FX Biology 30 Reproduction and Development
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Epididymis
Duct located above seminiferous tubules
-Storage and maturation of sperm
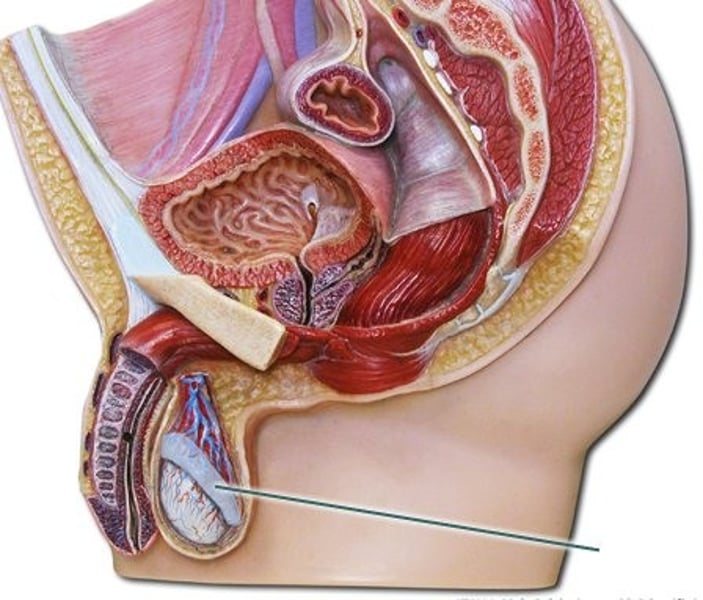
Testes
Site of production of male gametes (sperm) and sex hormones (testosterone)
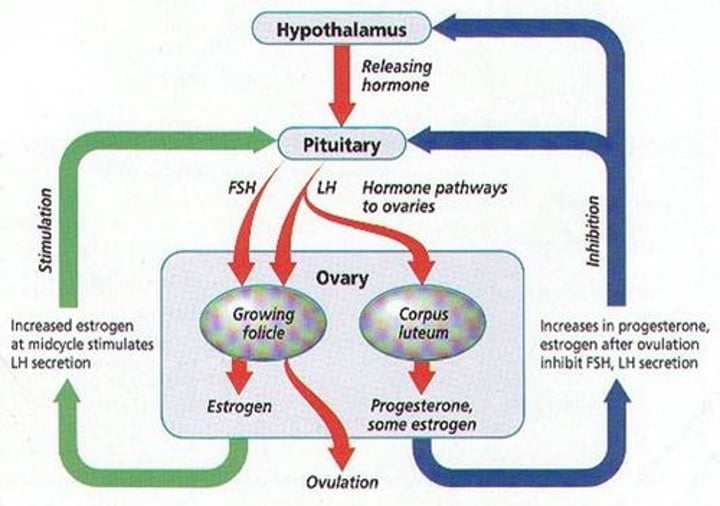
FSH
In the ovary-acts on primary follicles to develop into secondary follicle (which containing ovum/egg) In the testes, acts to start spermatogenesis
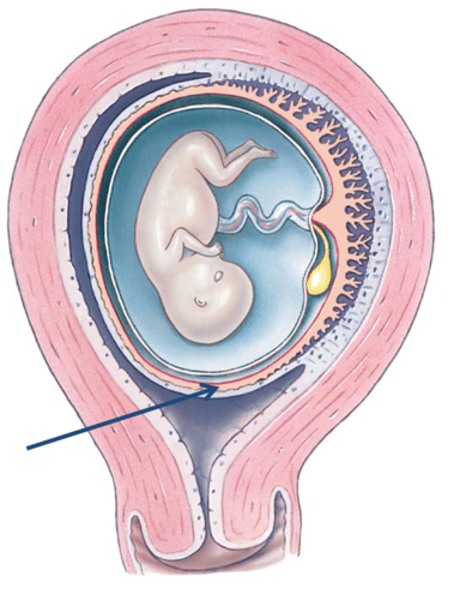
Chorion
develops into the placenta
2nd Trimester
-all organs form,
-Placenta begins to secrete estrogen and progesterone
gastrula
An embryonic stage in animal development encompassing the formation of three layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
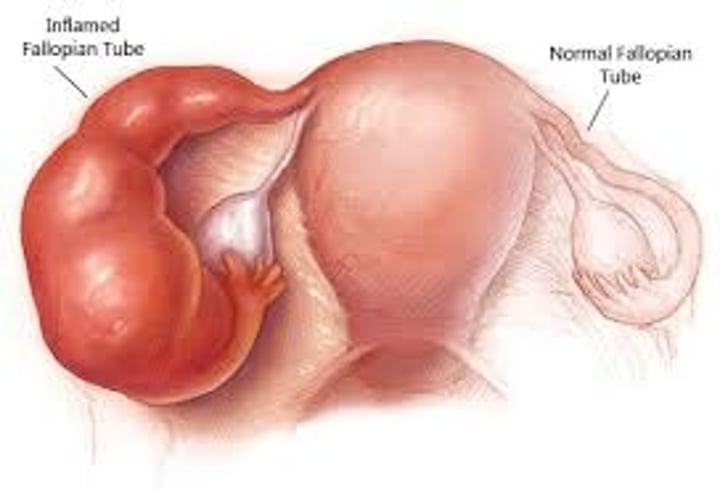
pelvic inflammatory disease
an inflammation of the female reproductive organs. Can lead to infertility by causing permanent blockage of fallopian tubes
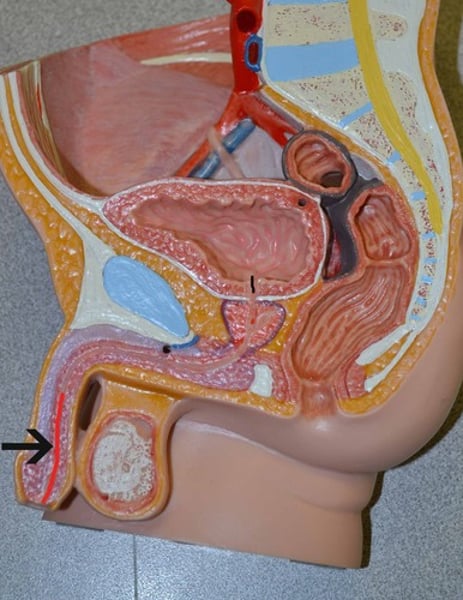
Prostate gland
Alkaline buffer and mucus that protects sperm against acidic environments in the urethra and vagina
Urethra
Duct carrying both semen and urine through penis
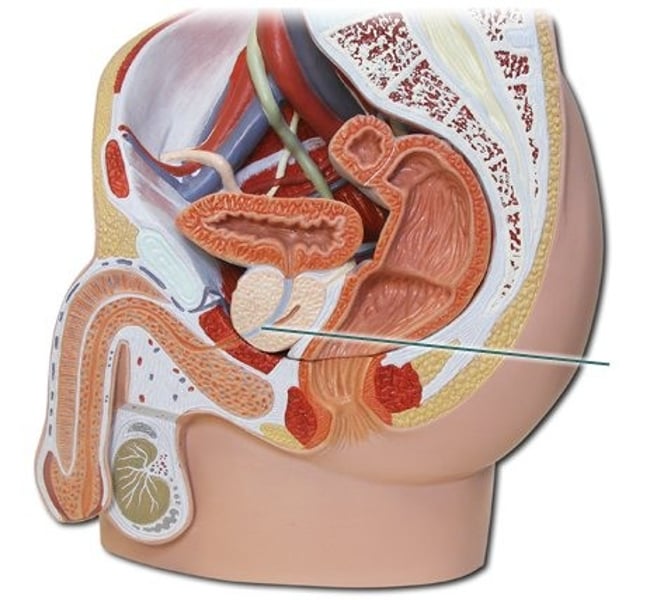
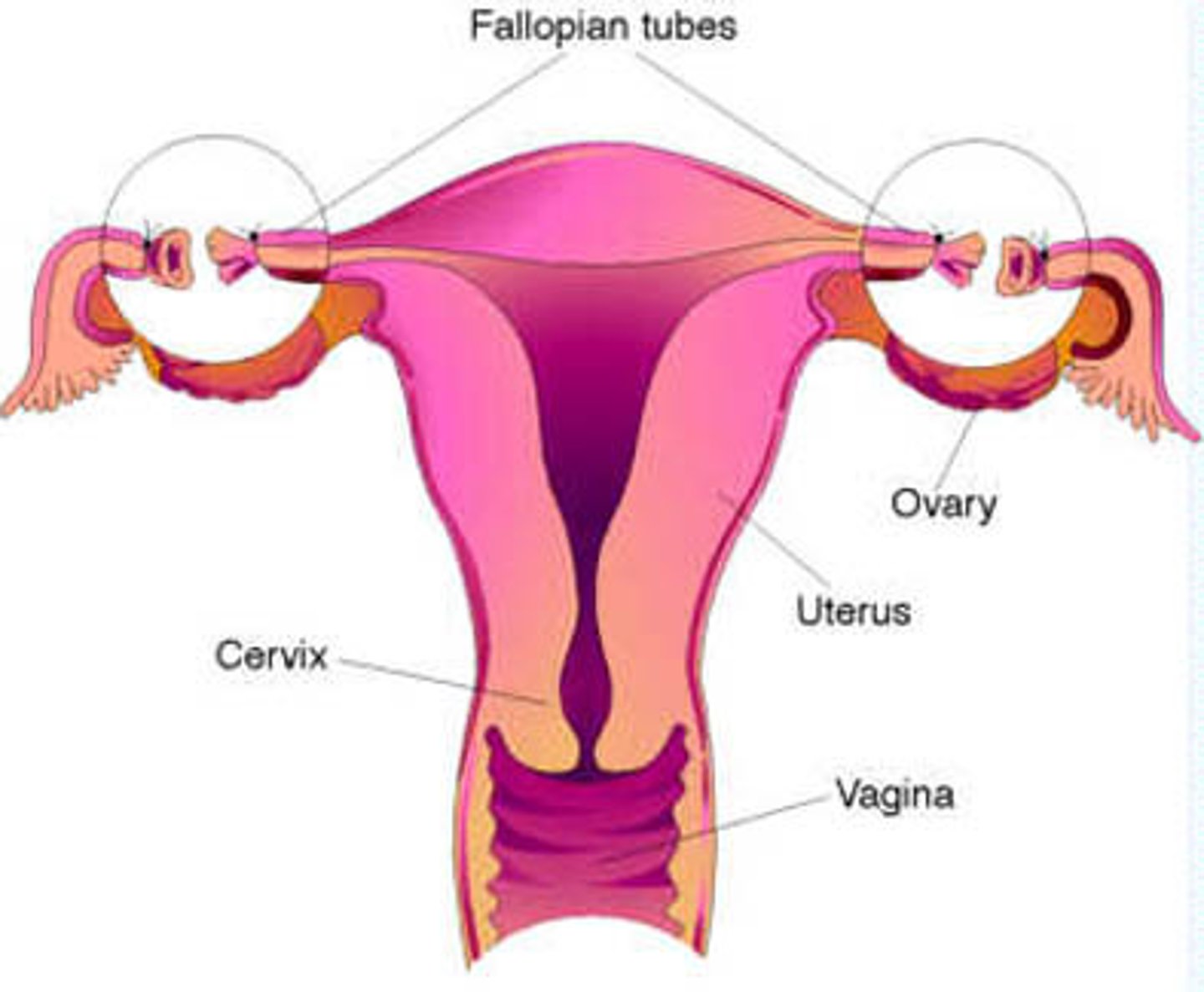
Ovaries
Site of oogenesis (creation of eggs / ovum) and release of estrogen and progesterone
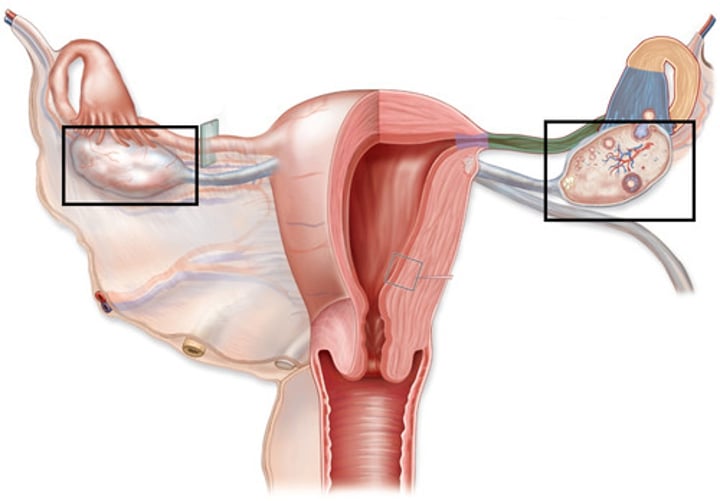
Penis
Carries semen into the female reproductive tract.
