Marketing exam 3 chapters 11-15
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Product Complexity
A. Actual product (Brand name, Quality Level, Packaging, Features/design)
B. Core Customer value
C. Associated services (Financing, Product warranty, Product support)
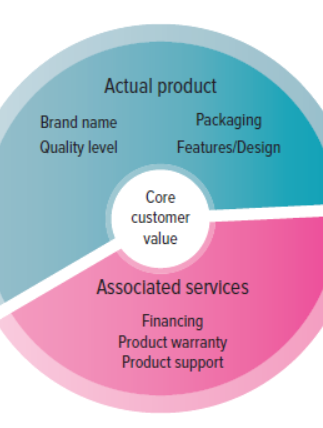
Core Customer Value
The basic problem-solving benefits that consumers are seeking.
Actual Product
The physical attributes of a product including the brand name, features/design, quality level, and packaging.
associated services/augmented product
The nonphysical attributes of the product, including product warranties, financing, product support, and after-sale service.
Consumer products
products and services used by people for their personal use
Specialty products/services
products and services a customer wants to find the best of and will put much effort into finding the best (Luxury cars, medical/legal professionals, designer apparel)
shopping products/services
products and services customers compare with other options and substitutes (furniture, clothes, perfumes)
convenience products/services
products and services for which the customer will buy without considering other products (gas, beverages, bread soap)
unsought products/services
Products or services consumers either do not normally think of buying or do not know about. (can be new product)
product mix
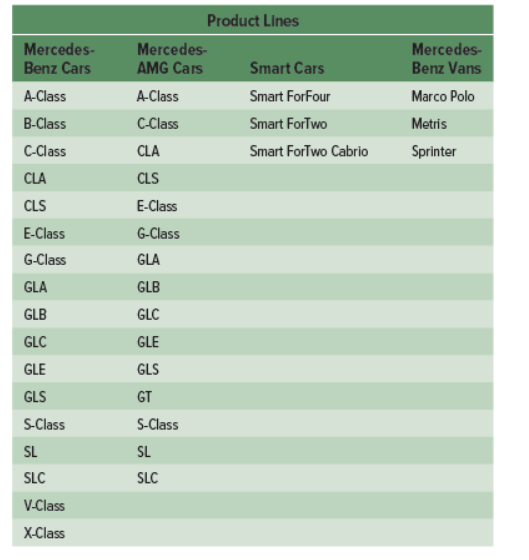
all products and services a firm offers, typically composed of product lines (E.G. every single Mercedes car that can be purchased from Mercedes dealerships)
breadth
a count of the number of product lines offered by the firm (Mercedes Benz, AMG, Smart cars, Vans) (going across)
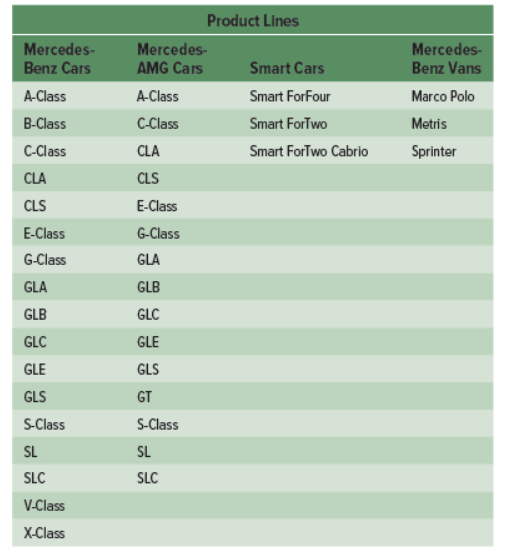
depth
number of categories in a product line (A class, B class, C class) (going down)
cannibalize
From a marketing perspective, it is the negative impact on a firm’s sales, profits, or market share when one product competes closely with a similar product offered by the same company. (Cars that look similar might steal sales from each other)
5 Things that make a brand
Brand Name
URL’s
Logos/symbols
slogans
jingles/sounds

Brand Equity
The set of assets and liabilities linked to a brand that add to or subtract from the value provided by the product or service.
