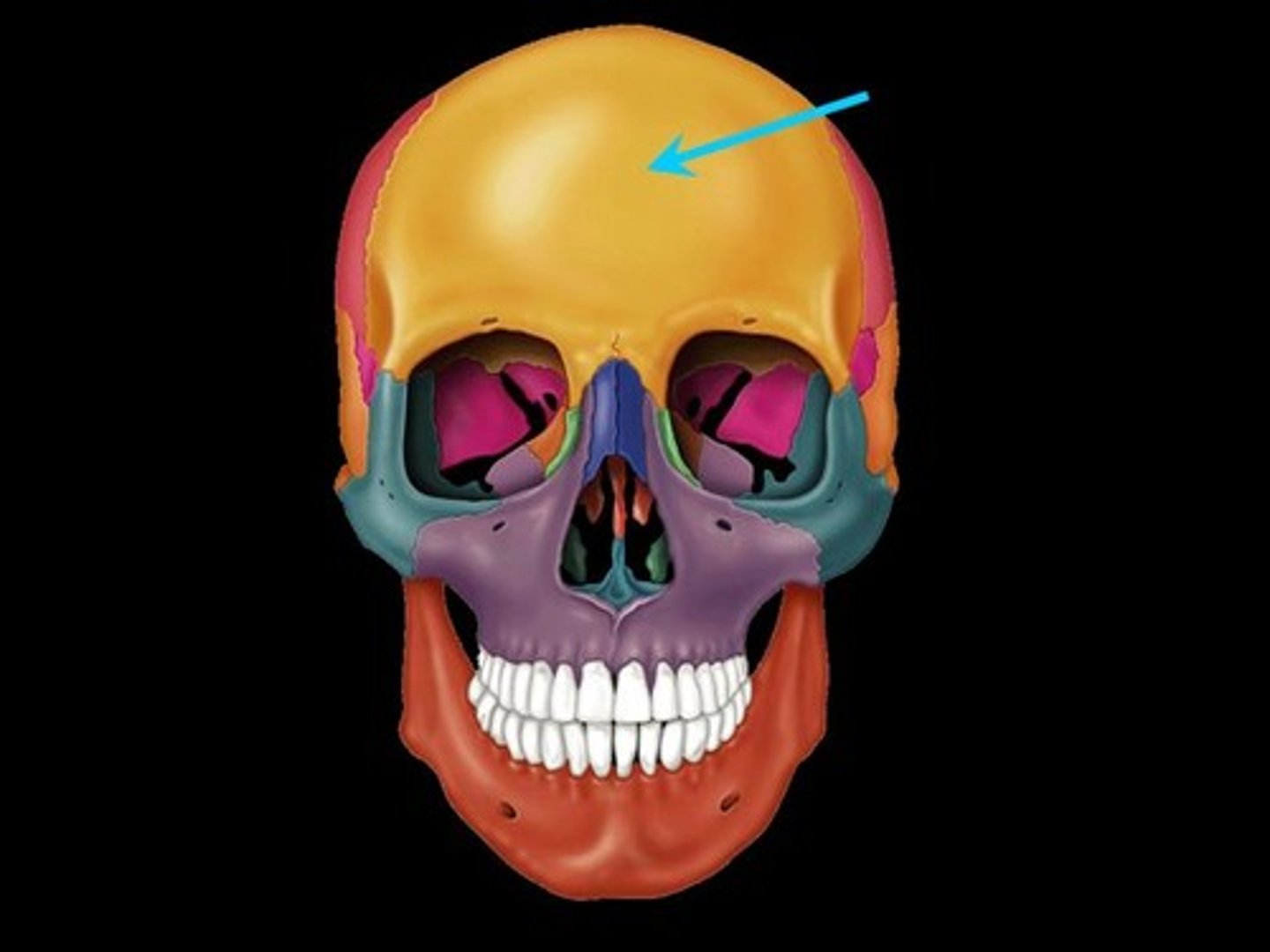
the 8 cranial bones
frontal, parietal (2), temporal (2), occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid
frontal squama
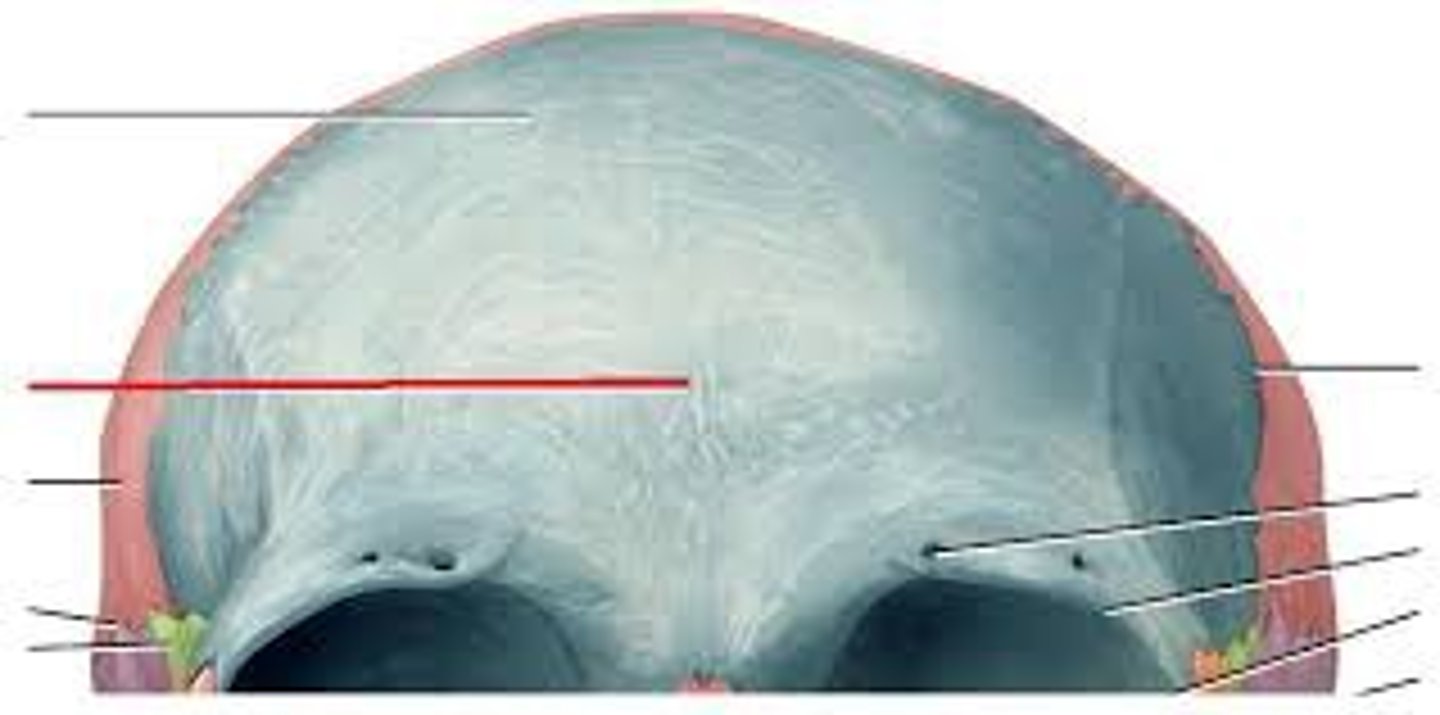
supraorbital margin
supraorbital foramen
frontal sinuses
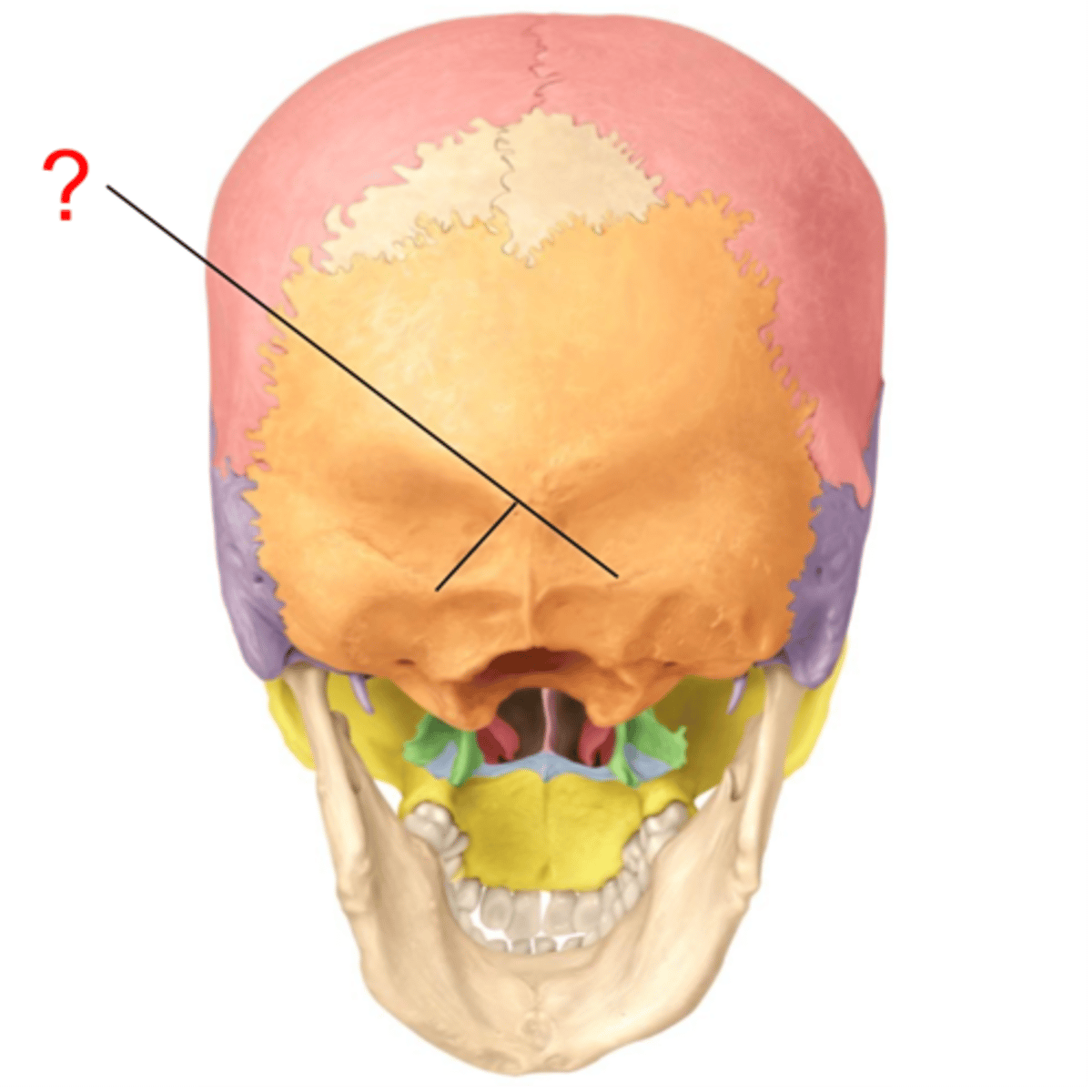
parietal bones
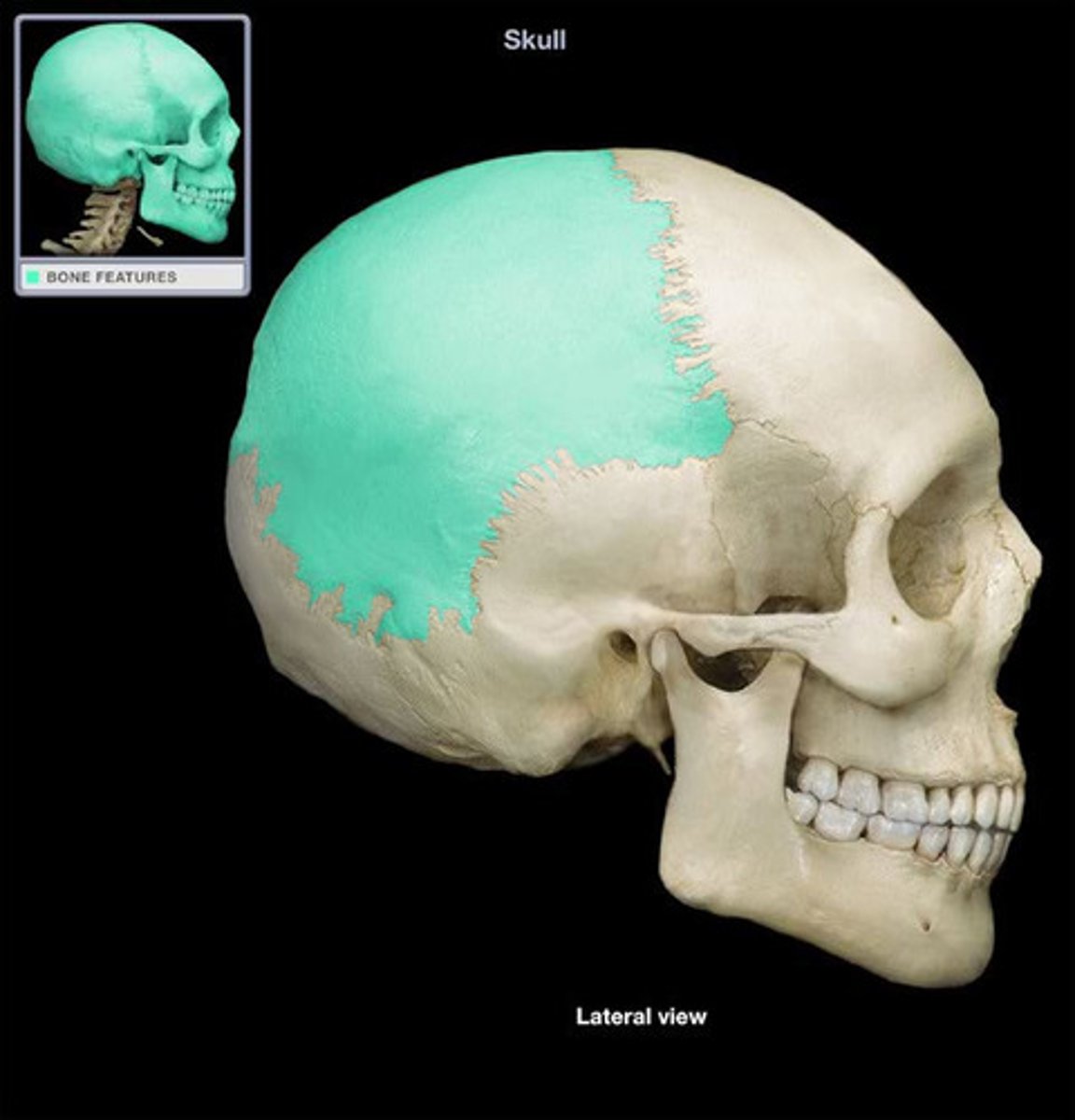
frontal bone
temporal bone
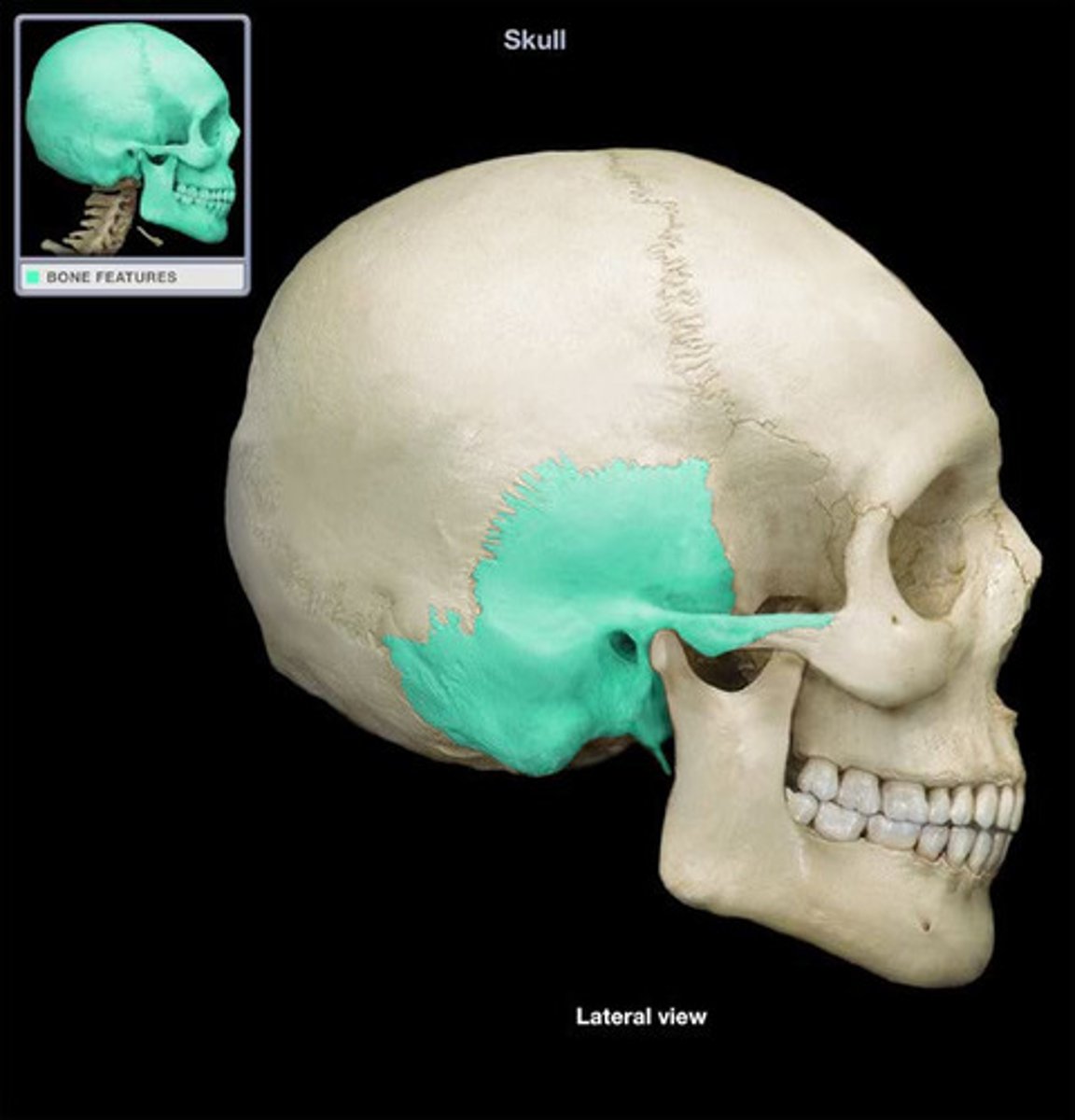
temporal squama
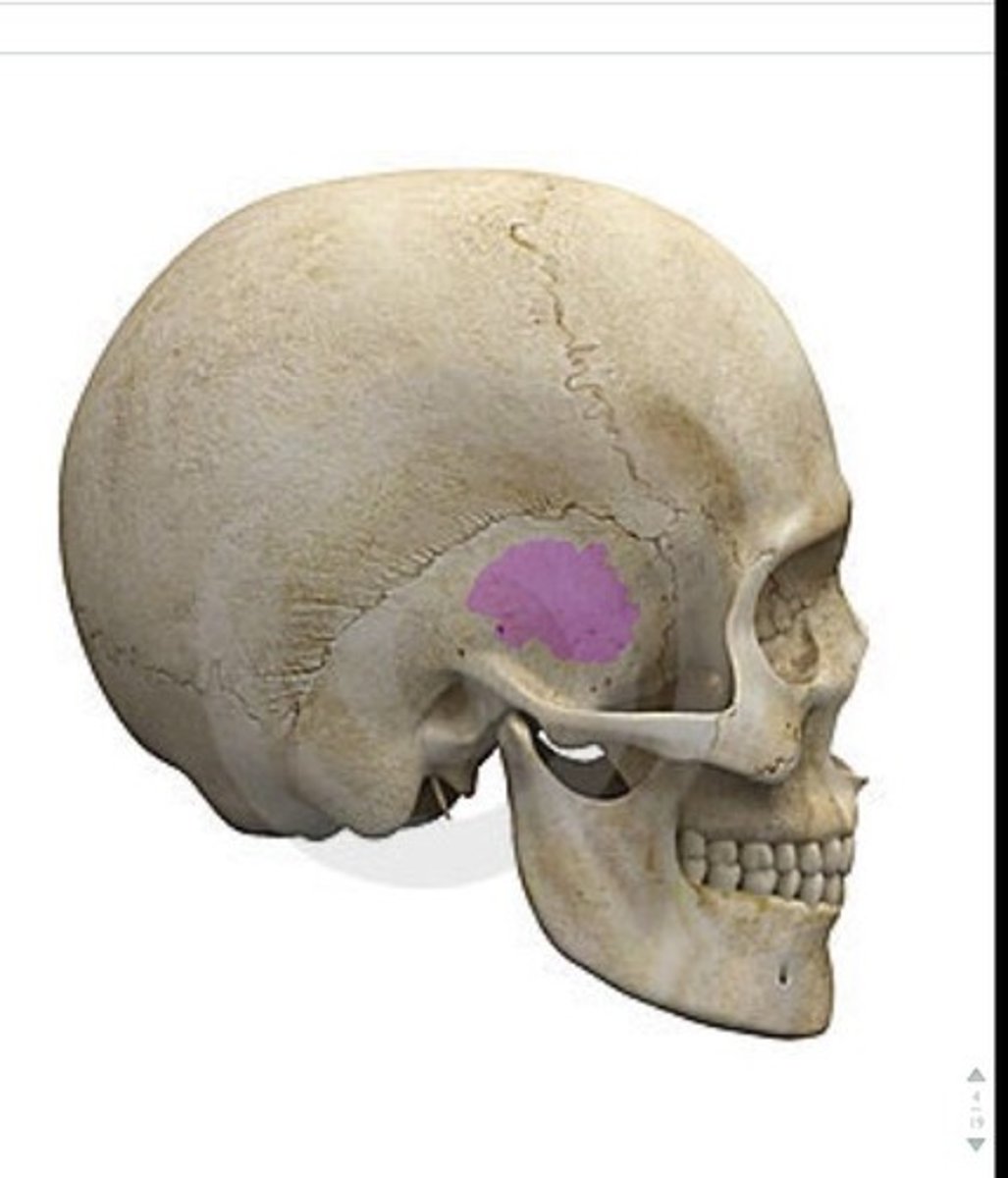
zygomatic process
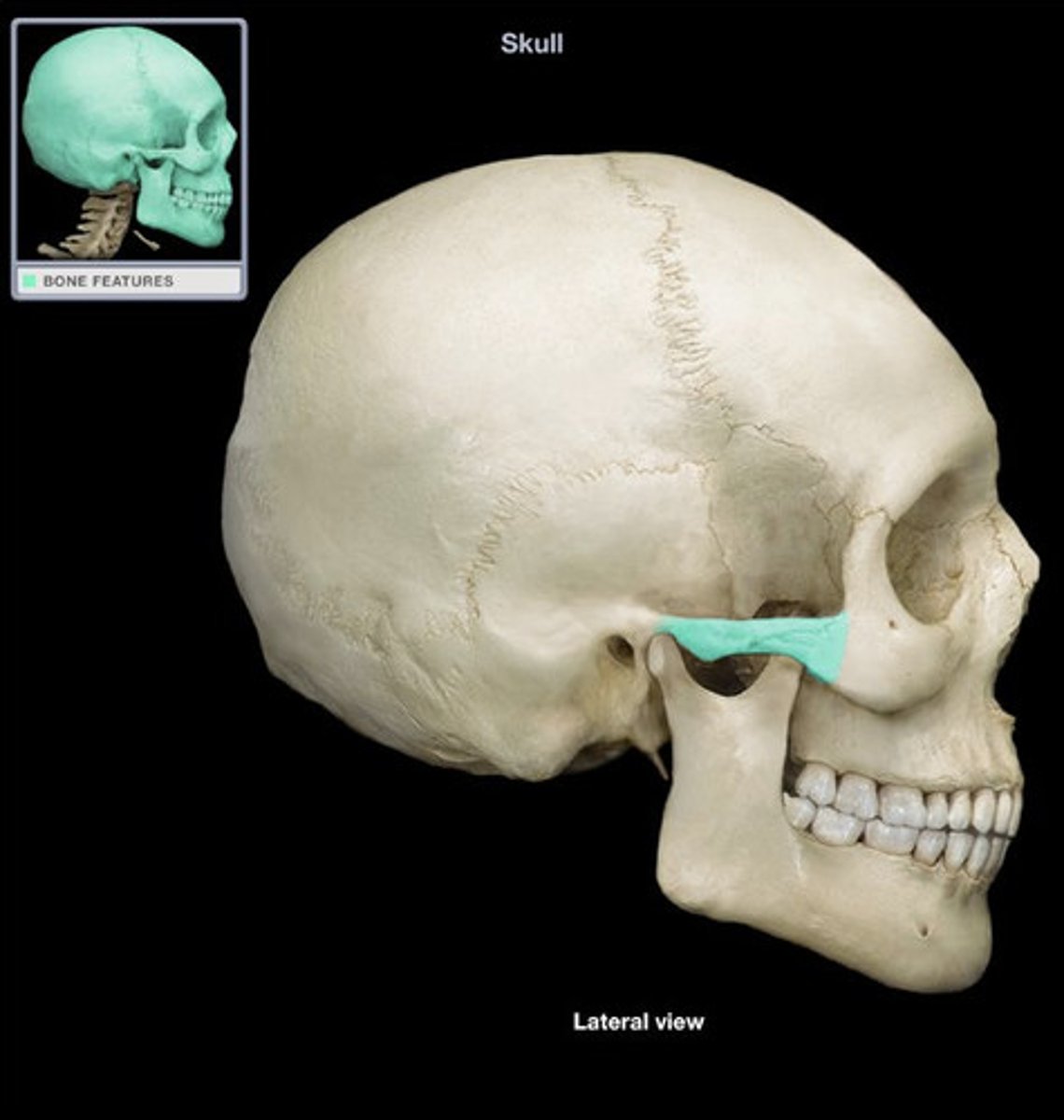
madibular fossa
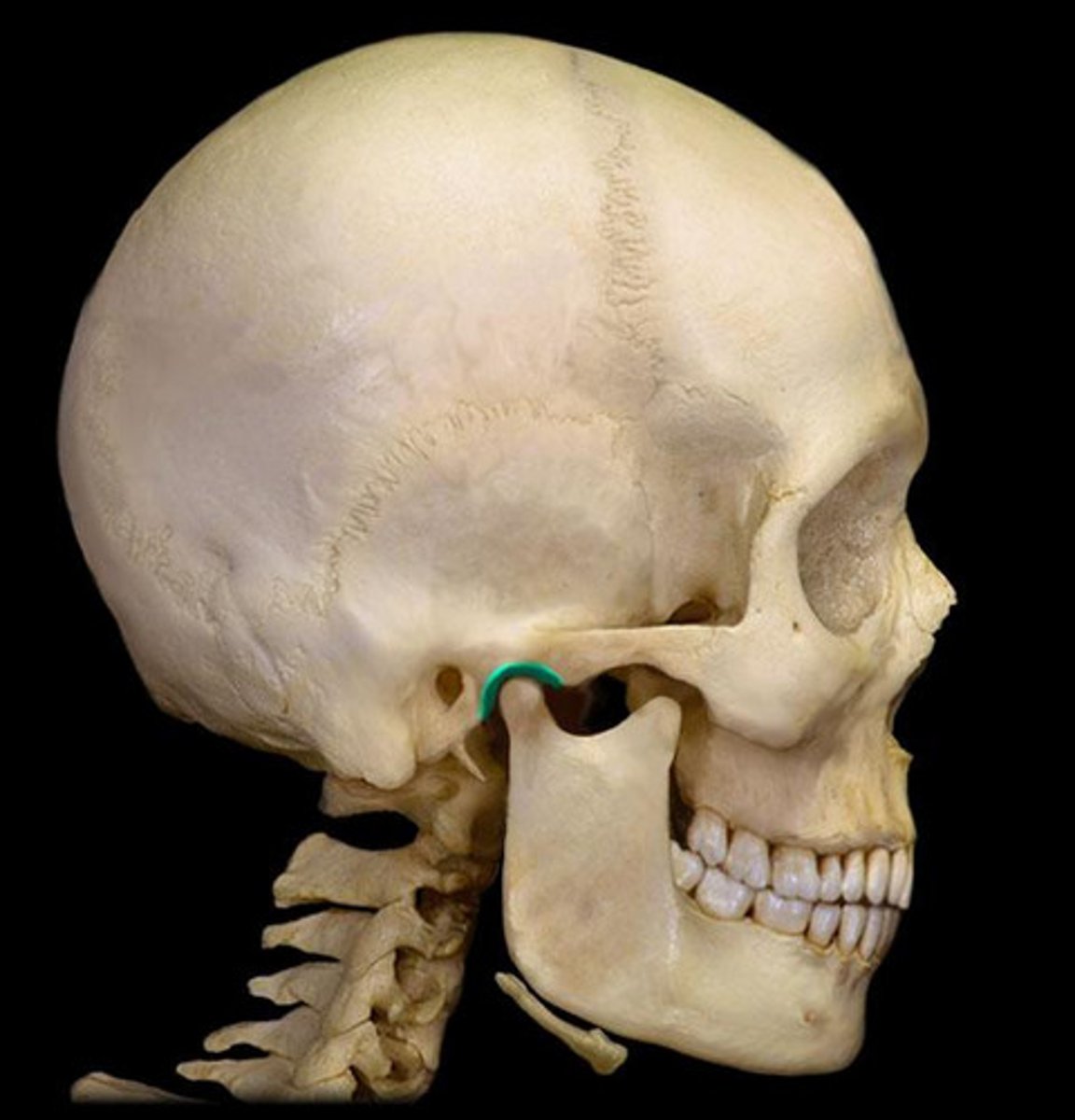
