Ch5 Bonding Theories - Explaining Molecular Geometry
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Concepts: molecular geometry, isomers, dipoles, valance bond theory, hybridization, chirality, valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Valence-shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
electrons have negative charges & will repel each other; predicts arrangement of valence e- pairs around a central atom
Steric Number (SN) formula
SN = (# of atoms bonded to central atom) + (# of lone e- pairs on central atom)
To be a polar molecule…
asymmetrical molecular geometry, contain polar bonds
If SN = 2+0 = 2, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
linear; 180°
If SN = 3+0 = 3, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
trigonal planar; 120°
If SN = 2+1 = 3, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
bent; <120°
If SN = 4+0 = 4, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
tetrahedral; 109.5°
If SN = 3+1 = 4, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
trigonal pyramidal; <109.5°
If SN = 2+2 = 4, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
bent; <120°
If SN = 5+0 = 5, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle(s)?
trigonal bipyramidal; 90°, 120°
If SN = 4+1 = 5, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle(s)?
seesaw; <90°, <120°
If SN = 3+2 = 5, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
t-shaped; <90°
If SN = 2+3 = 5, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
linear; 180°
If SN = 6+0 = 6, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
octahedral; 90°
If SN = 5+1 = 6, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
square pyramidal; <90°
If SN = 4+2 = 4, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
square planar; 90°
If SN = 3+3 = 6, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
t-shaped; <90°
If SN = 2+4 = 6, what is the molecular geometry? Bond angle?
linear; 180°

Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
linear; 180° (image)
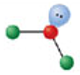
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
bent; <120° (image)
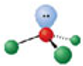
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
trigonal planar; 120° (image)
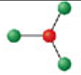
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
trigonal pyramidal; <109.5° (image)
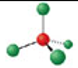
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
tetrahedral; 109.5° (image)
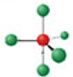
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
trigonal bipyramidal; 90°, 120° (image)
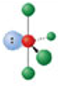
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
seesaw; <90°, <120° (image)
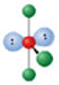
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
t-shaped; <90° (image)
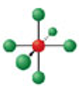
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
octahedral; 90° (image)
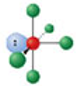
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
square pyramidal; <90° (image)
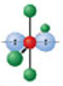
Identify the molecular geometry & bond angle? (image)
square planar; 90° (image)
Dipole (Debye unit) equation
µ = q*r (separated charge*distance between center of charges)
Valence Bond Theory
a chemical bond forms when atomic orbitals overlap
sp3 hybrid orbital
4 hybrid orbitals, SN = 4, single bond
sp2 hybrid orbital
3 hybrid orbitals, SN = 3, double bond
sp hybrid orbital
2 hybrid orbitals, SN = 2, triple bond
Sigma Bond (σ)
covalent bond in which the highest e- density lies between the 2 atoms along the bond axis
Pi Bond (π)
covalent bond in which the highest e- density lies above & below the internuclear axis
Bond Conjugation
alternation of single & double bonds in a molecule
In an organic structure, what signals delocalized electrons?
when the electron pair of a double bond cannot be moved anywhere else & still make sense
In an organic structure, what signals localized electrons?
when the electron pair of a double bond can be moved anywhere else & still make sense
Rank NH3, CH4, and H2O in order of decreasing bond angles.
NH3 < CH4< H2O
Do either of these molecules have a permanent dipole?
CH2O (formaldehyde), CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane)
CH2O (formaldehyde): yes
CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane): yes
Which of the following halocarbons are polar & which are nonpolar?
CF2Cl2, CCl4, CH3Cl, CF3-CF3
polar: CF2Cl2, CH3Cl
nonpolar: CCl4, CF3-CF3
Determine the hybridization of carbon & oxygen in CO2.
SN = 2 —> sp-hybridization
Determine the hybridization of carbon in CH2Cl2.
SN = 4 —> sp3-hybridization
Determine the hybridization of carbon in H2C=O.
SN = 3 —> sp2-hybridizaton
Determine the hybridization of carbon in HC=-CH
SN = 2 —> sp-hybridization
Determine the hybridization of carbon in C=-O.
SN = 2 —> sp-hybridization
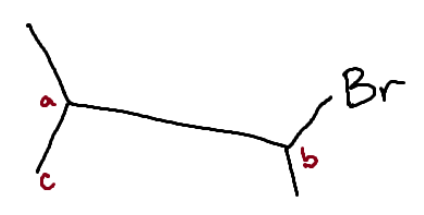
Identify the chiral center(s).
b
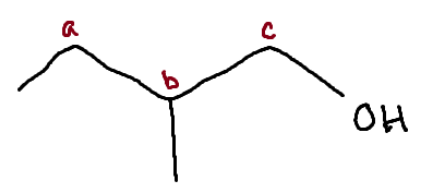
Identify the chiral center(s).
b
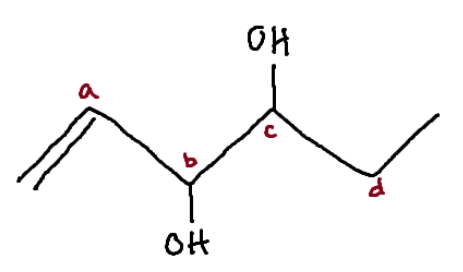
Identify the chiral center(s).
b, c
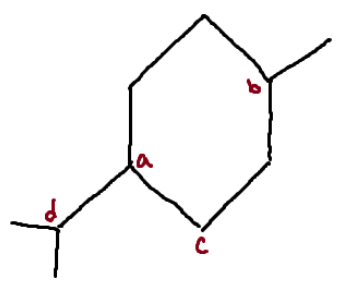
Identify the chiral center(s).
a
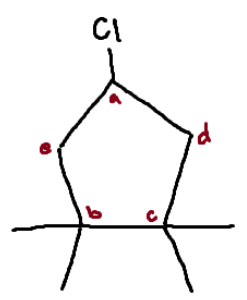
Identify the chiral center(s).
none
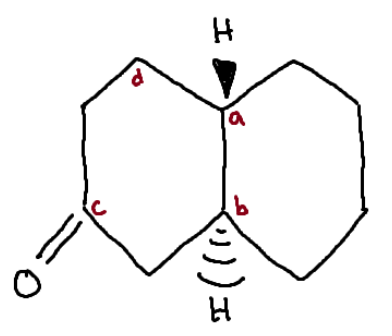
Identify the chiral center(s).
a, b
Structural Isomer
molecules w/ the same composition, different structure
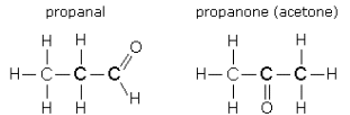
Identify the type of isomer.
structural isomer
Stereo Isomer
atoms in molecules are joined the same way, arranged differently in space
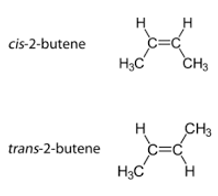
Identify the type of isomer.
stereo isomer
Optical Isomer
molecules obtained by mirror-image of each other
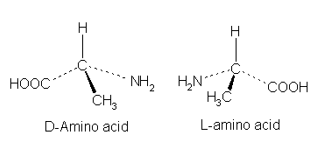
Identify the type of isomer.
optical isomer
To be a chiral molecule…
contain at least one chiral center, asymmetrical