(brands are assets a firm can manage
Brand Awareness
Measures how aware consumers are of brand (Companies live or die based on how aware customers are of brand)
perceived value
The relationship between a product’s or service’s benefits and its cost. (is it worth it to customers)
brand association
mental links consumers make between a brand and its key product attributes (when you see apple symbol you think of apple)
brand loyalty
when a customer chooses the same brands products repeatedly over time rather than many different suppliers of the product
manufacturer/national brands
brands owned and managed by manufacturer
retail/store/private label brands
Brands developed and marketed by a retailer and available only from that retailer
family brands
A firm’s own corporate name used to brand its product lines and products. (one brand name on many items, like Kraft)
individual brands
use of individual brand name for each of a firms product
brand extension
same brand name for new products being introduced to the same or new markets (increase in breadth, same brand name, different product)
line extension
use of the same brand name within same product line; shows increase in product line depth (increase in depth, same brand name, same product)
brand dilution
when brand extension negatively affects how customers see attributes of core brand (when a product/brand extension fails)
co-branding
marketing two or more brands together on the same product
brand licensing
A contractual arrangement between firms, whereby one firm allows another to use its brand name, logo, symbols, or characters in exchange for a negotiated fee. (company pays to use your name, logo, symbol, etc)
brand repositioning aka rebranding
marketers change strategy and focus on targeting different markets or realigning core attributes to match market preferences (e.g aunt Jemima becoming pearl Miller company, it is same product, different name)
Primary Packaging
The packaging the consumer uses, such as the toothpaste tube, from which they typically seeks convenience in terms of storage, use, and consumption
secondary packaging
wrapper or exterior carton with the upc label and extra information
innovation
The process by which ideas are transformed into new products and services that will help firms grow.
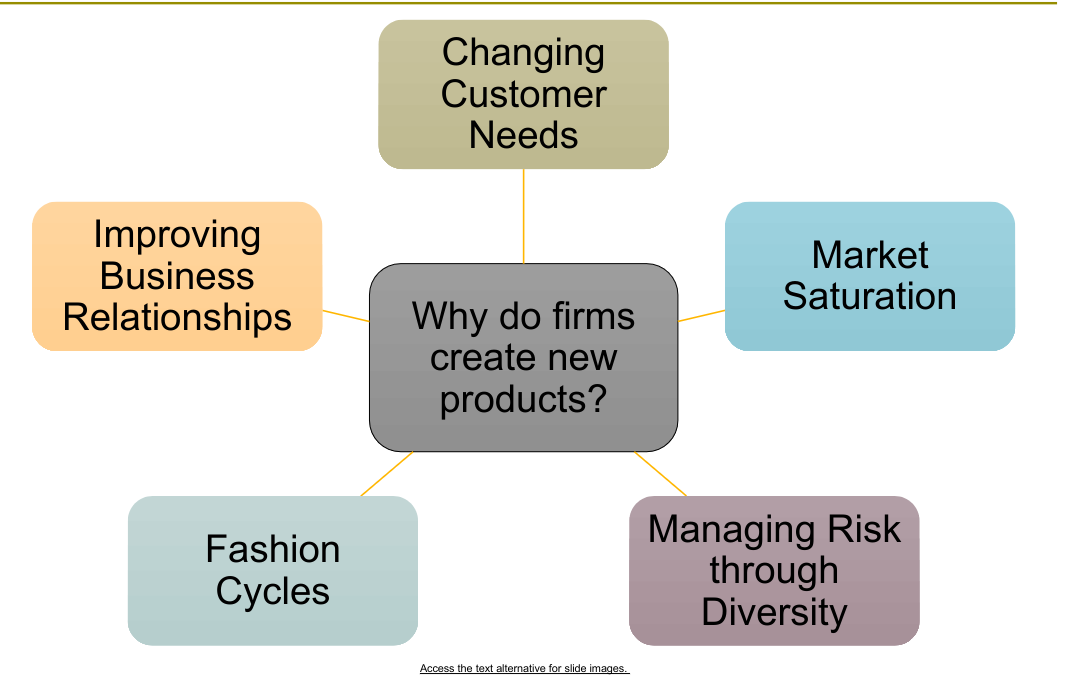
Innovation and value (See why do firms create new products graph)
Changing Customer needs
Market Saturation (People get bored of same products)
Managing Risk through Diversity (diversity in products)
Fashion Cycles
Improving business relationships
Diffusion of innovation
The process by which the use of an innovation, whether a product or a service, spreads throughout a market group over time and over various categories of adopters.