articular tubercle
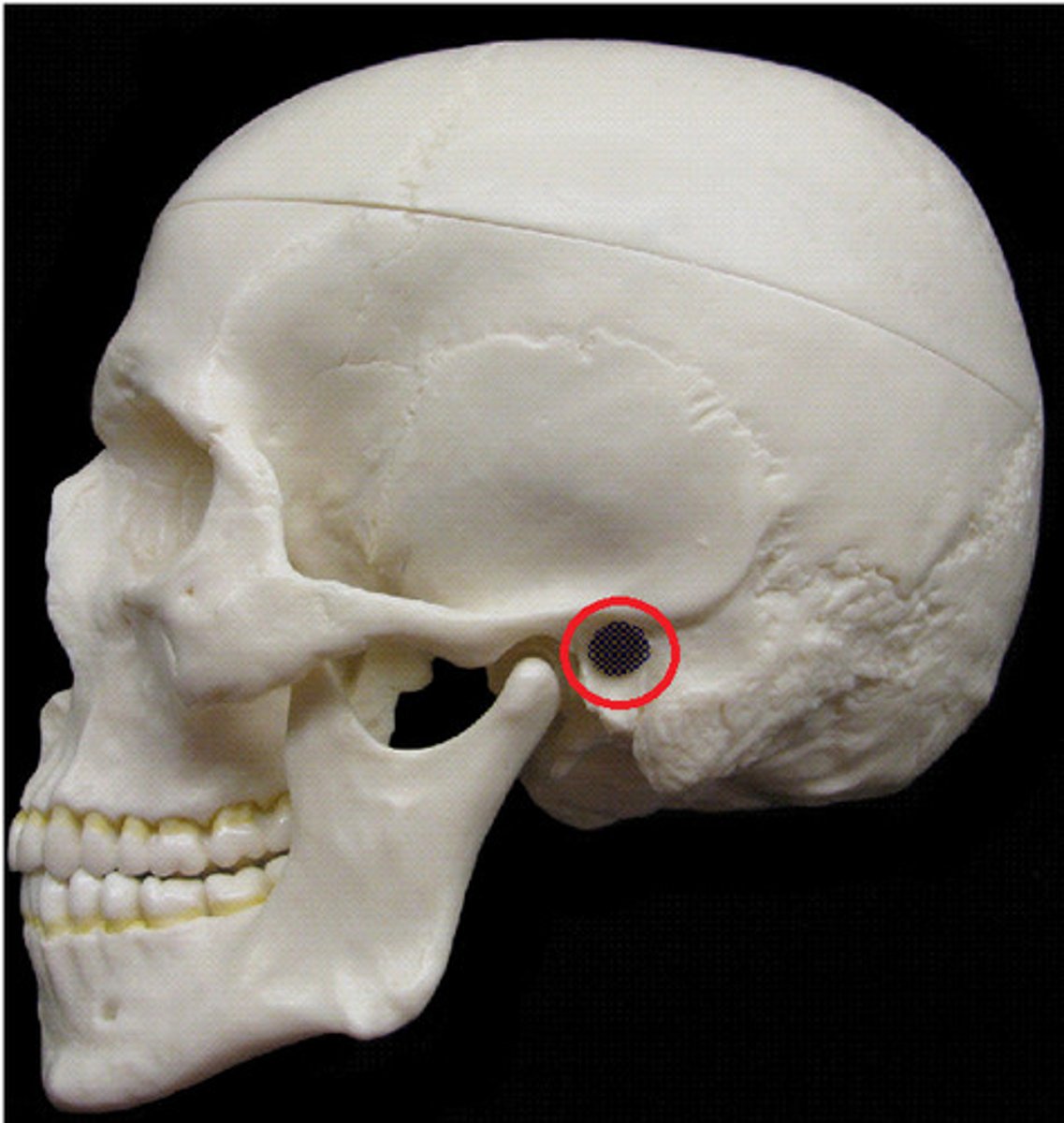
external auditory meatus
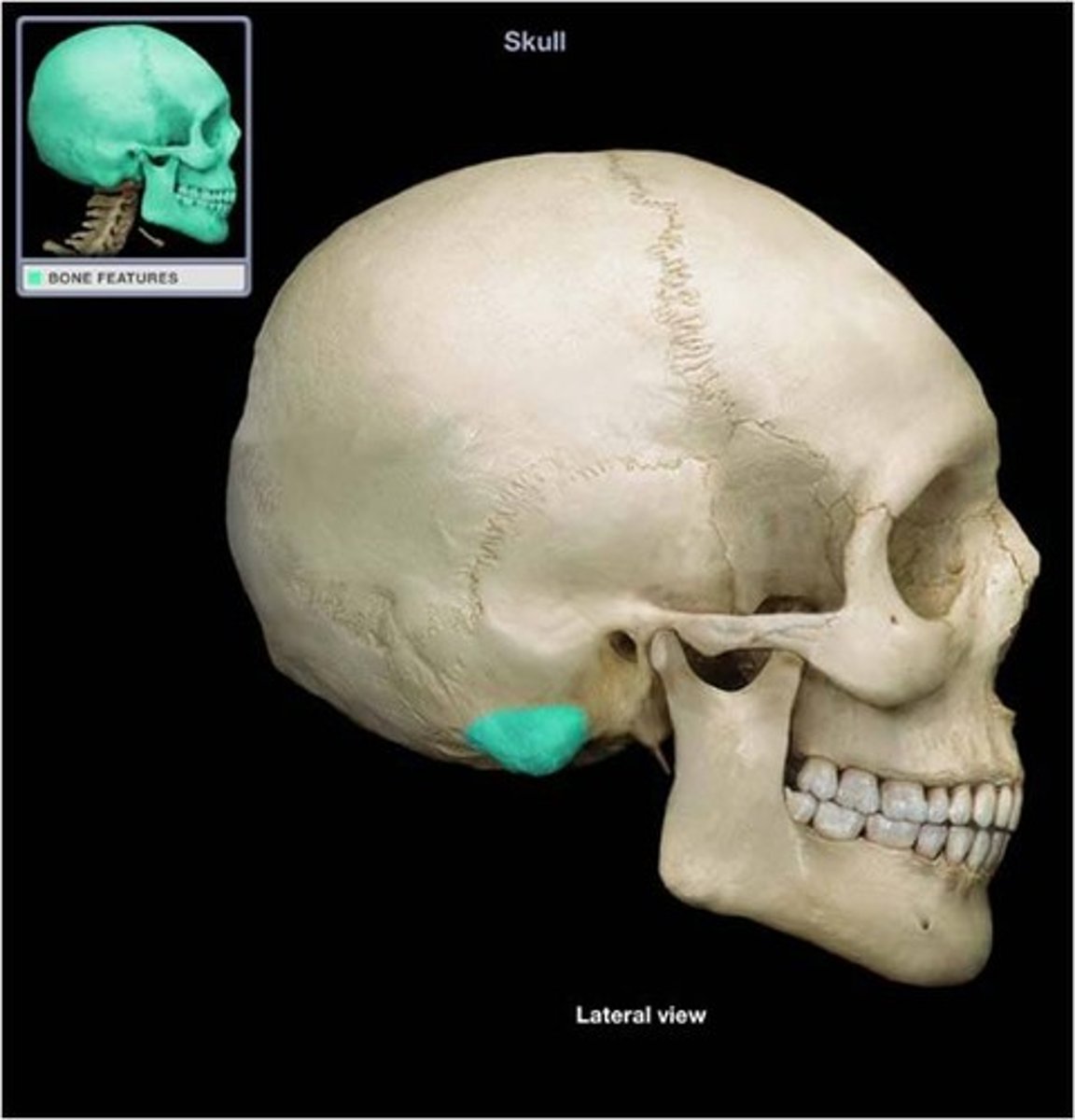
mastoid process
internal auditory meatus
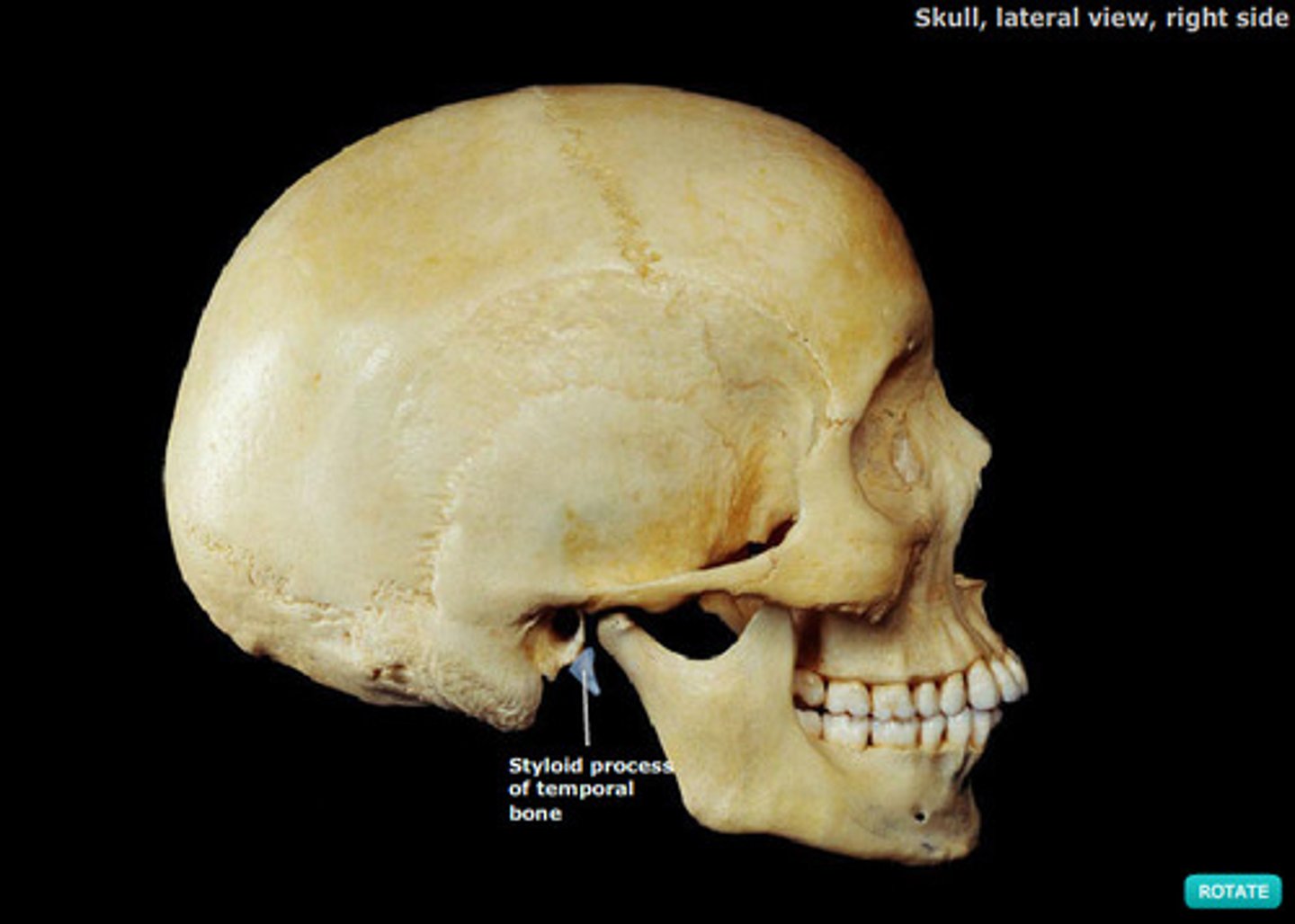
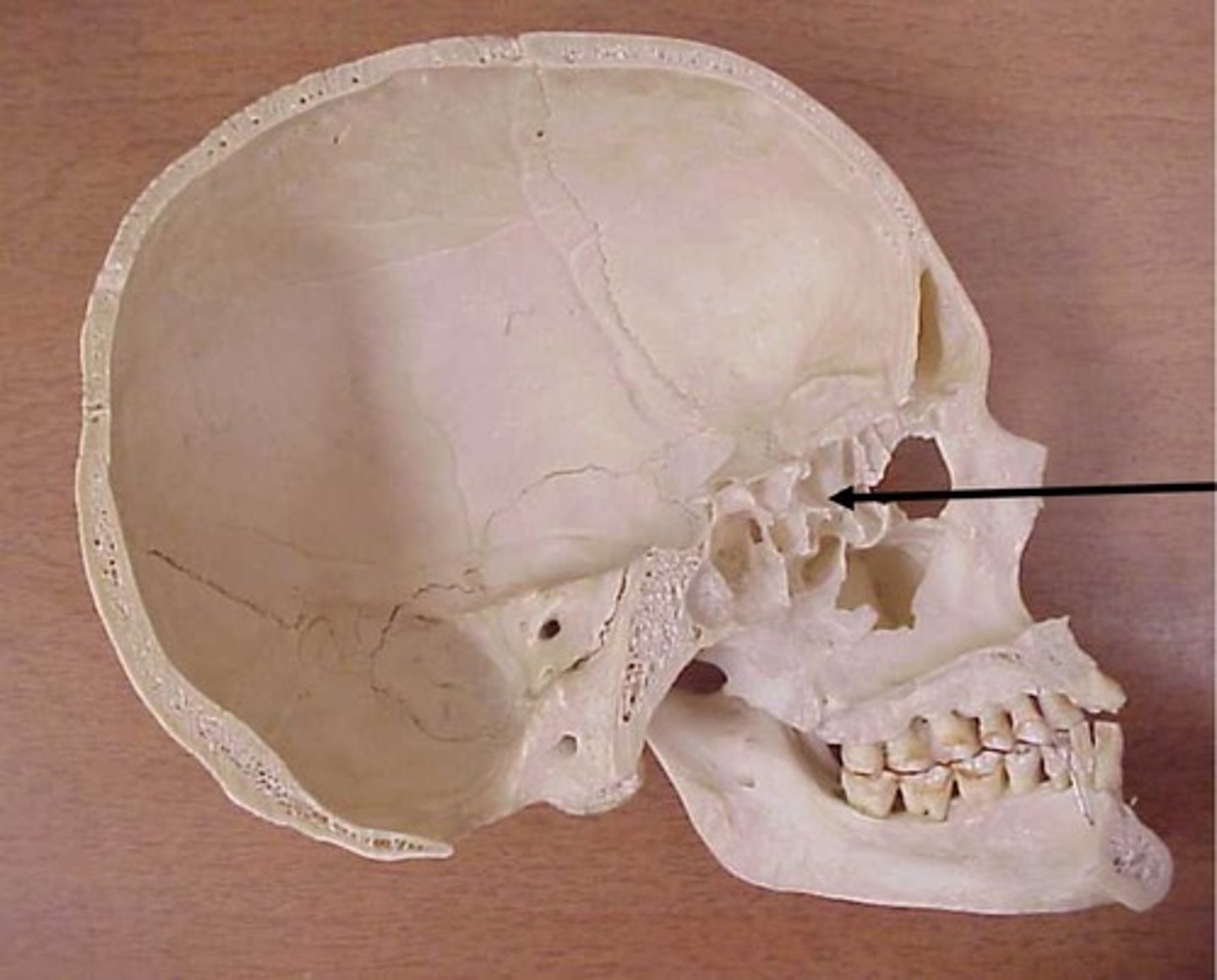
styloid process
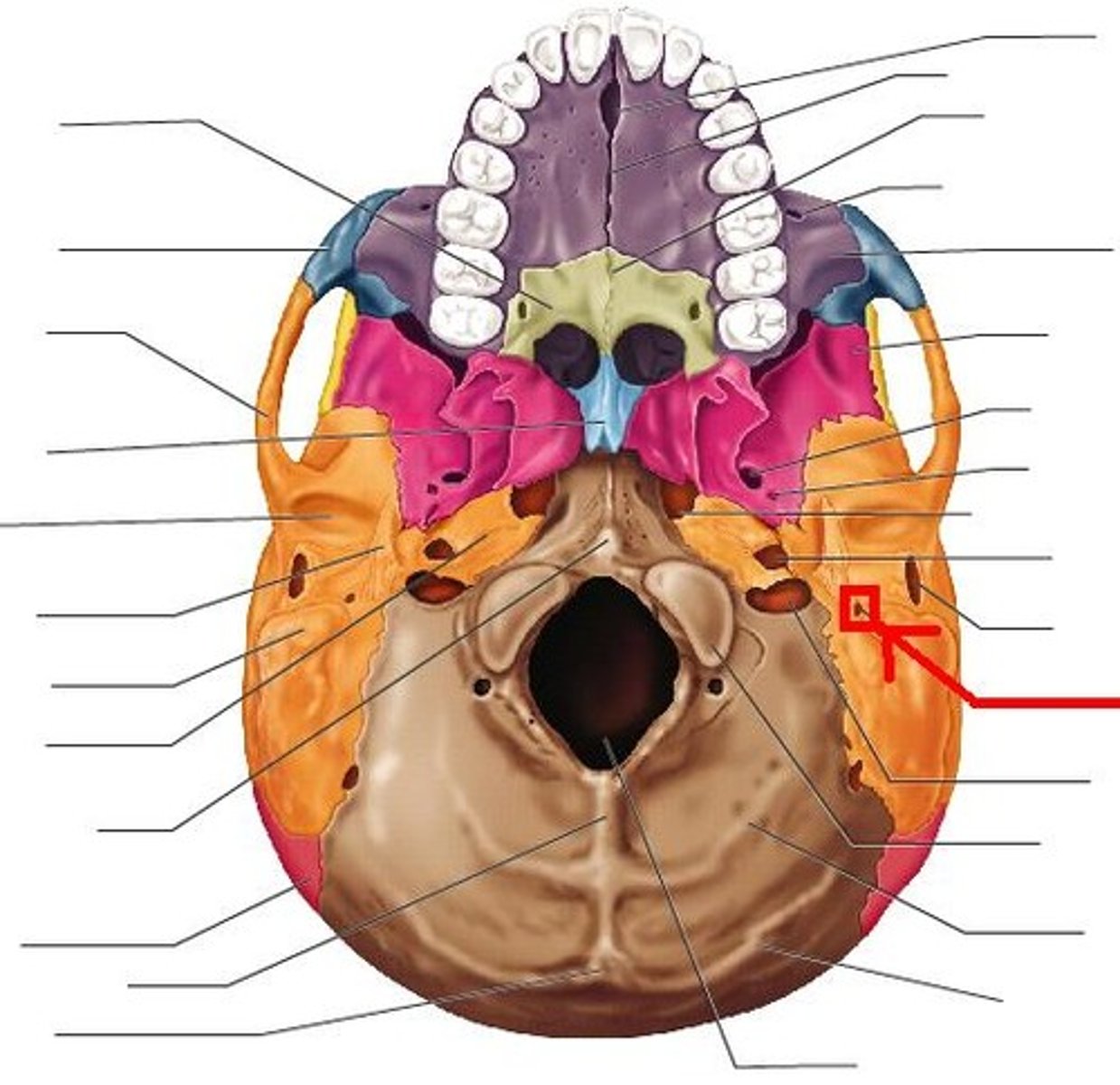
stylomastoid foramen
cartoid foramen
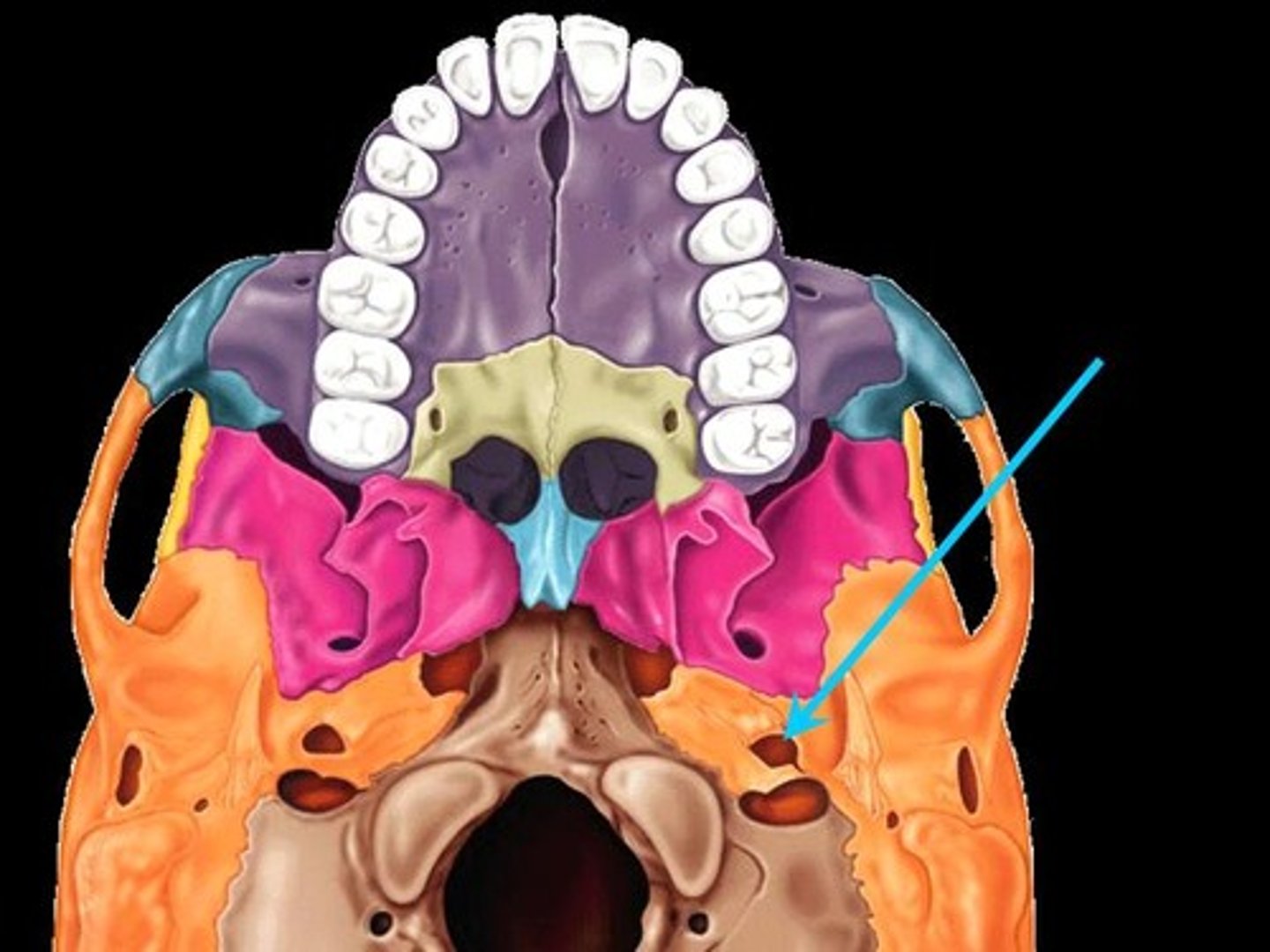
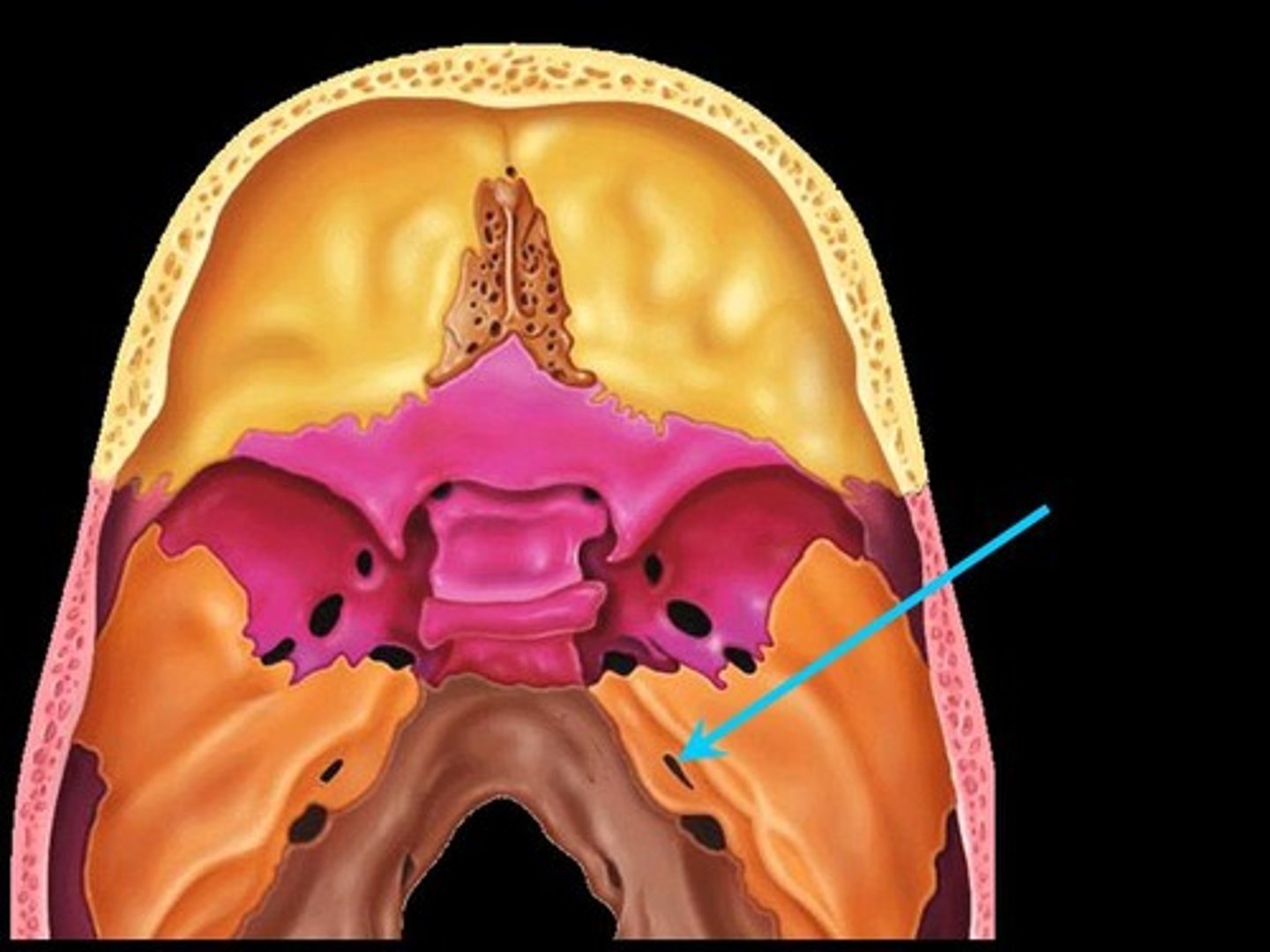
jugular foramen
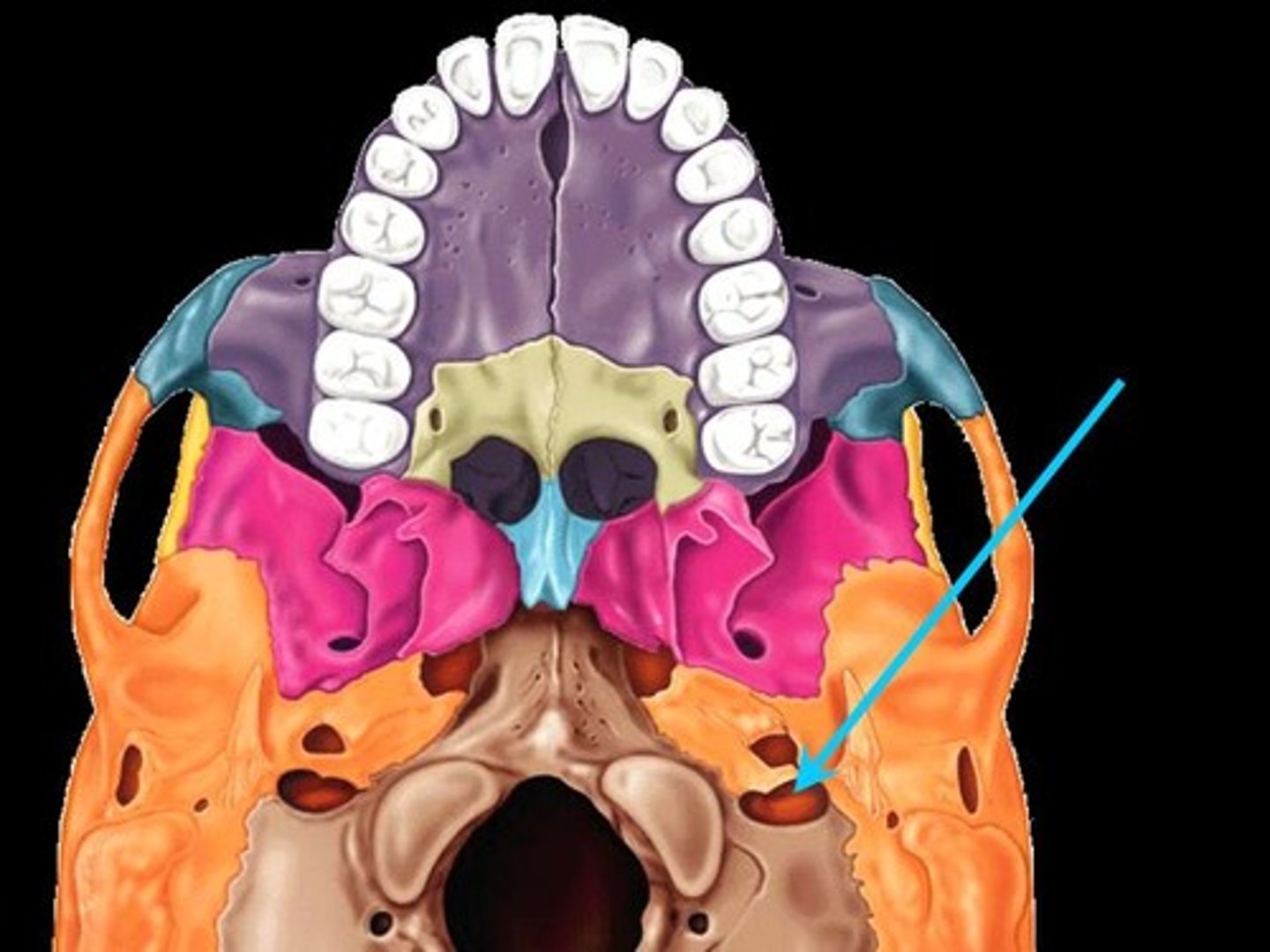
occipital bone
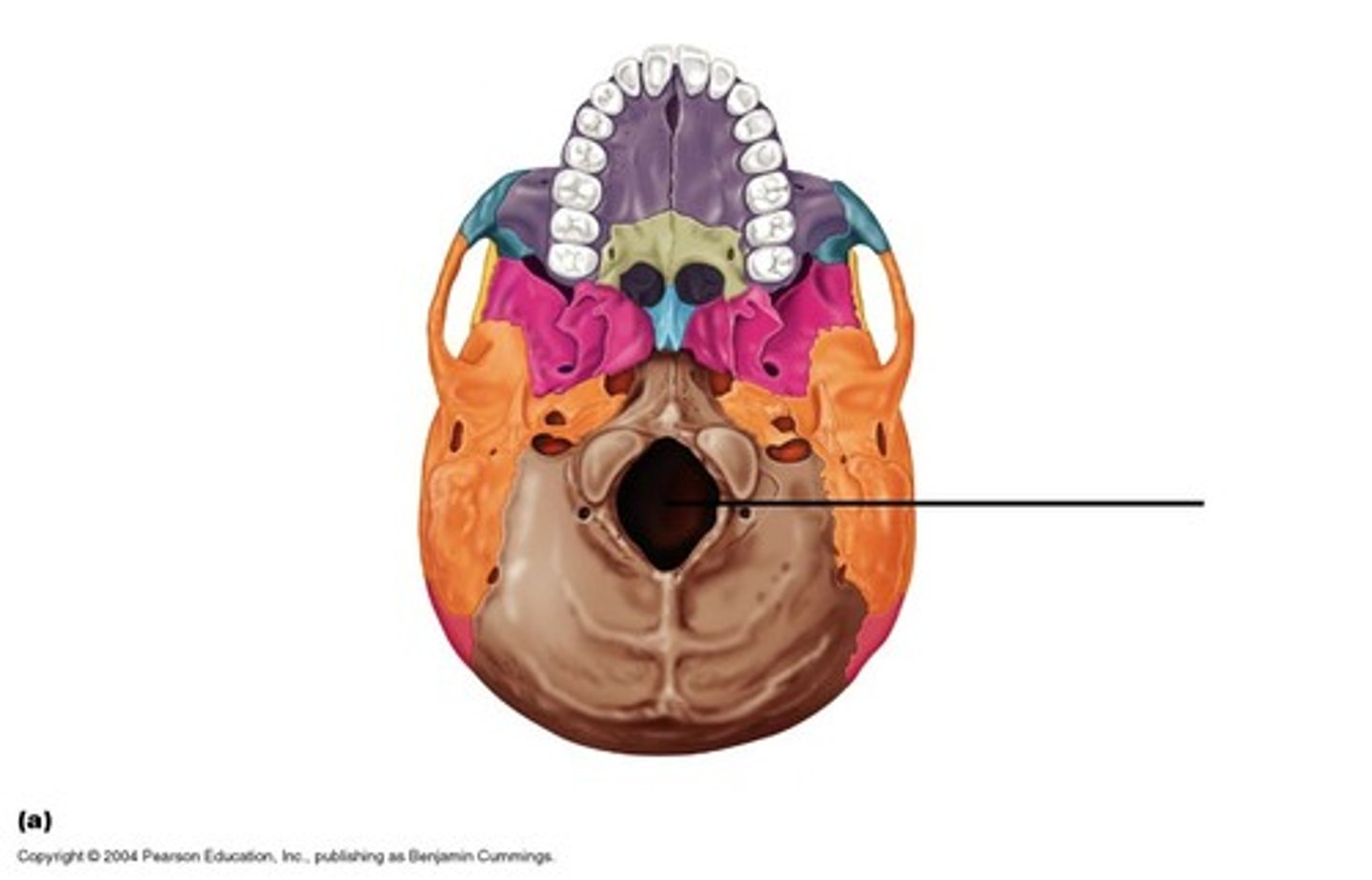
foramen magnum
occipital condyles