Secondary sex characters
Associated with male/female traits (i.e. facial hair, wide hips)
Seminiferous Tubules
Site of sperm production within the testes (process called spermatogenesis)
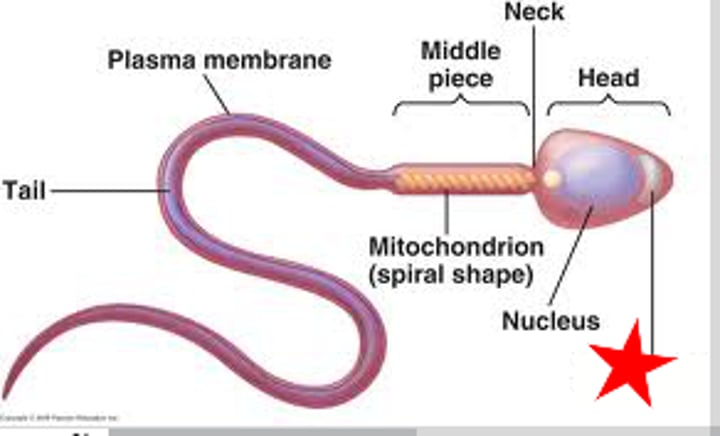
Sperm cell
Male haploid gamete
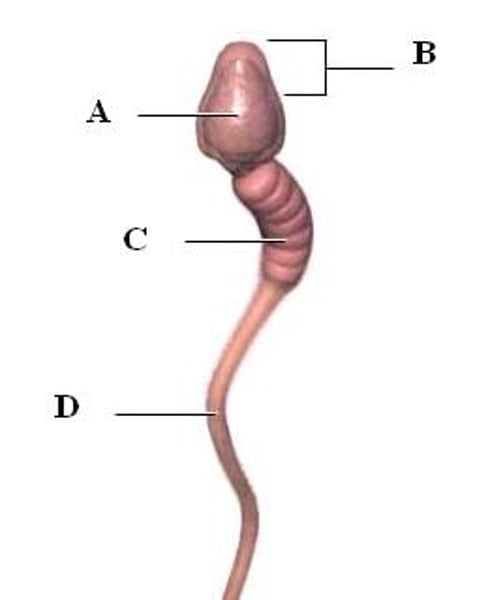
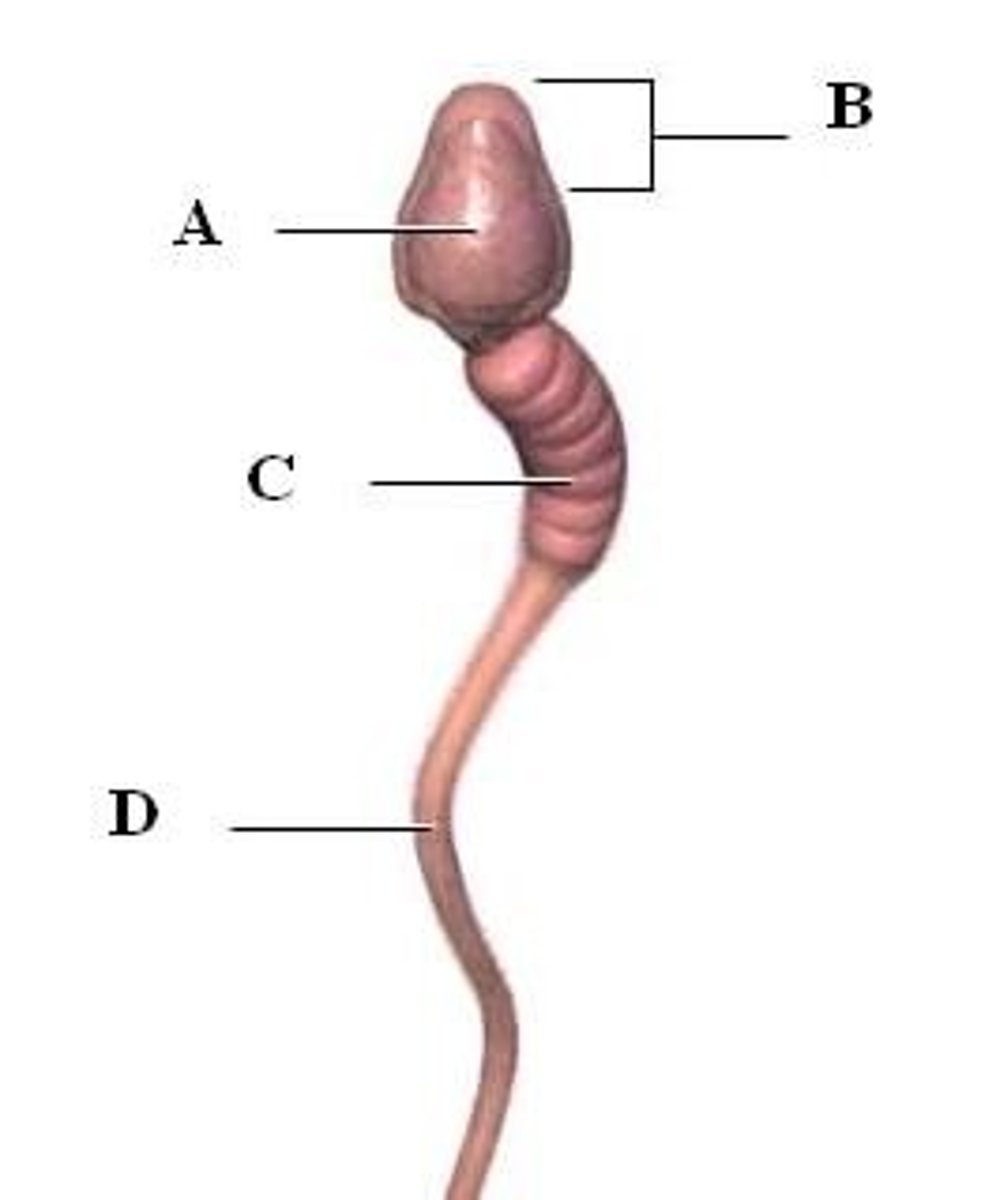
Flagellum
for sperm locomotion (labelled D)
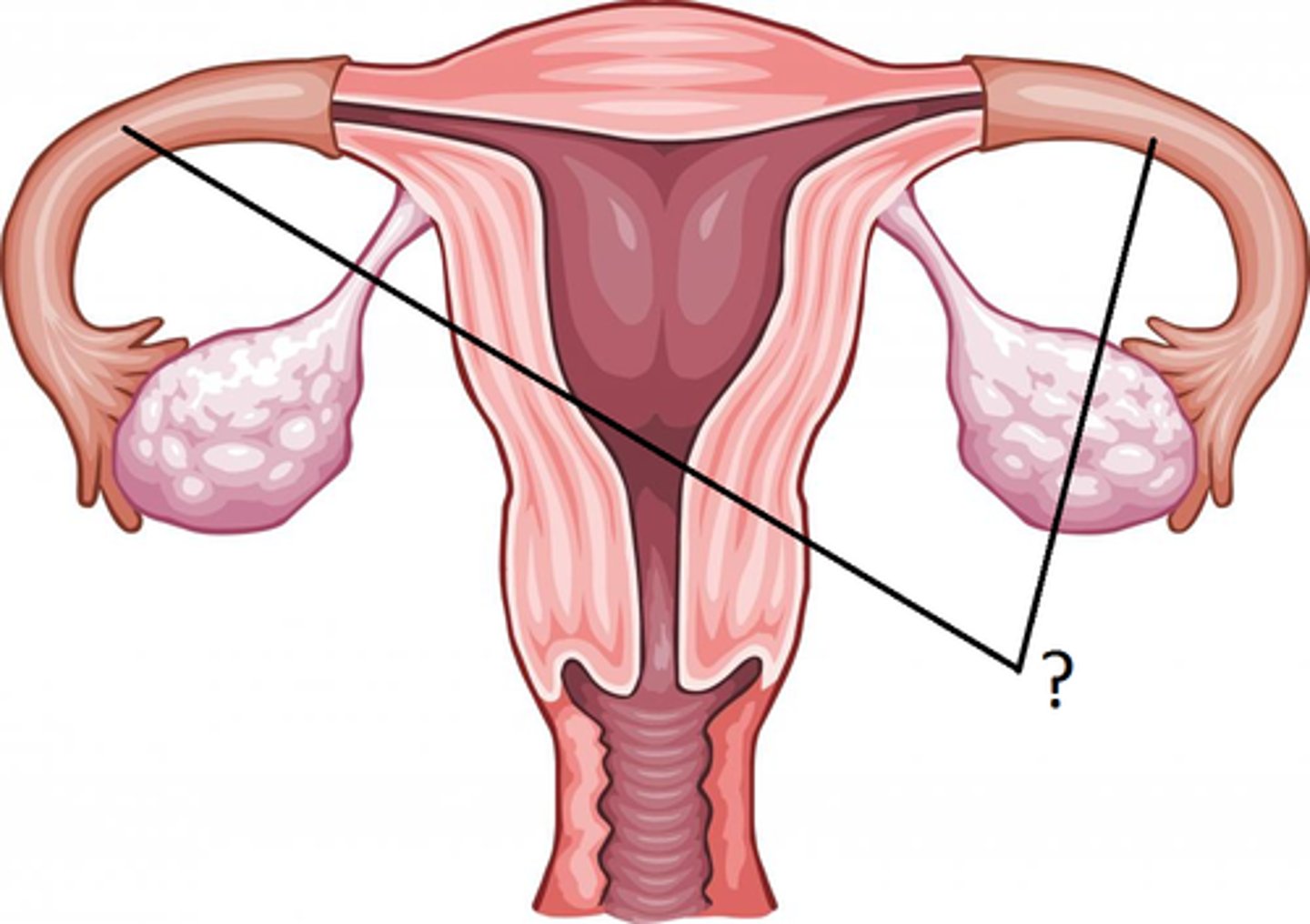
Fallopian Tube
-Carries ovum to Uterus
-FERTILIZATION occurs here
Uterus
Holds and nourishes developing fetus
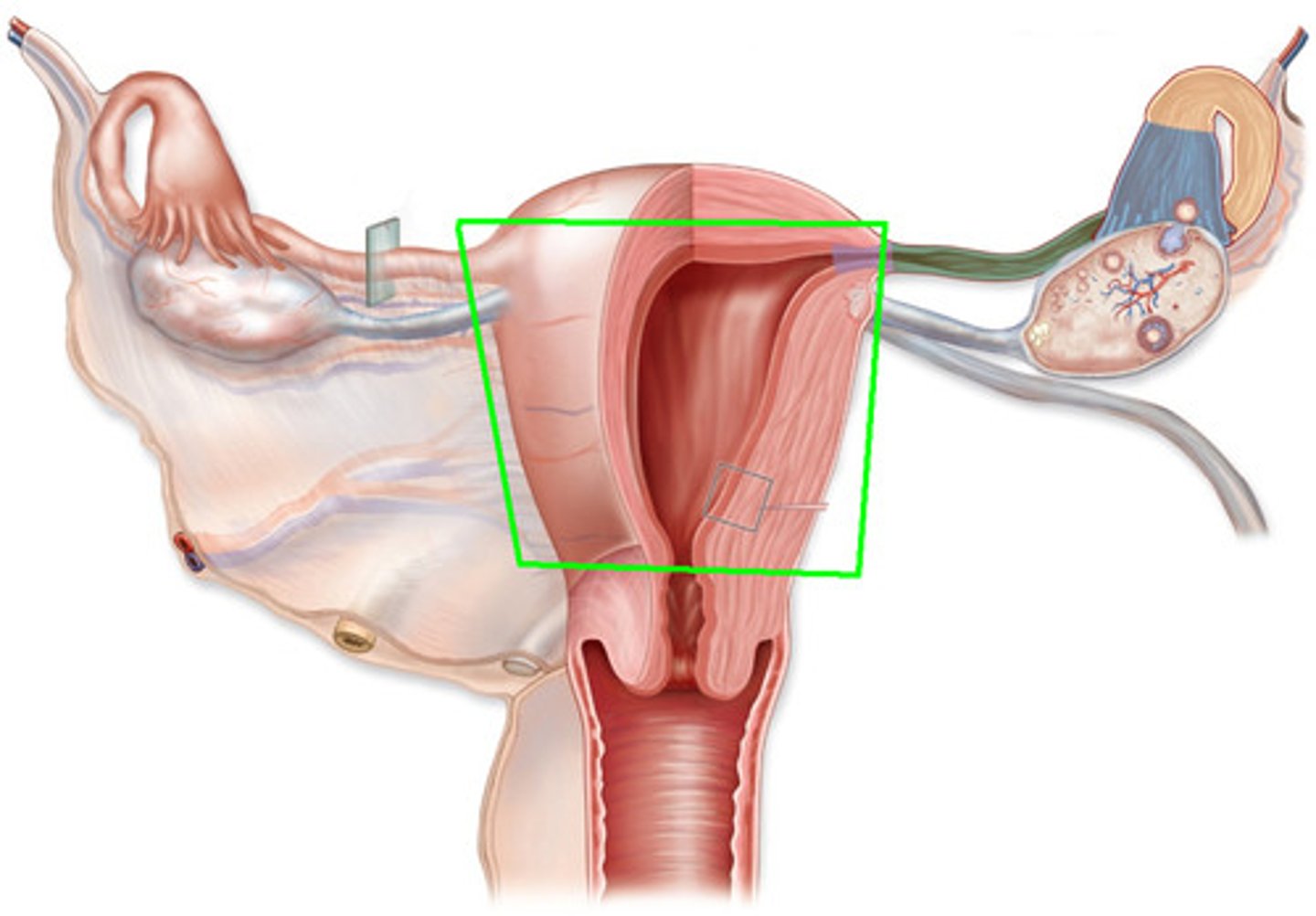
Cervix
Muscular band separating vagina from uterus
secrete reproductive hormones
(Holds fetus in place)
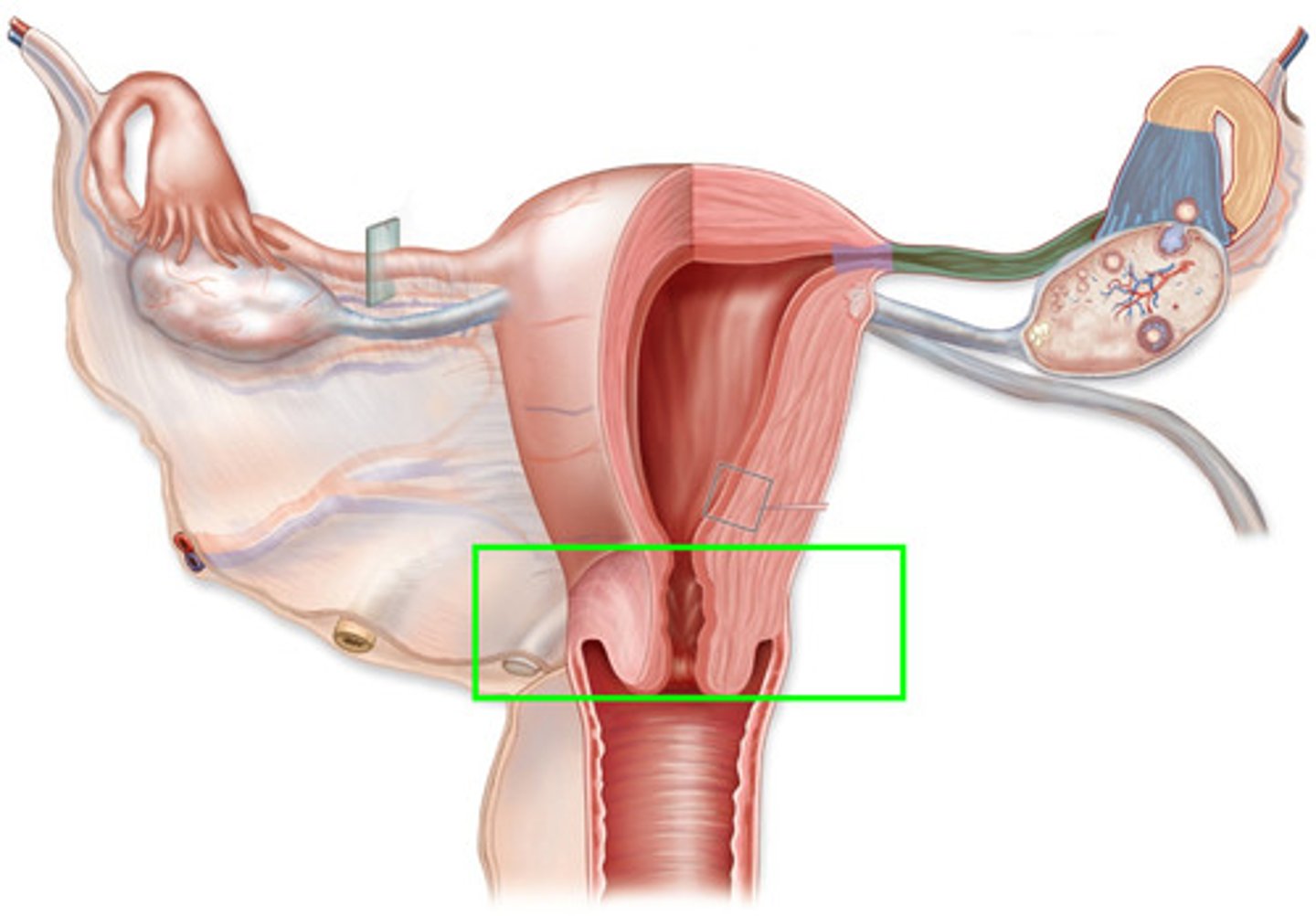
Vagina
Connects uterus with outer environment
-Sexual intercourse occurs here
LH
in females, promotes ovulation and the formation of corpus luteum within ovary, producing progesterone.
