Lecture 07
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:23 AM on 10/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
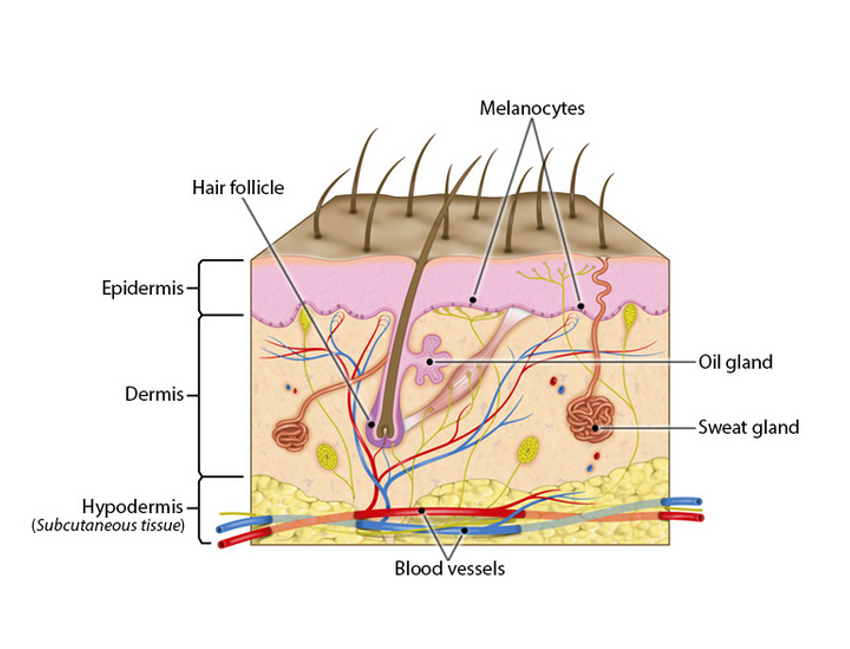
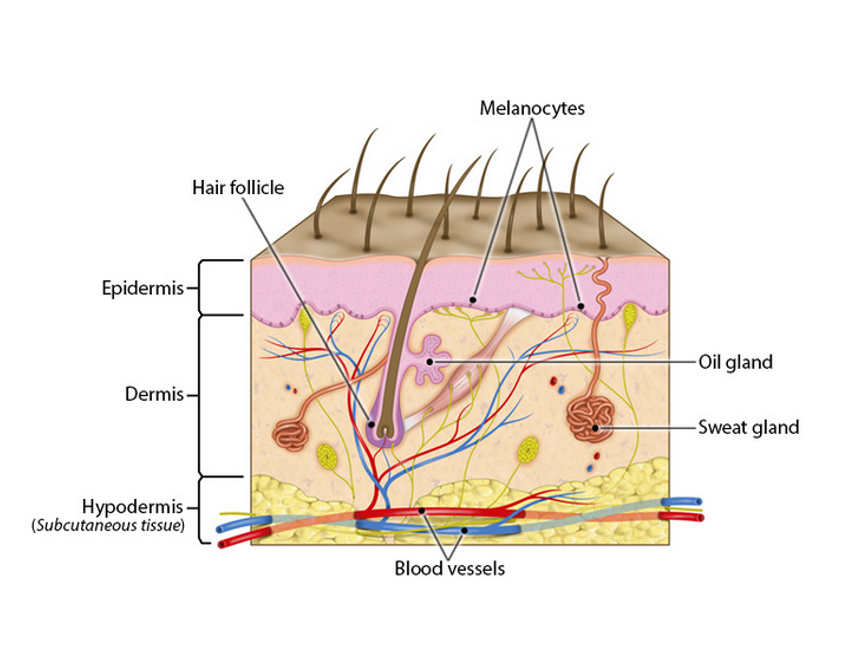
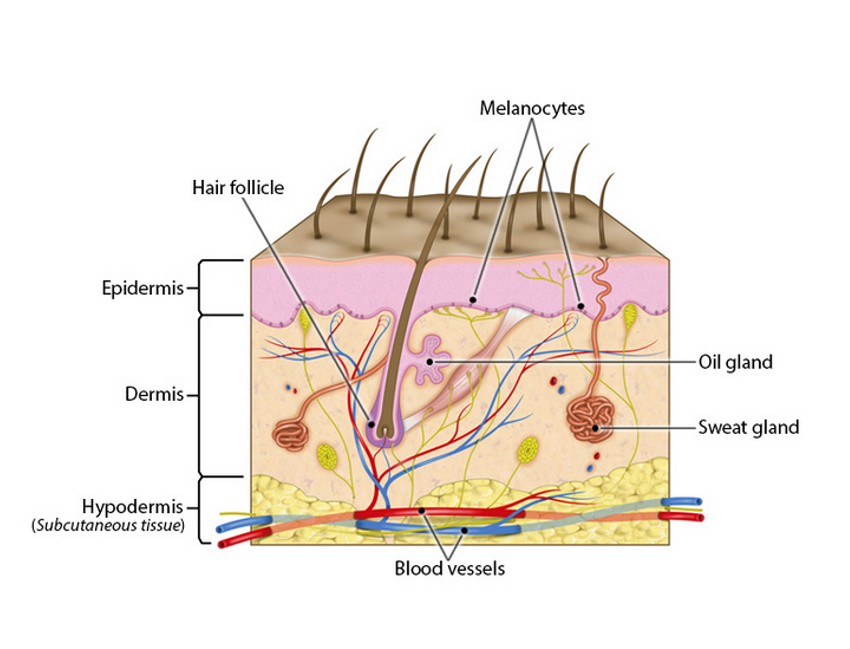
Epidermis
-outermost layer
-composed of epithelium
-avascular
-protects underlying layers
-composed of epithelium
-avascular
-protects underlying layers
2
New cards
Dermis
-underlying layers
-vascular & innervated
-provides strength and resilience
-composed of CT
-contains smooth muscles (associated w/ hair follicles) and nerve fibers to detect and monitor sensory input
-vascular & innervated
-provides strength and resilience
-composed of CT
-contains smooth muscles (associated w/ hair follicles) and nerve fibers to detect and monitor sensory input
3
New cards
Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis)
-composed of areolar and adipose CT
-not technically part of the skin
-anchors the skin to underlying structures
-acts as a shock absorber & insulator
-not technically part of the skin
-anchors the skin to underlying structures
-acts as a shock absorber & insulator
4
New cards
Function of the ___
Protection
-chemical barrier
-physical barrier
-biological barrier
-temp. barrier
-radiation (UV) barrier
Prevention of Water Loss
-water resistant
Metabolic Regulation
-vitamin D production
-other minor metabolic roles
Secretion & Absorption