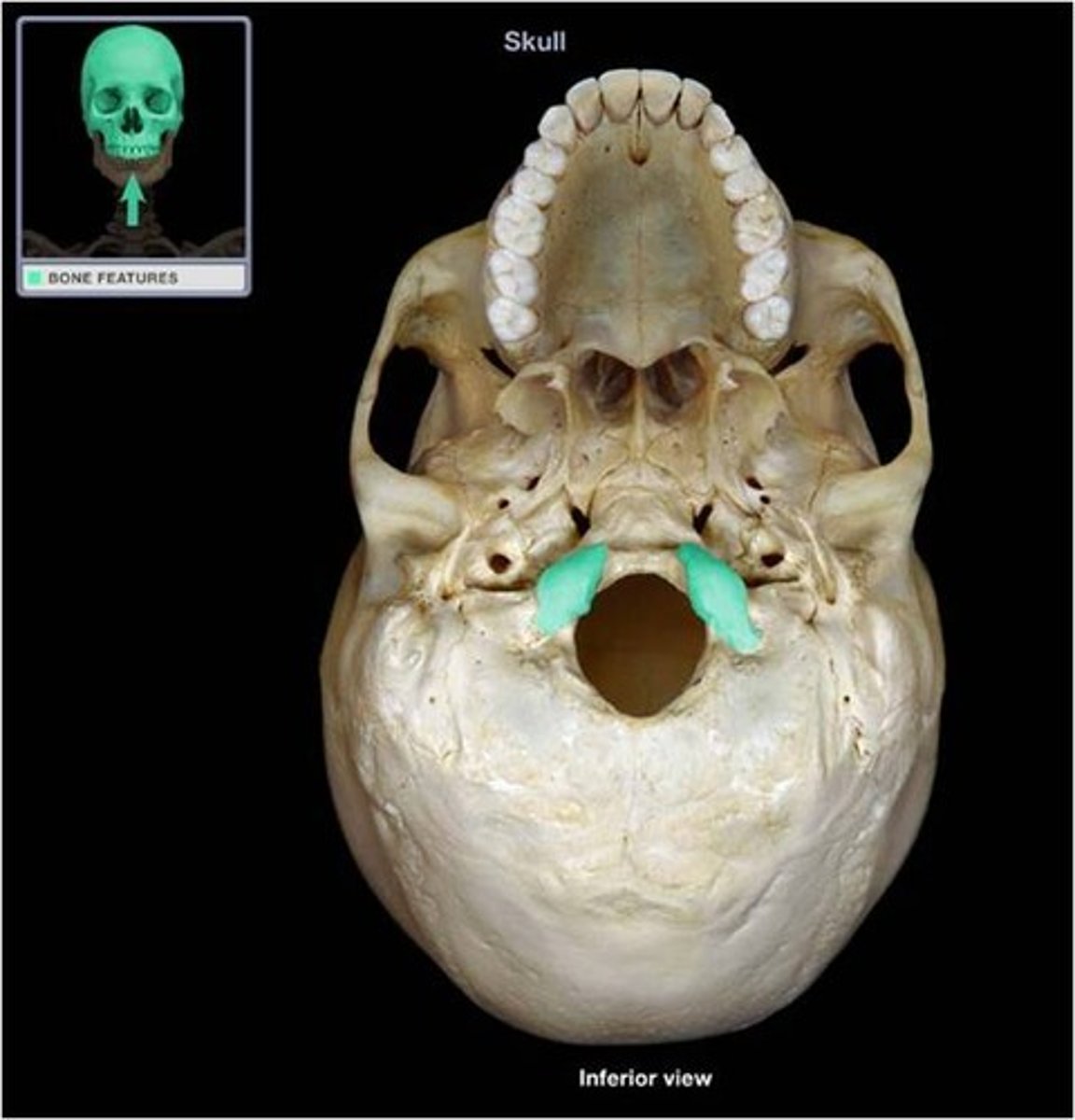
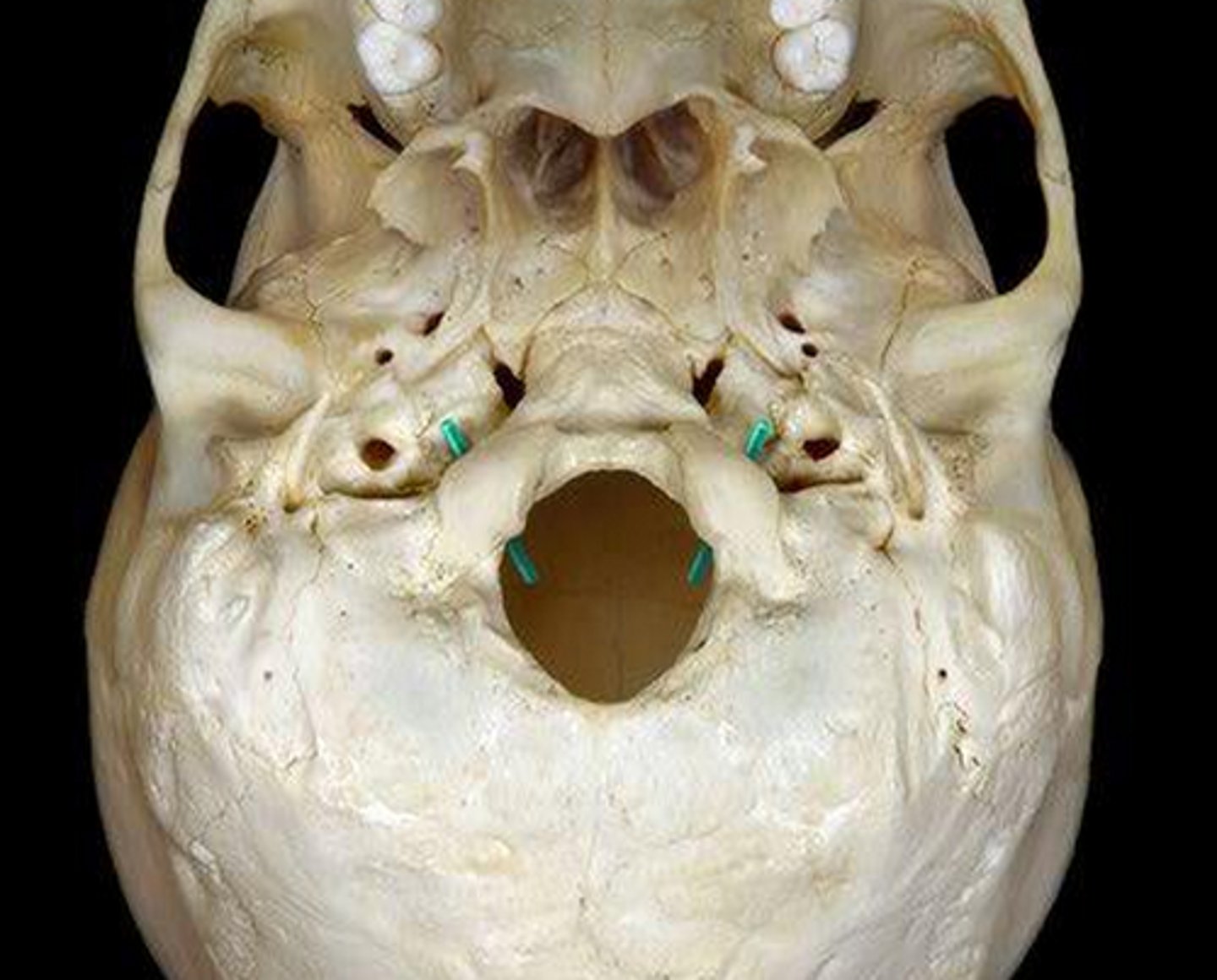
hypoglossal canal
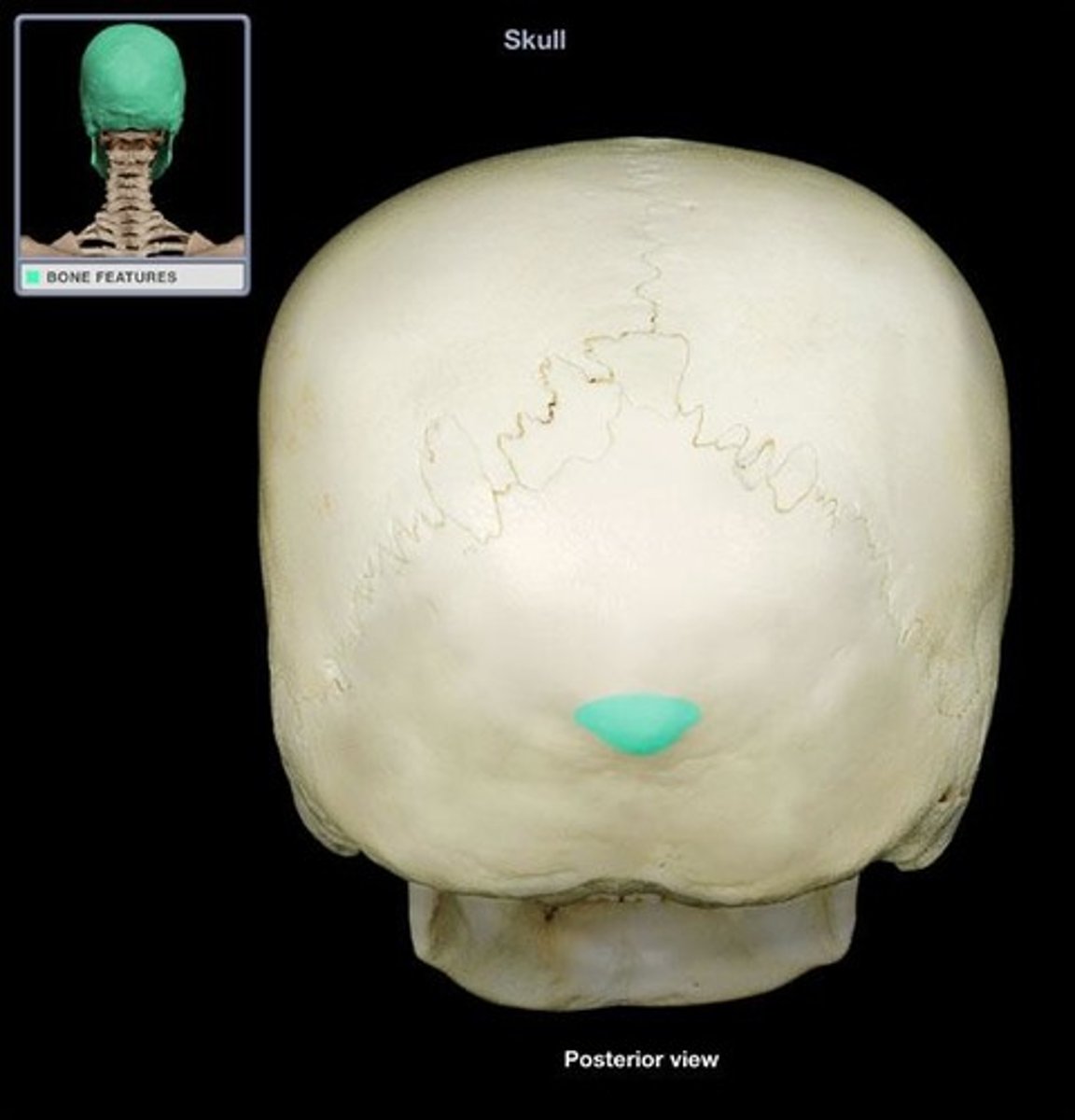
external occipital protuberance
superior nuchal lines
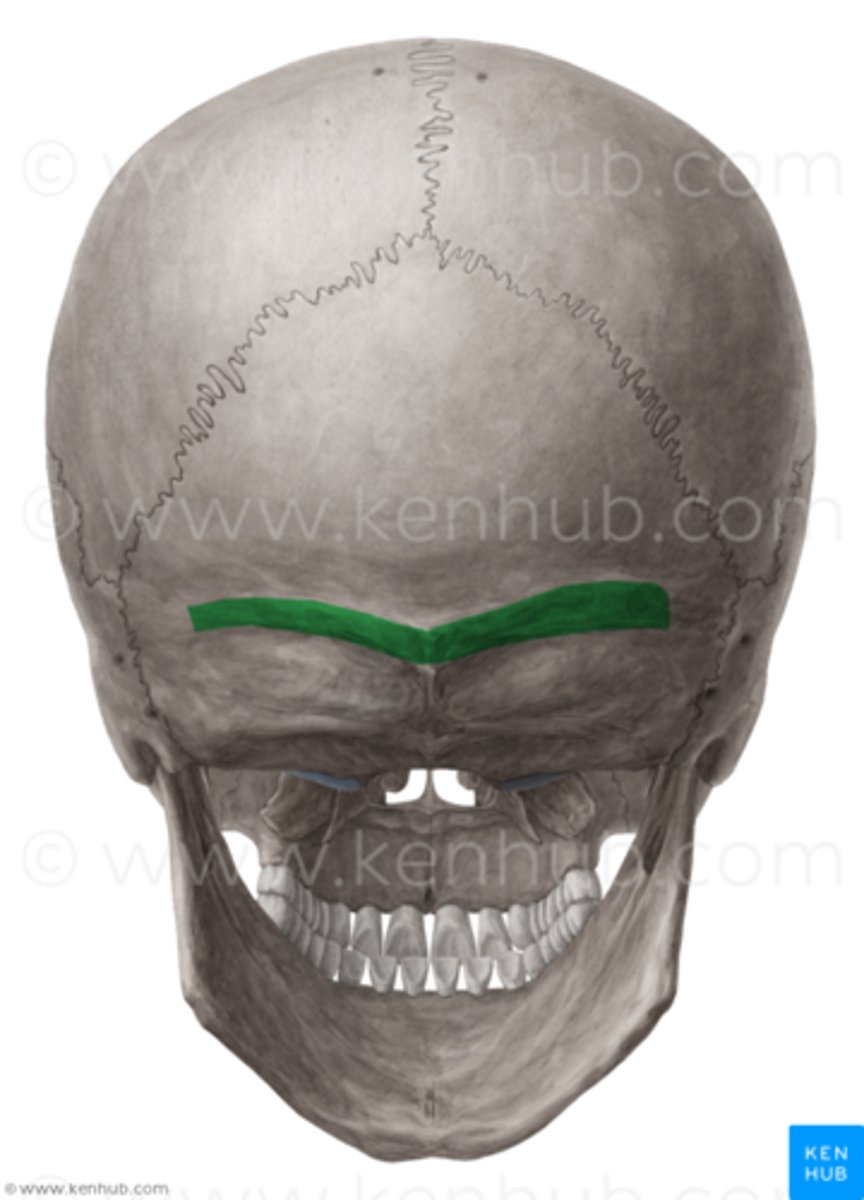
inferior nuchal lines
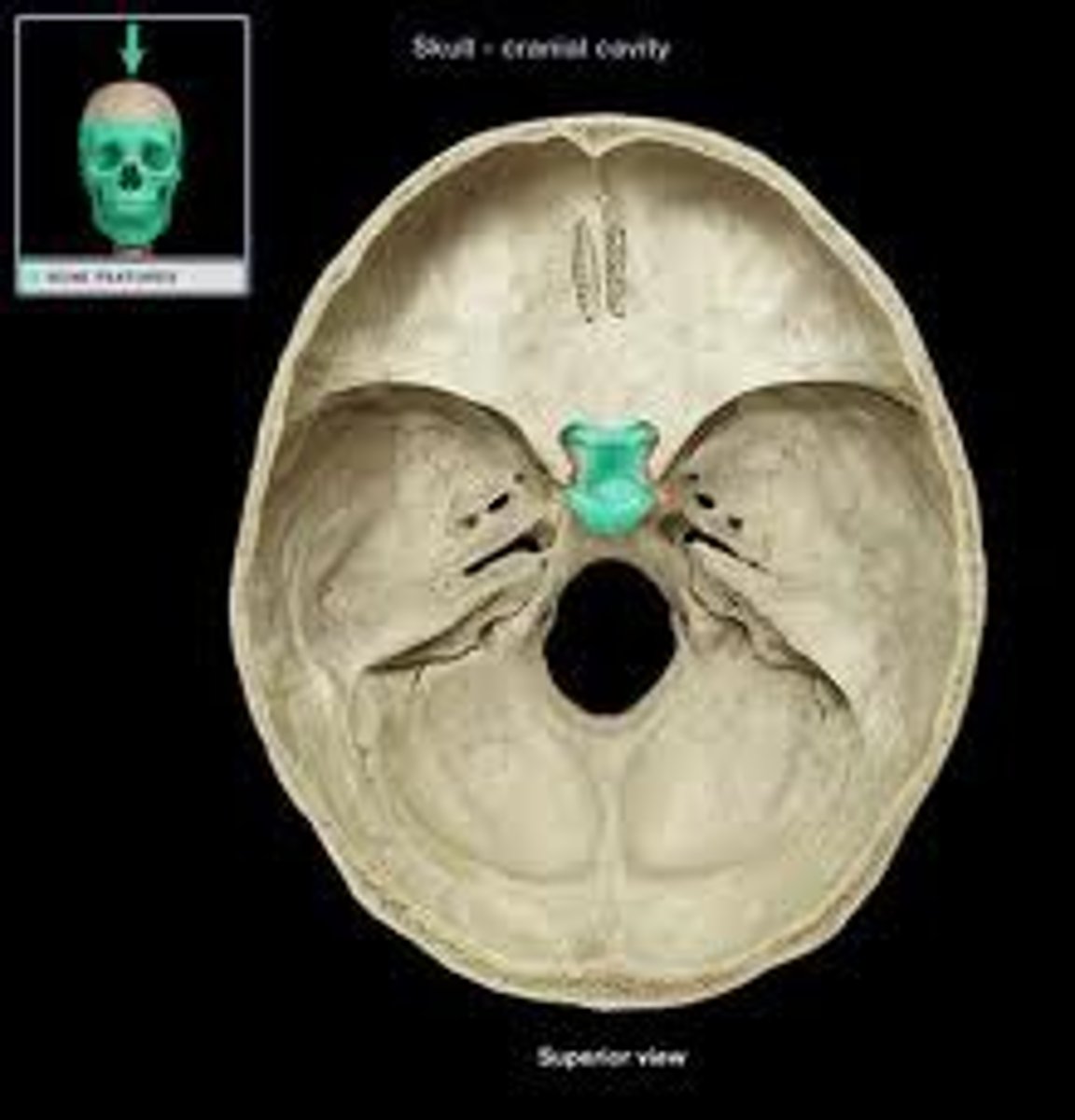
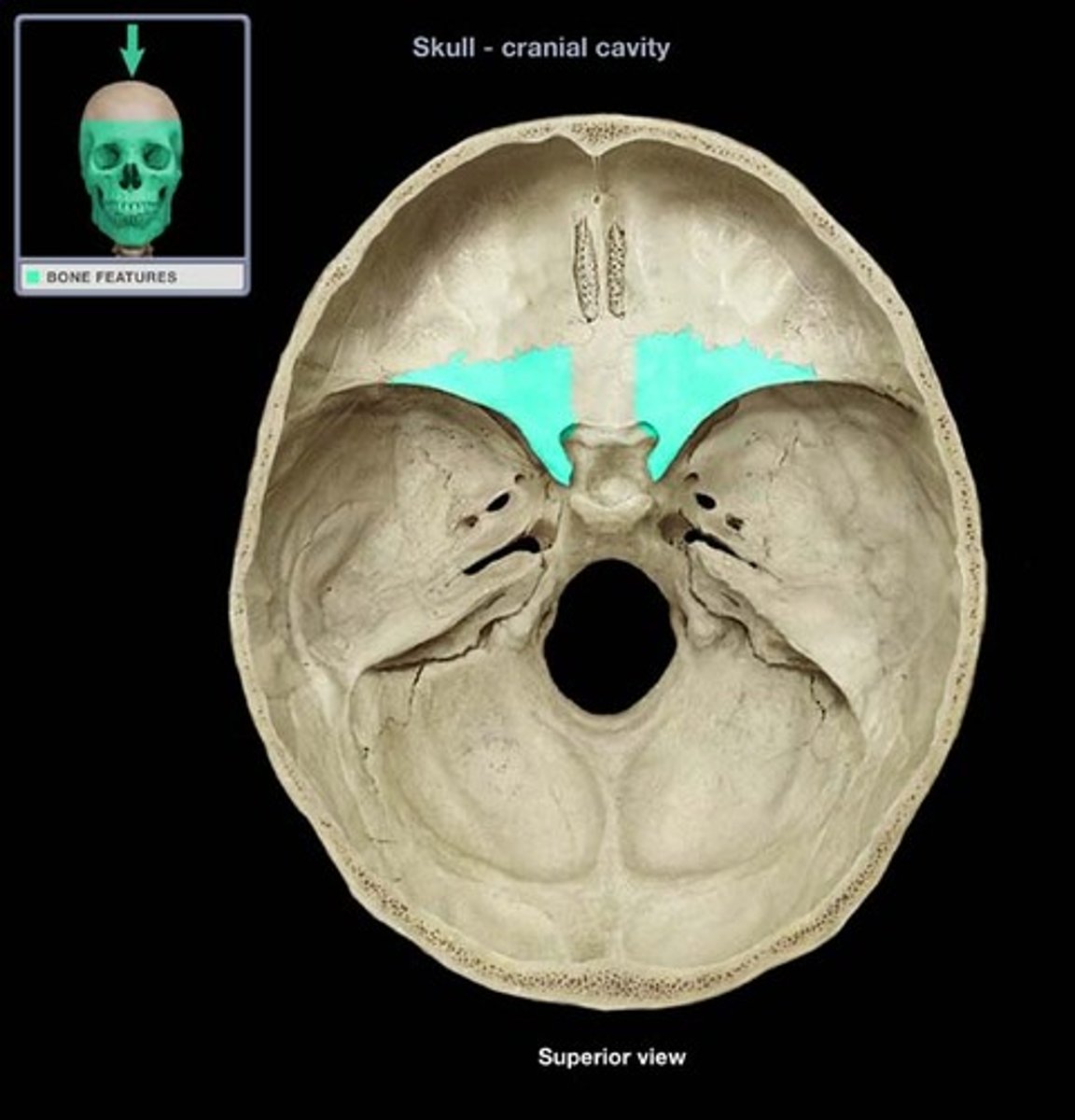
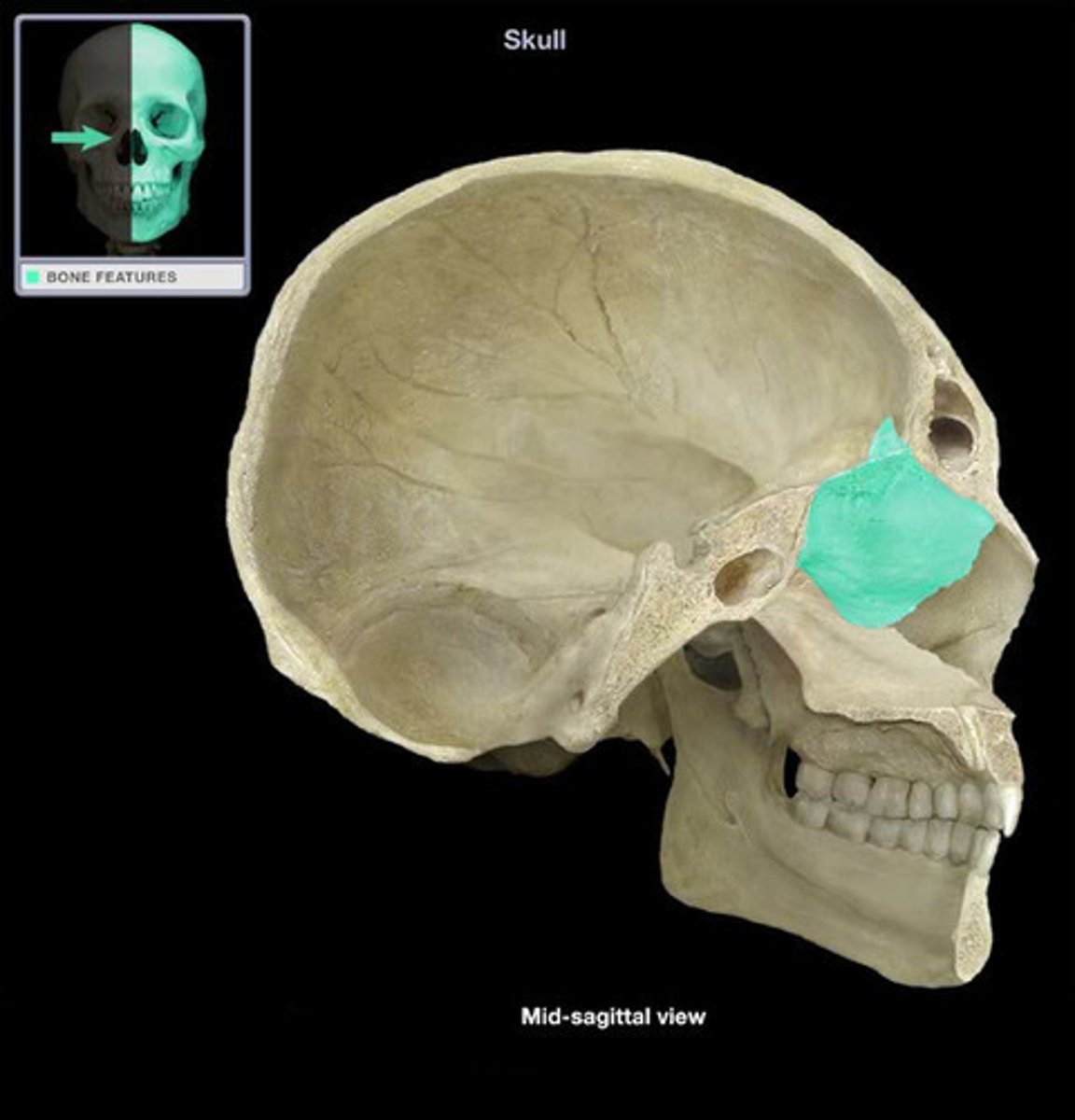
sphenoid bone
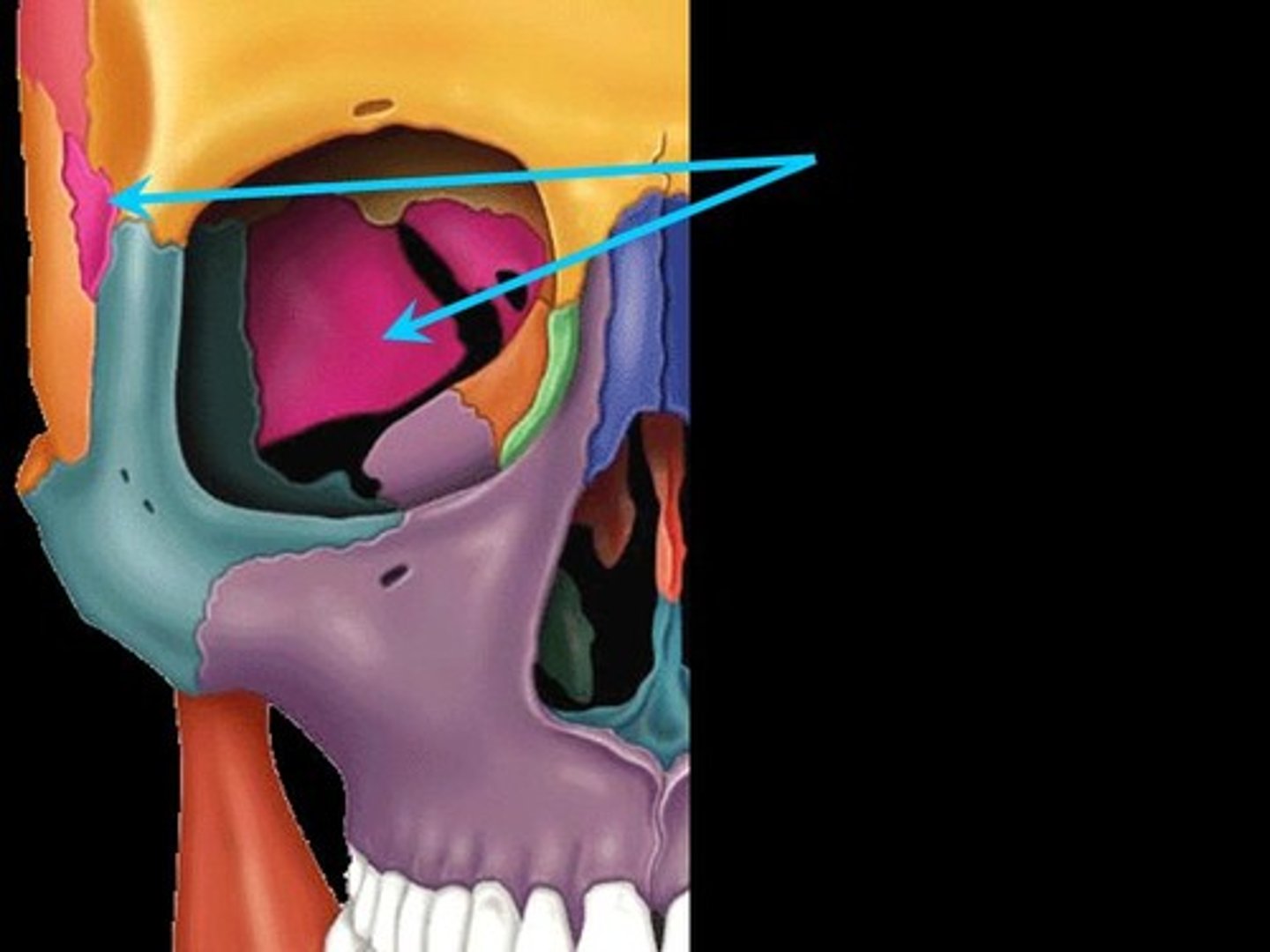
body of sphenoid bone
sphenoidal sinus
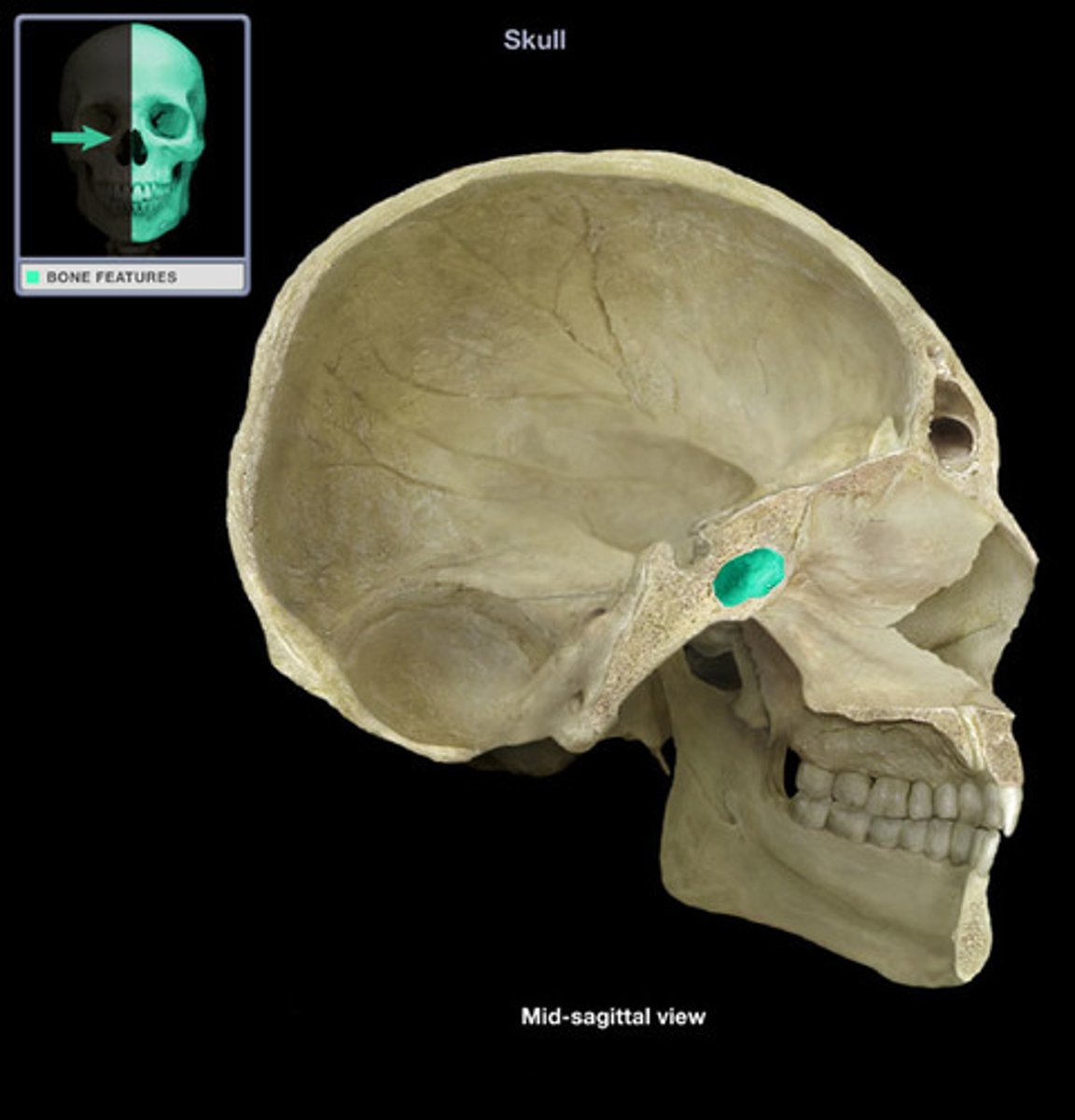
sella turcica
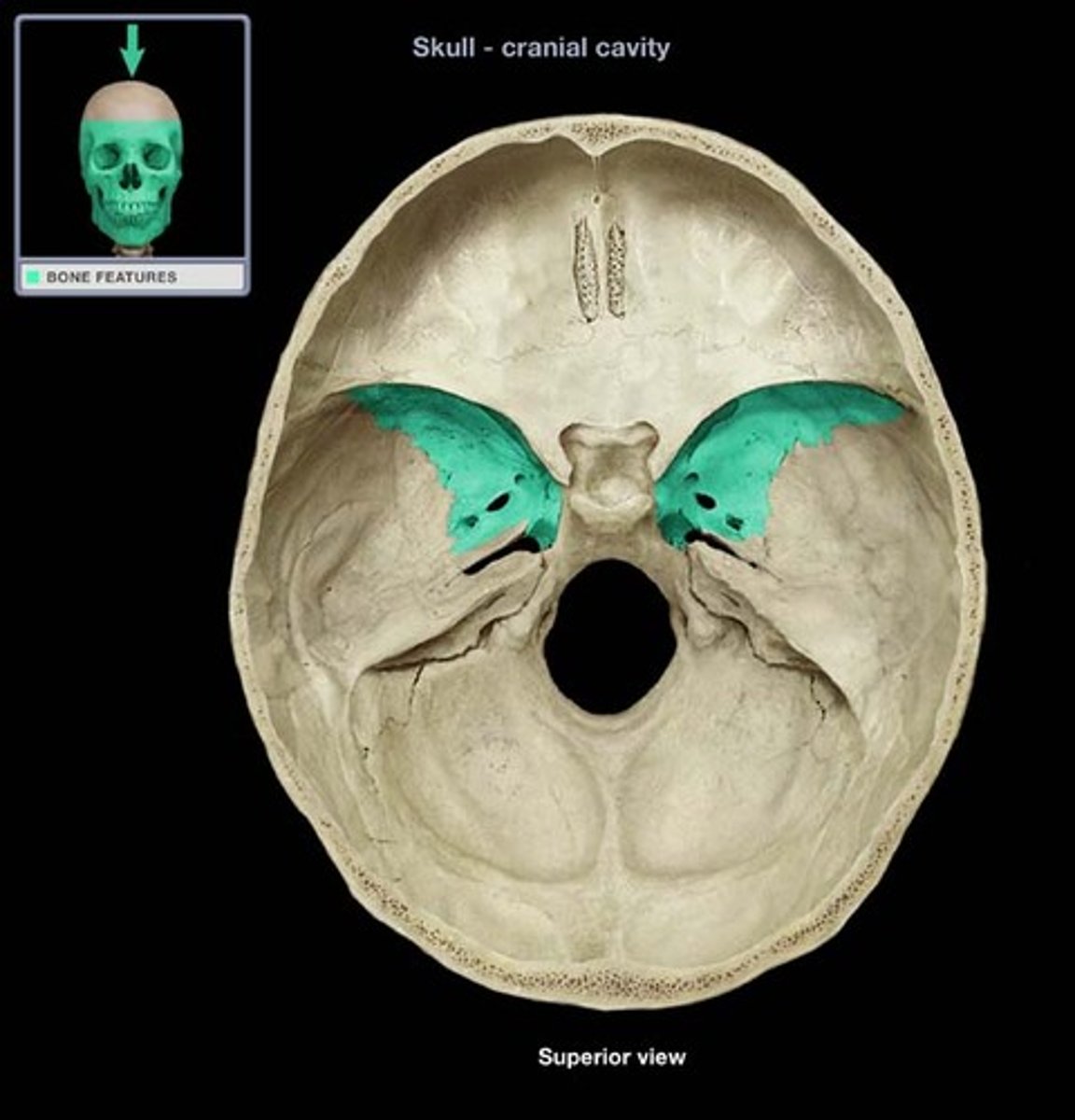
greater wings of sphenoid bone