In males, stimulates the interstitial cells of the testes to produce testosterone
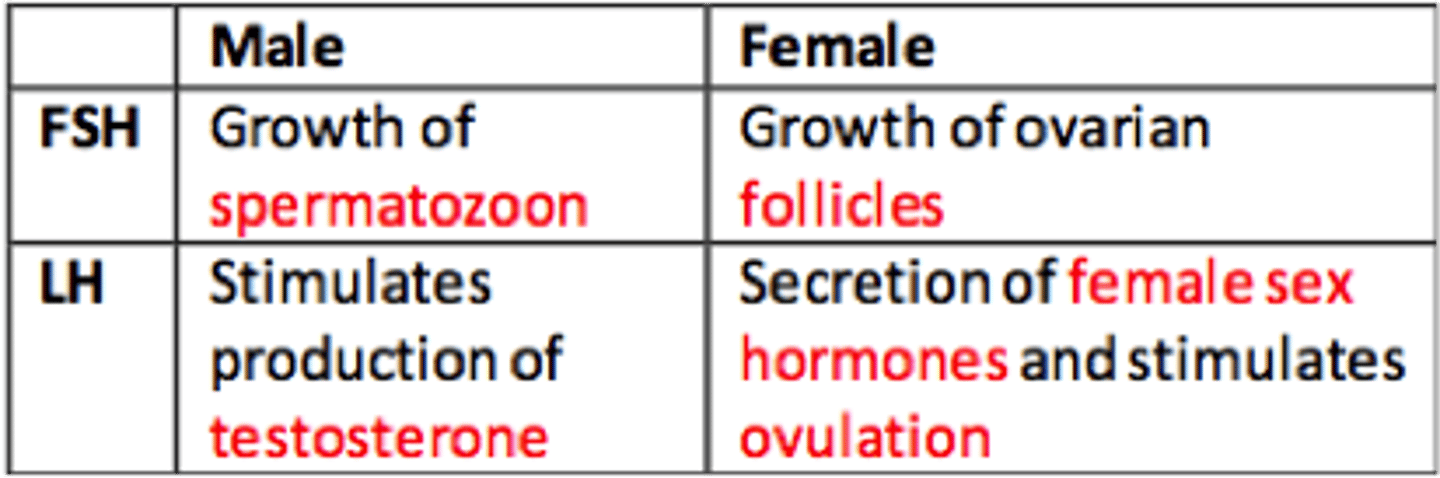
Menstrual Cycle
28-day pattern that prepares the uterus for pregnancy
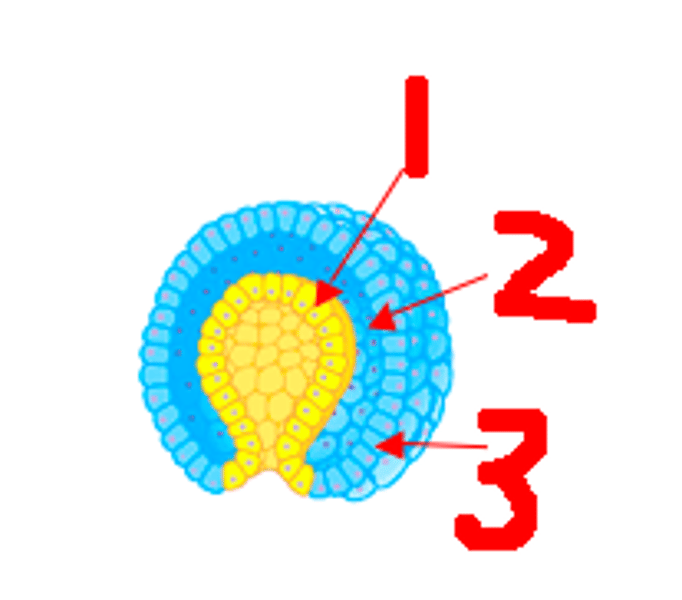
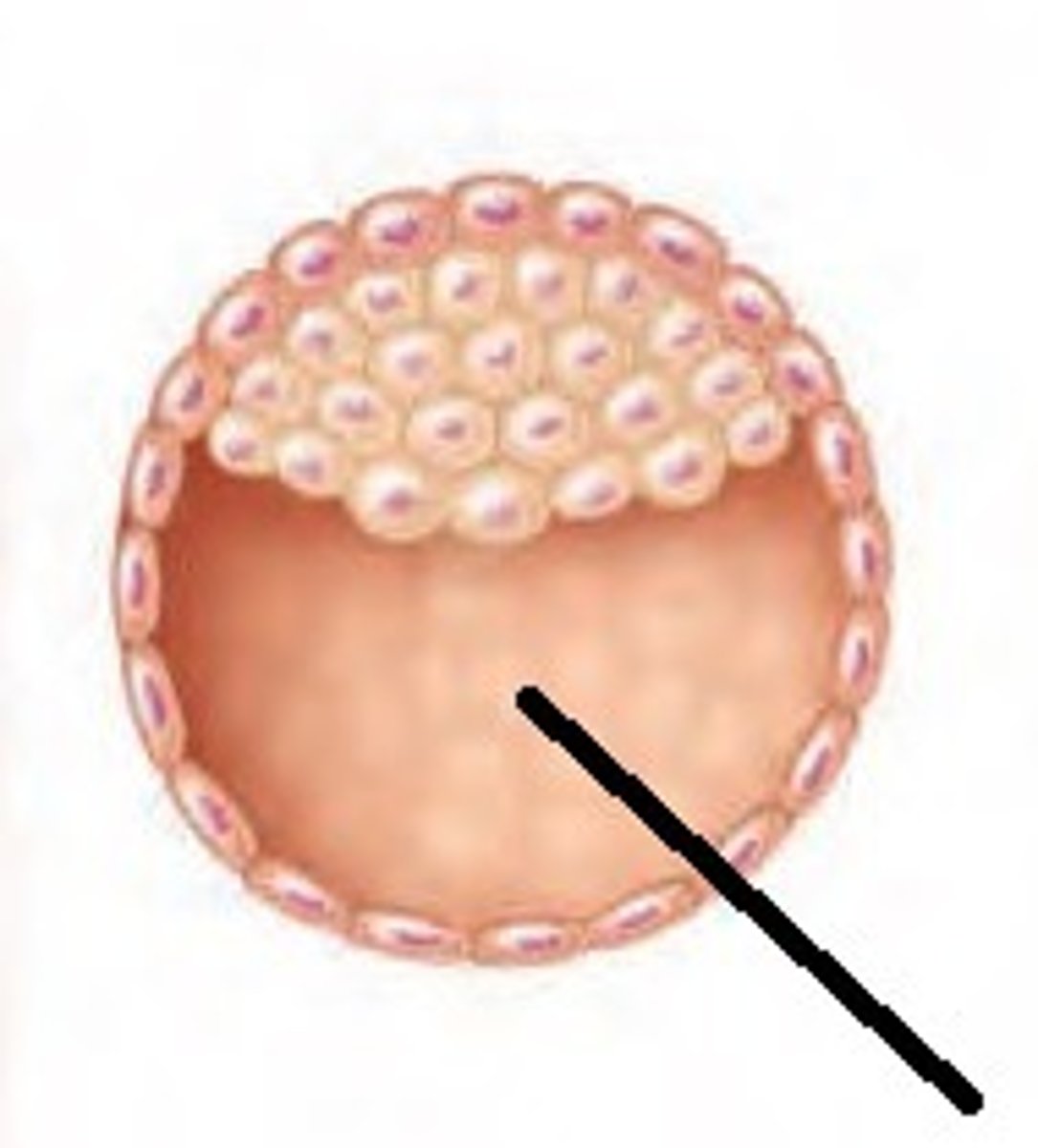
Blastocyst
Contains an inner cell mass that will develop into the embryo
Amnion
Fluid filled sac, which protects the embryo from trauma and temperature fluctuations allows freedom and movement, and prevents limbs from sticking to the body
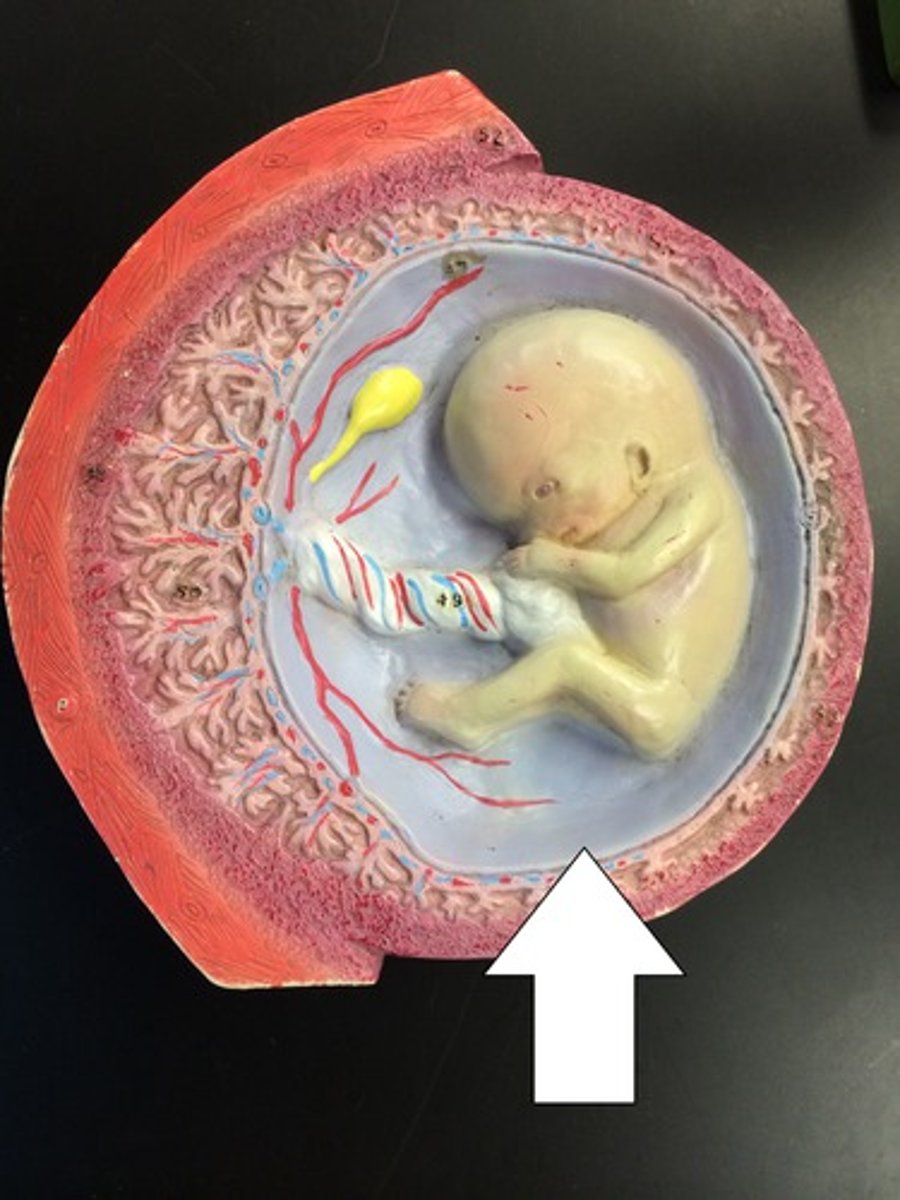
Allantois
Forms the foundation for the umbilical cord.
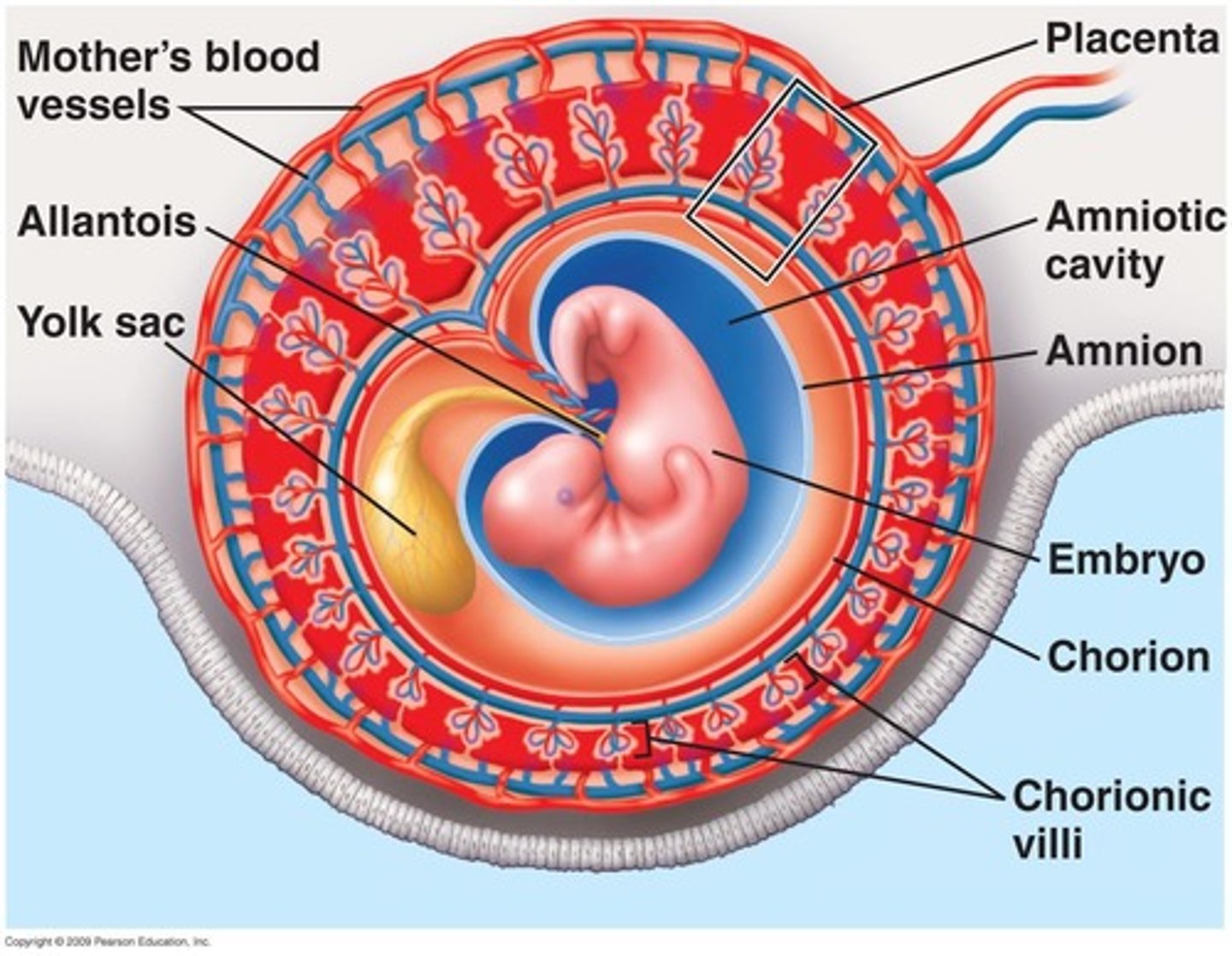
Placenta
structure provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby and removes waste products from the baby's blood
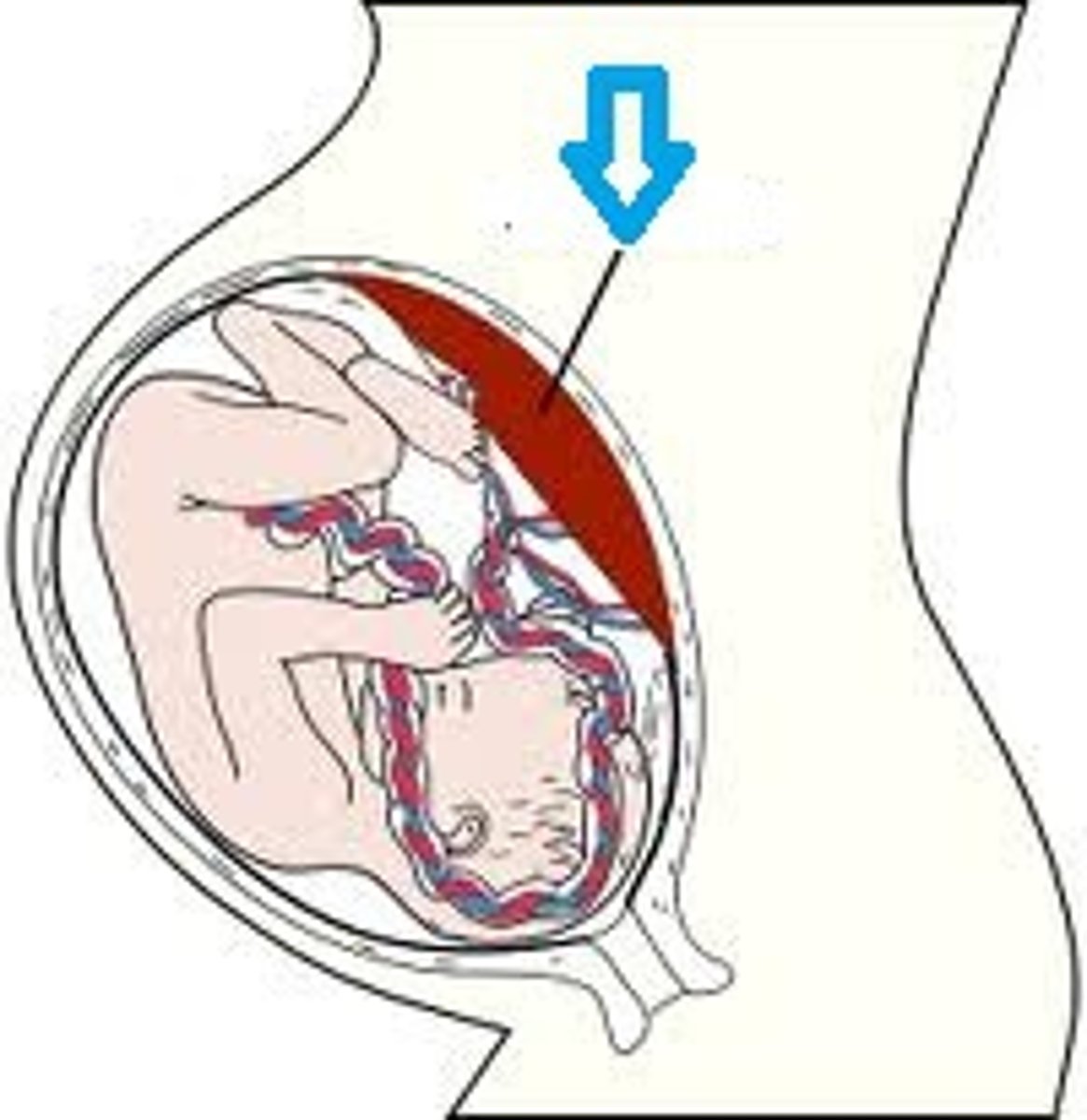
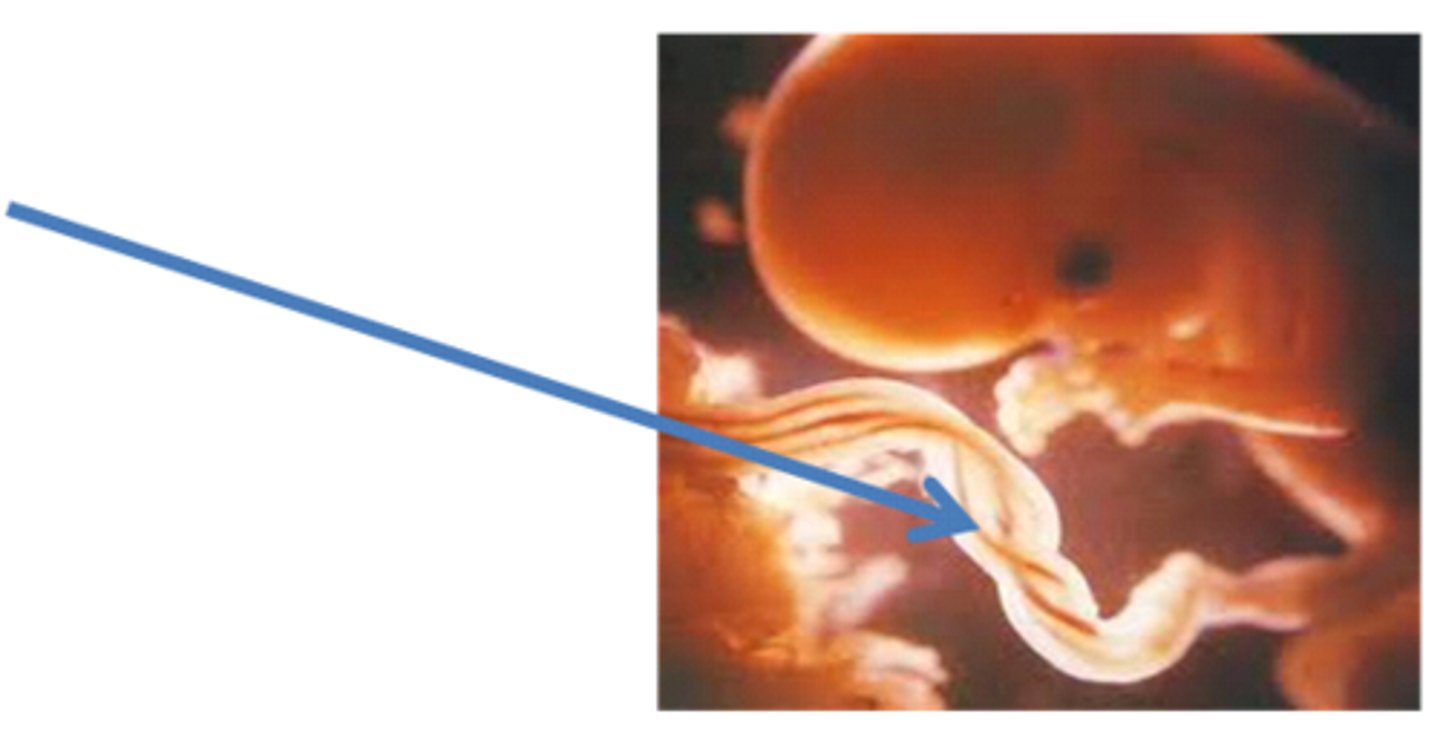
Umbilical cord
Site of exchange of oxygen-rich blood between fetus and mother
1st Trimester
-Development of germ layers, extra-embryonic structures and nervous system and heart
3rd Trimester
Fetus grows rapidly
-Organ systems mature, respiratory system matures last
Teratogens
Refers to any agent that causes a structual abnormality due to exposure during pregnancy. (I.e. Cigarette smoke, alcohol)
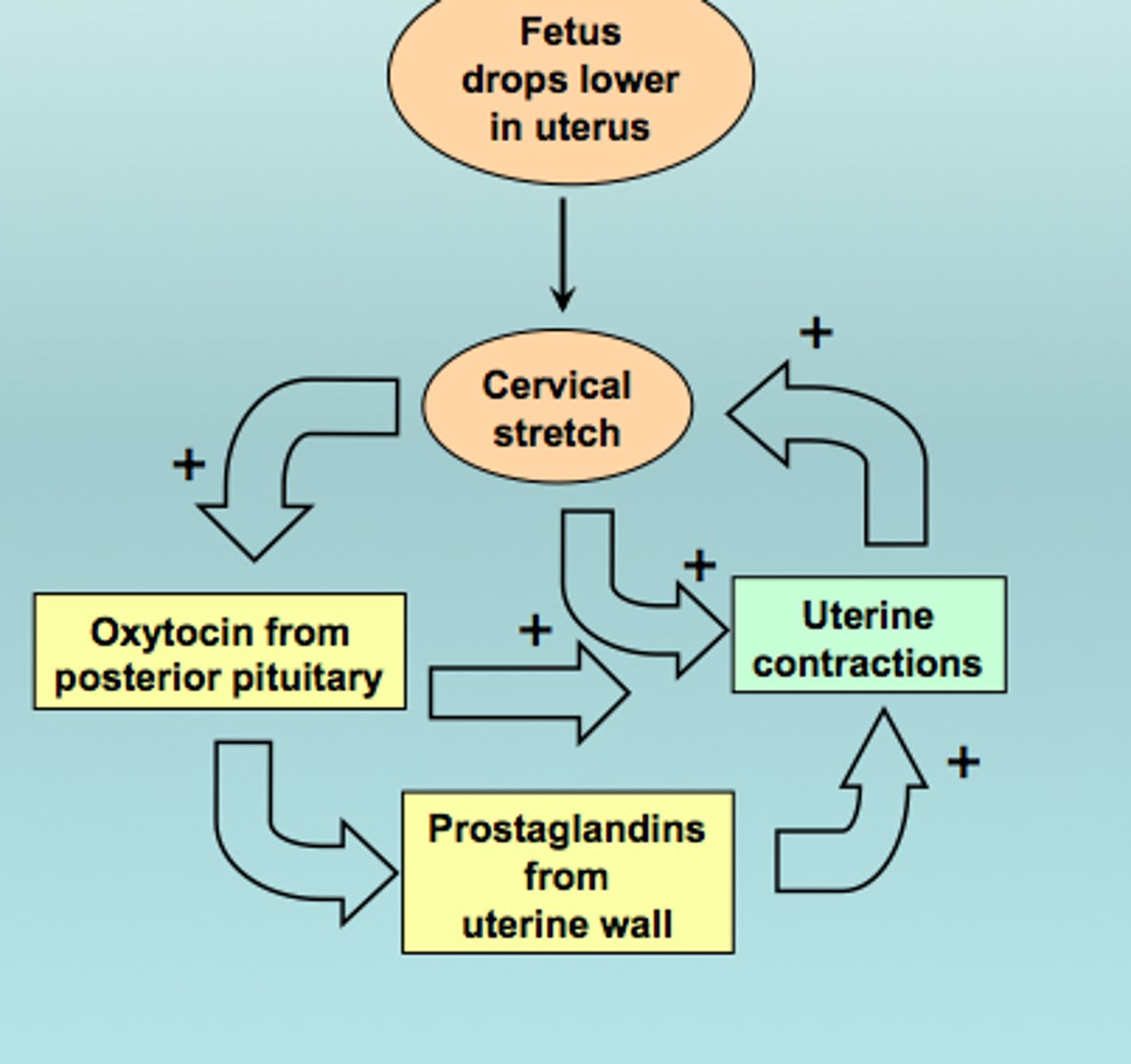
Parturition
Act of giving birth. commonly referred to as Labour.