-small amounts of metabolic waste (water, salts, urea, etc.)
-selectively permeable
Immunity
-identify and destroy pathogens
-alerts immune system & initiates immune response
Protection
-chemical barrier
-physical barrier
-biological barrier
-temp. barrier
-radiation (UV) barrier
Prevention of Water Loss
-water resistant
Metabolic Regulation
-vitamin D production
-other minor metabolic roles
Secretion & Absorption
-small amounts of metabolic waste (water, salts, urea, etc.)
-selectively permeable
Immunity
-identify and destroy pathogens
-alerts immune system & initiates immune response
Epidermis
5
New cards
Function of the ___
Temp. Regulation
-blood vessels
-sweat glands
-adipose
Sensory Reception
-mechanoreceptor (touch, pressure, vibration, etc.)
-nociceptor (pain)
-thermoreceptor (temperature)
Temp. Regulation
-blood vessels
-sweat glands
-adipose
Sensory Reception
-mechanoreceptor (touch, pressure, vibration, etc.)
-nociceptor (pain)
-thermoreceptor (temperature)
Dermis
6
New cards
Keratinocytes (cells of epidermis)
-most abundant
-produces keratin (fibrous protein that forms intermediate filaments) that provides the protective properties of the skin
-tightly connected to one another by desmosomes
-produces keratin (fibrous protein that forms intermediate filaments) that provides the protective properties of the skin
-tightly connected to one another by desmosomes
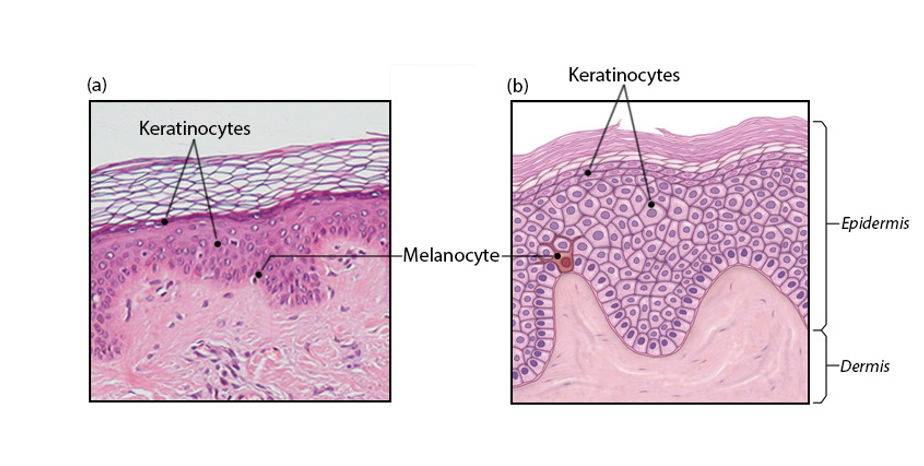
7
New cards