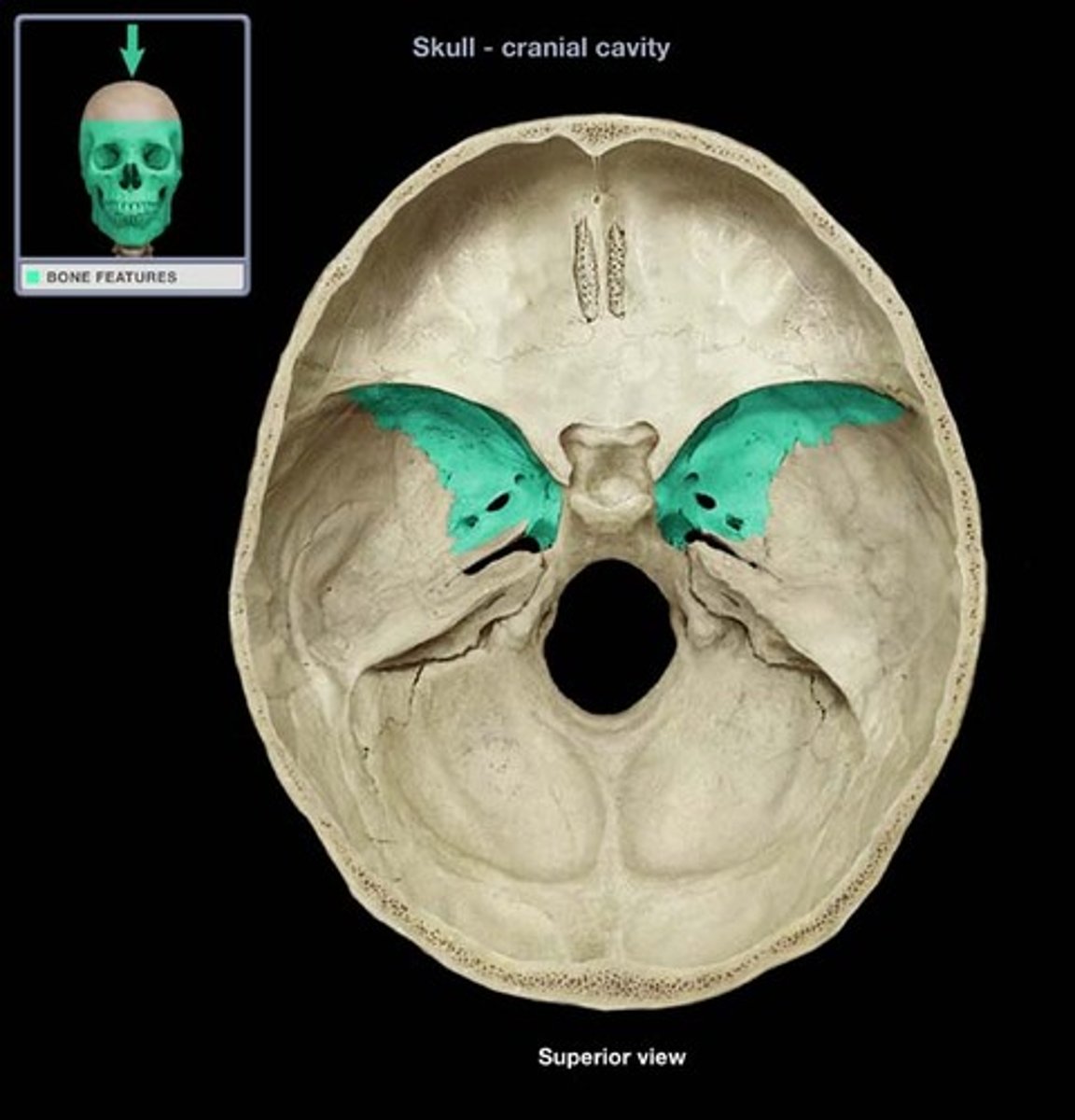
lesser wings of sphenoid bone
optic foramen
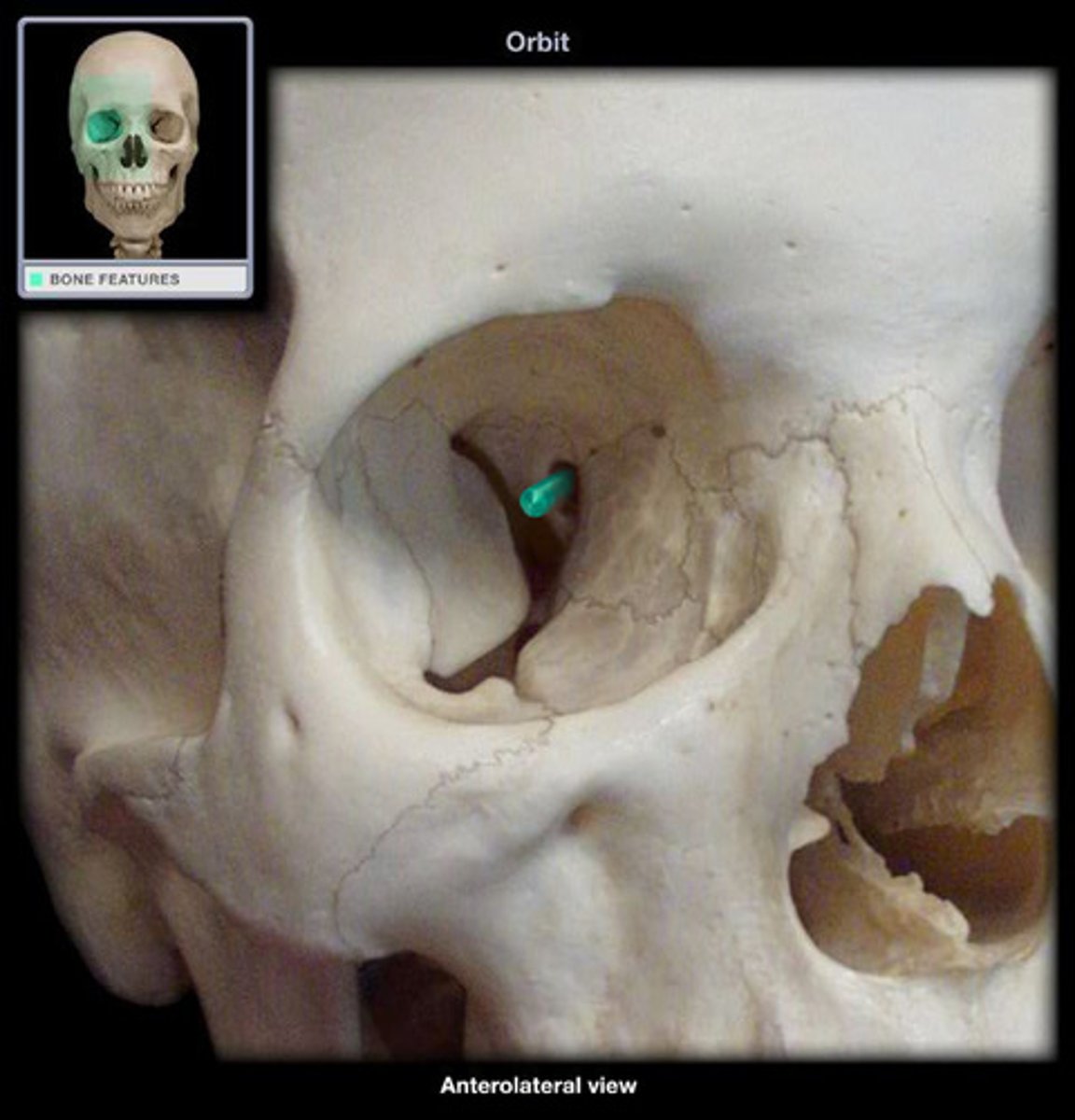
superior orbital fissure
pterygoid process
ethmoid bone
lateral masses
ethmoidal sinuses
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
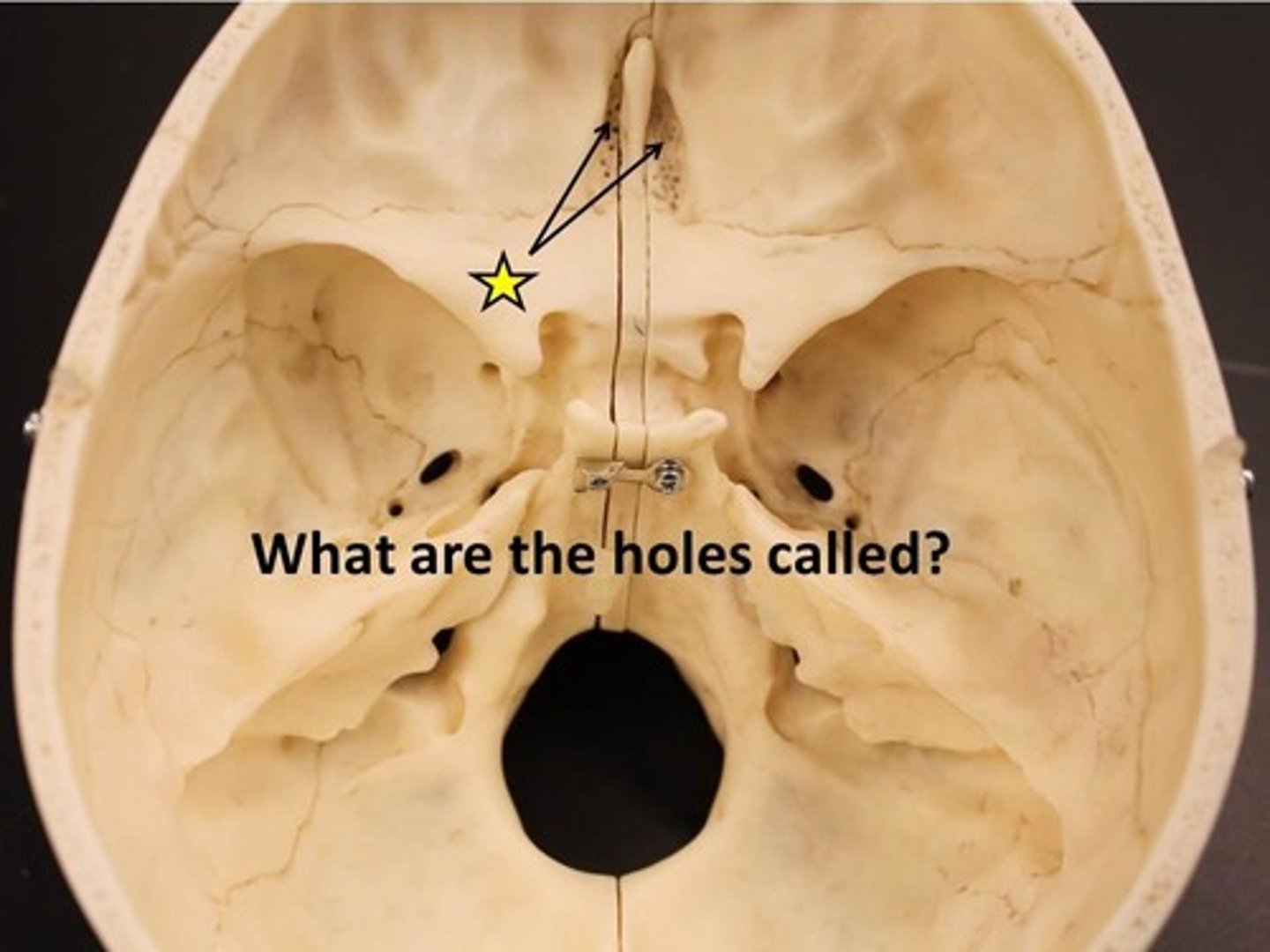
cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
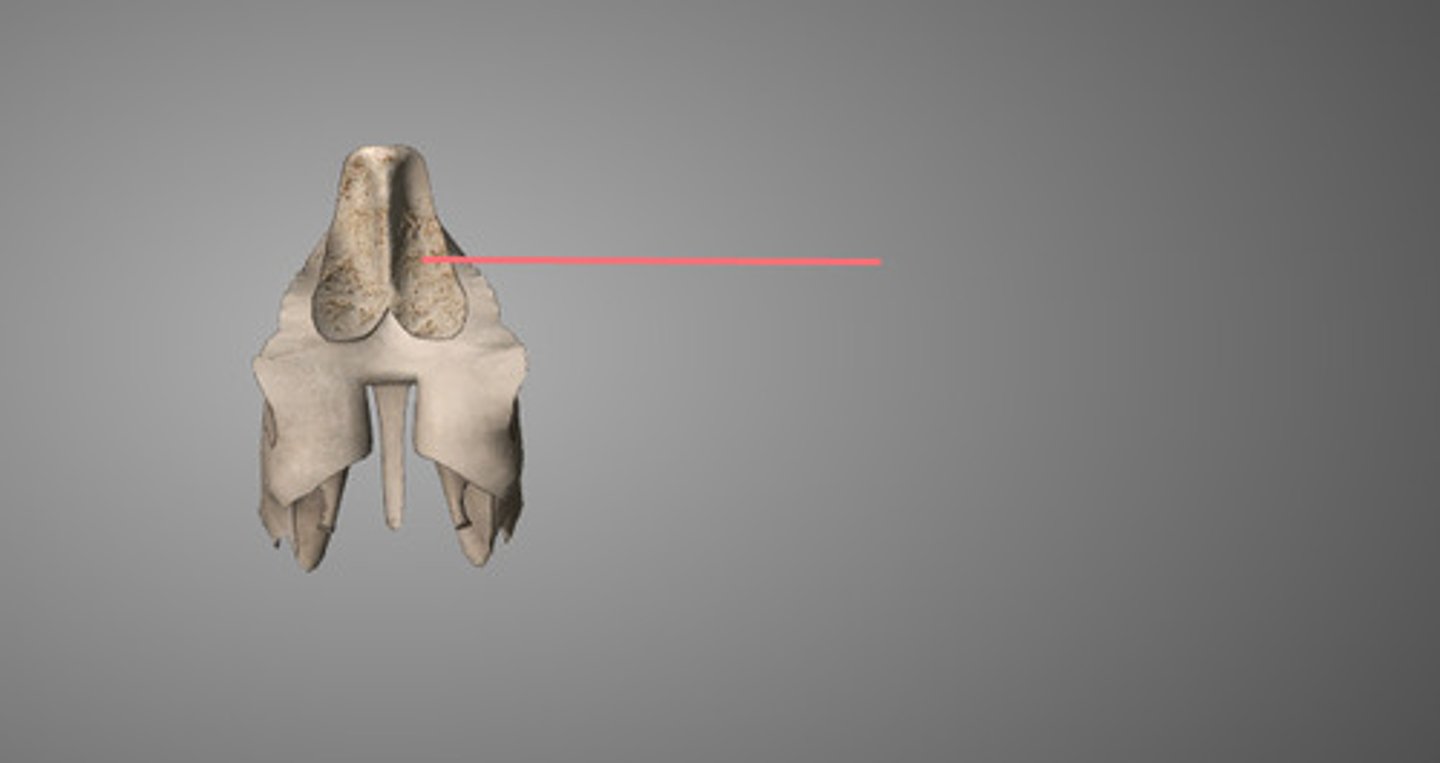
olfactory foramina
crista galli of ethmoid bone
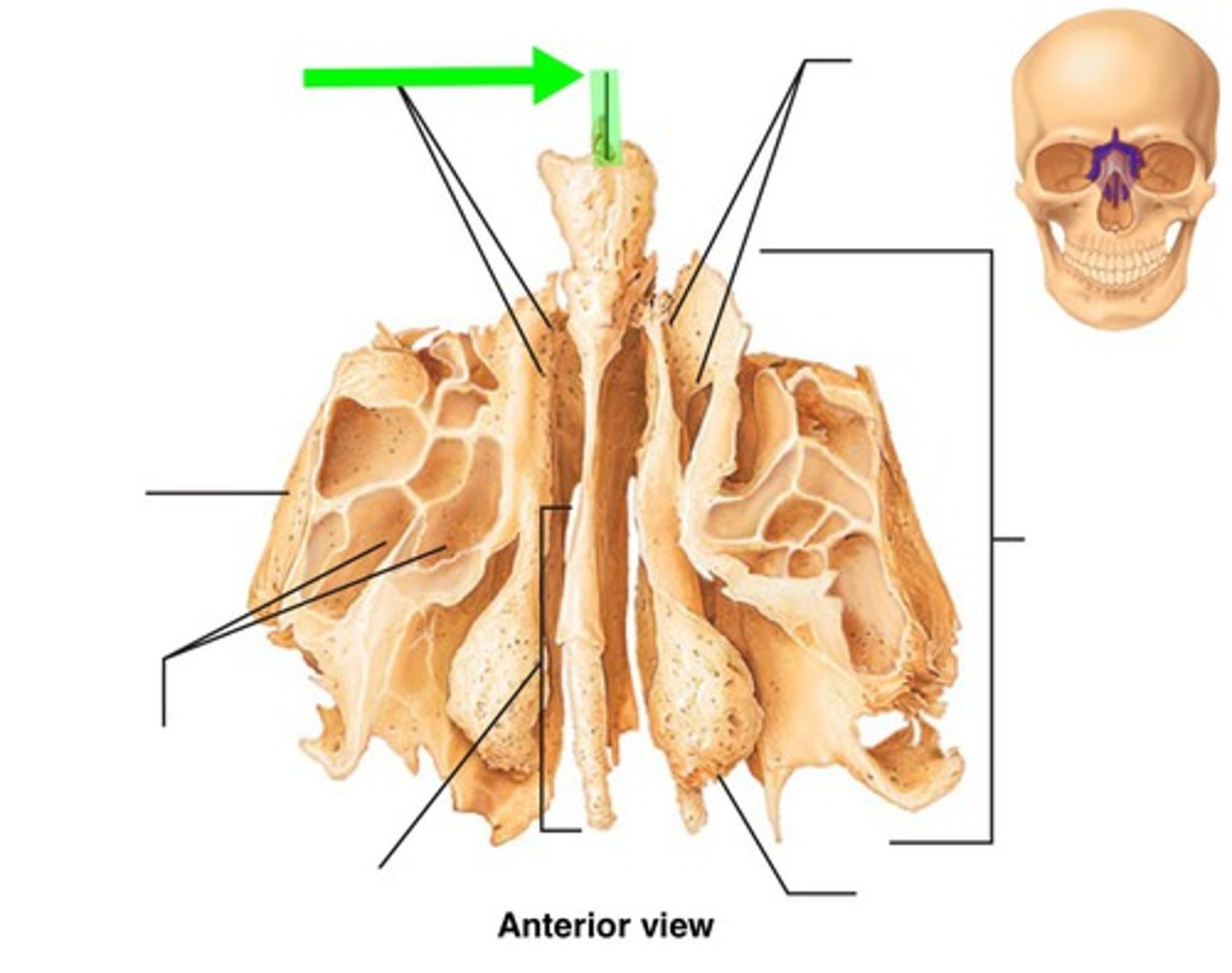
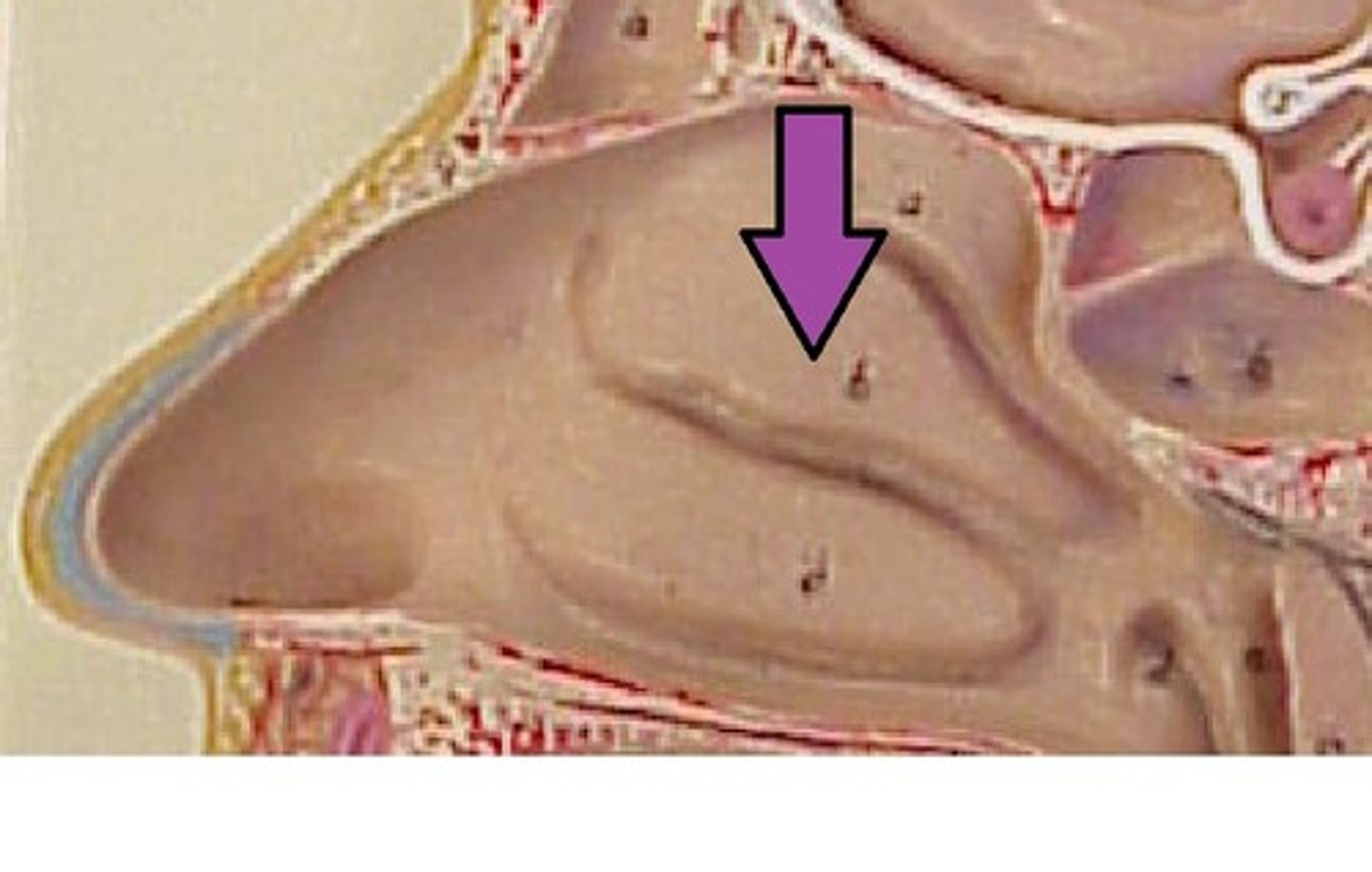
superior nasal conchae (turbinates)