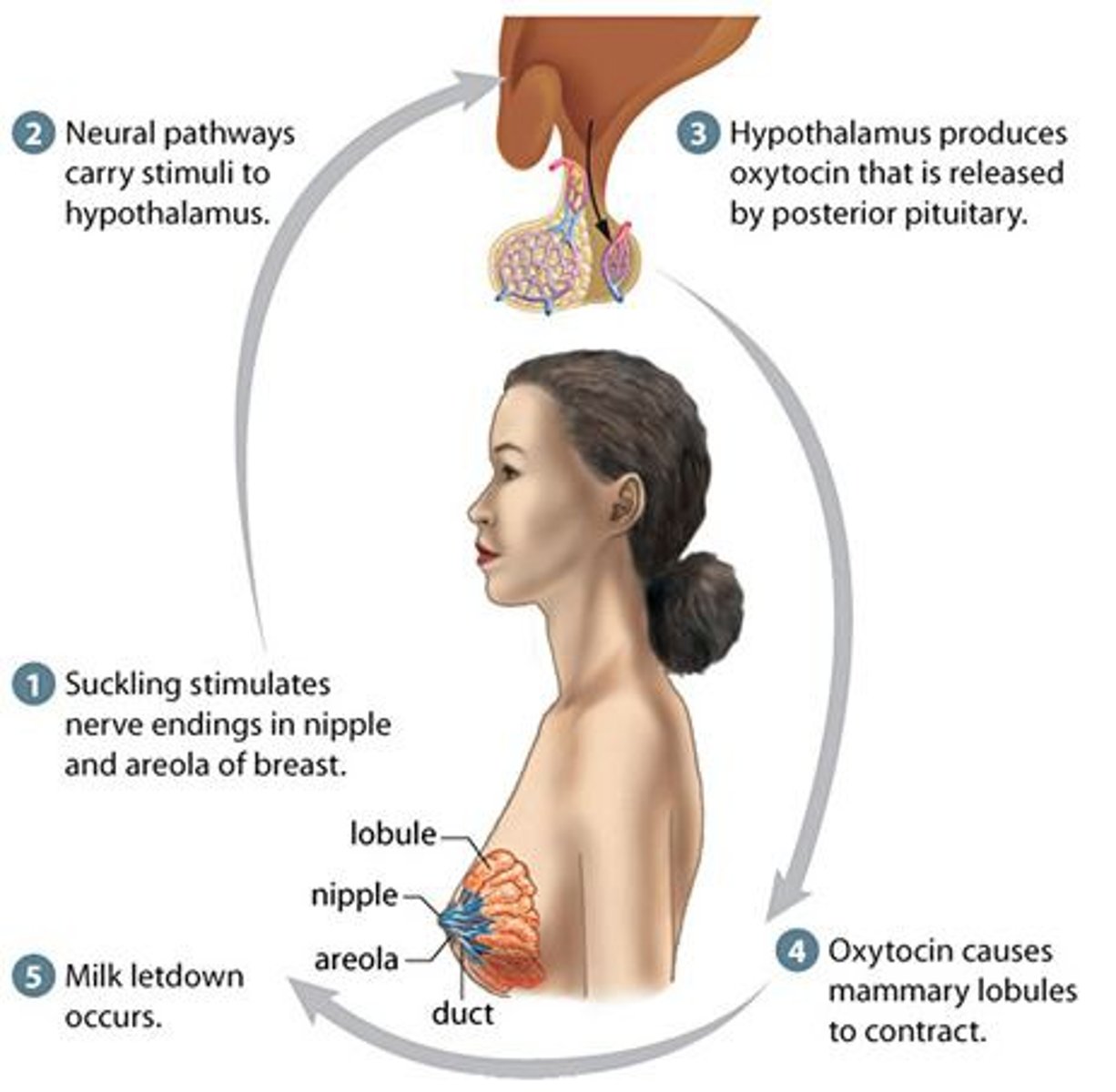
Lactation
secretion and formation of breast milk in the mother.
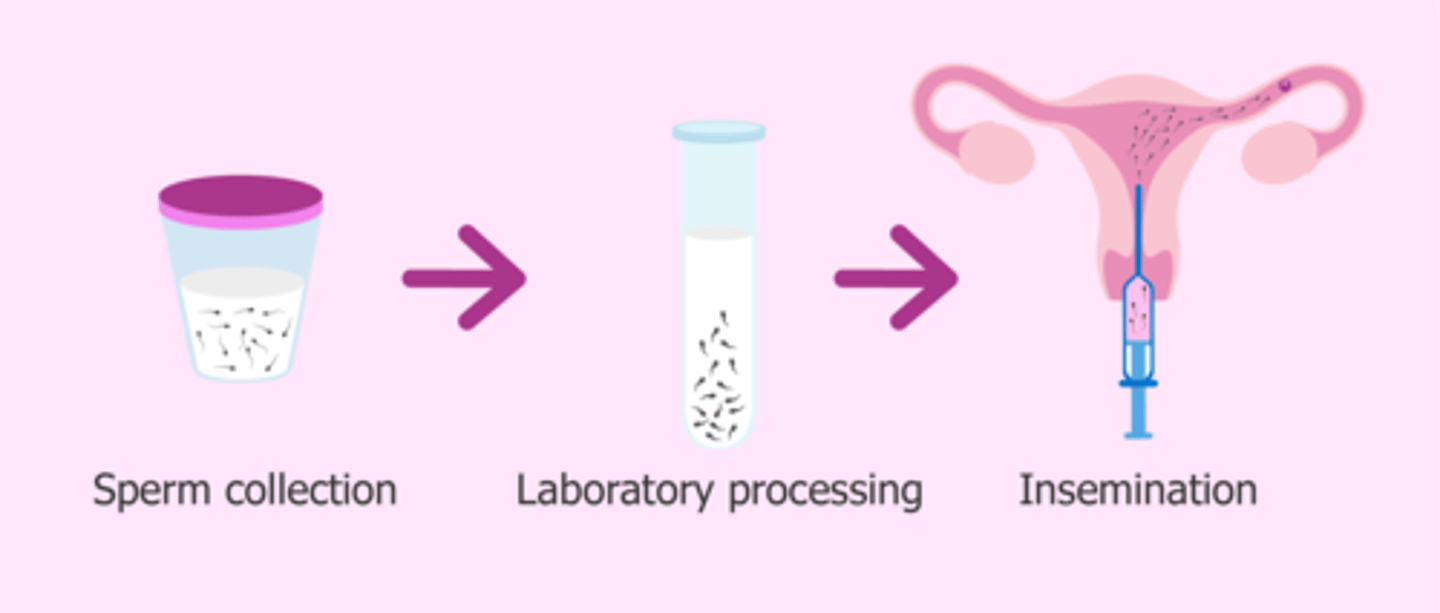
Artificial Insemination (AI)
Sperm are collected and concentrated before being placed in the women's vagina.
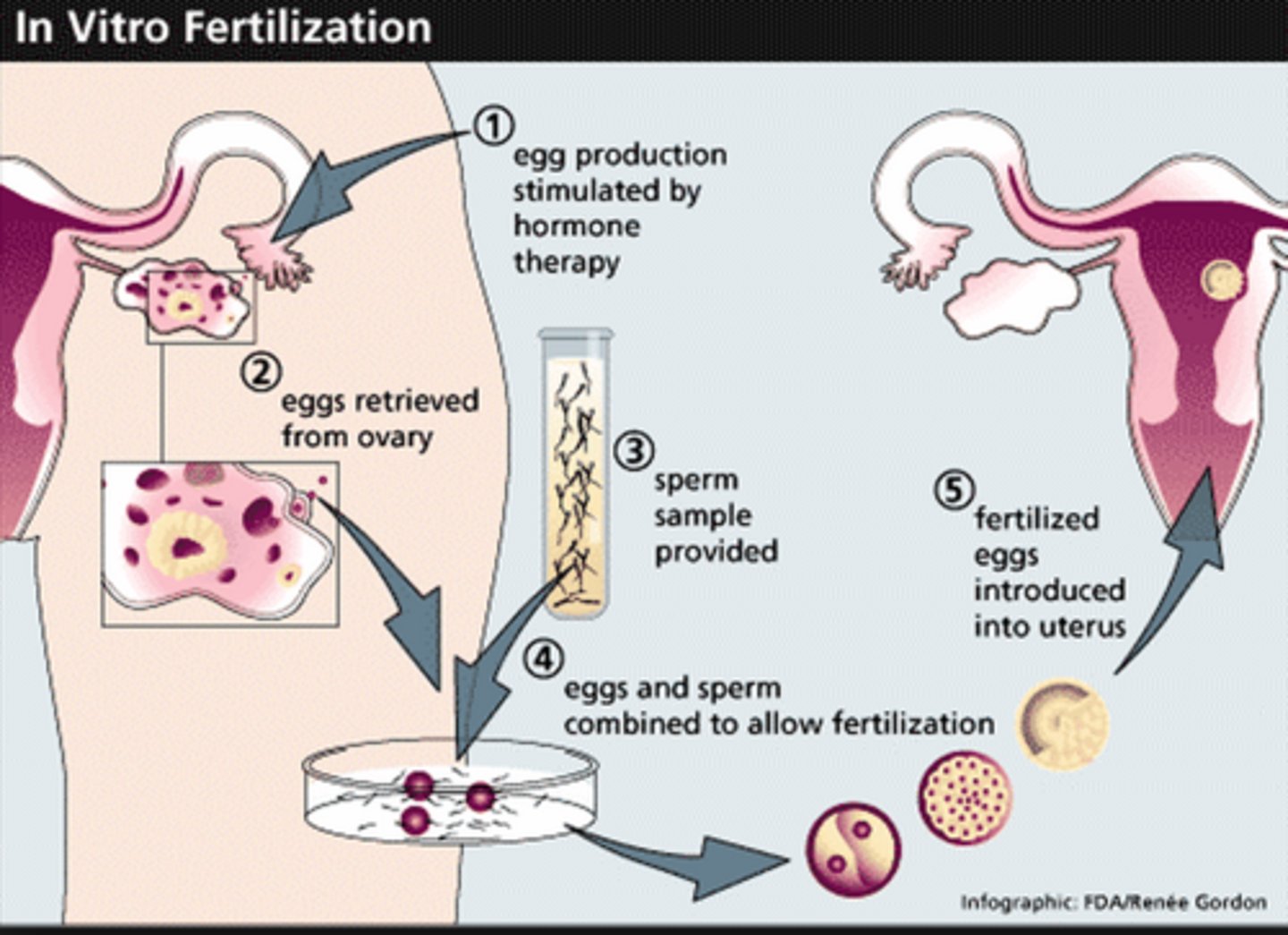
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Possible solution for women with blocked oviducts. Fertilization occurs outside the body and the developing embryo is later placed in the uterus.