Pioneers or Breakthroughs
New product introductions that establish a completely new market or radically change both the rules of competition and consumer preferences in a market. (Pioneers are first movers
first movers
Product pioneers that are the first to create a market or product category, making them readily recognizable to consumers and thus establishing a commanding and early market share lead.
Diffusion of Innovation curve
(N2K)(ESSAY/MUlTIPLE CHOICE)(Diffusion = Spread)
Innovators
Early adopters
Early majority
late majority
laggards
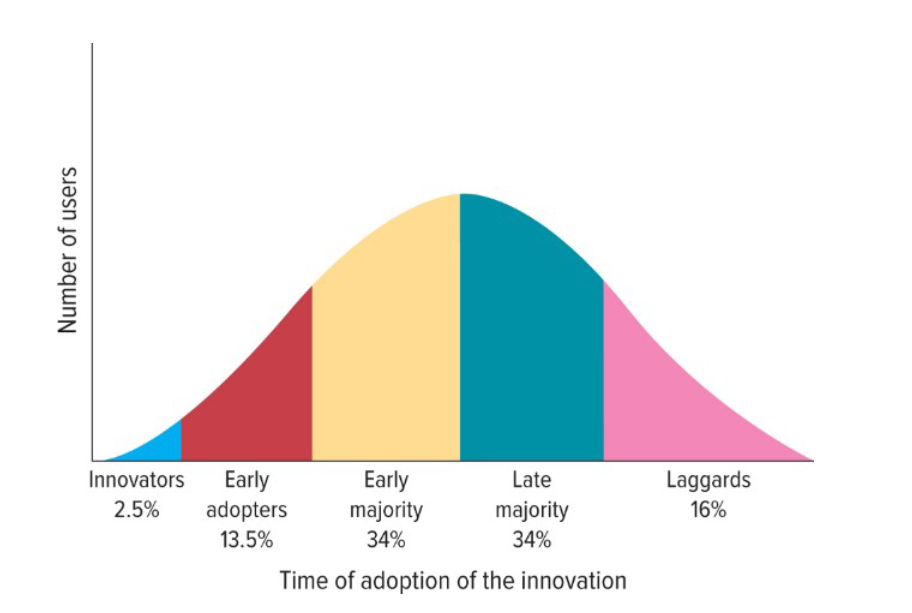
Innovators (% of users?)
buyers who want to be the first to have a product (2.5%)
early adopters (% of users?)
The second group of consumers in the diffusion of innovation model, after innovators, to use a product or service innovation. They generally don’t like to take as much risk as innovators but instead wait and purchase the product after careful review.
(13.5%)
Early Majority (% of users?)
A group of consumers in the diffusion of innovation model. Members don’t like to take much risk and therefore tend to wait until bugs are worked out of a particular product or service; few new products and services can be profitable until this large group buys them.
(34%)
Late Majority (% of users?)
The last group of buyers to enter a new product market, When they do, the product has achieved its full market potential. (34%)
Laggards (% of users?)
Consumers, who like to avoid change and rely on traditional products until they are no longer available. Sometimes laggards never adopt a product or service.
(16%)
Factors affecting Product Diffusion
(using the innovation diffusing theory)
Relative Advantage
Compatibility
observability
Complexity/trialability
Relative Advantage
The advantage of the product, a product that is better than its substitutes, diffusion is quicker
Compatibility
A diffusion process may be faster or slower, depending on various consumer features, including international cultural differences.
observability
when products are easily observed, their benefits or uses are easily communicated to others, enhancing diffusion
Complexity/trialability
Products that are relatively less complex are also relatively easy to try. These products will generally diffuse more quickly and lead to greater and faster adoption than will those that are not so easy to try.