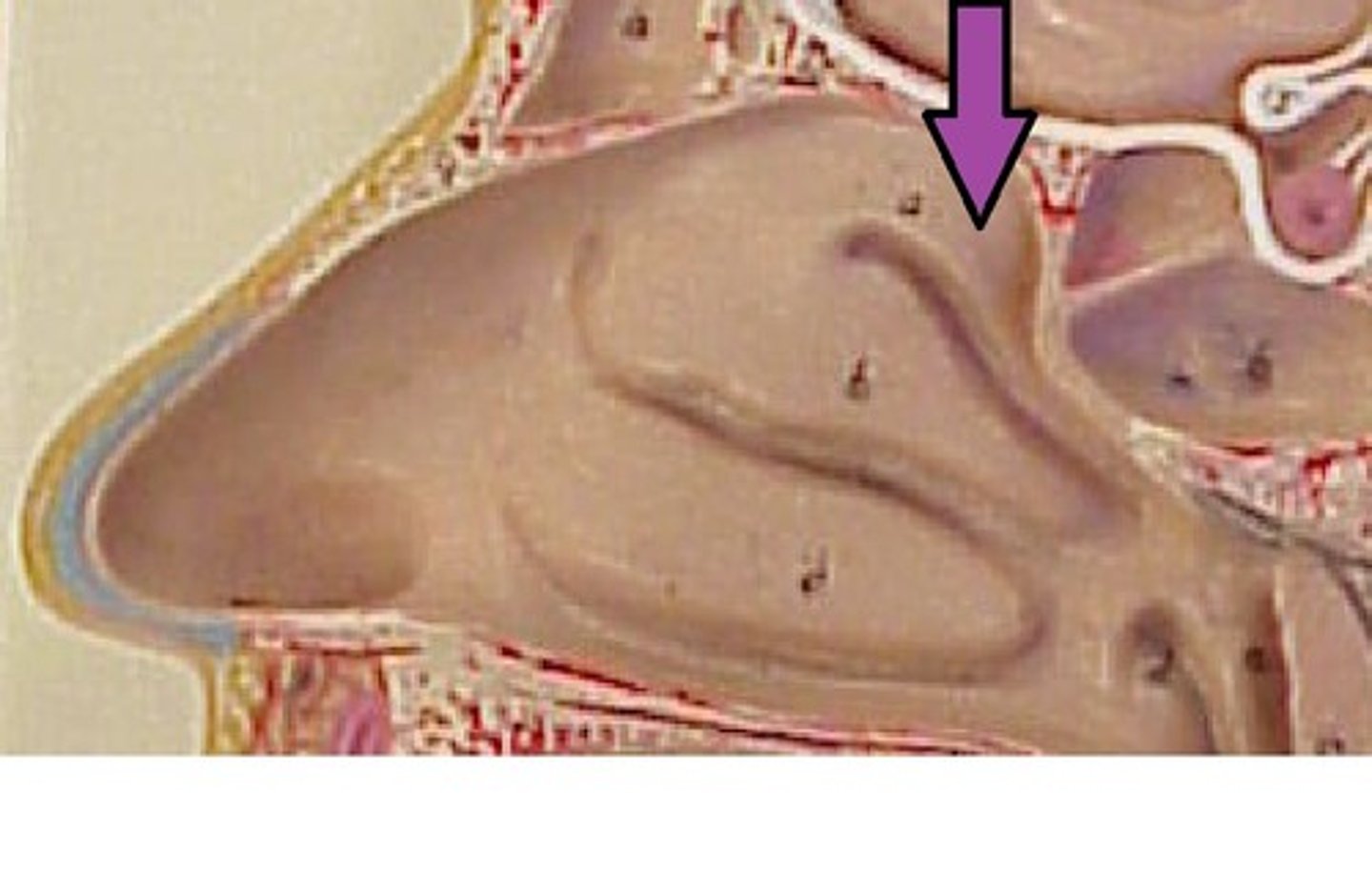
middle nasal conchae (turbinates)
how many facial bones are there?
14
what 14 bones make up the face?
nasal bones (2), lacrimal bones (2), palatine bones (2), inferior nasal conchae (2), vomer, maxillae (2), zygomatic bones (2), mandible
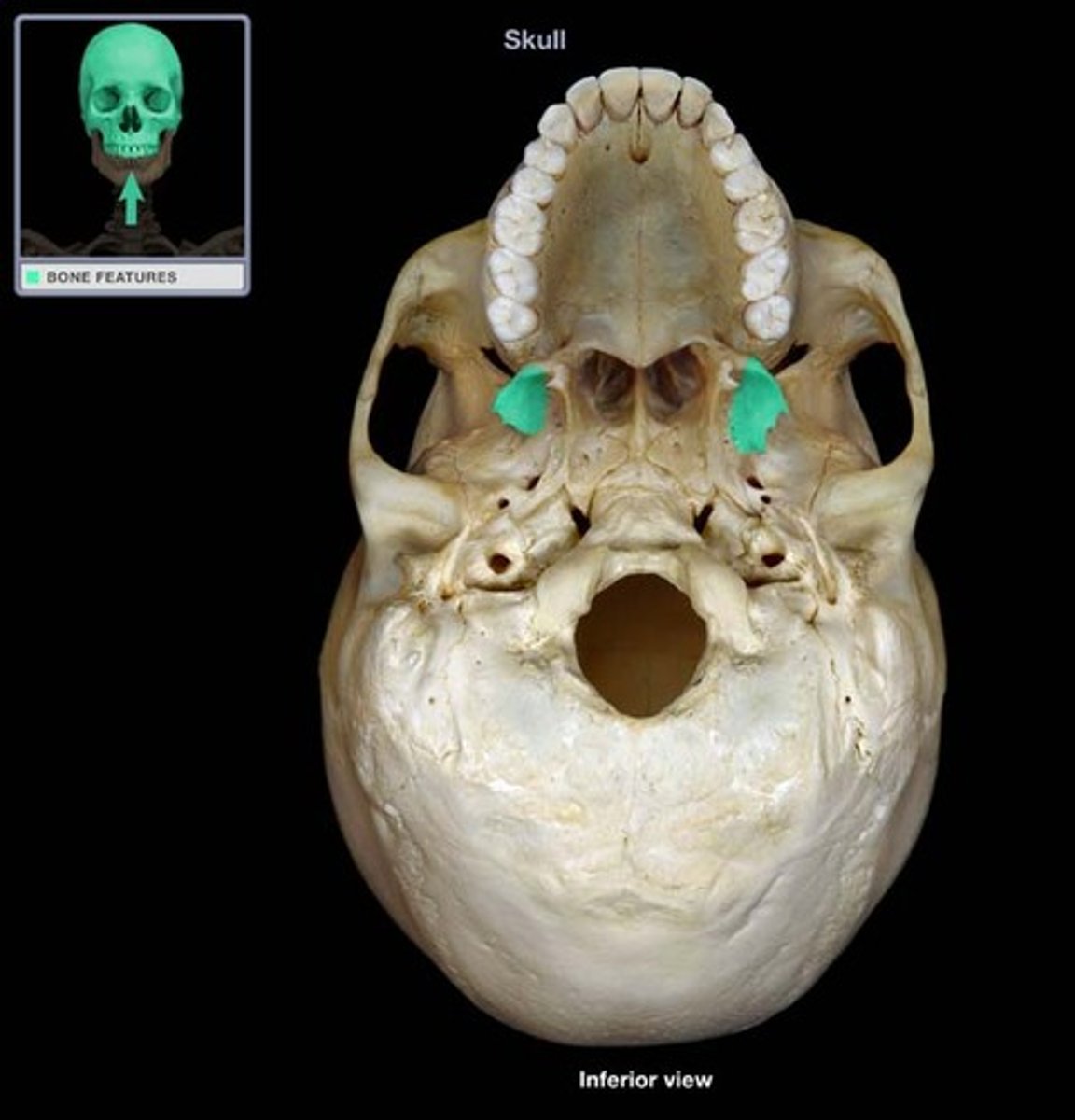
lacrimal fossa of lacrimal bone
horizontal plate of palatine bone
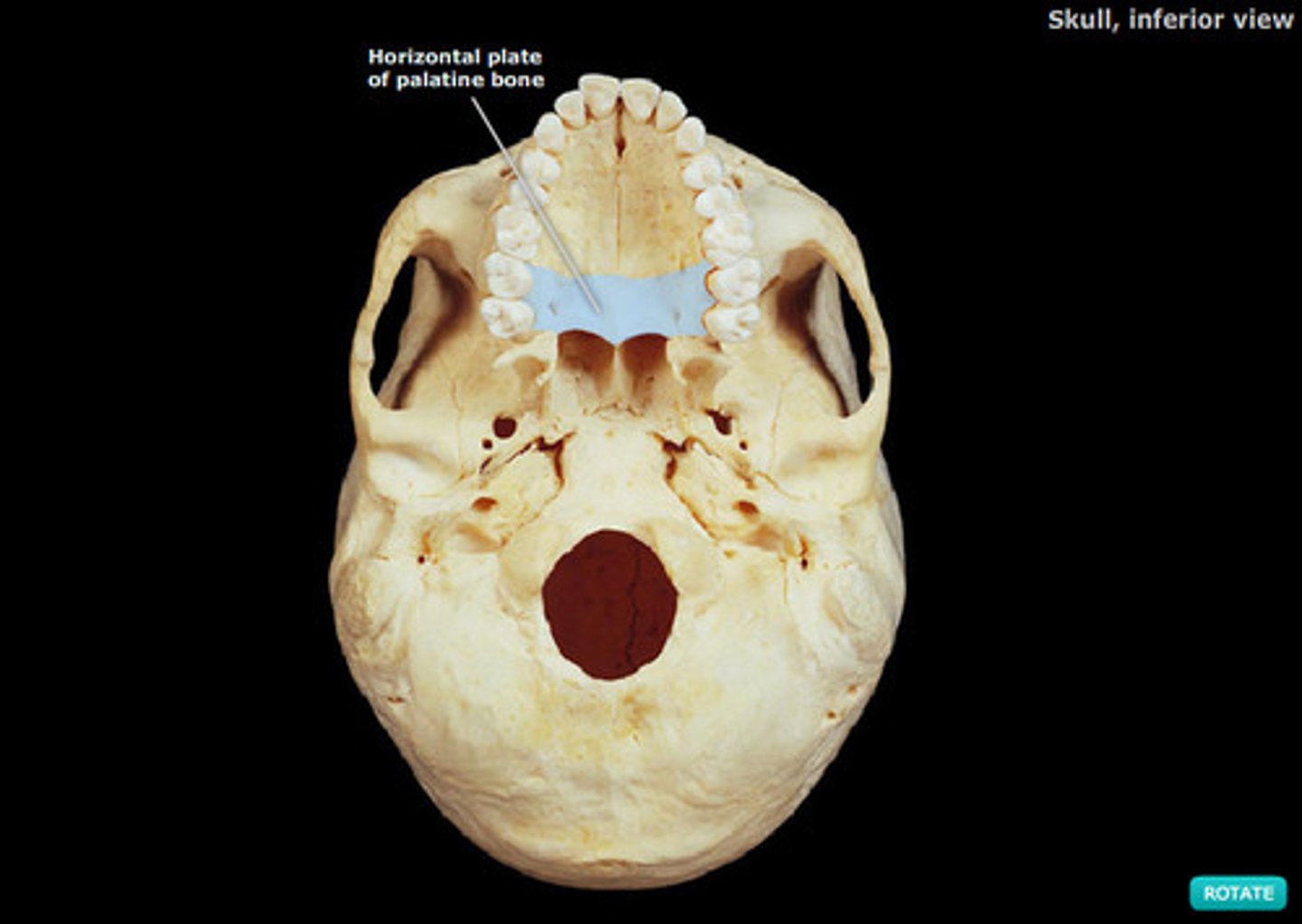
palatine bone

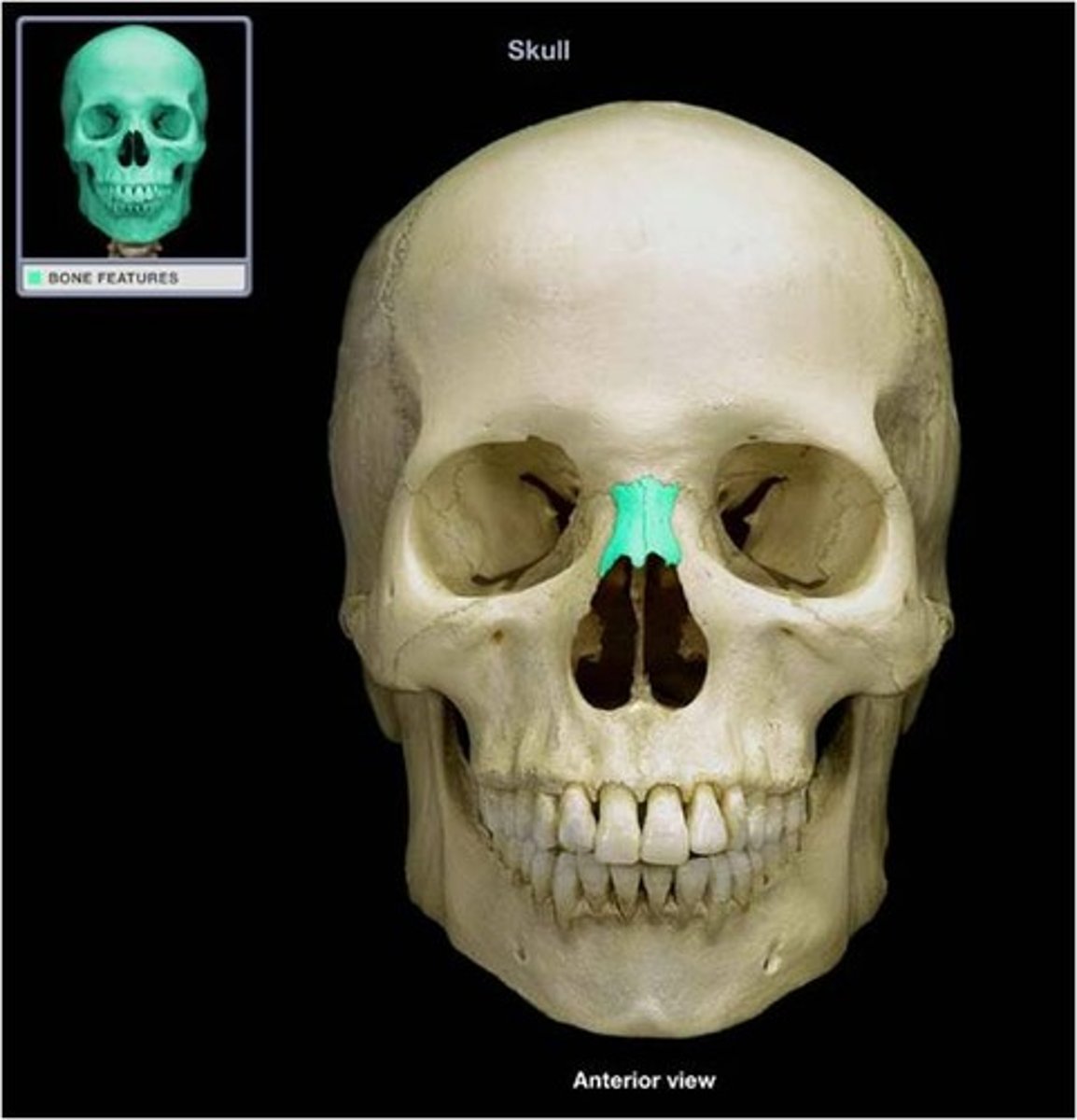
nasal bones
inferior nasal conchae
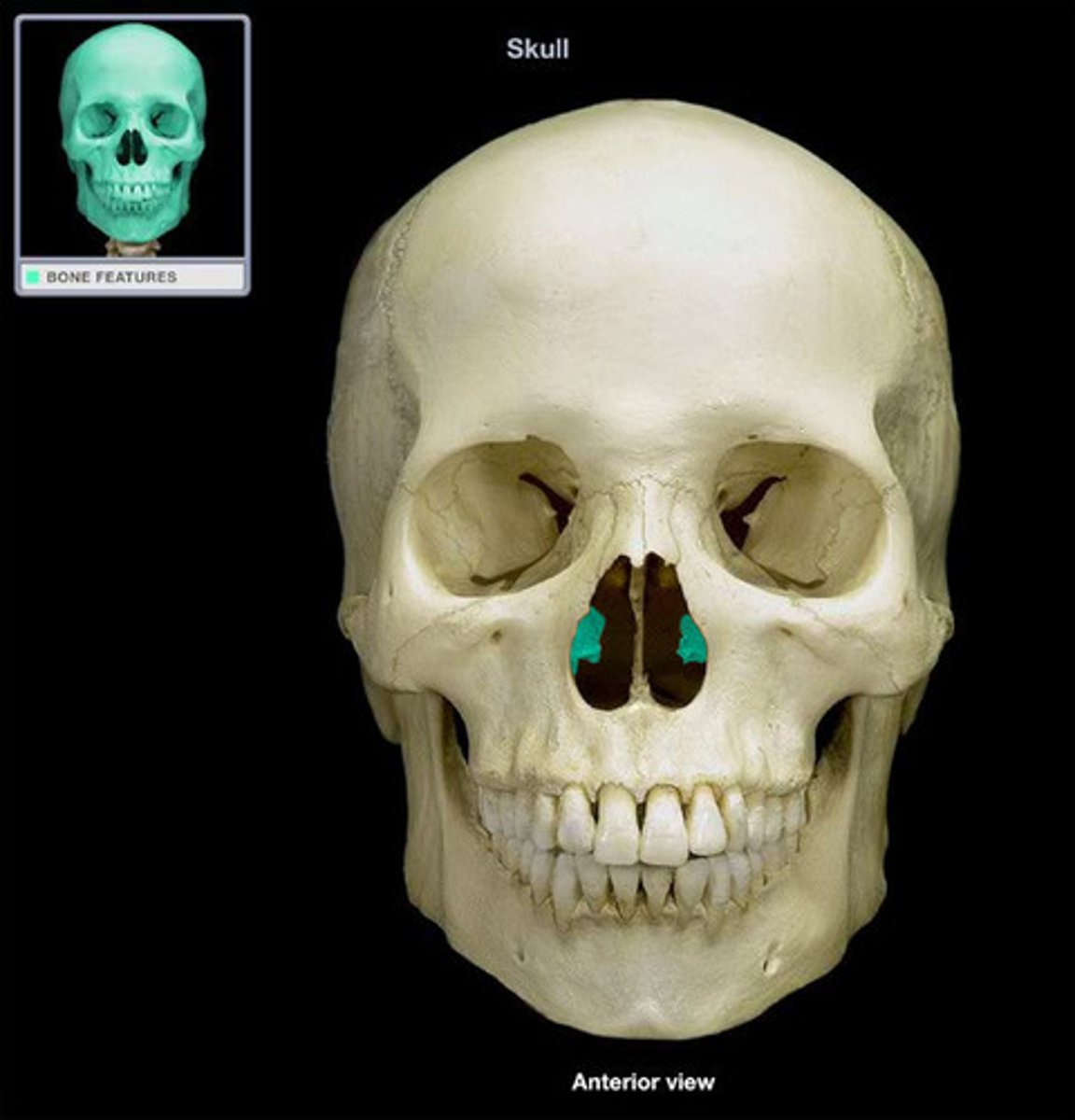
lacrimal bones
vomer
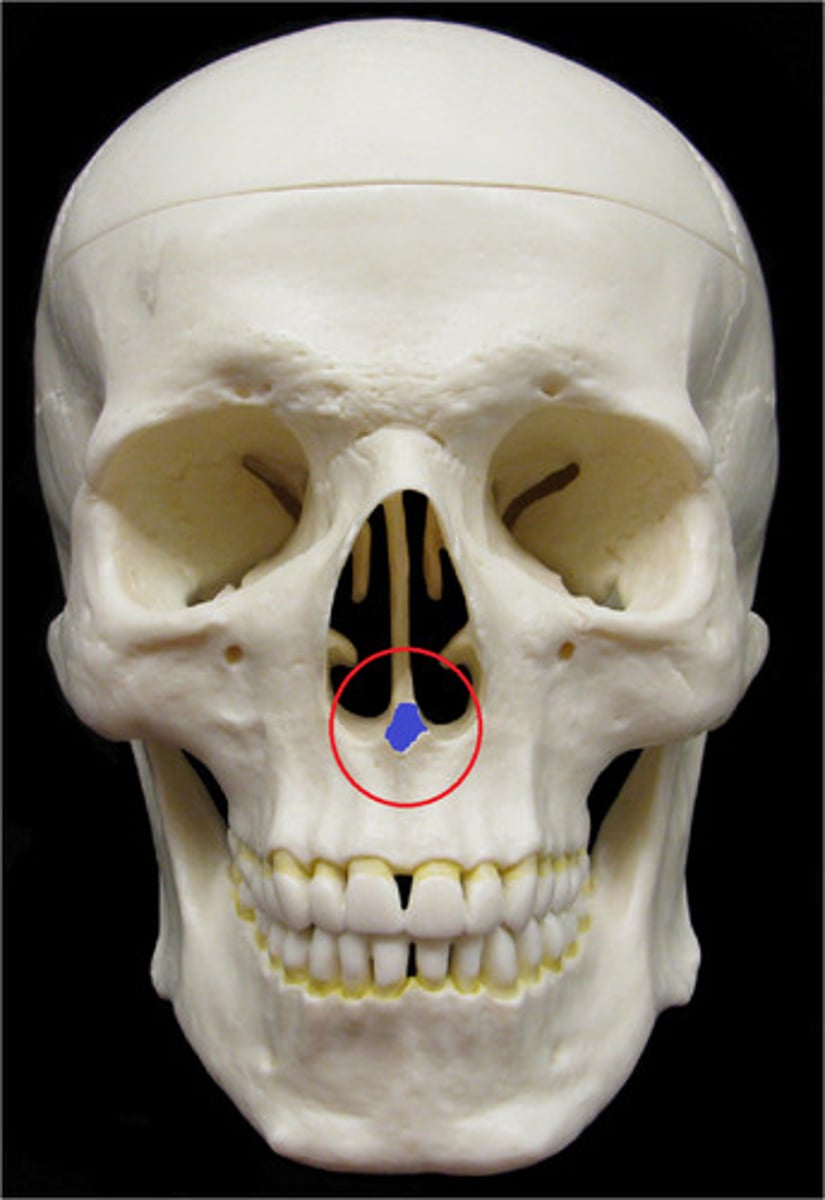