head of sperm
contains haploid DNA (labelled B)
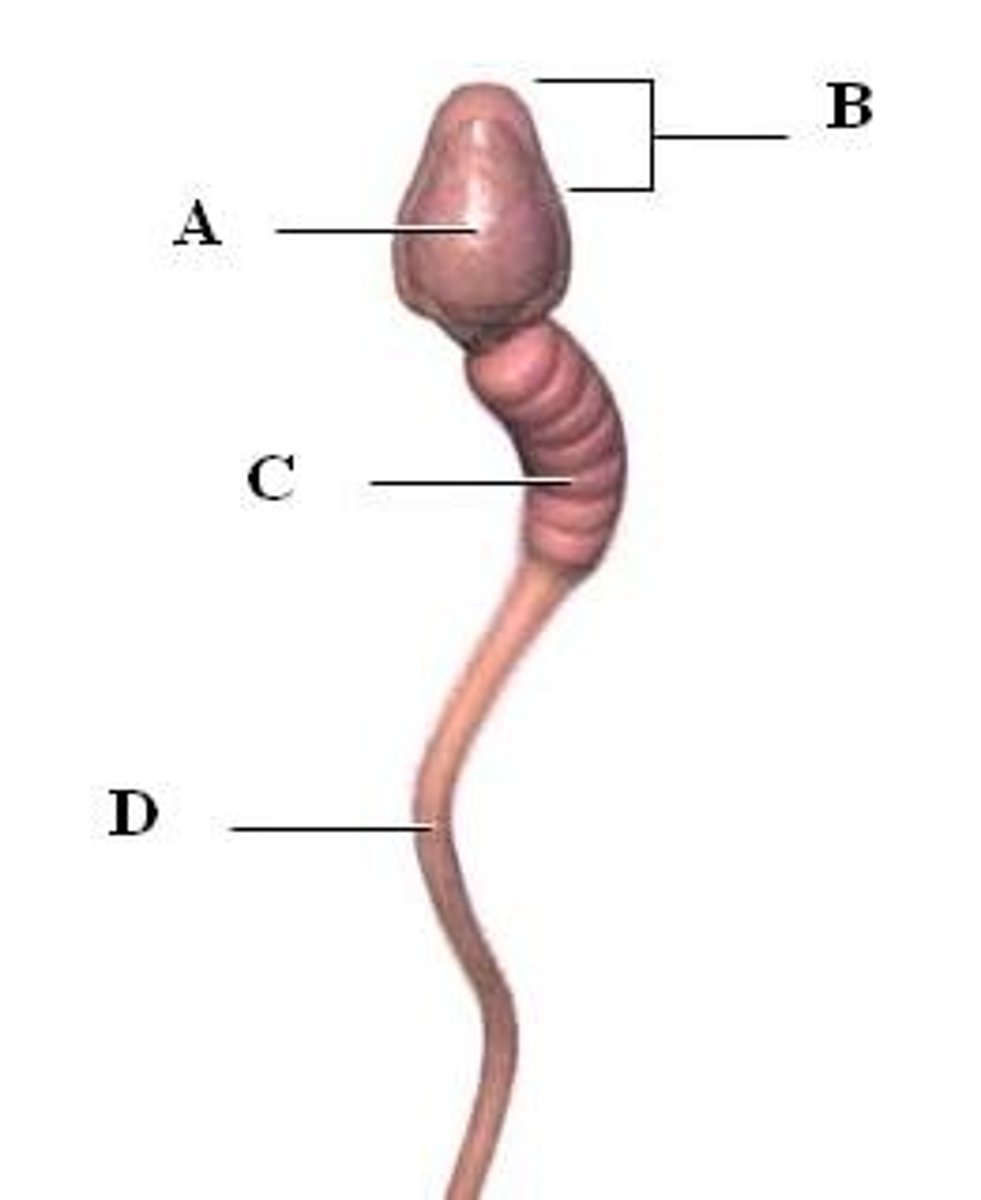
midpiece
the portion of the tail of a sperm closest to the head, containing mitochondria (labelled C)
Endoderm
the inner germ layer that develops into the lining of the digestive and respiratory systems
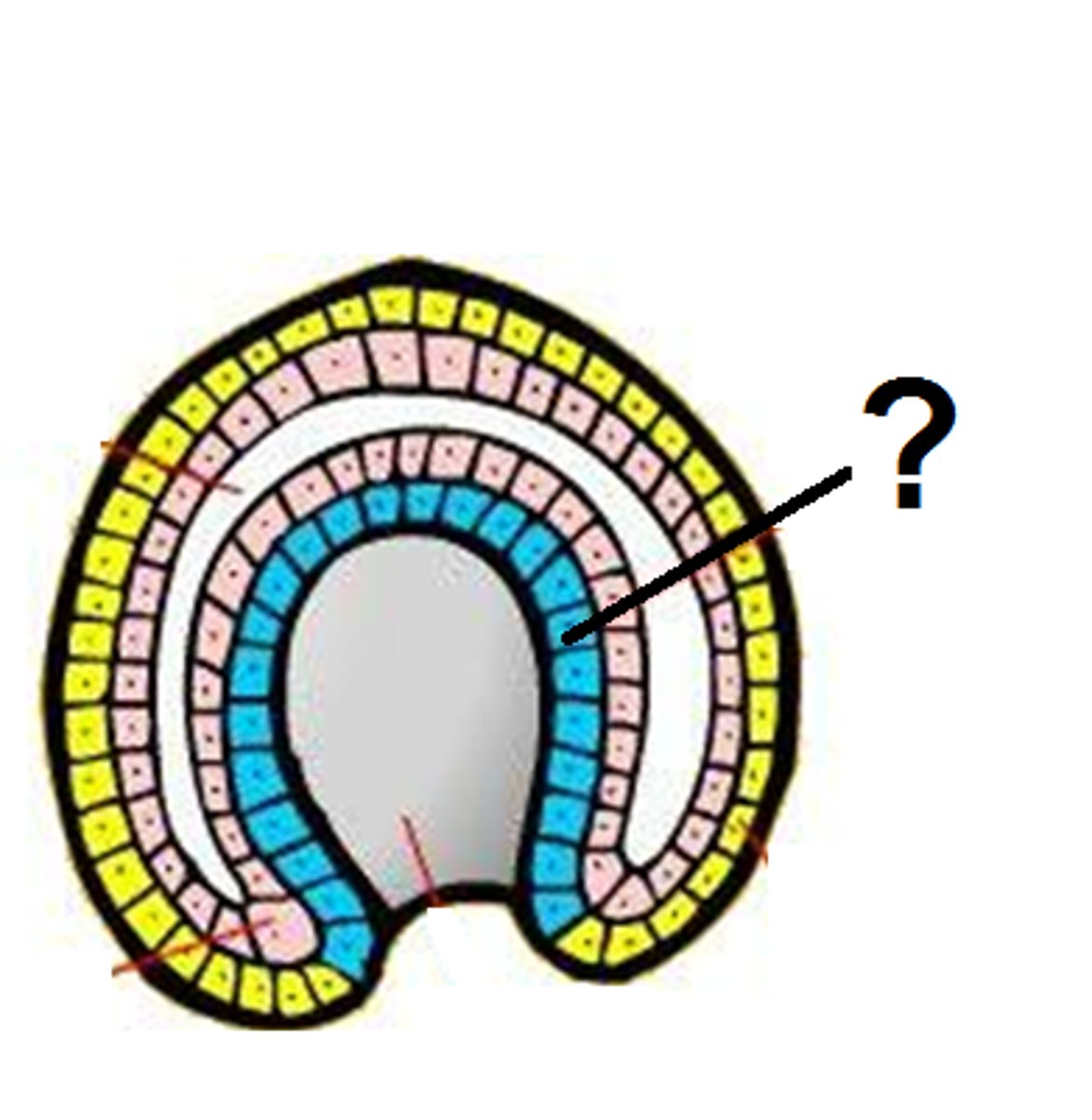
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces brain, sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
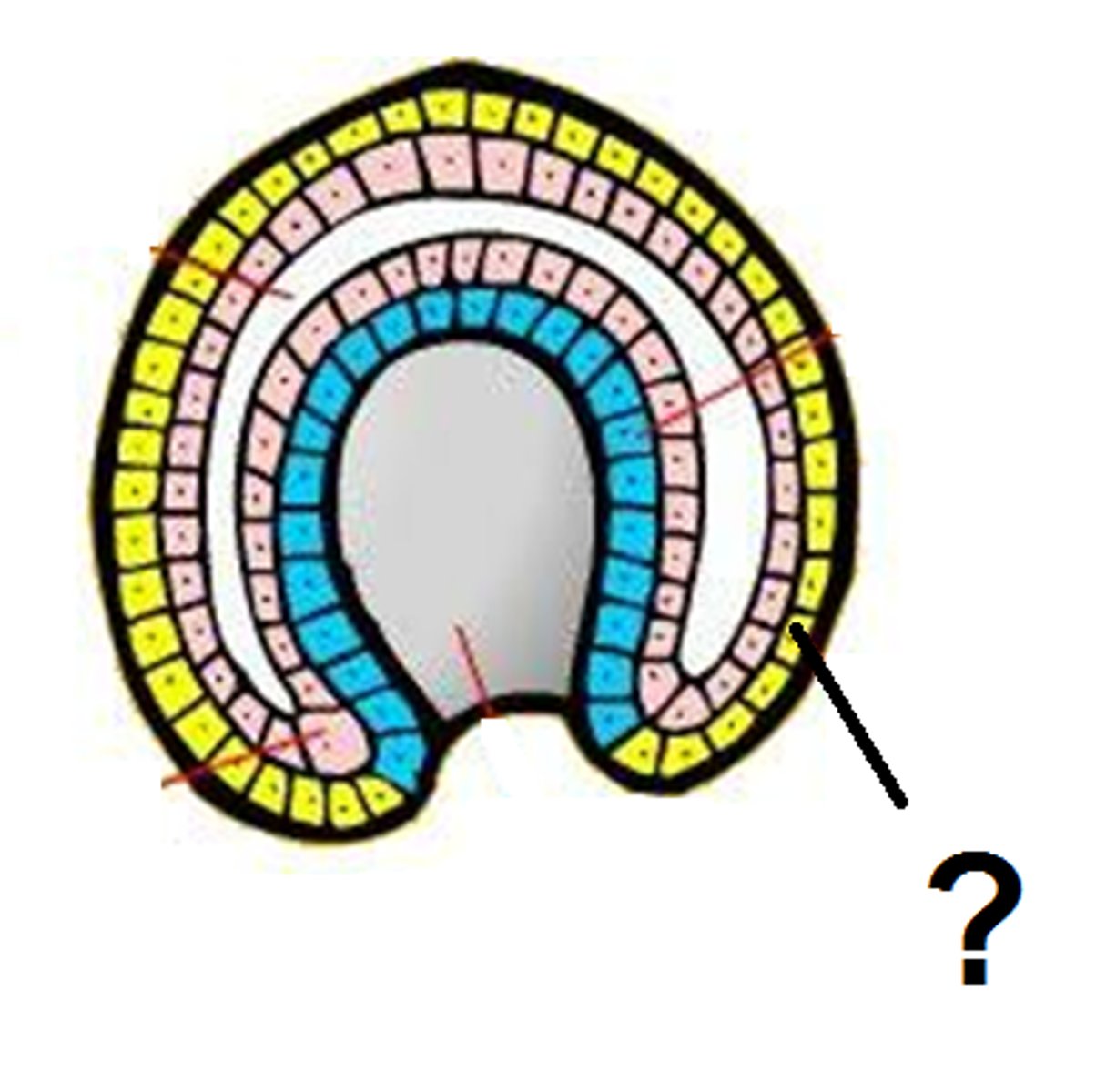
Mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, blood and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
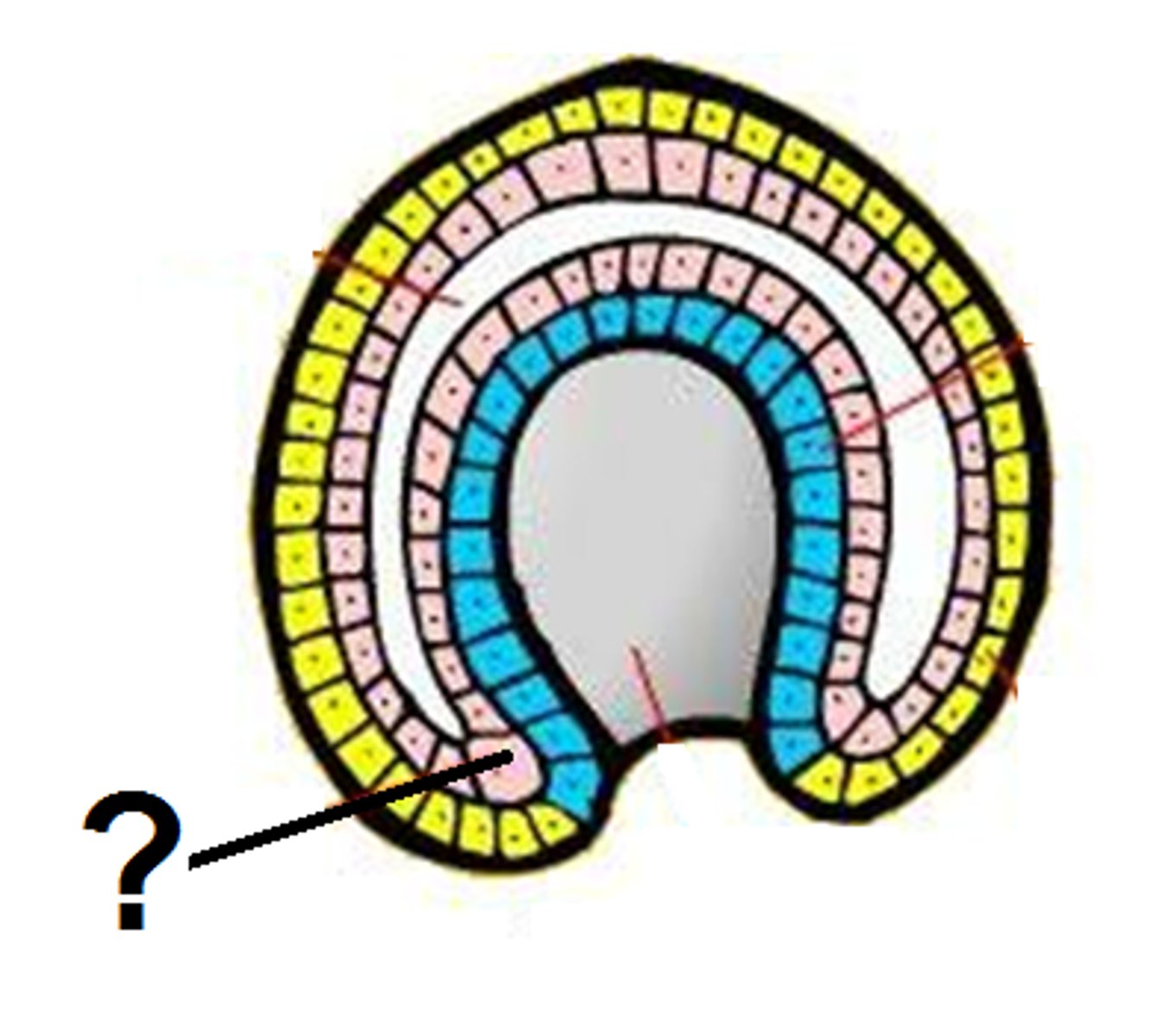
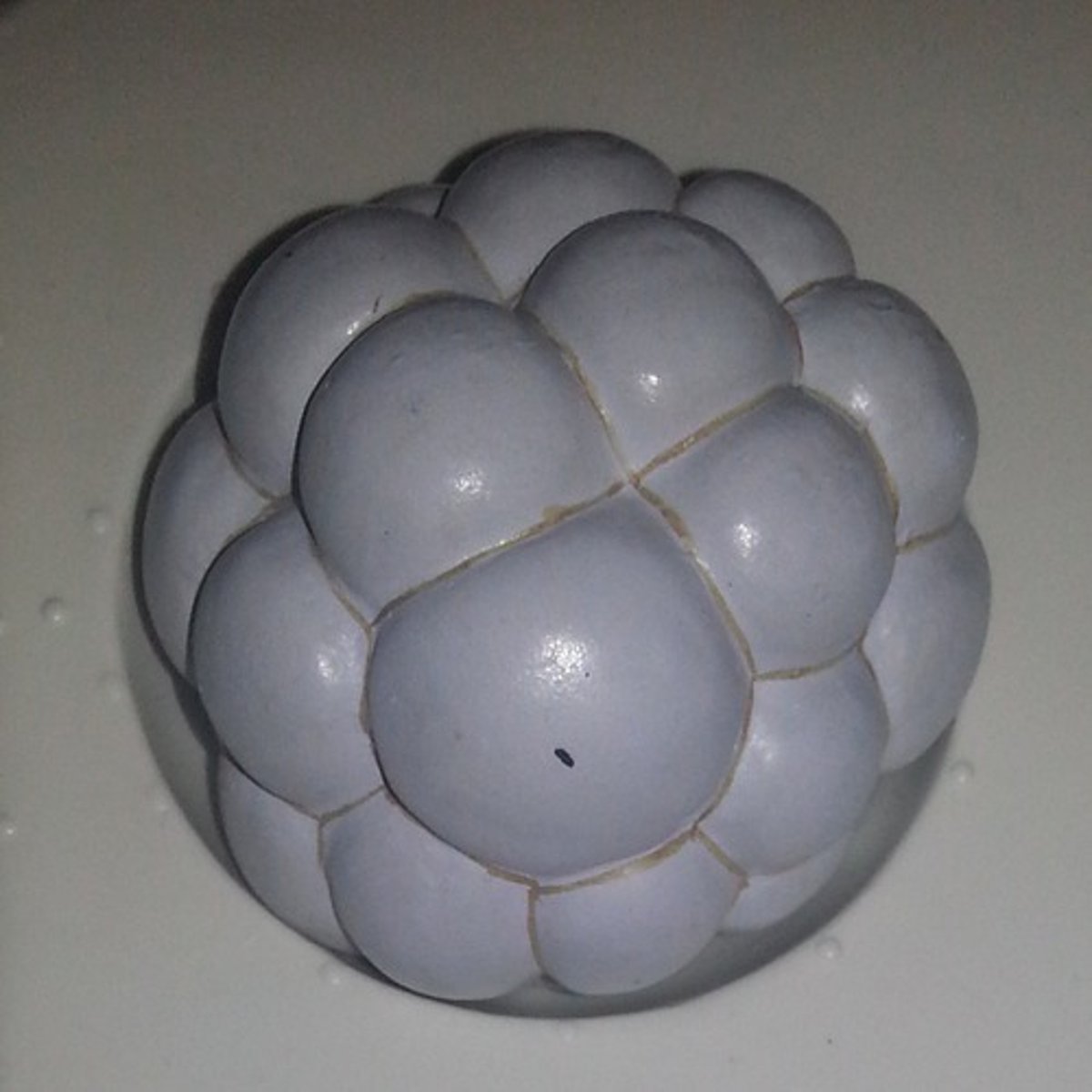
Morula
a solid ball of cells resulting from division of a fertilized ovum, and from which a blastula is formed.