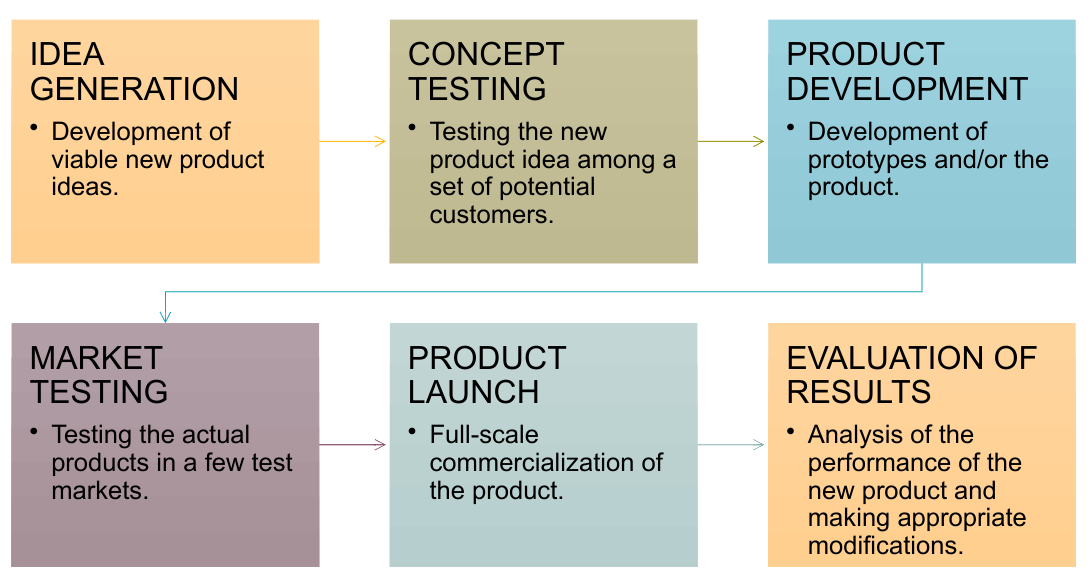
6 phases of the product development process
Idea Generation
Concept testing
product development
market testing
product launch
evaluation of results
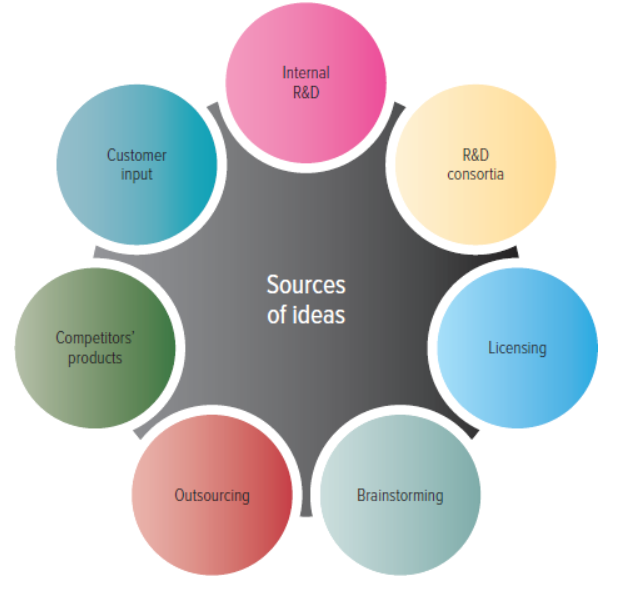
Sources of new product ideas
Internal Research and Development
Research and development Consortia
Licensing
brainstorming
outsourcing
competitors products
Customer input
R & D Consortia (idea generation)
A group of firms and institutions, possibly including government and educational institutions, that explore new ideas or obtain solutions for developing new products.
Lowest costs/risks, benefits all firms,
Licensing (idea generation)
A method used in developing new products in which a firm buys the rights to use a technology or idea from another firm.
brainstorming (idea generation)
A group activity used to generate ideas.
outsourcing (idea generation)
A practice in which the client firm hires an outside firm to facilitate some aspect of its business. In the context of new product development, the outsourced firm helps its client develop new products or services.
competitors products (idea generation)
A new product entry by a competitor may trigger a market opportunity for a firm, which can use reverse engineering to understand the competitor’s product and then bring an improved version to market.