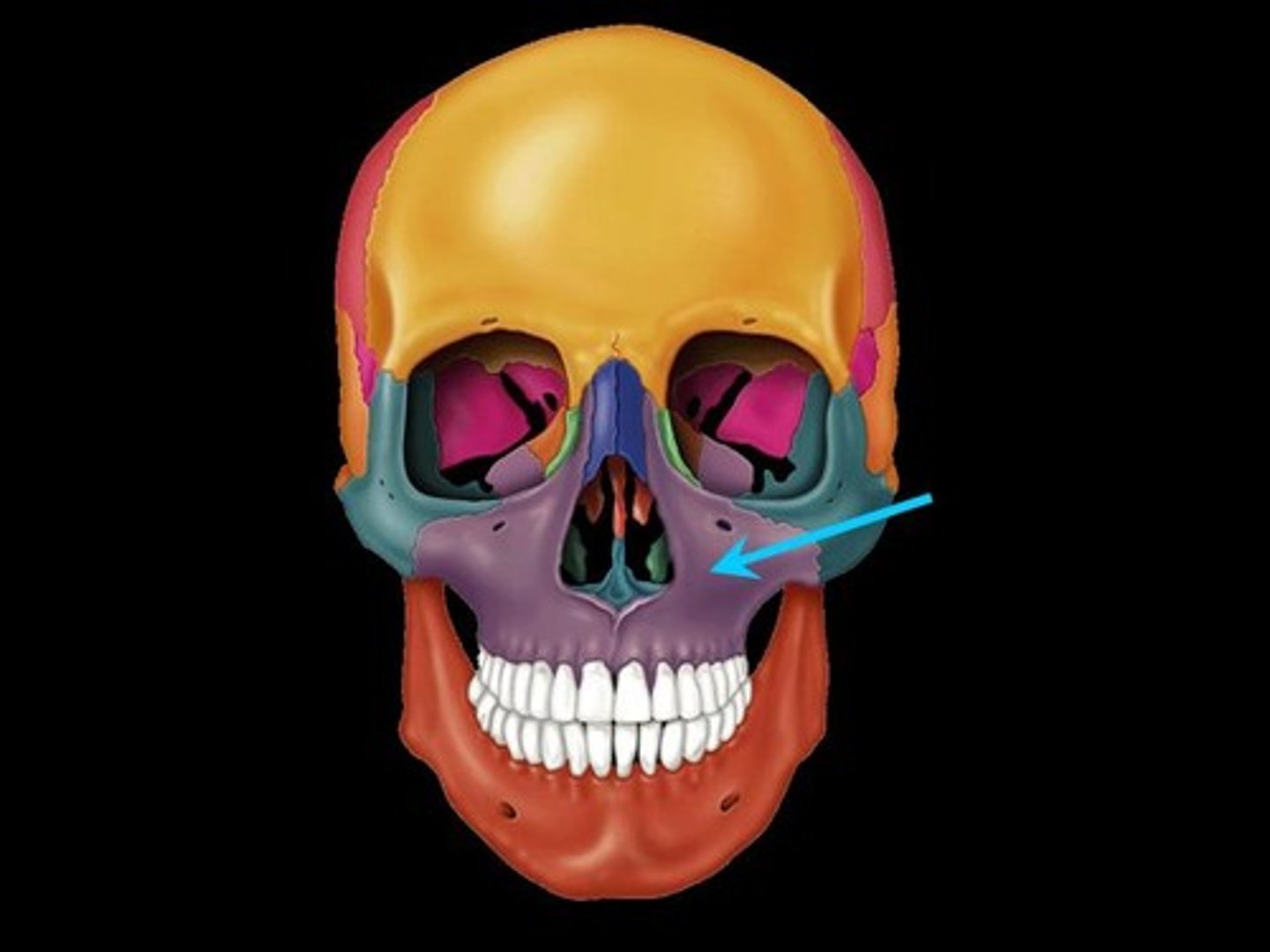
maxilla
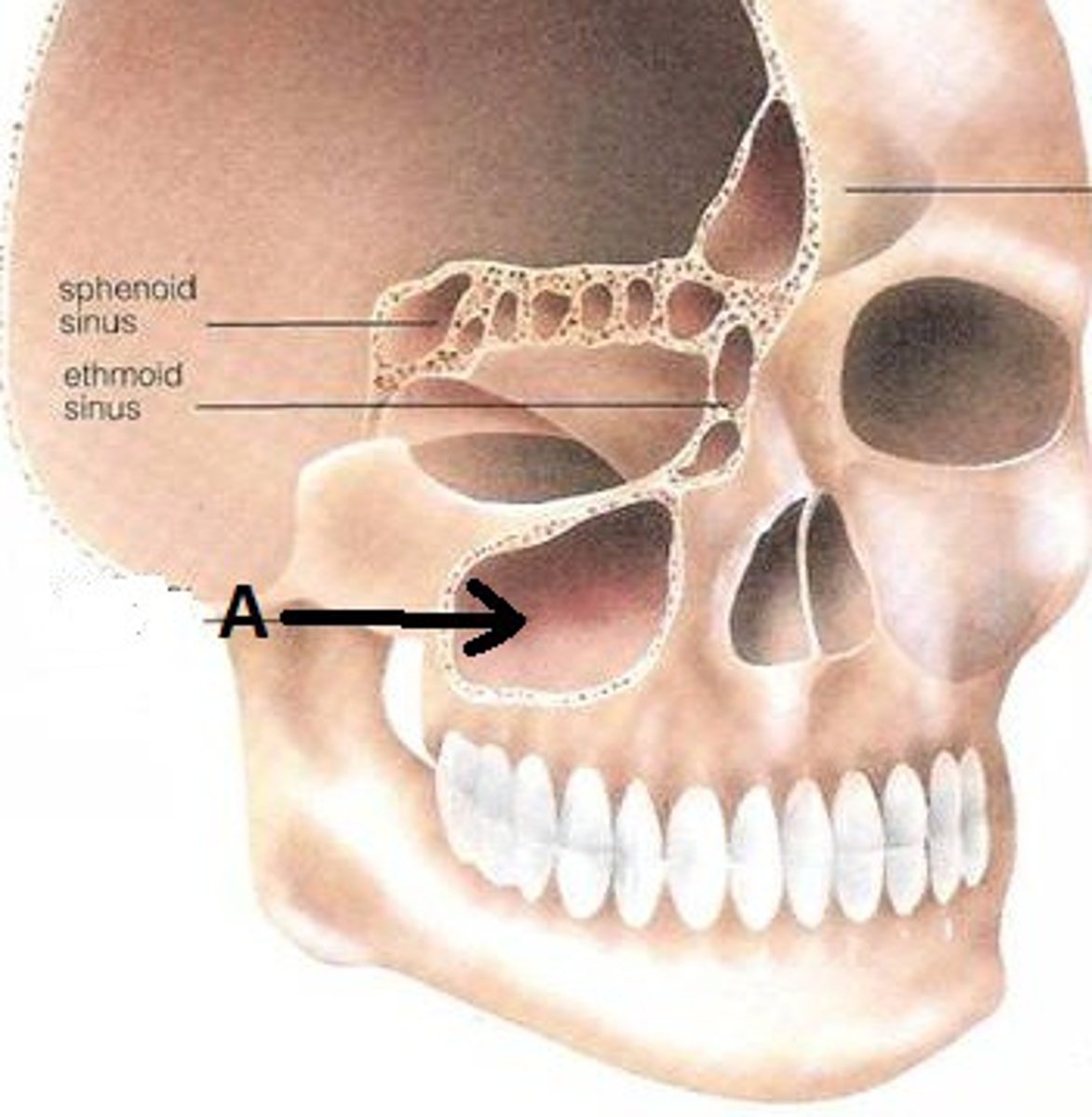
maxillary sinuses
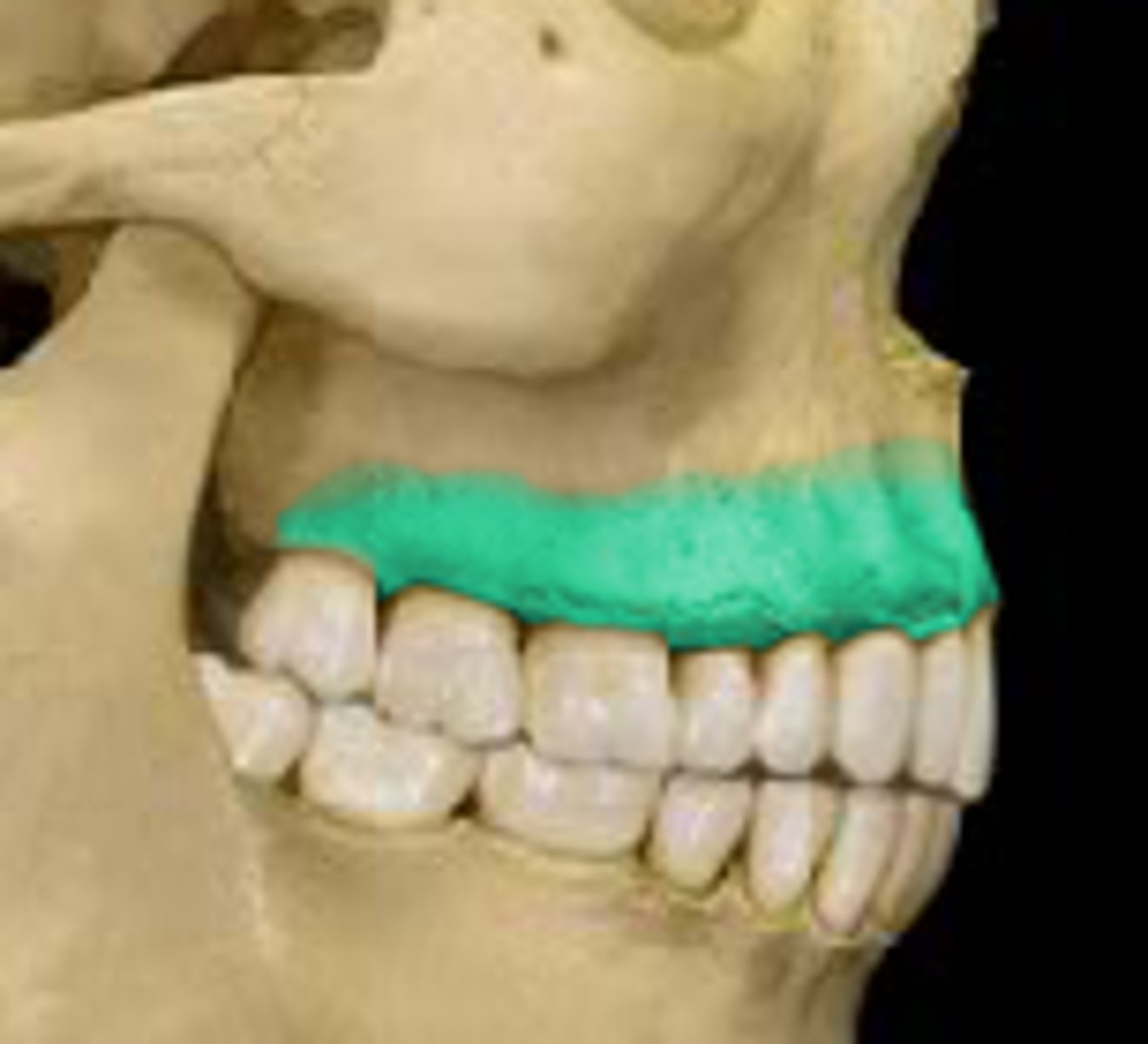
alveolar process of maxilla
palatine process
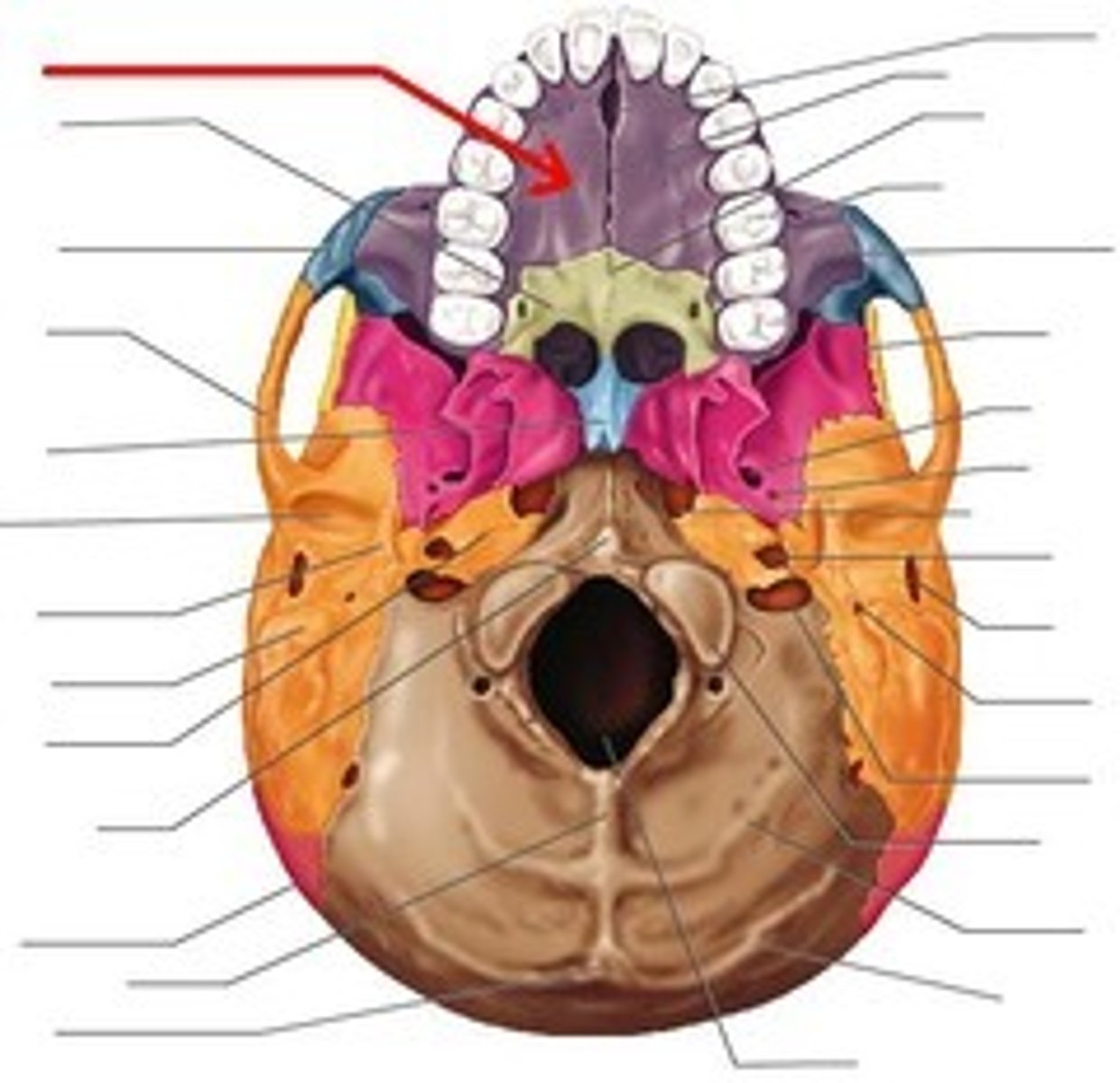
infraorbital foramen
incisive foramen of maxilla
inferior orbital fissure
zygomatic bone
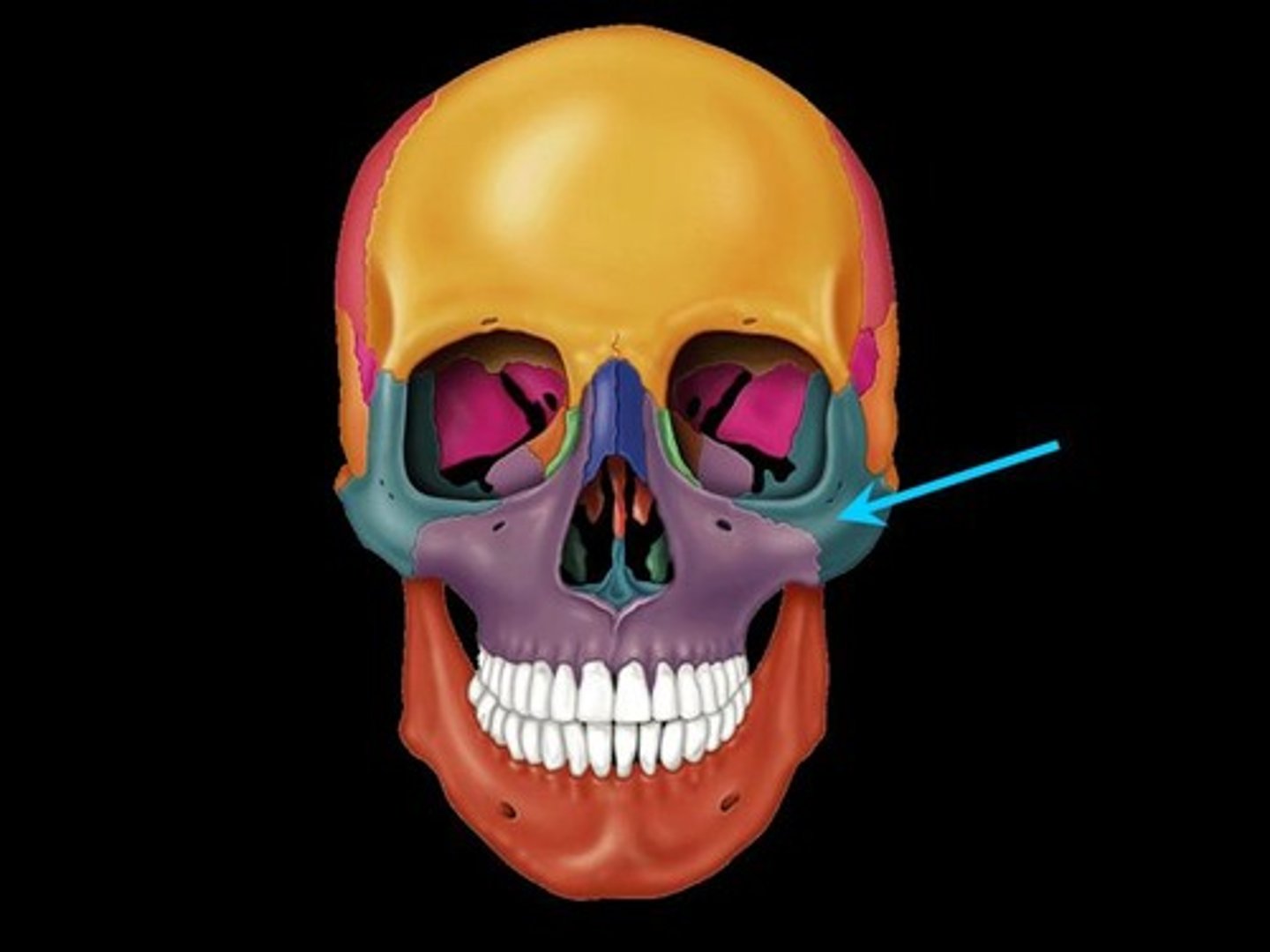
temporal process of zygomatic bone
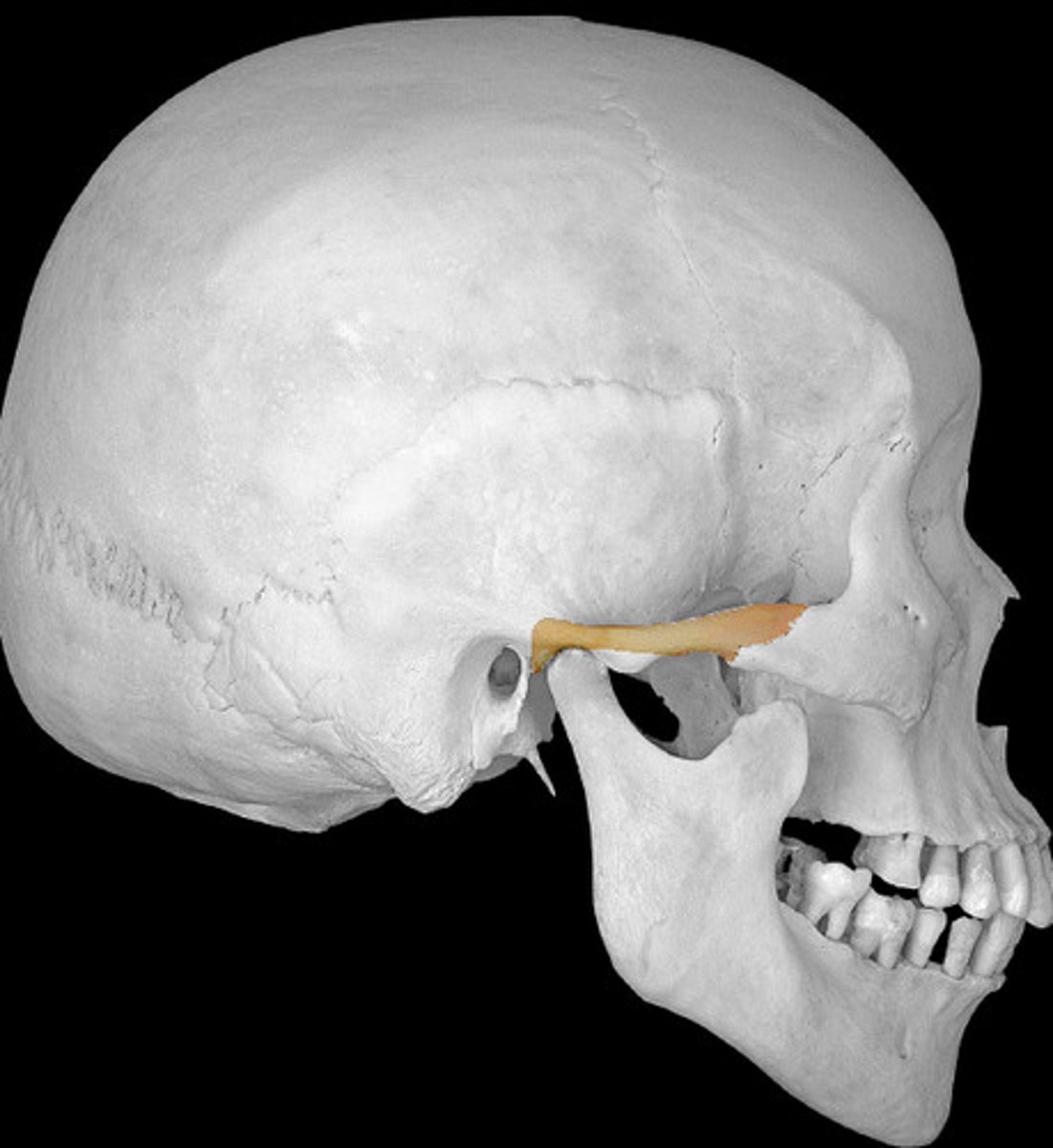
zygomaticofacial foramen
mandible
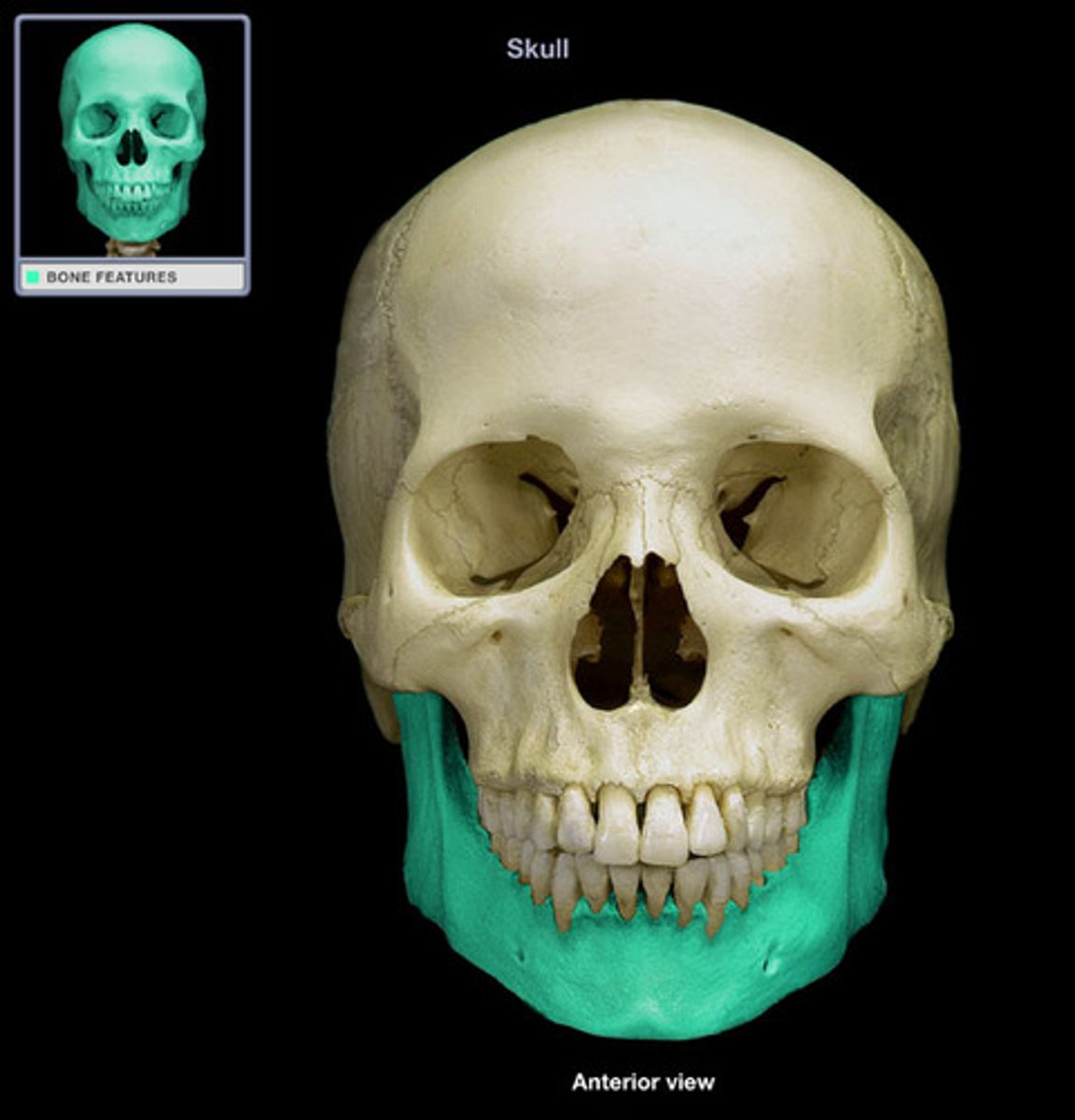
body of mandible
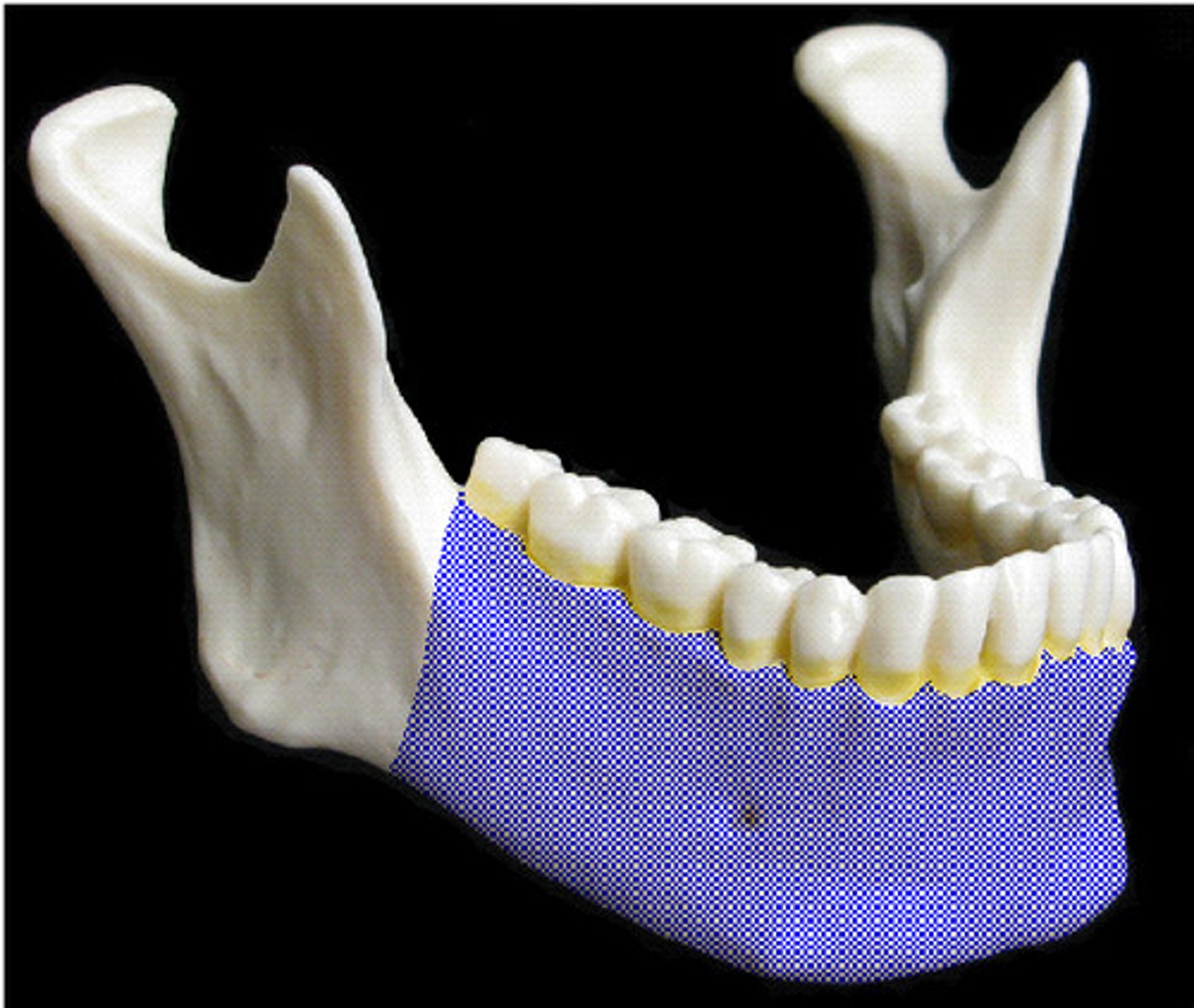