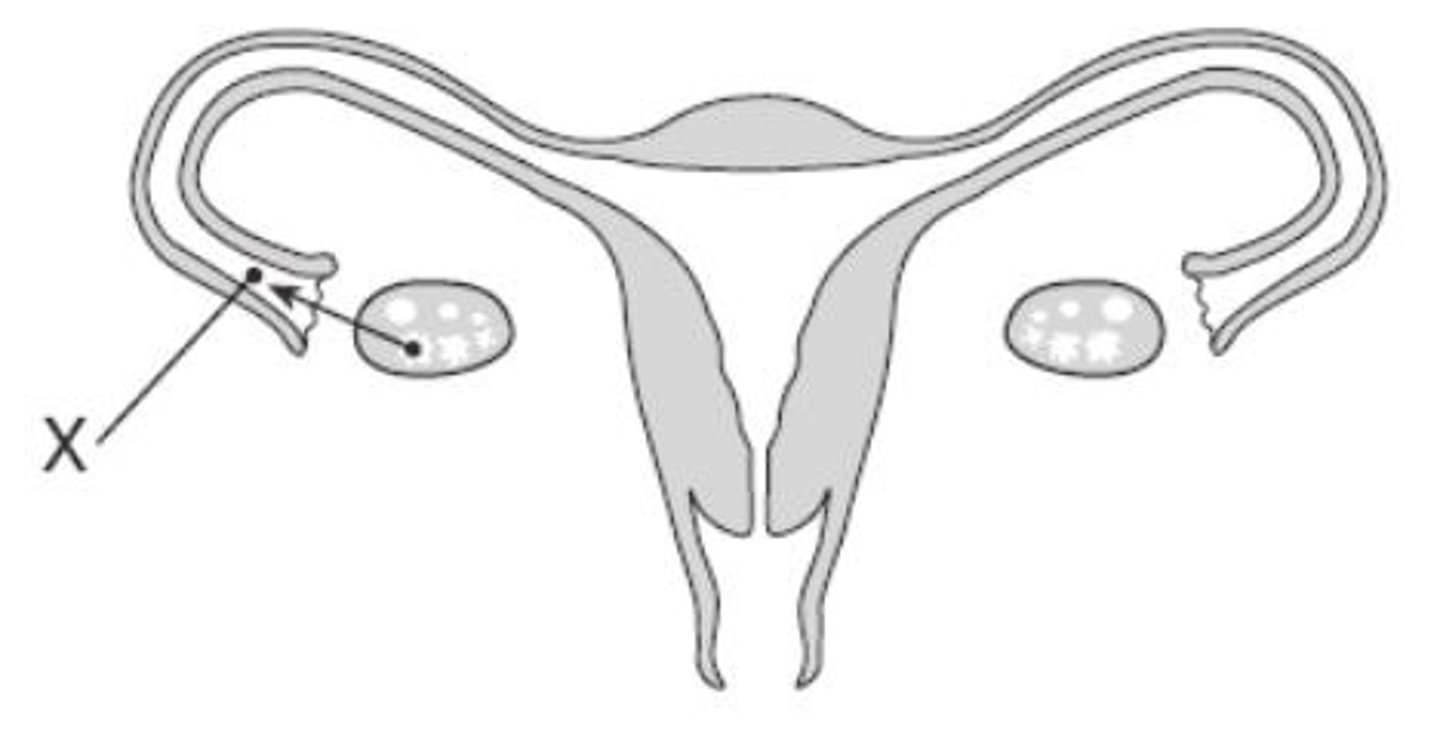
Fertilization
Fusion of an egg and sperm cell. in humans, this occurs in the falloipian tubes
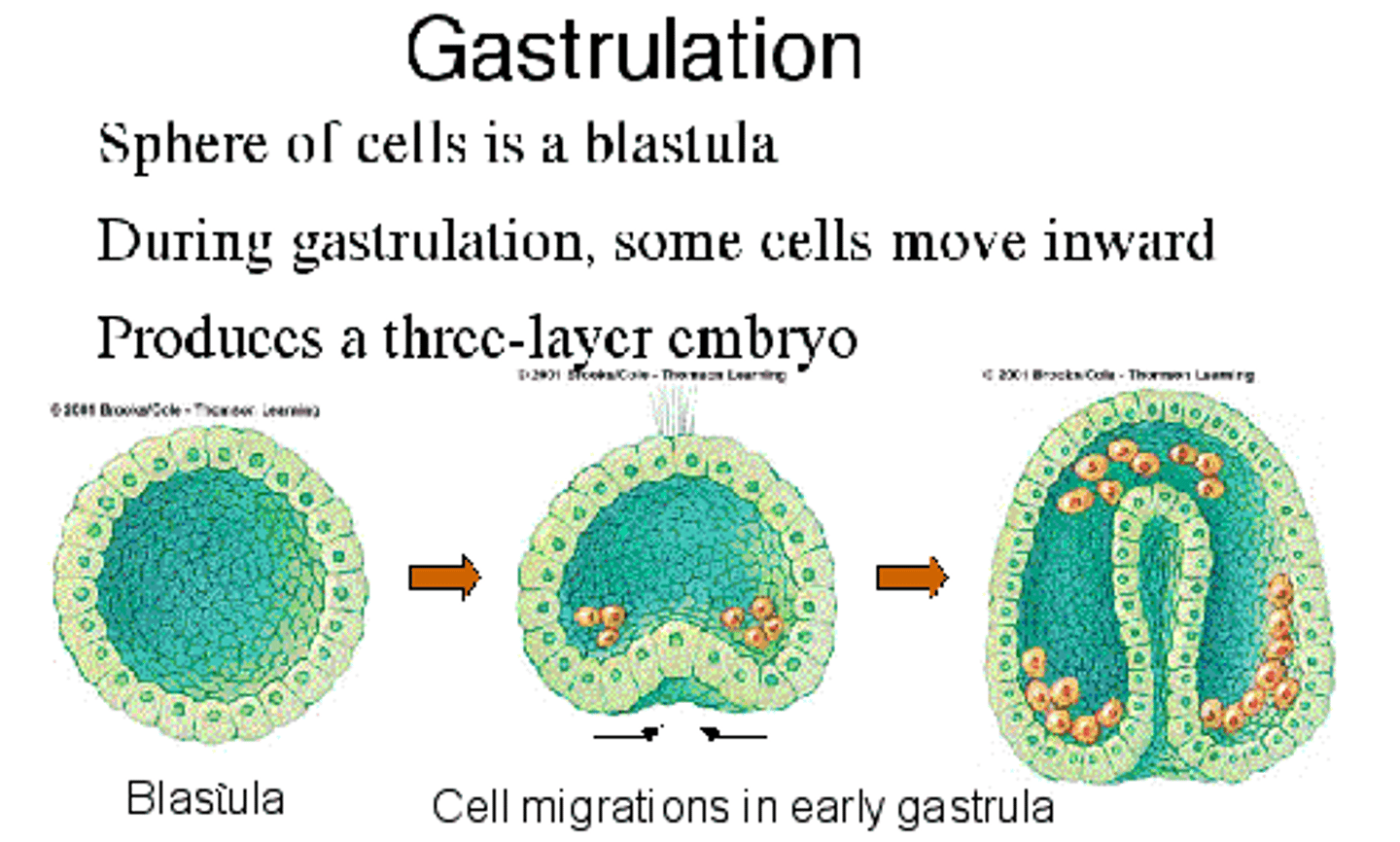
gastrulation
In animal development, a series of cell and tissue movements in which the blastula-stage embryo folds inward, producing a three-layered embryo, the gastrula.
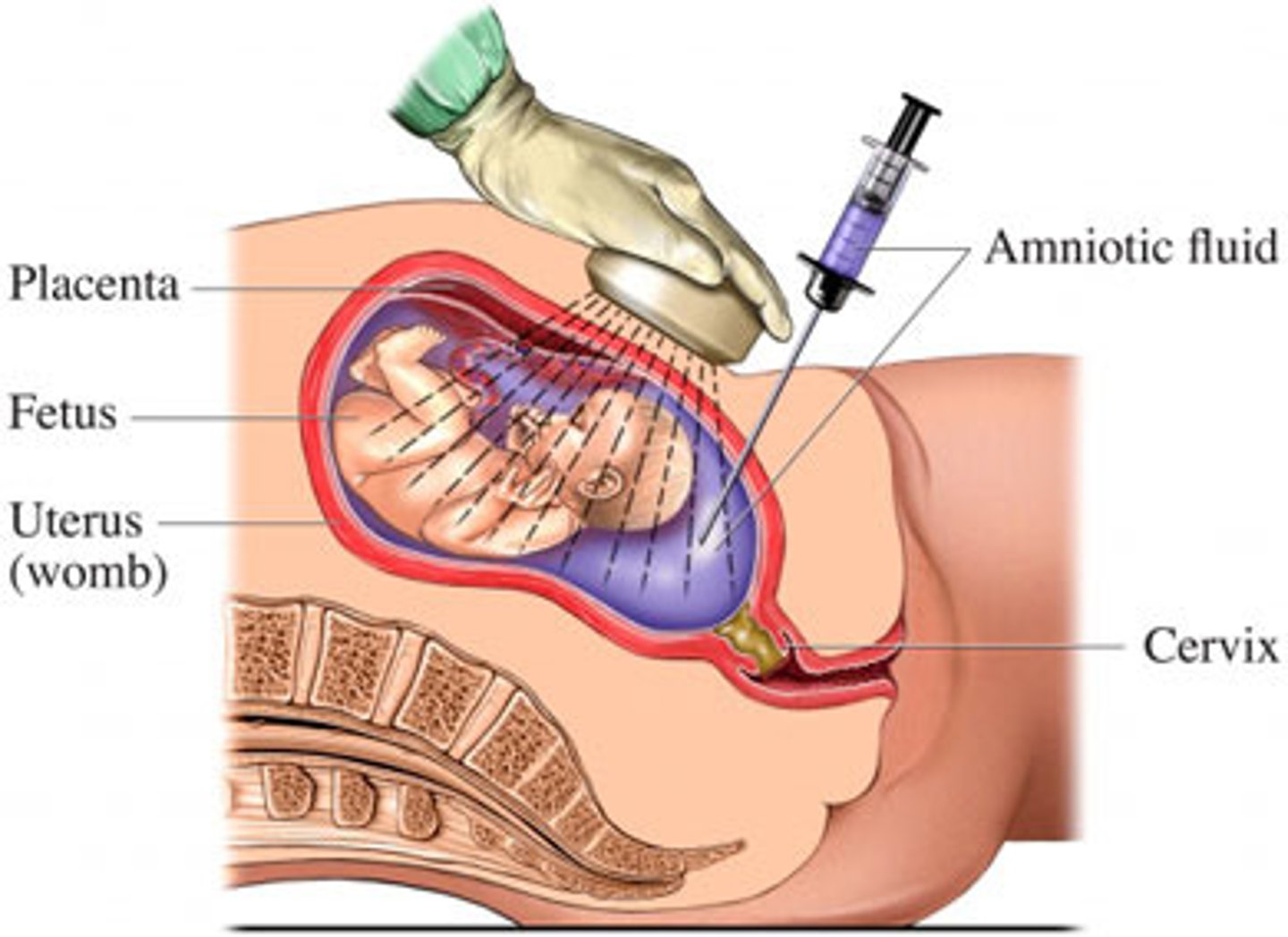
amniocentesis
needle puncture of the amniotic sac to withdraw amniotic fluid for analysis. Can determine chromosome abnormalities in the fetus
chorionic villus sampling
sampling of placental tissues for prenatal diagnosis. Can be done earlier than amniocentesis
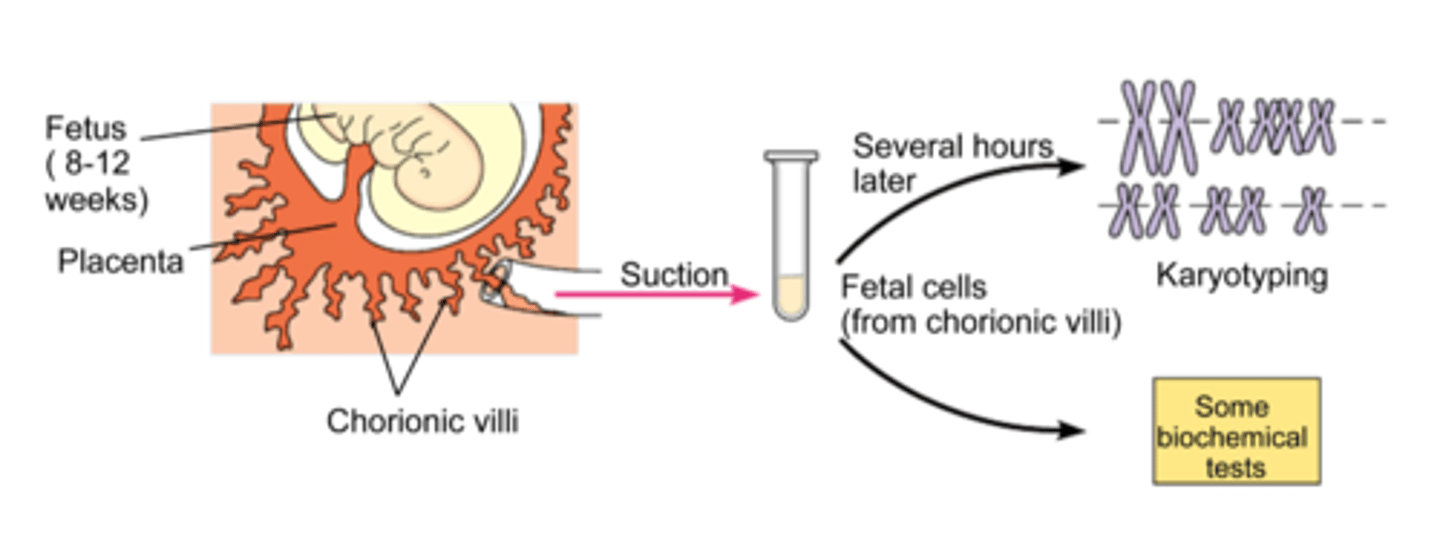
Surrogacy
the act of giving birth to a child for another person or a couple who then adopts or takes legal custody of the child

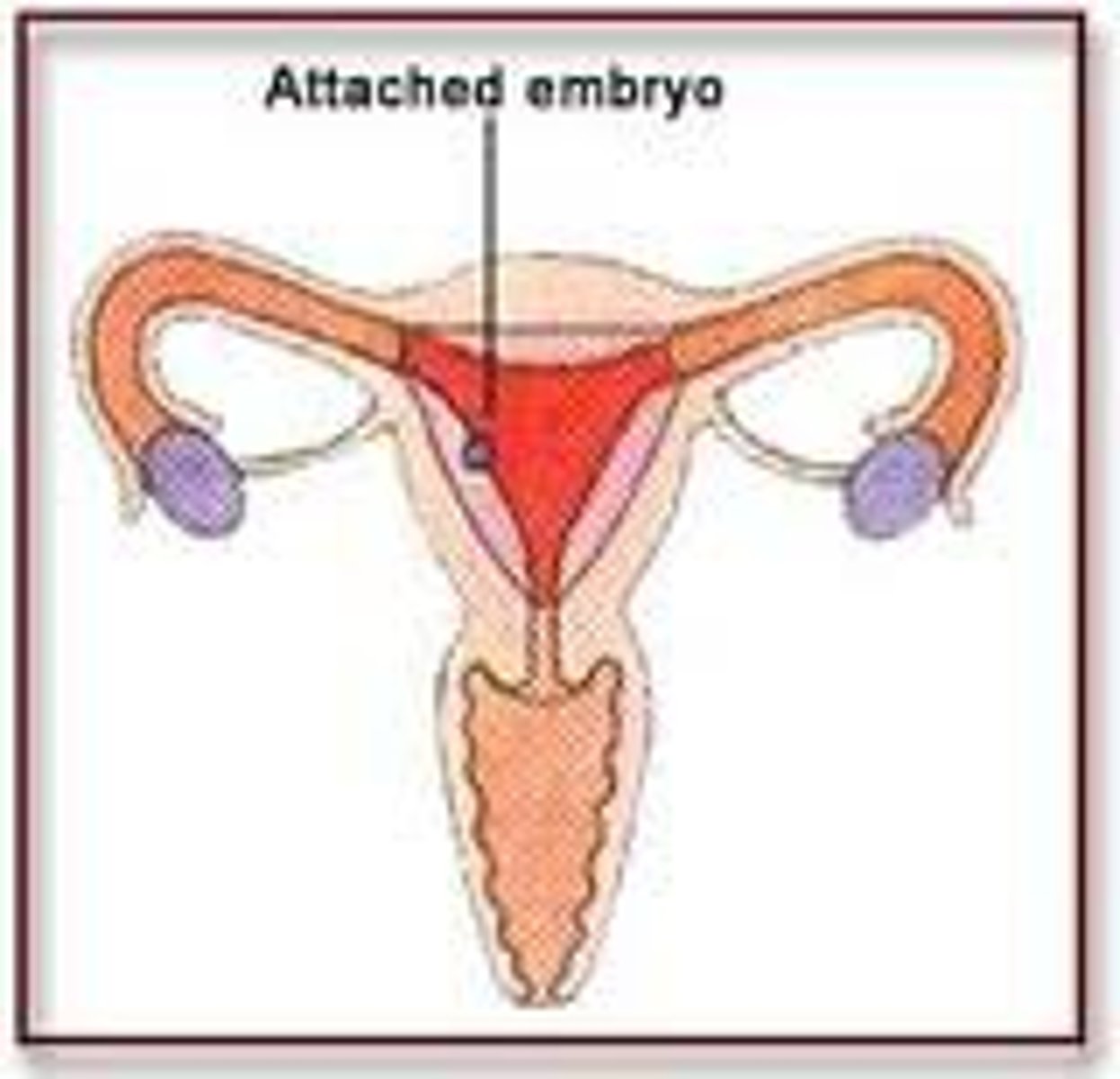
implantation
The process by which the zygote attaches to the uterine wall
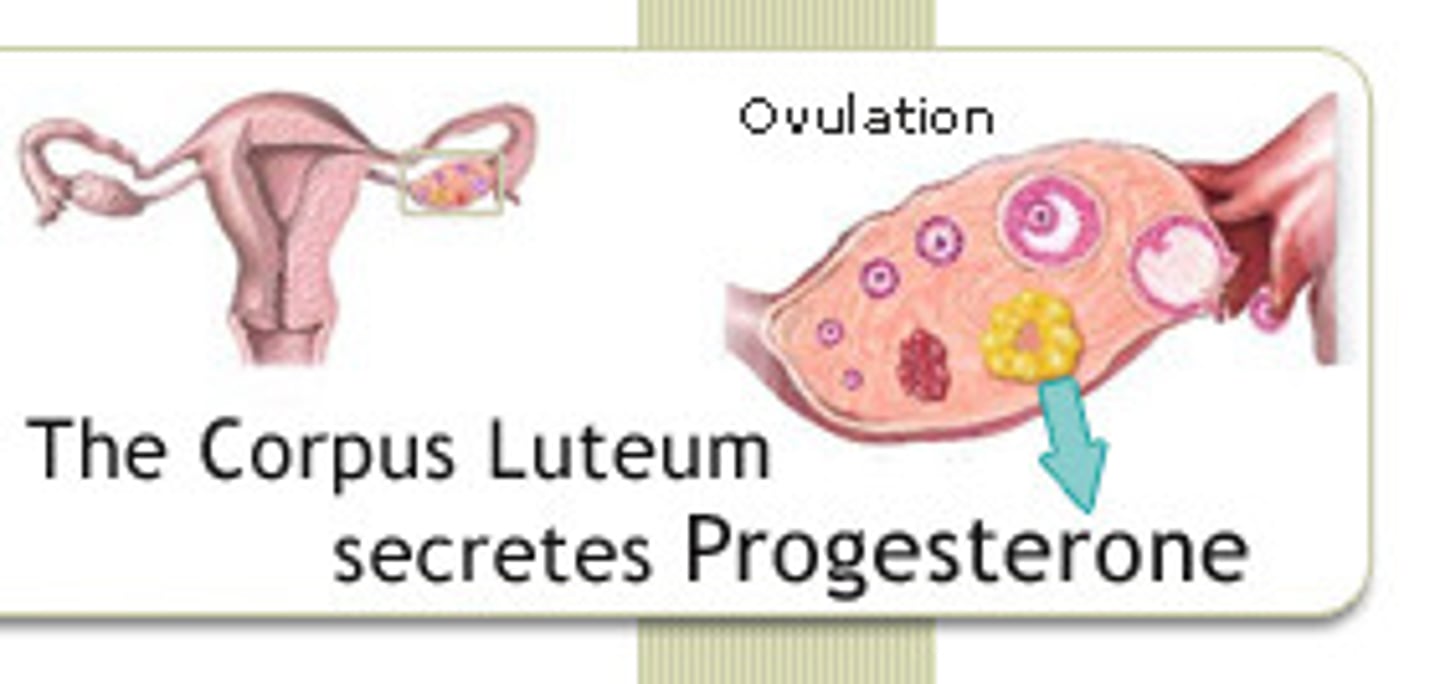
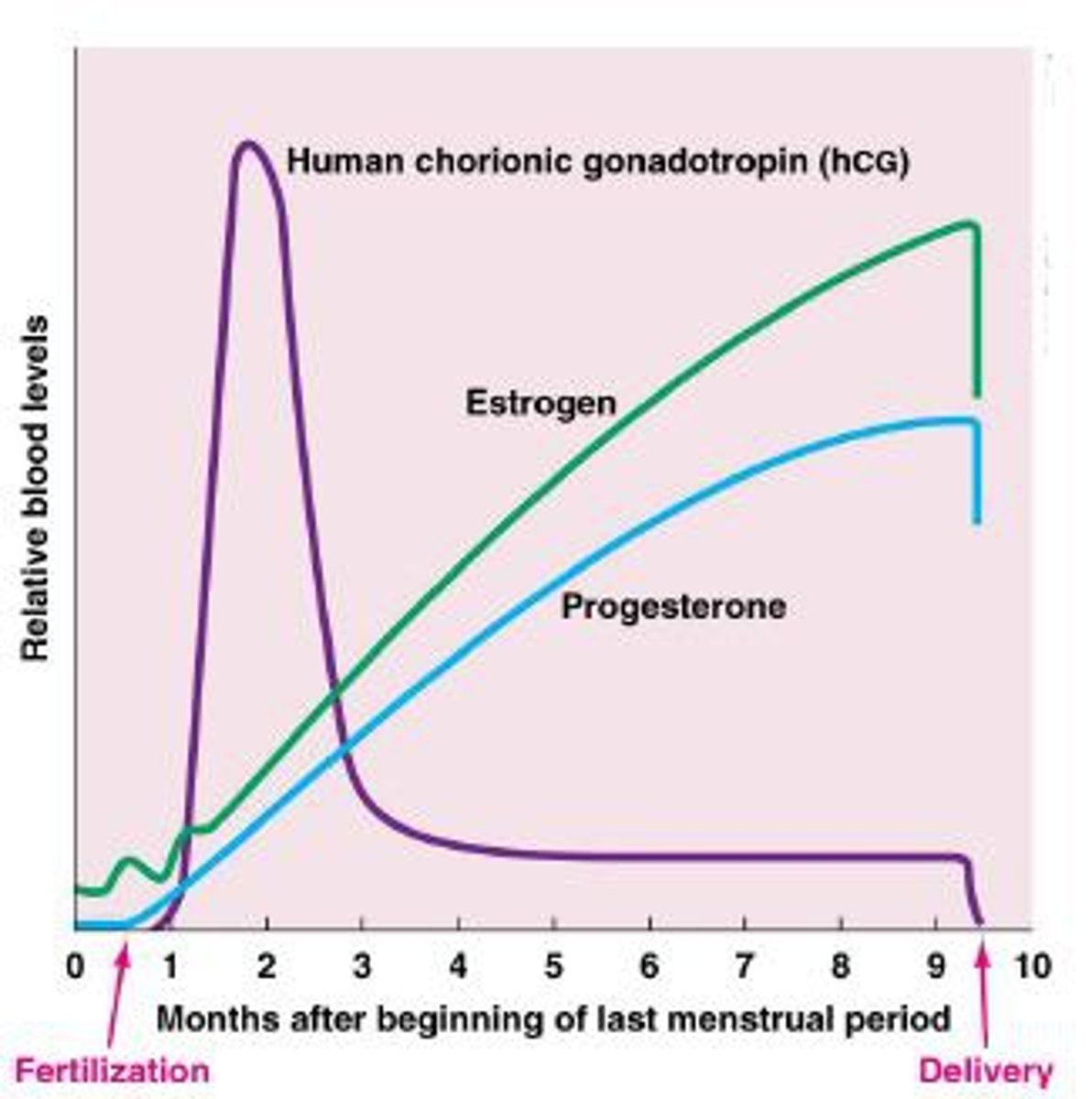
Progesterone
hormone produced by the corpus luteum in the ovary and the placenta of pregnant women. Maintains the lining of the endometrium