Customer input (idea generation)
Co creating with customers
Internal R & D (idea generation)
When a company generates ideas through their own departments.
Highest product development costs, typically source of technological and breakthrough products
Market Testing
Premarket tests
Test Marketing
Premarket Tests
Conducted before a product or service is brought to market to determine how many customers will try and then continue to use it.
customers exposed
customers surveryed
firm makes decision
Test Marketing
A method of determining the success potential of a new product; it introduces the offering to a limited geographic area prior to a national launch.
Mini product launch
more expansion
demand is estimated
Product Lifestyle cycle (PLC)(N2K!!!) and stages
Defines the stages that new products move through as they enter, get established in, and ultimately leave the marketplace and thereby offers marketers a starting point for their strategy planning. Bell shaped
Introduction stage
Growth stage
Maturity stage
decline stage
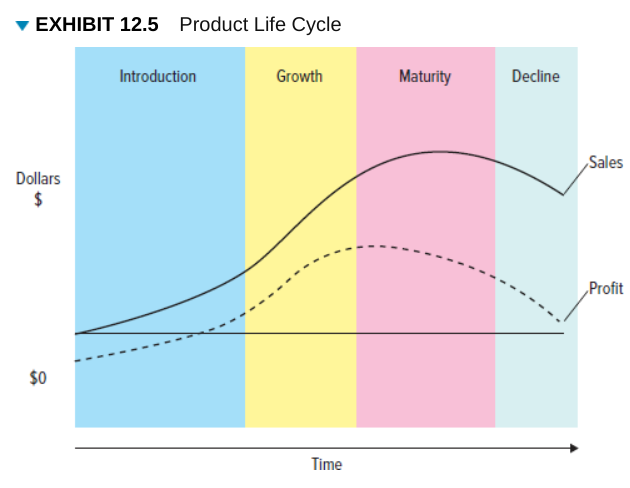
Introduction stage
Stage of the product life cycle when innovators start buying the product.
Growth Stage
Stage of the product life cycle when the product gains acceptance, demand and sales increase, and competitors emerge in the product category.
Maturity stage
Stage of the product life cycle when industry sales reach their peak, so firms try to rejuvenate their products by adding new features or repositioning them.
decline stage
Stage of the product life cycle when sales decline and the product eventually exits the market.
Limitations of product lifestyle
Each product or service has its own shape
challenging to know precise stage of plc
reverse engineering
Taking apart a competitor’s product, analyzing it, and creating an improved product that does not infringe on the competitor’s patents, if any exist.
lead users
Innovative product users who modify existing products according to their own ideas to suit their specific needs.
concept
an idea with potential, includes brief idea of what product will look like
concept testing
showing a product to consumers to see their reaction, triggers marketing research process
product development/design
Entails a process of balancing various engineering, manufacturing, marketing, and economic considerations to develop a product’s form and features or a service’s features.
prototypes
first form of a product, in rough shape
alpha testing
An attempt by the firm to determine whether a product will perform according to its design and whether it satisfies the need for which it was intended; occurs in the firm’s research and development (R&D) department.
beta testing
Having potential consumers examine a product prototype in a real-use setting to determine its functionality, performance, potential problems, and other issues specific to its use.
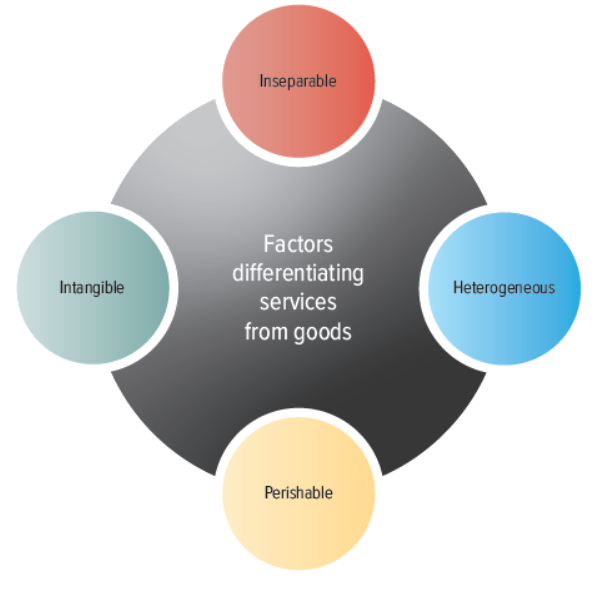
Intangible
A characteristic of a service; it cannot be touched, tasted, or seen like a pure product can.