rami of mandible
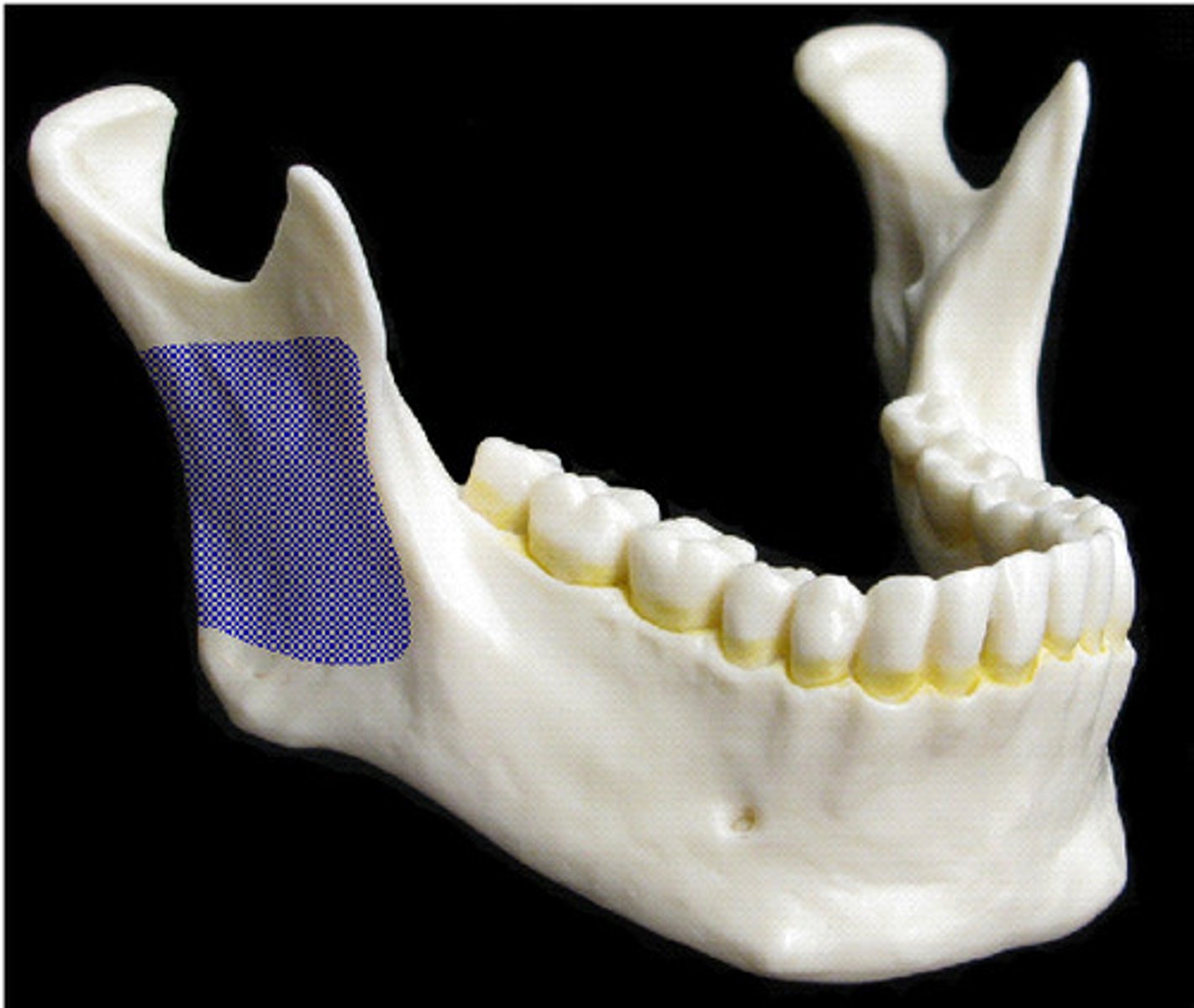
angle of mandible
condylar process of mandible
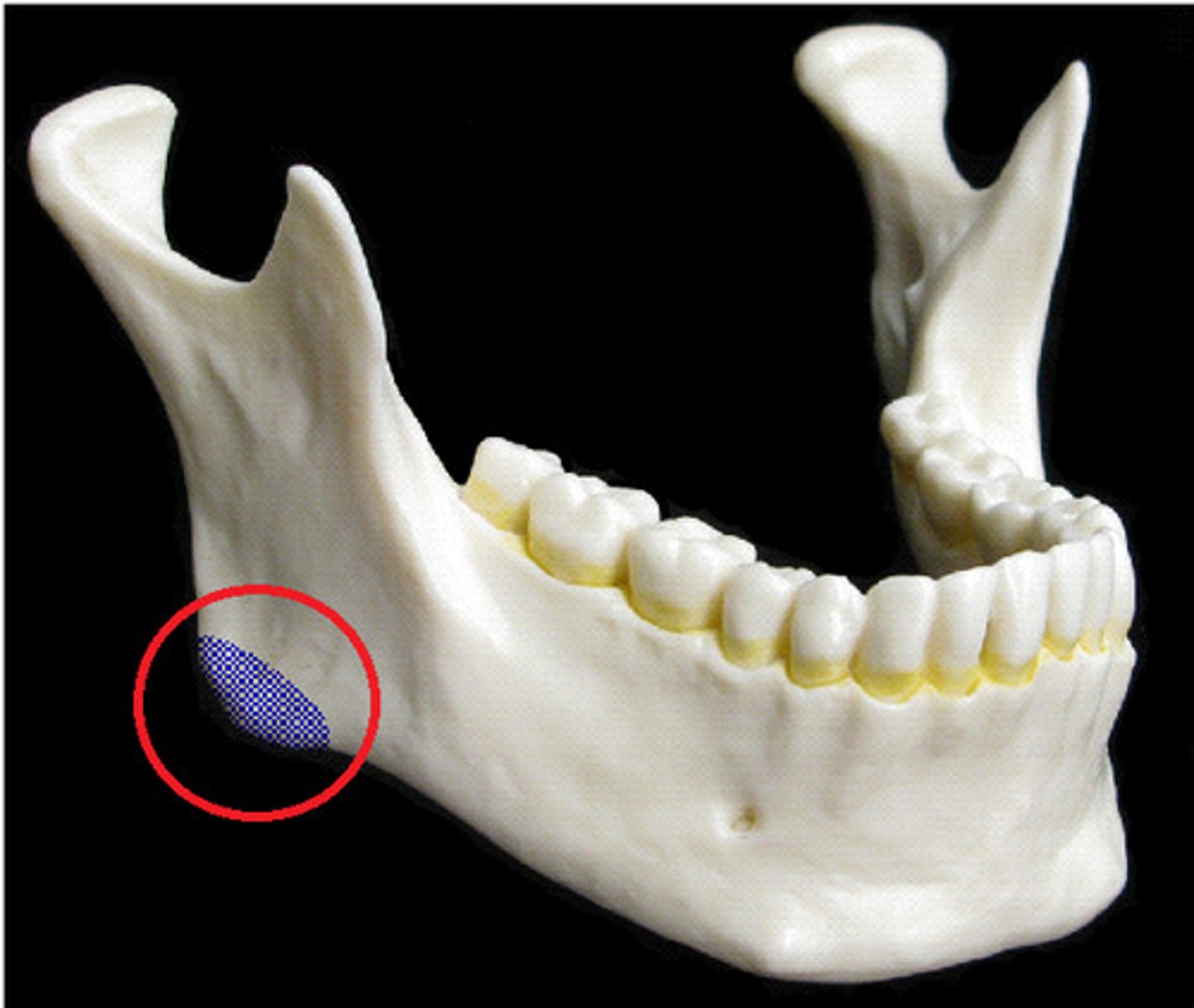
mandibular notch
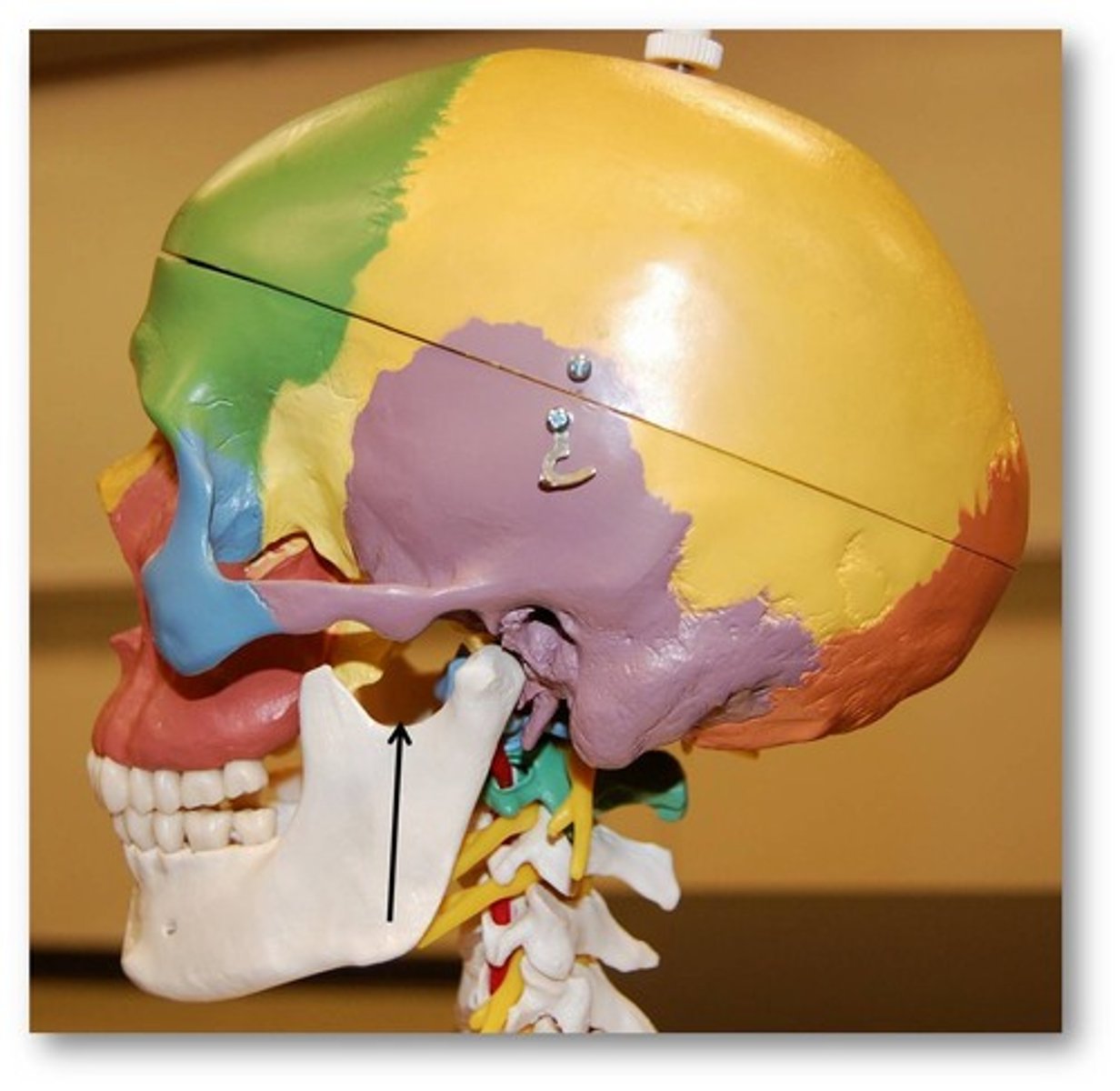
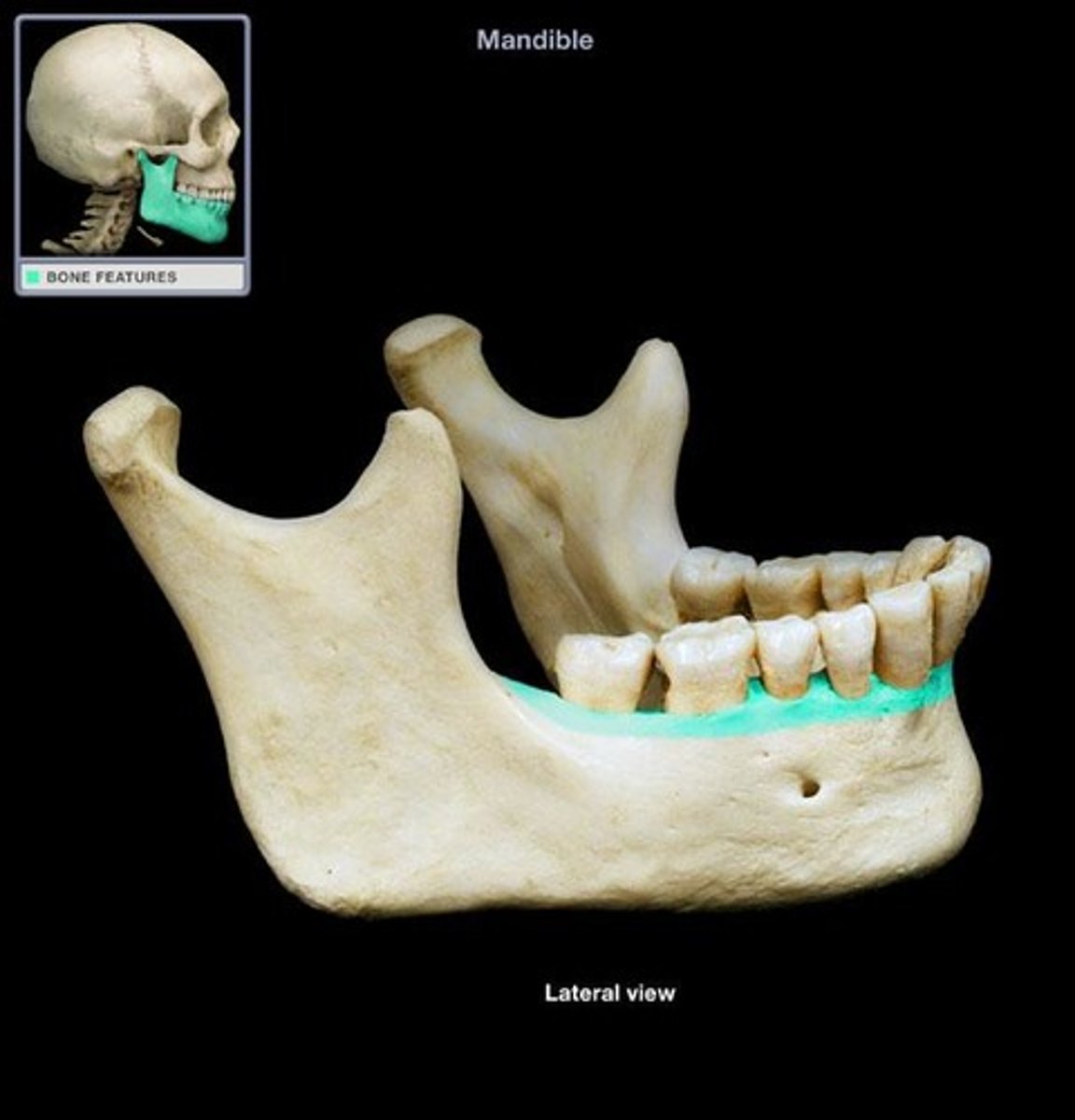
alveolar process of mandible
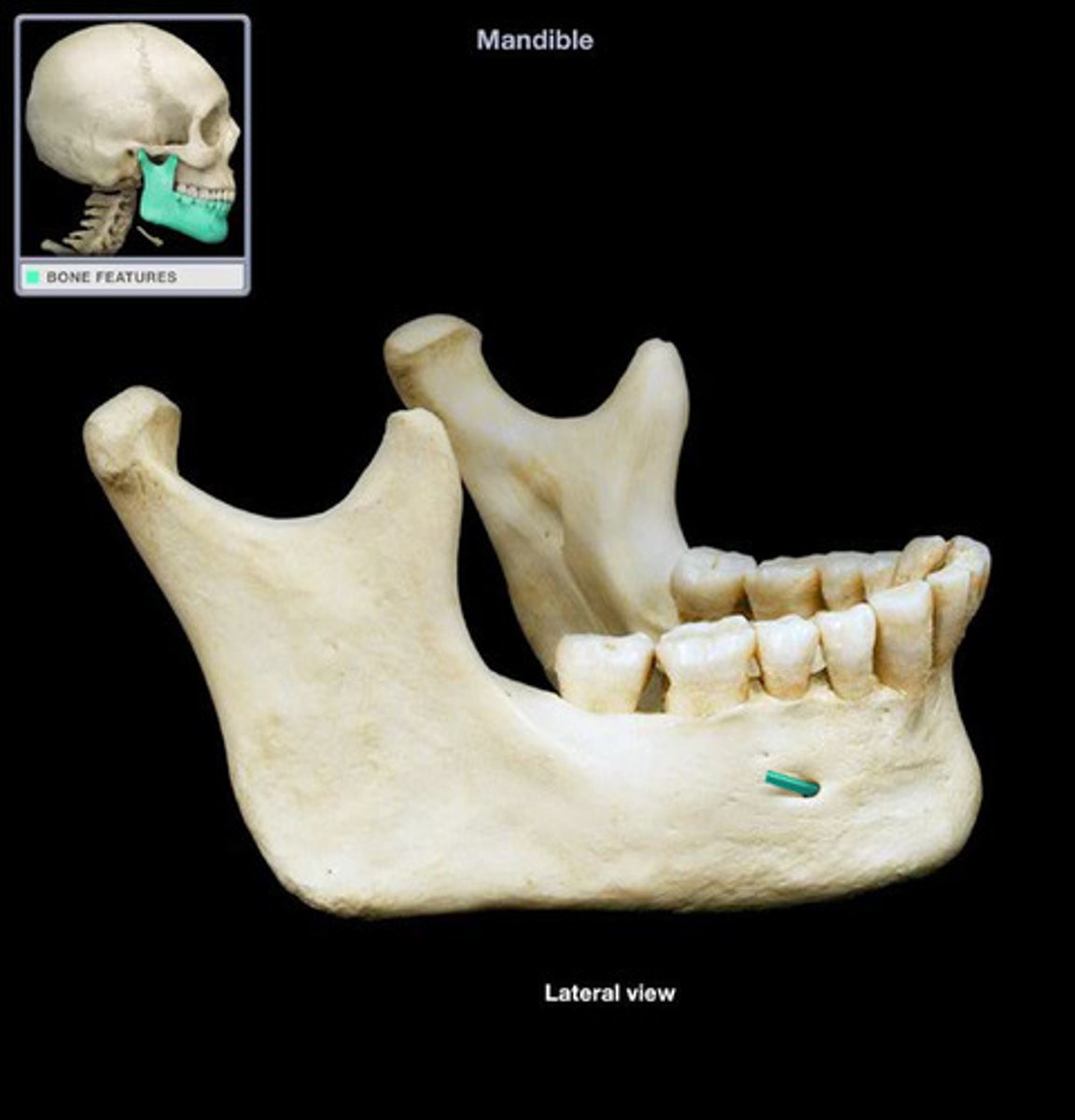
mental foramen of mandible
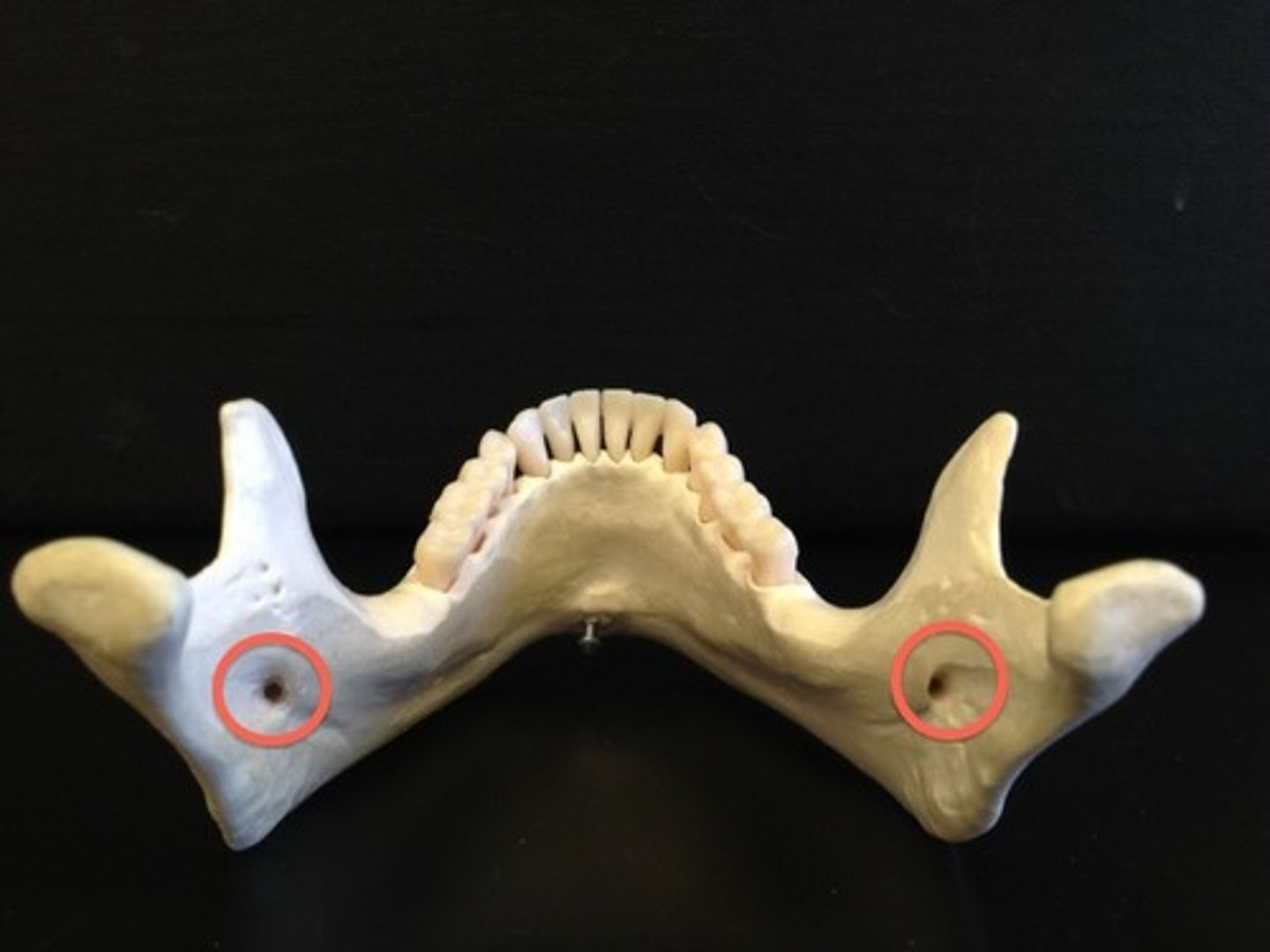
mandibular foramen of mandible
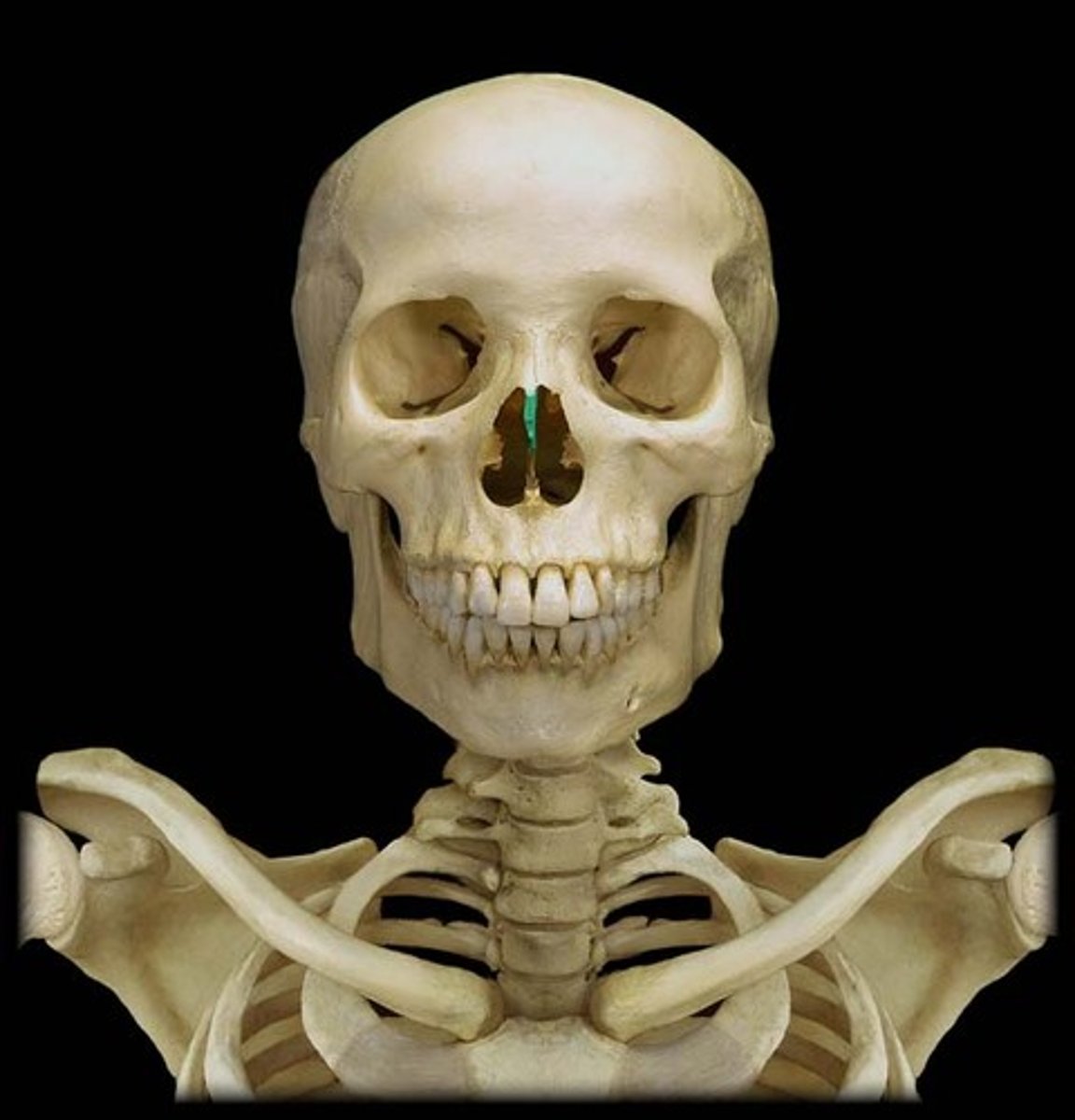
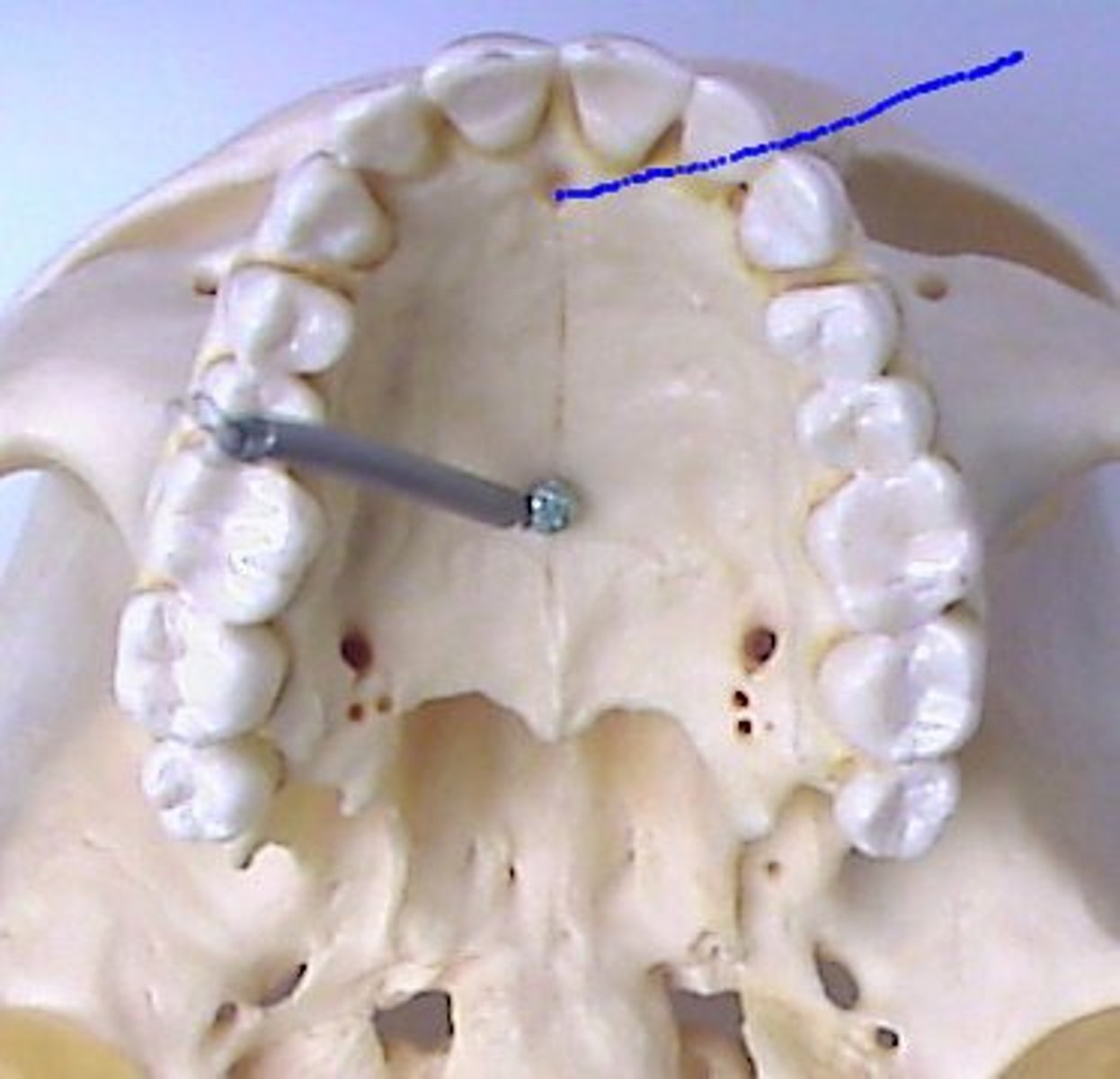
nasal septum
partition separating the right and left nasal cavities
what forms the nasal septum?