endometrium
inner lining of the uterus
secretes reproductive hormones
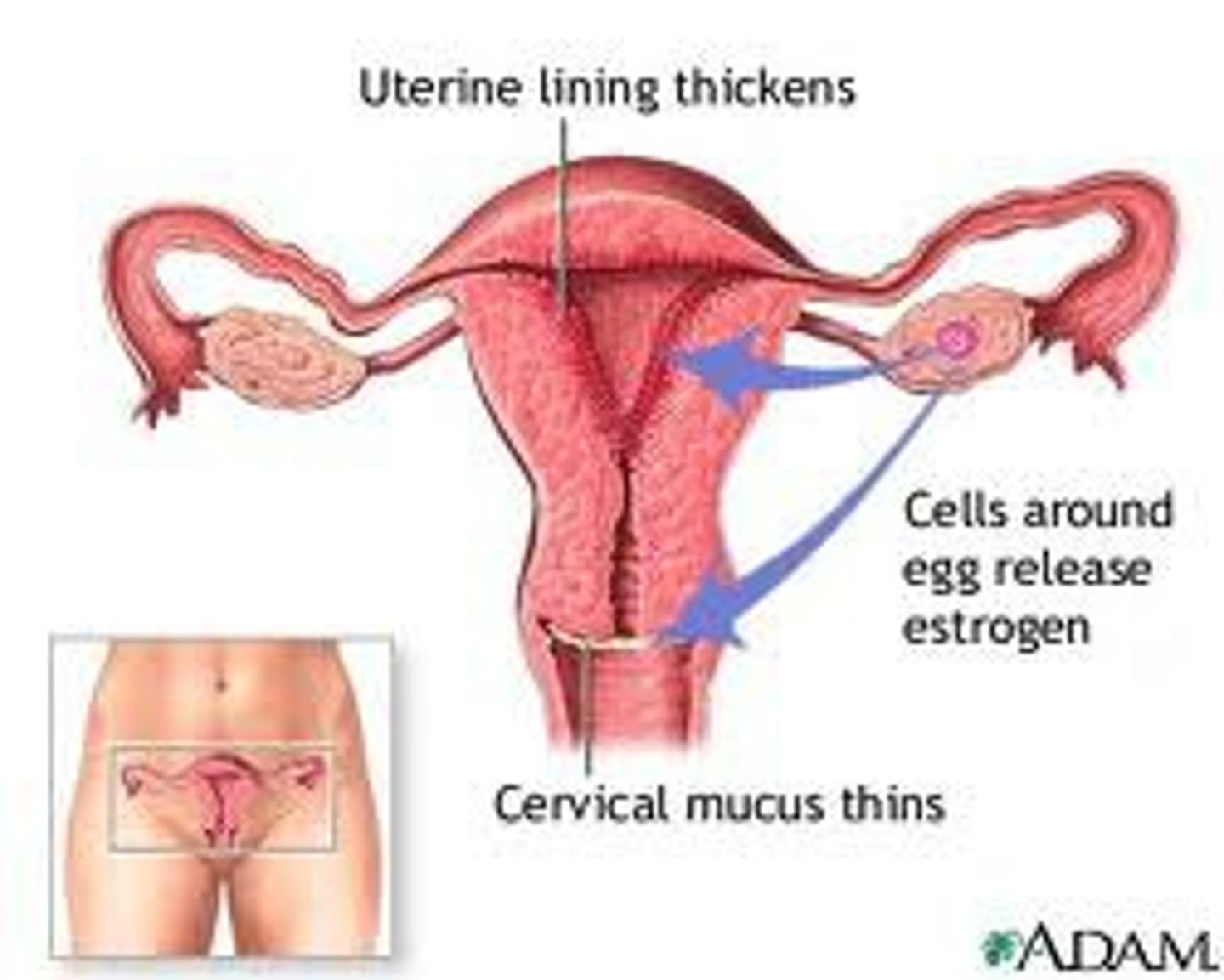
Estrogen
hormone released by the ovaries.
- responsible for primary and secondary sex characteristics in females.
Released during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle to build up the lining of the endometrium.
luteal phase
period of corpus luteum activity (days 14-28). The corpus luteum of the ovary secretes high levels of estrogen and progesterone
follicular phase
days 1-14 of the ovarian cycle. FSH stimulates the ovaries to develop an egg in side a follicles. Estrogen is produced
Ovulation
The process of releasing a mature ovum into the fallopian tube each month. Occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle. Is caused by High levels of FH.
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
secreted by the embryo. Stimulates the corpus luteum to continue to produce estrogen & progesterone. Used in pregnancy tests.
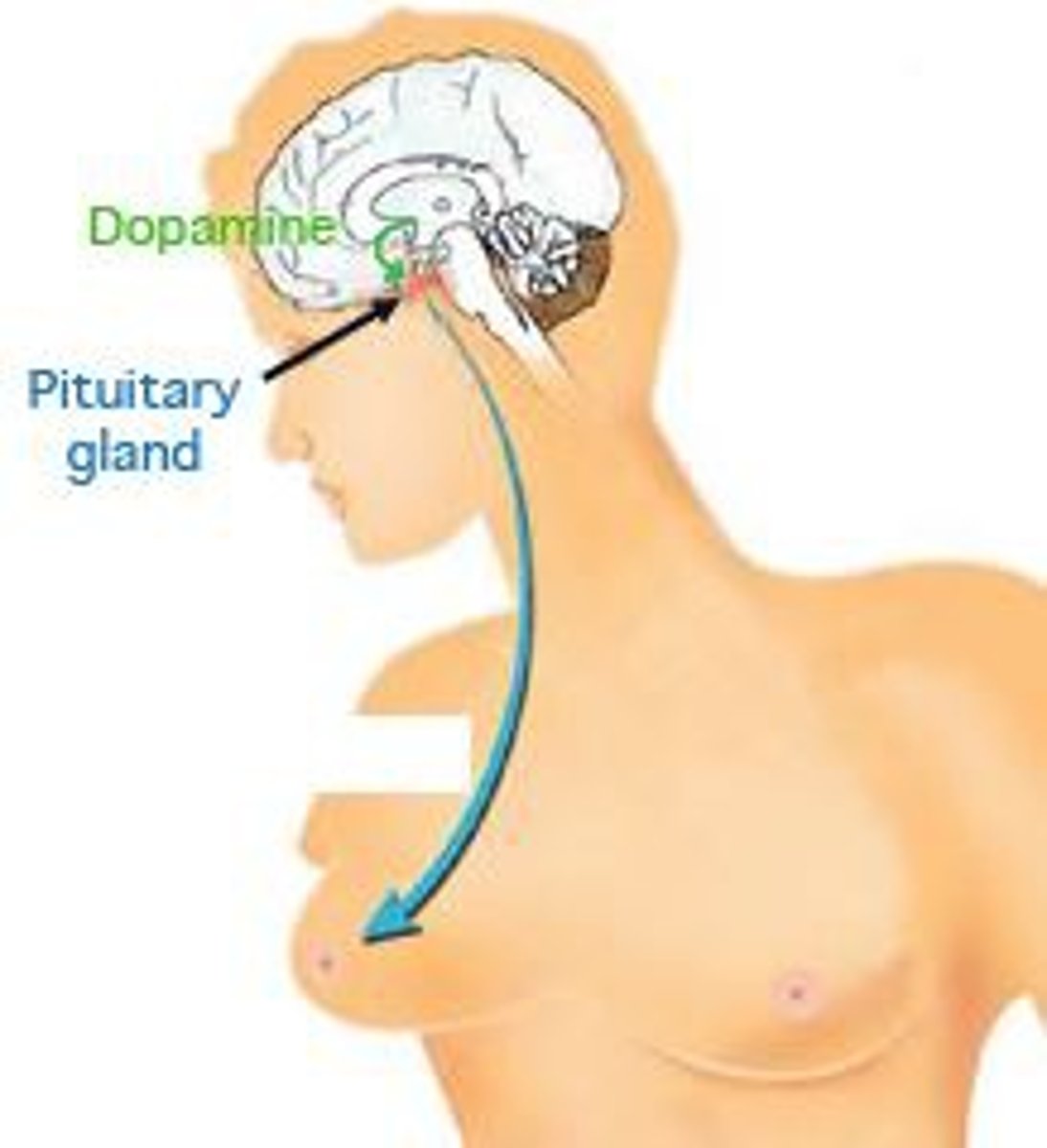
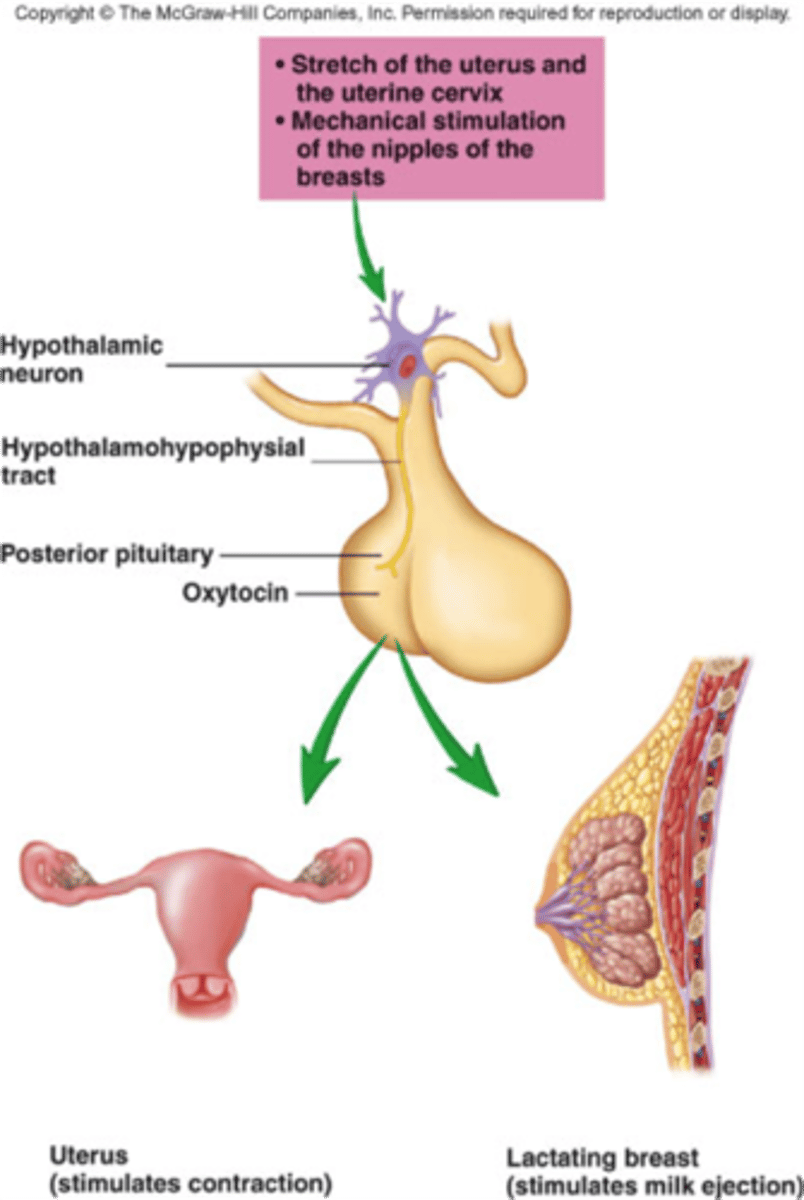
Prolactin
a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary. It stimulates milk production.