Requires cues to aid customers
atmosphere and images help convey value
Inseparable
A characteristic of a service: it is produced and consumed at the same time; that is, service and consumption are inseparable. (haircut, hotel stay)
Heterogeneity
As it refers to the differences between the marketing of products and services, the delivery of services is more variable. (Think valeting, each customer receives a slightly different experience because Valet drivers have more or less experience)
Heterogeneous
The more humans are needed to provide a service, the more likely there is to be Heterogeneity or variability.
perishable
A characteristic of a service: it cannot be stored for use in the future. (can be things such as trips)
Value of Brands
Brands facilitate purchases (helps consumers make quick buying decisions)
Brands Establish Loyalty
Brands protect from competition and Price competition (customers like brand more so they choose that brand over others)
Product labels
provide information the consumer needs for a purchase decision and consumption of the product.
Differences between stages in product life cycle
→
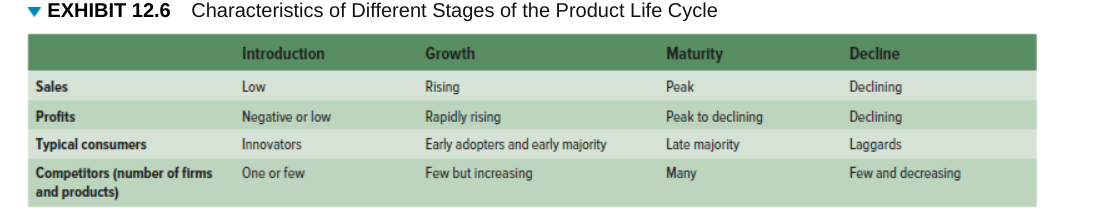
Service
Any intangible offering that involves a deed, performance, or effort that cannot be physically possessed; intangible customer benefits that are produced by people or machines and cannot be separated from the producer.
Customer Service
Specifically refers to human or mechanical activities firms undertake to help satisfy their customers’ needs and wants.
Service/Product continuum
Pure services to Pure goods

Core Differences Between services and goods
Inseparable
Intangible
Perishable
Heterogeneous
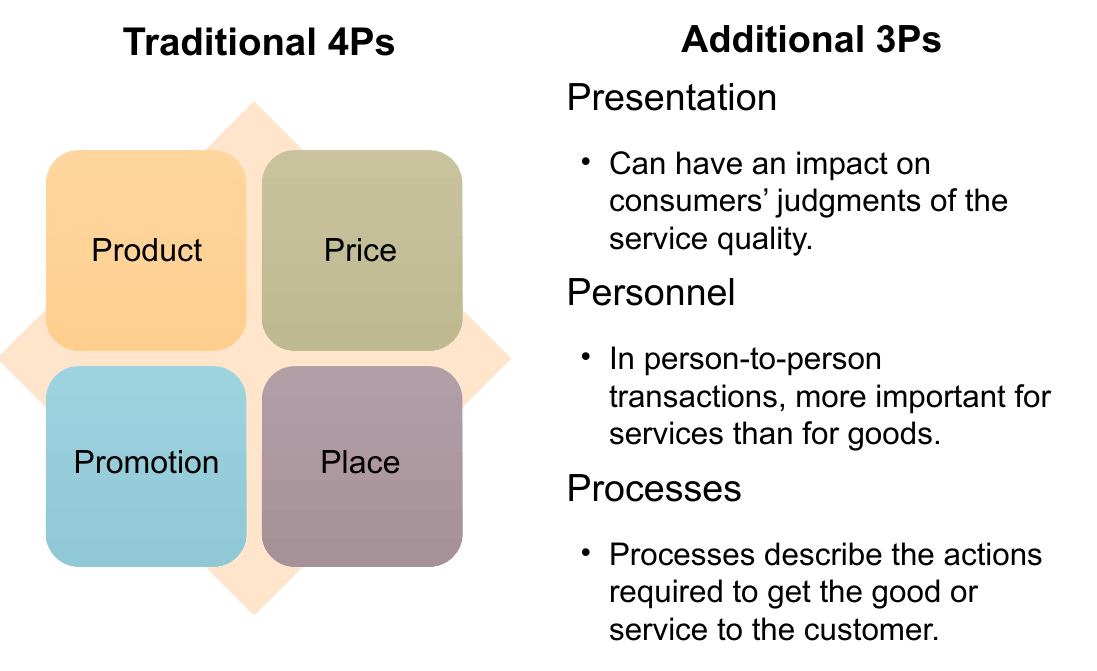
3 additional P’s of marketing mix in service businesses
(think in terms of valet drivers)
Presentation
Personnel
Processes
Service Gap
Results when a service fails to meet the expectations that customers have about how it should be delivered.