vomer, septal cartilage, and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
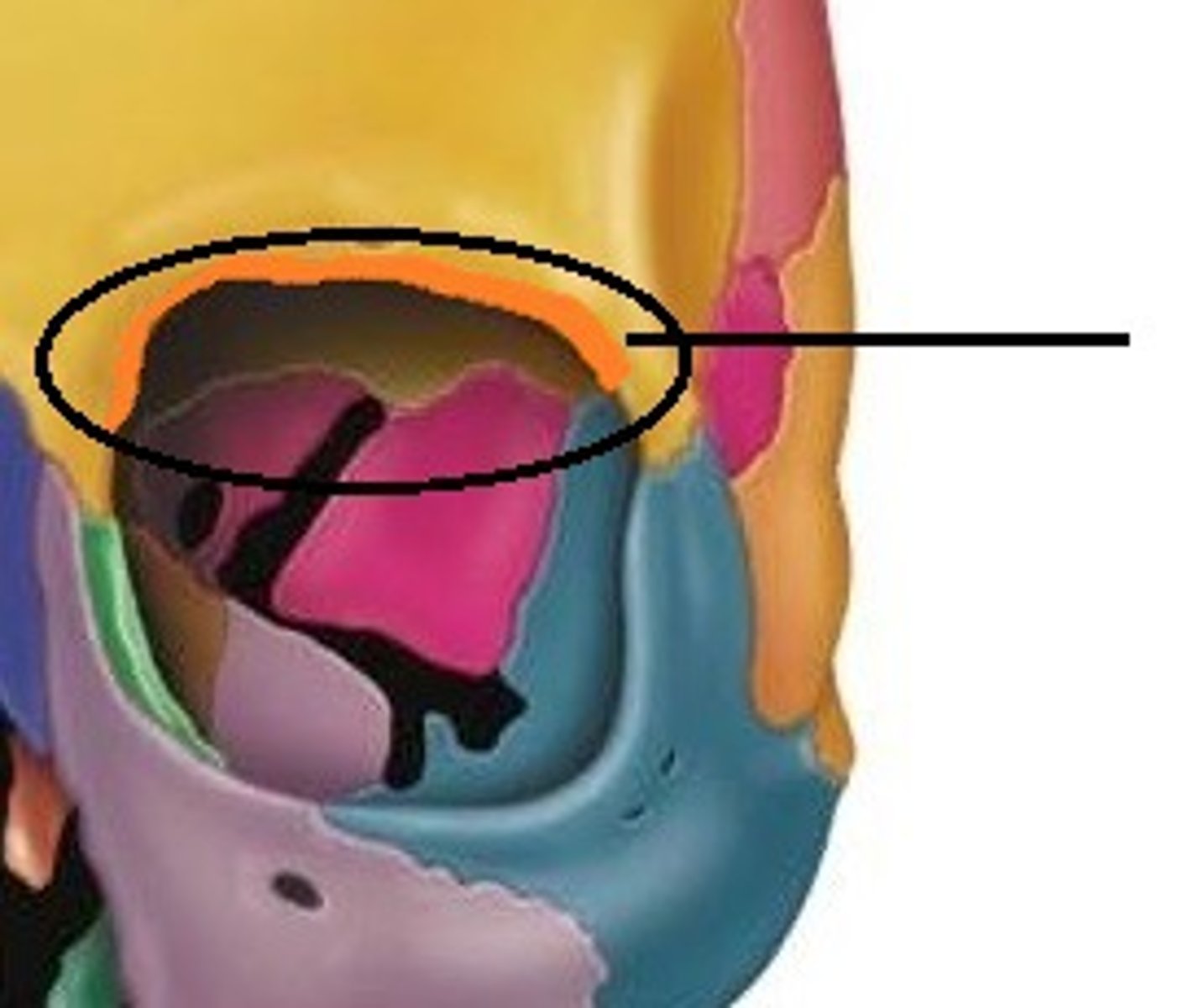
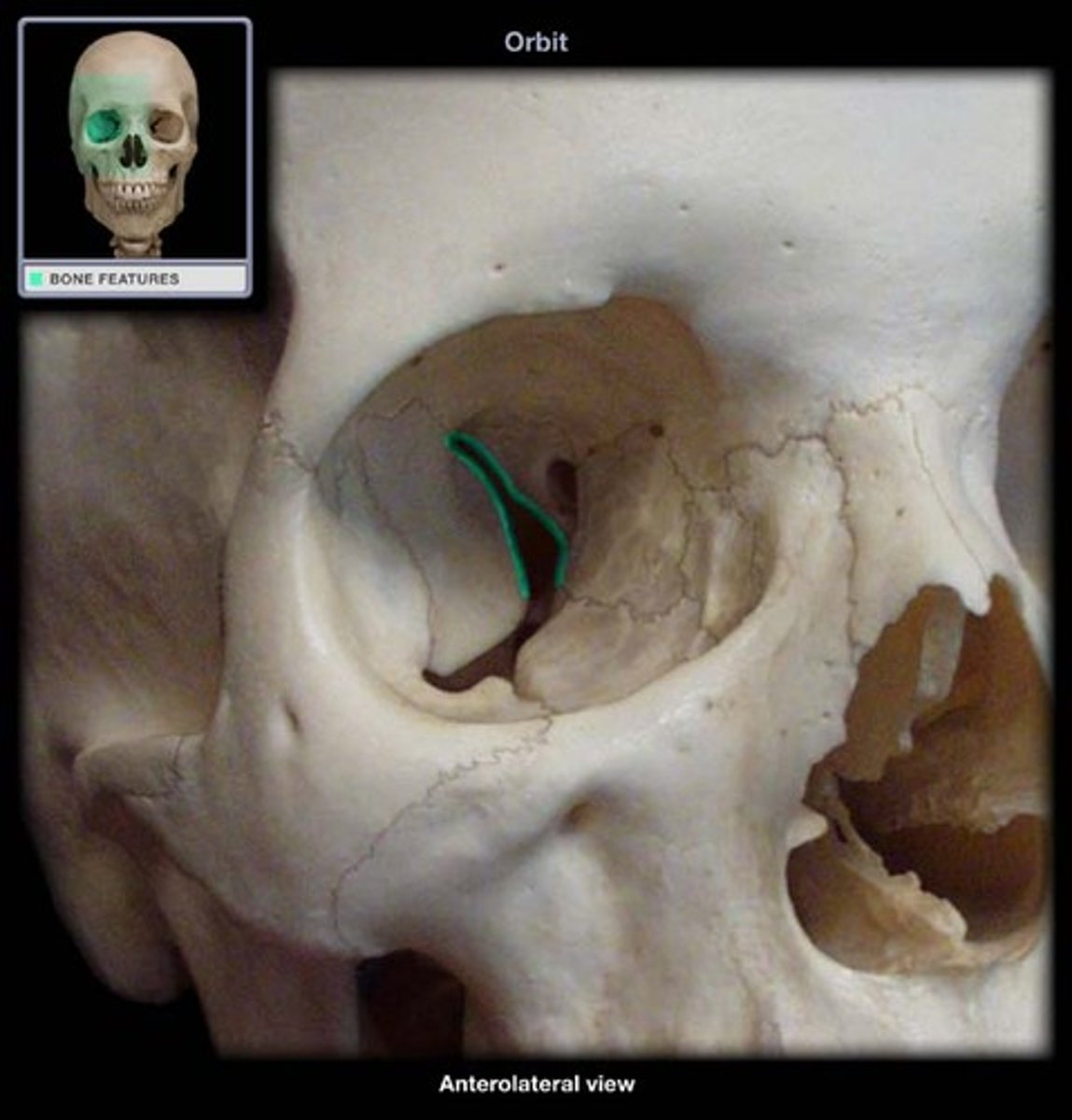
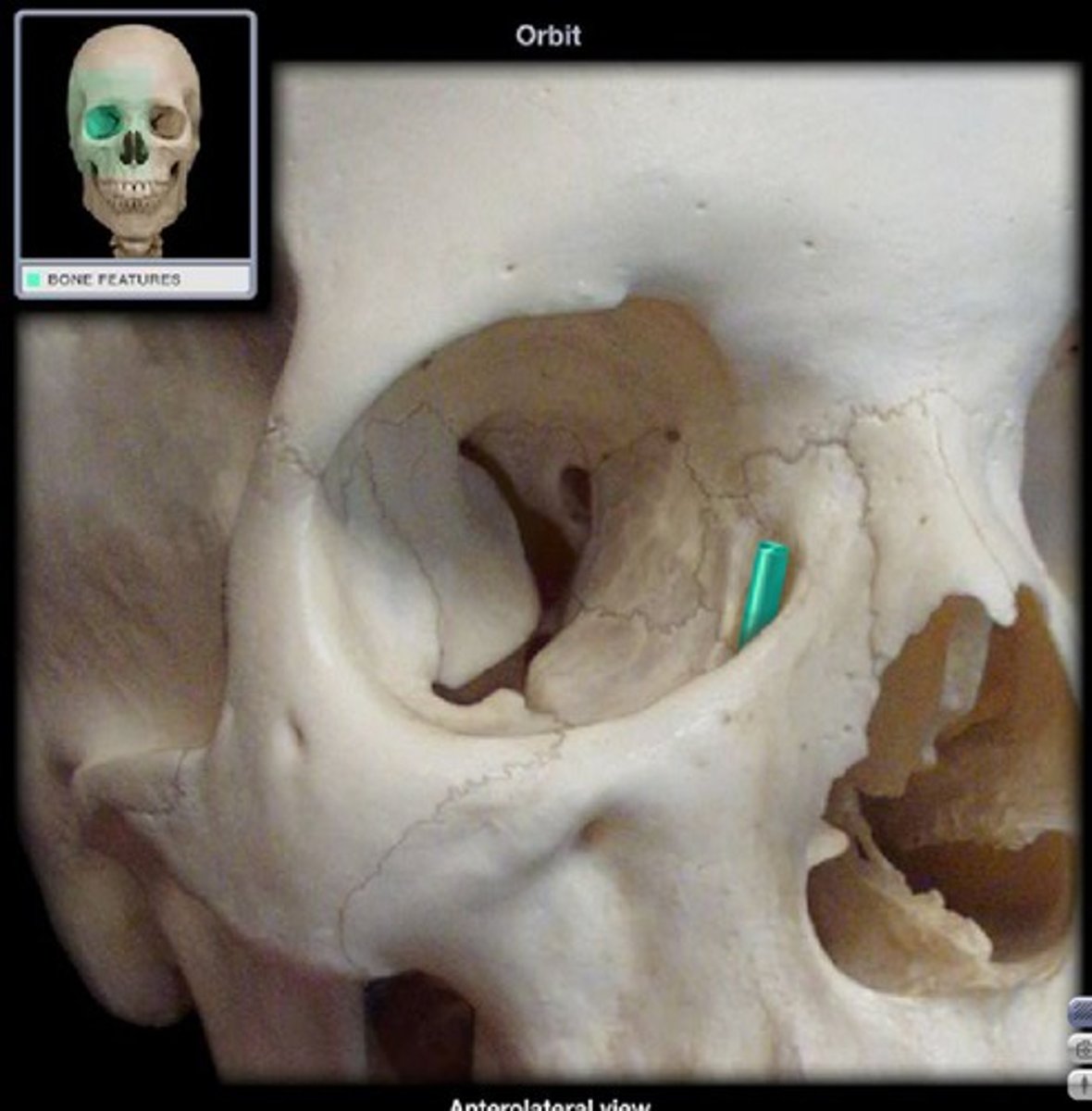
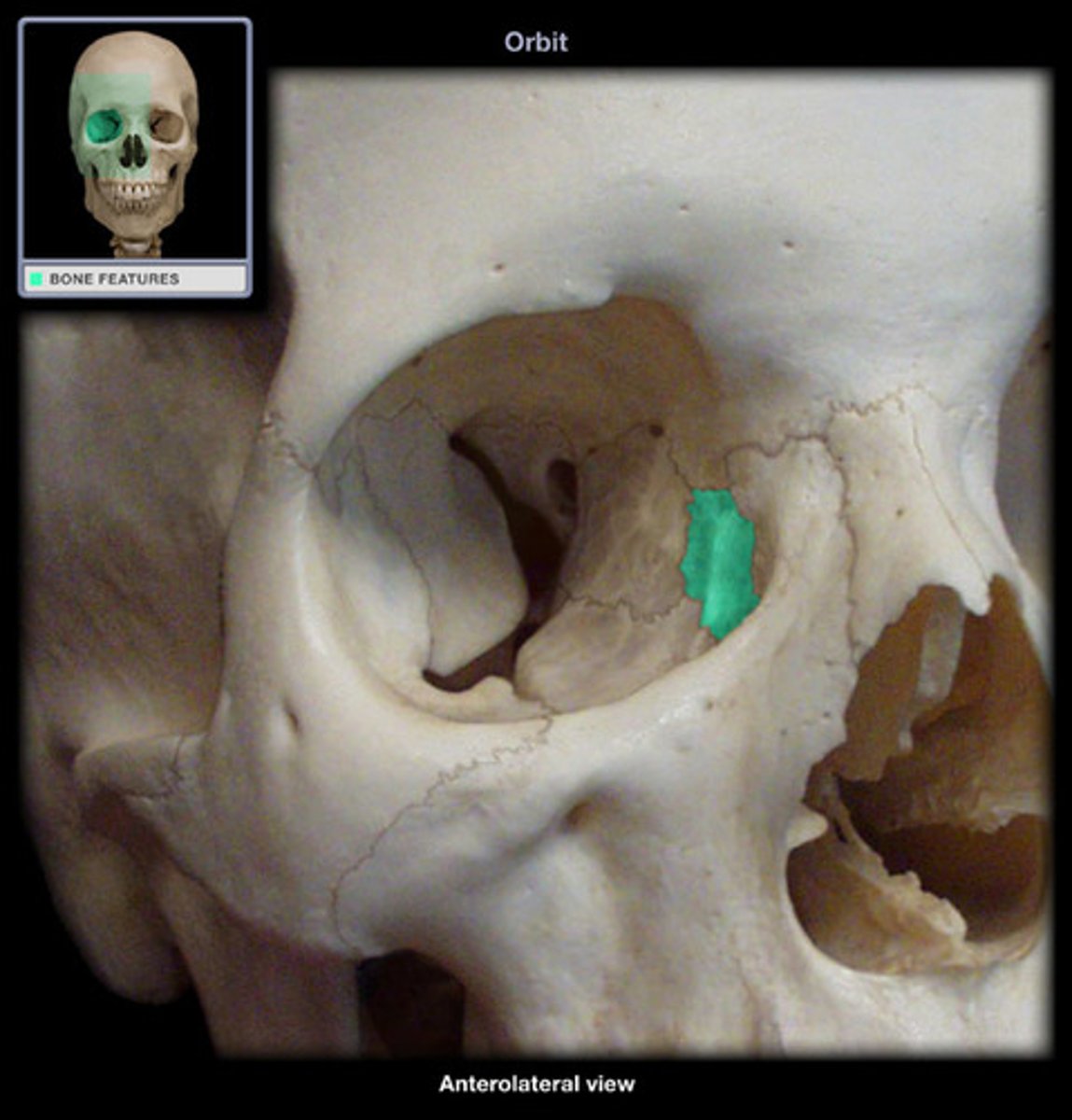
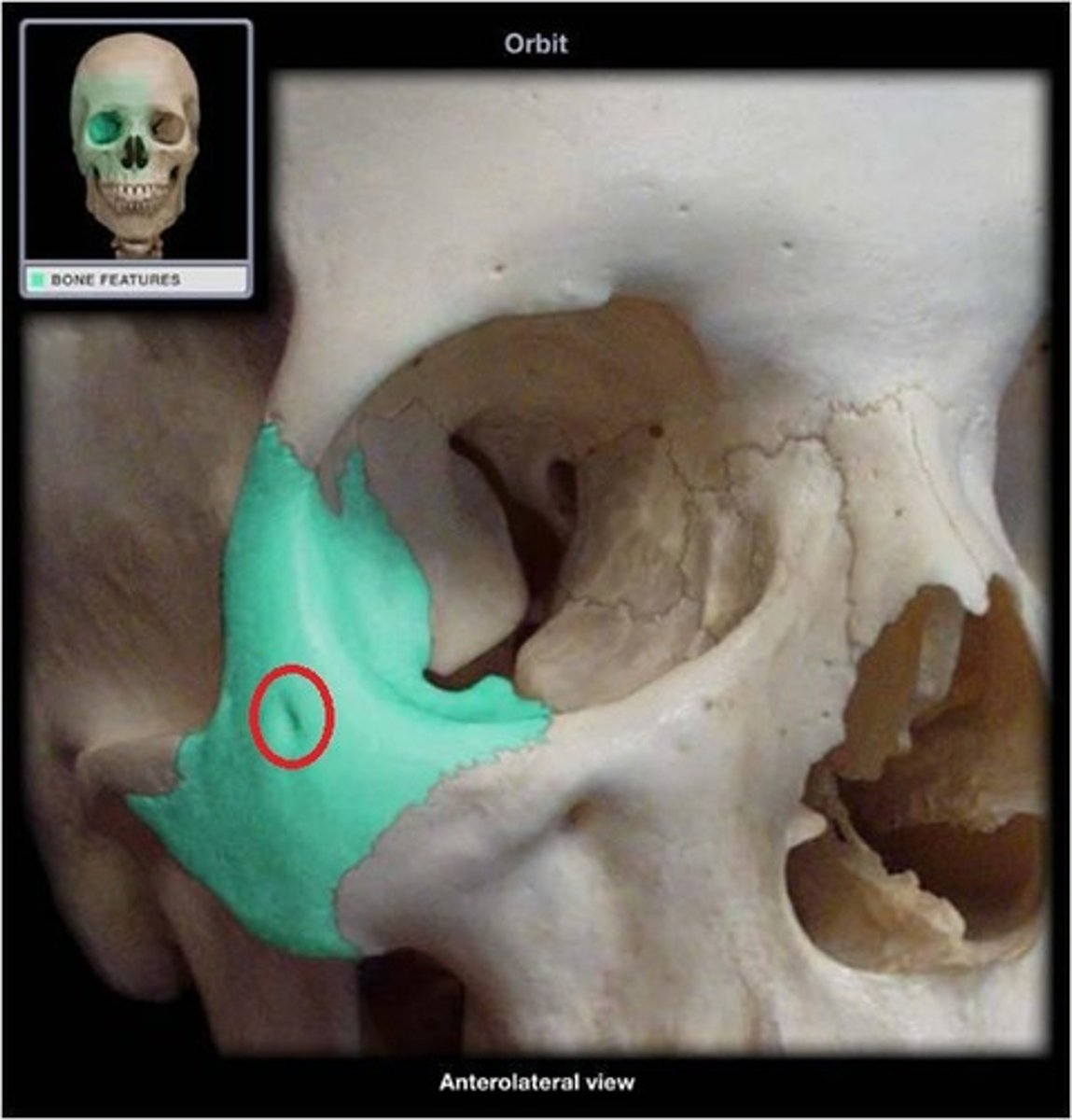
orbits (orbital cavities)
deep sockets that house the eyeballs and associated structures
each orbital has
a roof, lateral wall, floor, and medial wall
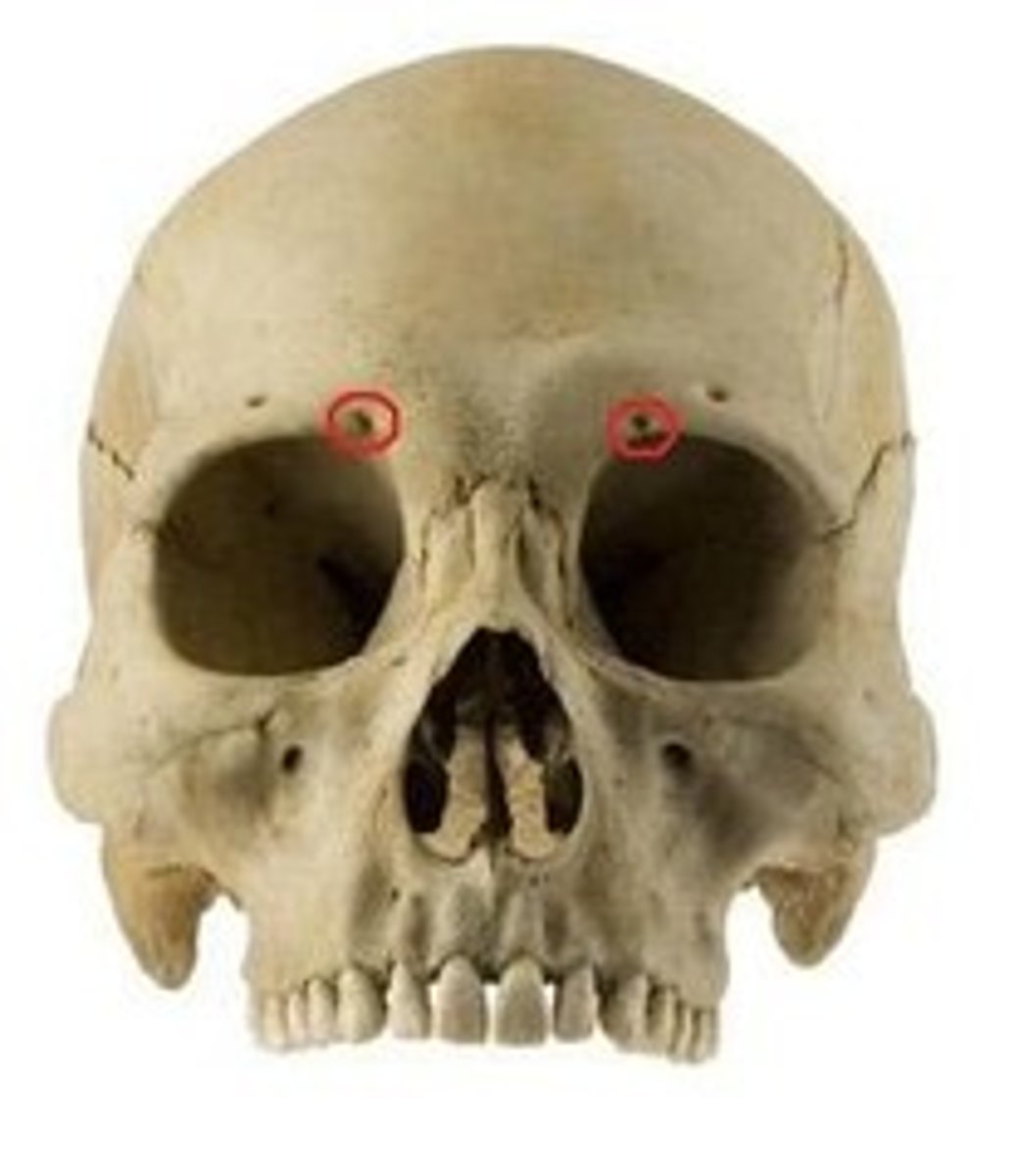
foramina
passageways for blood vessels, nerves, or ligaments
skull bones contain numerous
foramina
sutures
immovable joints located between skull bones
four notable sutures
coronal suture, sagittal suture, lambdoid suture, squamous sutures (2)
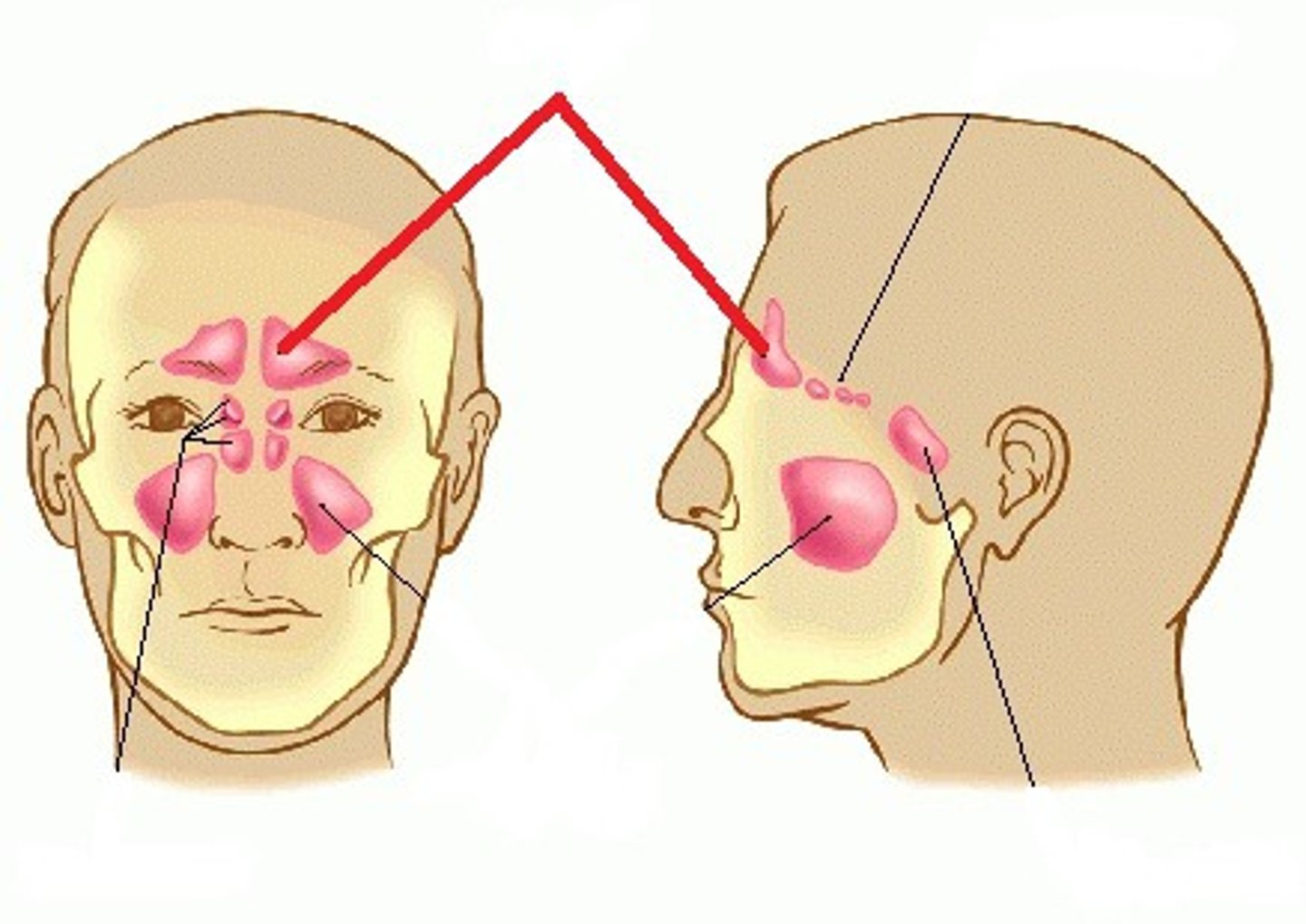
paranasal sinuses
paired air-filled cavities in the bones of the face that are connected to the nasal cavity
what are paranasal sinuses lined with?
mucus membranes
functions of paranasal sinuses
produce mucus and serve as resonating chambers for sound
where are paranasal sinuses located?
maxillae, frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones
fontanels
fibrous connective tissue membrane-filled spaces located between cranial bones of infants
functions of fontanels
enable the fetal skull to modify its shape as it passes through the birth canal, permit rapid growth of the brain during infancy
4 major fontanels
anterior fontanel, posterior fontanel, anterolateral fontanels (2), posterolateral fontanels (2)
shape of anterior fontanel
diamond shaped
shape of posterior fontanel
triangle shape
shape of anterolateral fontanel
irregular
shape of posterolateral fontanel
irregular
anterior fontanel closes up
in 24 months
posterior fontanel closes up
2 months after birth
anterolateral fontanels close up
3 months after birth
posterolateral fontanels close up
12 months after birth