Oxytocin
A hormone (made in the hypothalamus, released by the posterior pituitary) that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and milk release during breastfeeding.
fetus
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
Embryo
An organism in the earliest stage of development. In humans, this stage encompasses the first 9 weeks of development
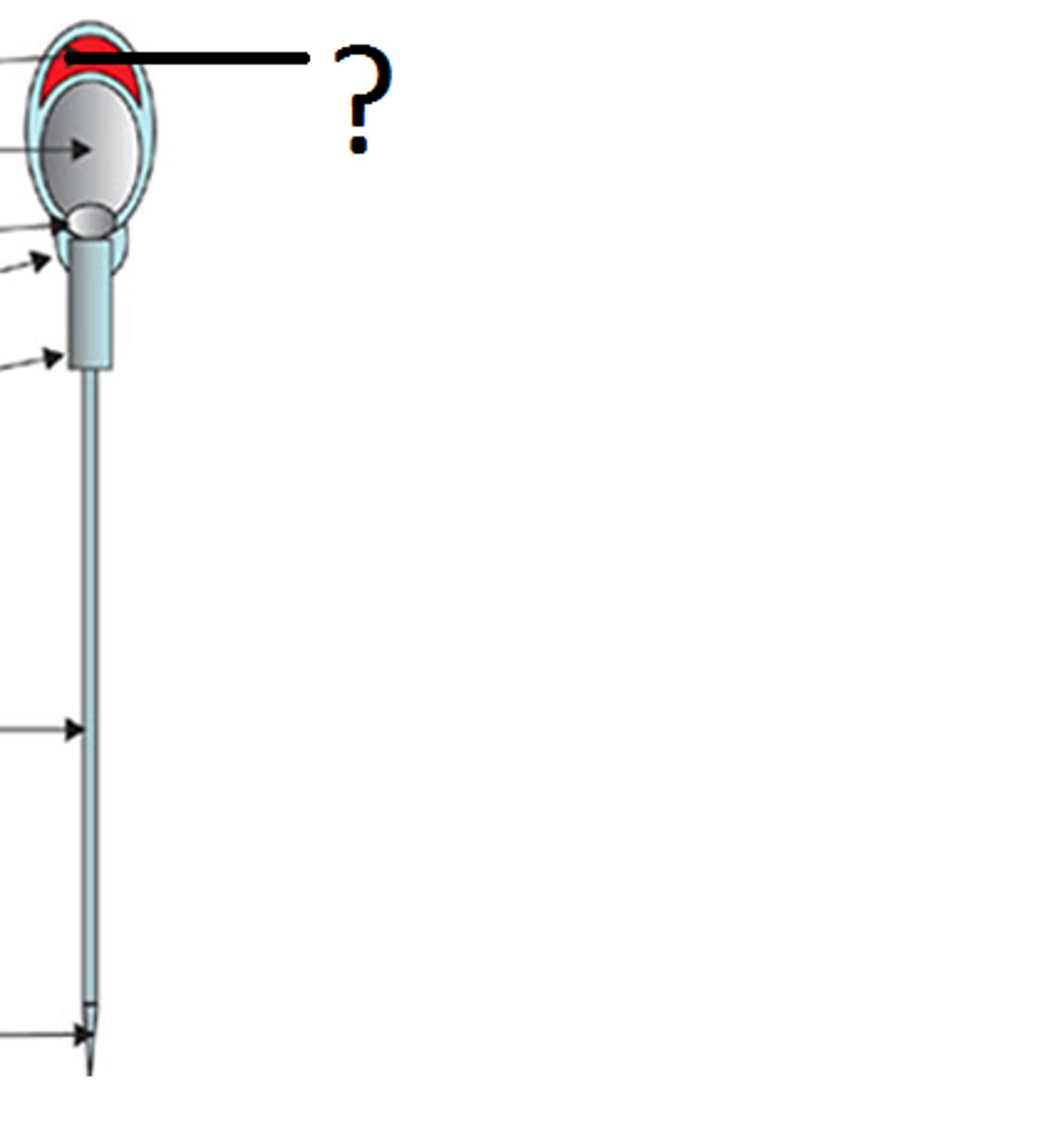
acrosome
A region at the head of a sperm cell that contains digestive enzymes that help to penetrate the egg
Sexually Transmitted Infection
Any pathogen that spreads from one person to another during sexual contact
tubal ligation
a surgical sterilization procedure in which the fallopian tubes are sealed or cut to prevent sperm from reaching a mature ovum
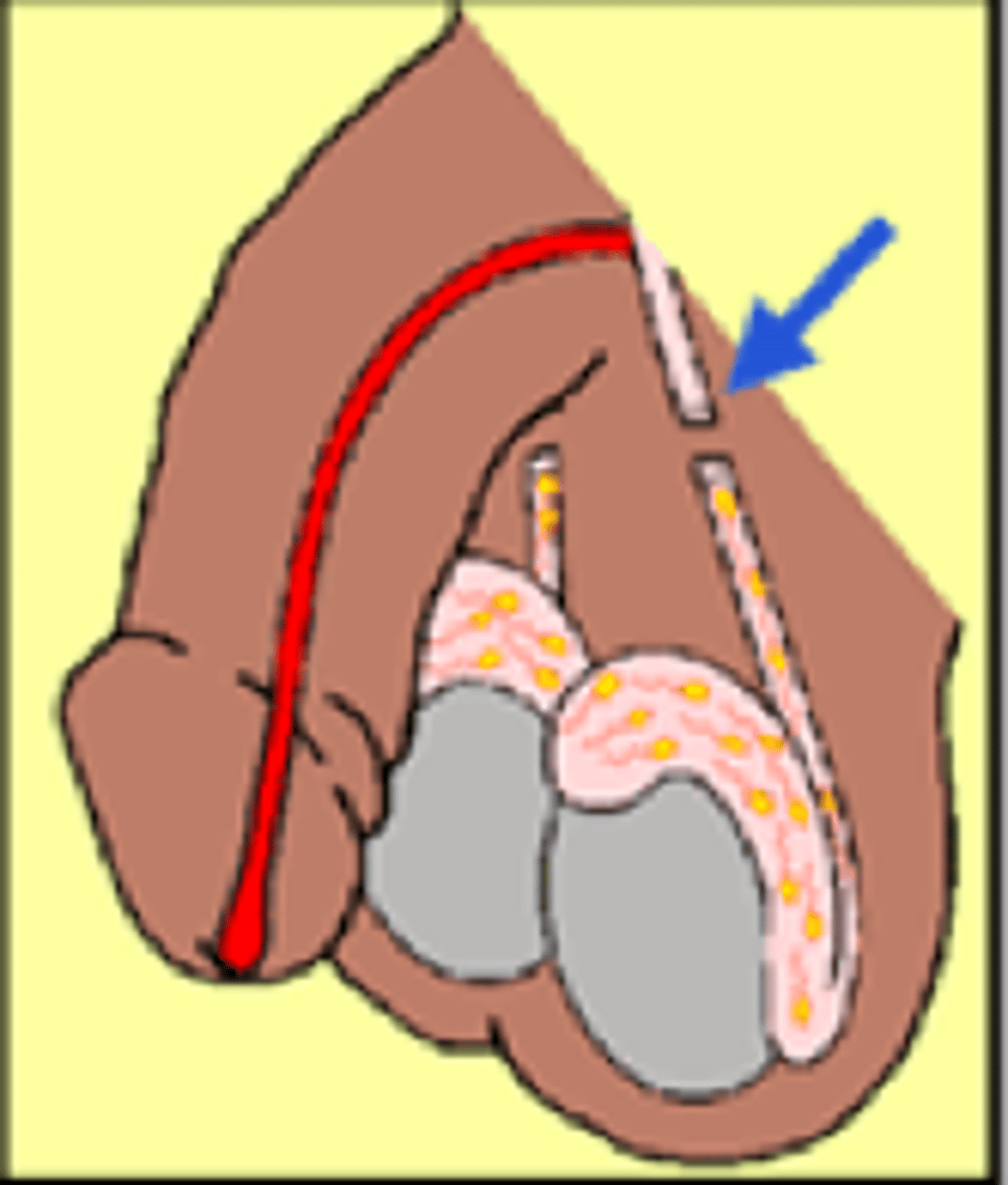
vasectomy
removal of a segment of the vas deferens to produce sterility in the male
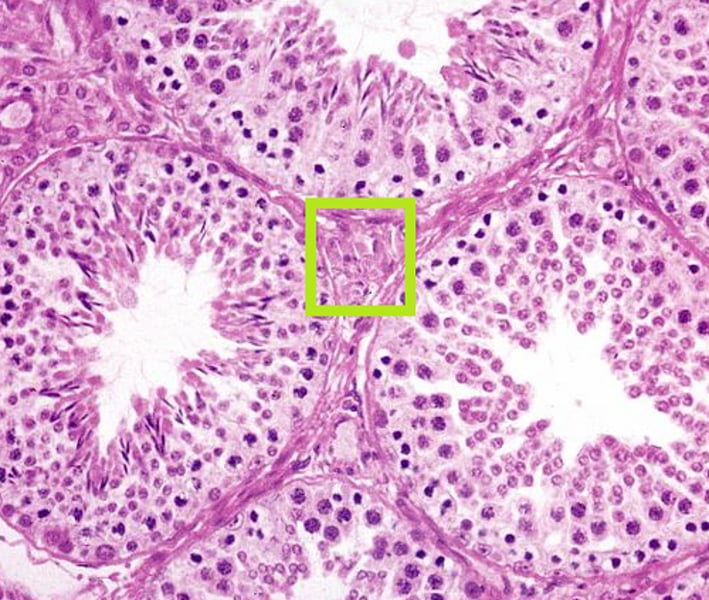
Interstitial cells
Lies between seminiferous tubules
Produce testosterone. Influenced by LH from the pituitary
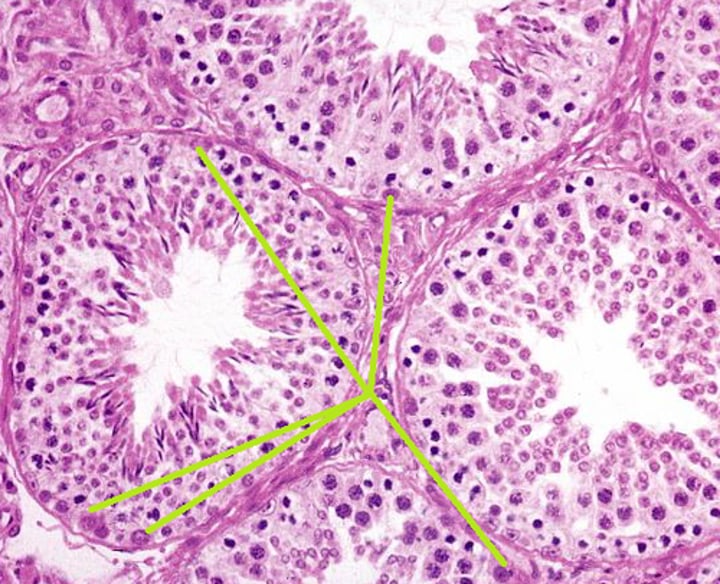
Sertoli cells
Secrete Chemicals required for the nourishment and development of sperm cells
-Responsible for spermatogenesis
Acrosome
Contains an enzyme to penetrate layers surrounding the ovum
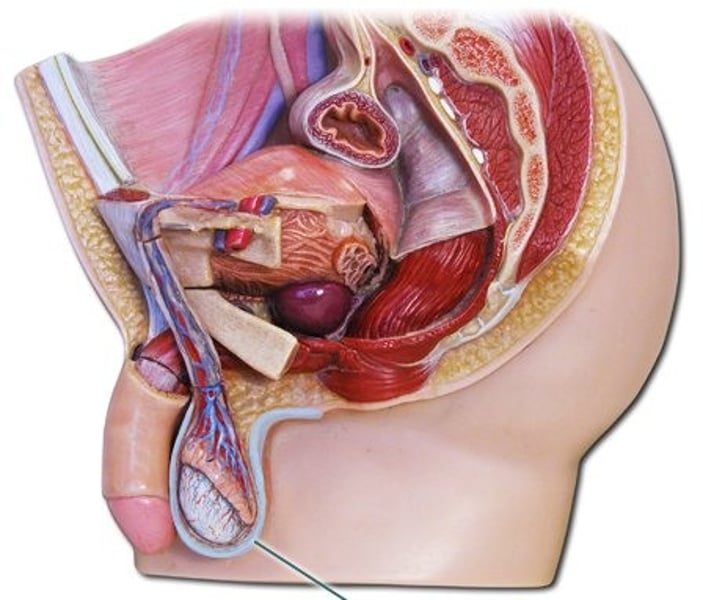
Scrotum
Sac holding testes outside body
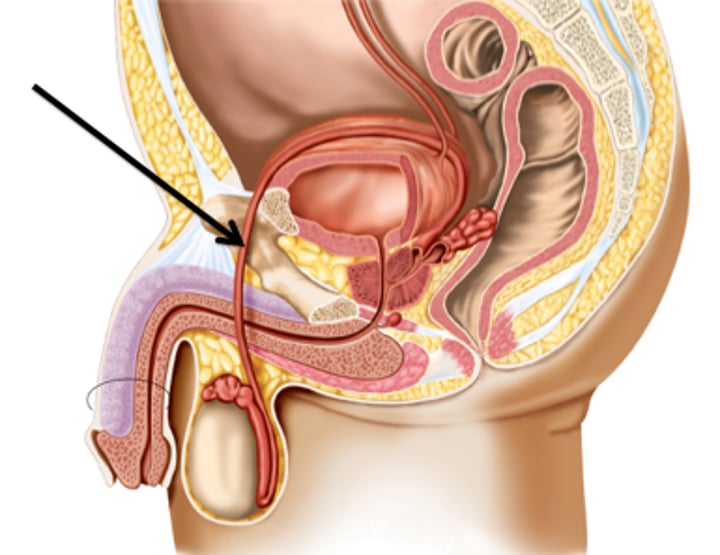
Vas Deferens
Carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
-Tubes connected (leads) to ejaculatory duct
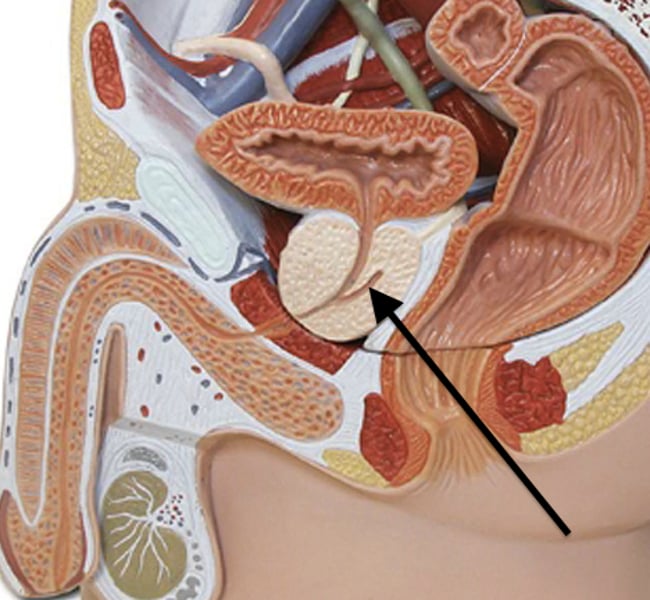
Ejaculatory Duct
Regulates the movement of semen into the urethra
Seminal vesicles
Produce mucus-like fluid containing sugar fructose which provides energy for sperm.
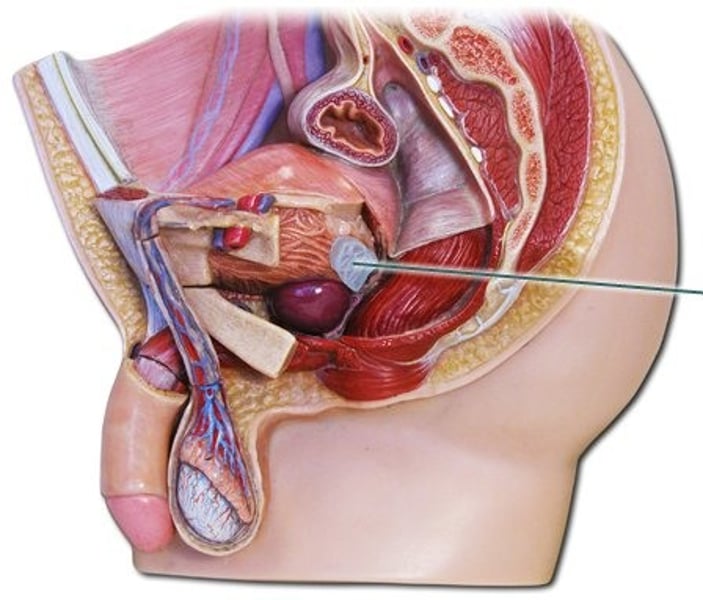
Cowper's gland / bulbourethral gland
Protects against acid in urethra and increases moblitily
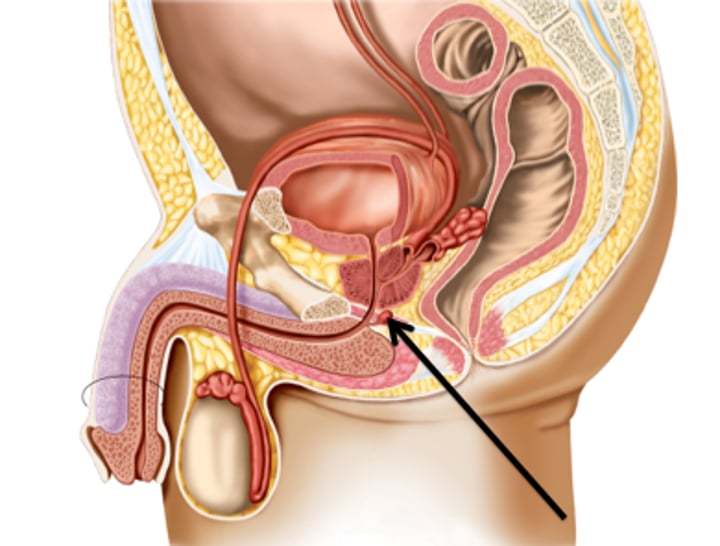
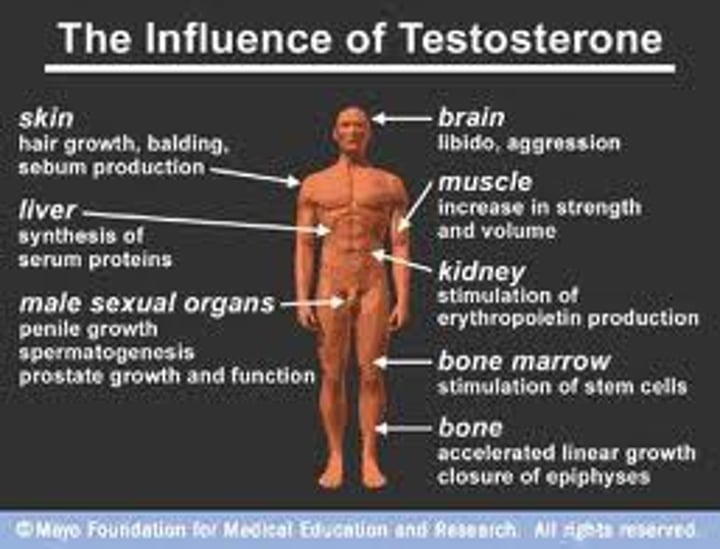
Testosterone
Influences development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics in males