Service Gaps Model
A managerial tool designed to encourage the systematic examination of all aspects of the service delivery process and prescribe the steps needed to develop an optimal service strategy.
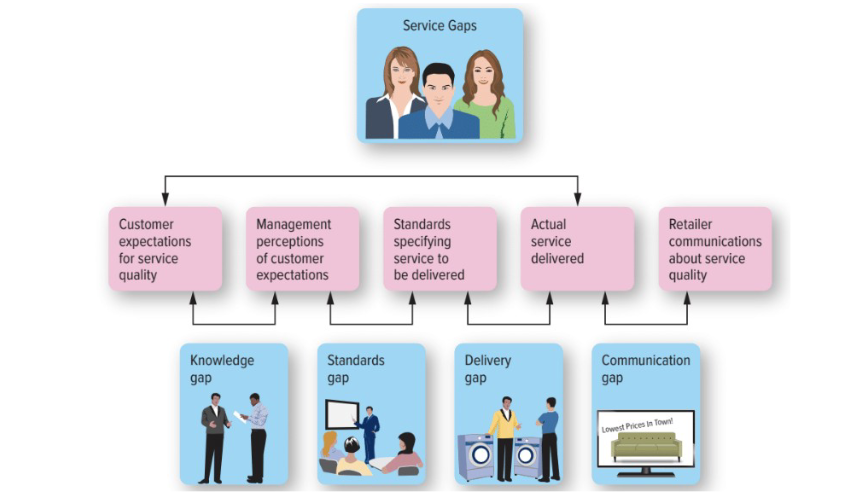
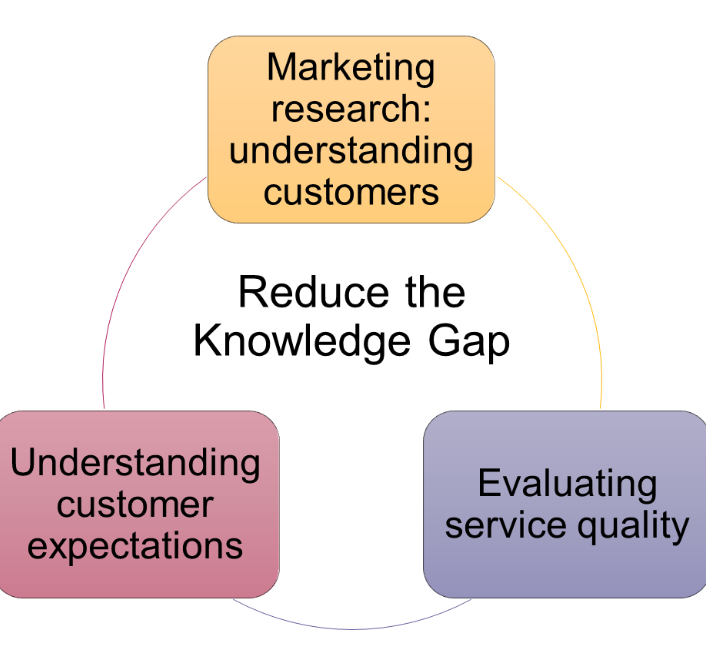
The knowledge Gap
reflects the difference between customers’ expectations and the firm’s perception of those customer expectations.
Firms can close this gap by determining what customers really want by doing research using marketing metrics such as service quality and the zone of tolerance
standards gap
difference between the firm’s perceptions of customers’ expectations and the service standards it sets
need to set standards for quality, need to ensure systems in place to set standards
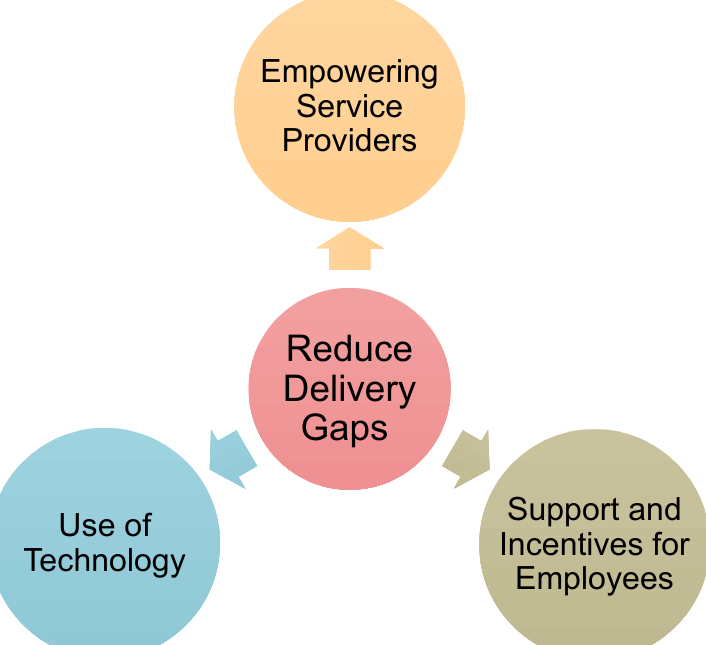
delivery gap
difference between the firm’s service standards and the actual service it provides to customers.
Communication gap
difference between the actual service provided to customers and the service that the firm’s promotion program promises
Customer expectations
Varies on service/situation
based on knowledge and experience
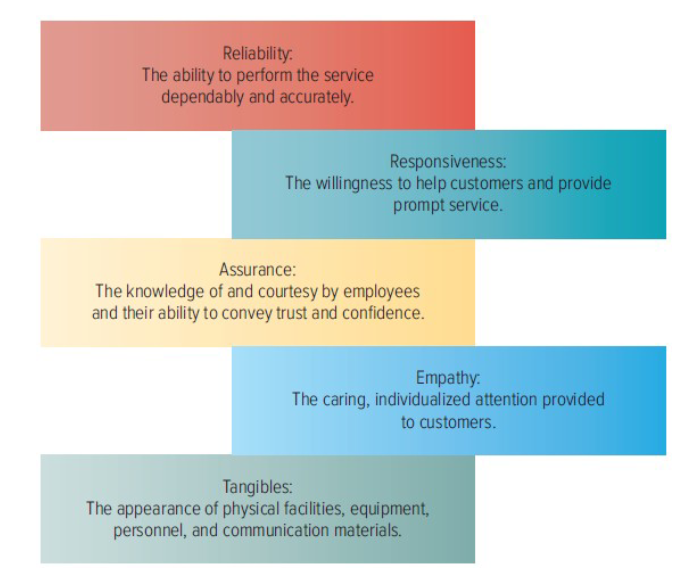
Dimensions of Service Quality
Reliability
Responsiveness
Assurance
Empathy
Tangibles
Zone of tolerance
The area between customers’ expectations regarding their desired service and the minimum level of acceptable service—that is, the difference between what the customer really wants and what they will accept before going elsewhere.
Voice of Customer (VOC) program
An ongoing marketing research system that collects customer inputs and integrates them into managerial decisions.
Empowerment
In the context of service delivery, means allowing employees to make decisions about how service is provided to customers.
Emotional Support
Concern for others’ well-being and support of their decisions in a job setting
Instrumental support
Providing the equipment or systems needed to perform a task in a job setting.
distributive fairness
Pertains to a customer’s perception of the benefits they received compared with the costs (inconvenience or loss) that resulted from a service failure.