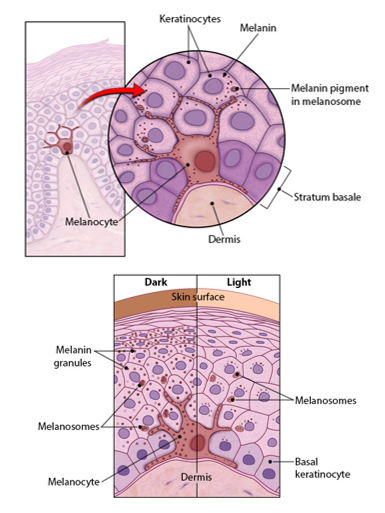
Melanocyte (cells of epidermis)
-have long, branching spiderlike processes
-synthesize and store up the pigment of melanin in response to UV light
-melanin granules are taken up by keratinocytes & accumulate on the superficial side of the nucleus to protect the nucleus from UV light
-synthesize and store up the pigment of melanin in response to UV light
-melanin granules are taken up by keratinocytes & accumulate on the superficial side of the nucleus to protect the nucleus from UV light
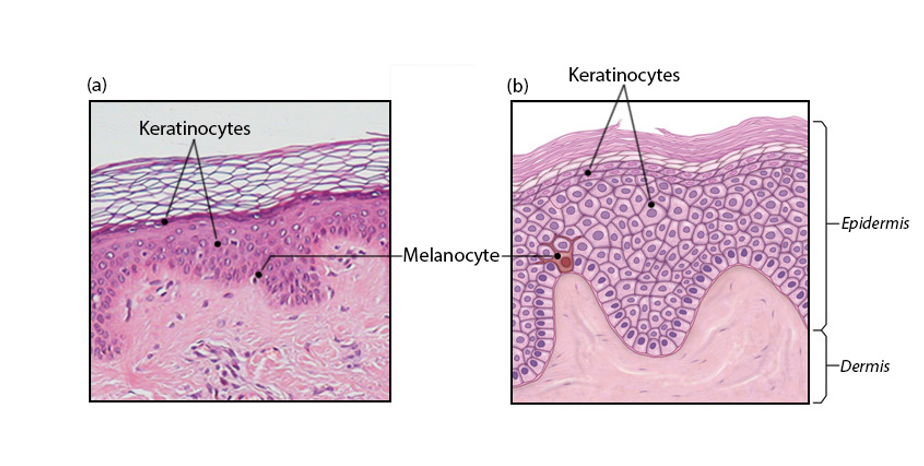
8
New cards
From outer-to innermost layer
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
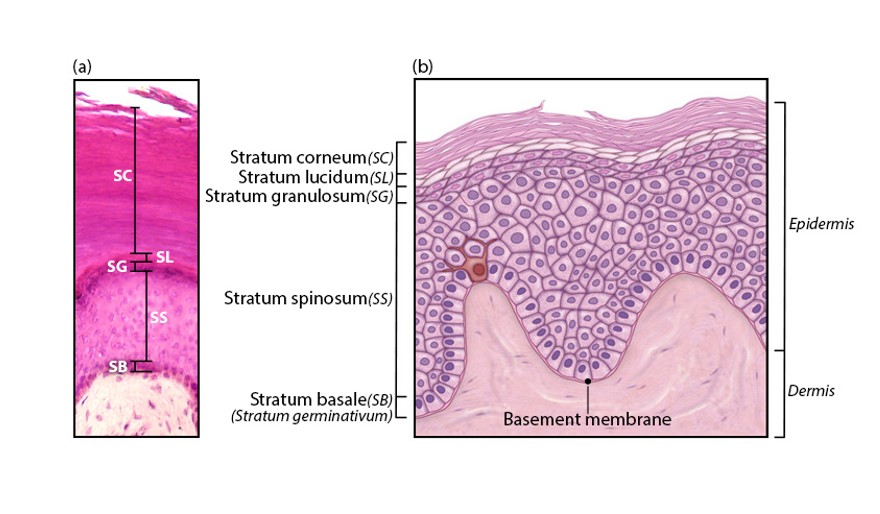
9
New cards
Epidermis consists of
-keratinized stratified, squamous epithelium
-3 innermost layer consists of living cells
-two outermost layers are dead cells
-3 innermost layer consists of living cells
-two outermost layers are dead cells
10
New cards
Stratum Basale
-deepest layer
-attached to a basement membrane that separates it from the underlying dermis
-epidermal ridges increase grip
-single layer of cuboidal to low columnar cells
*(most are keratinocytes)
*(small population of melanocytes)
-attached to a basement membrane that separates it from the underlying dermis
-epidermal ridges increase grip
-single layer of cuboidal to low columnar cells
*(most are keratinocytes)
*(small population of melanocytes)
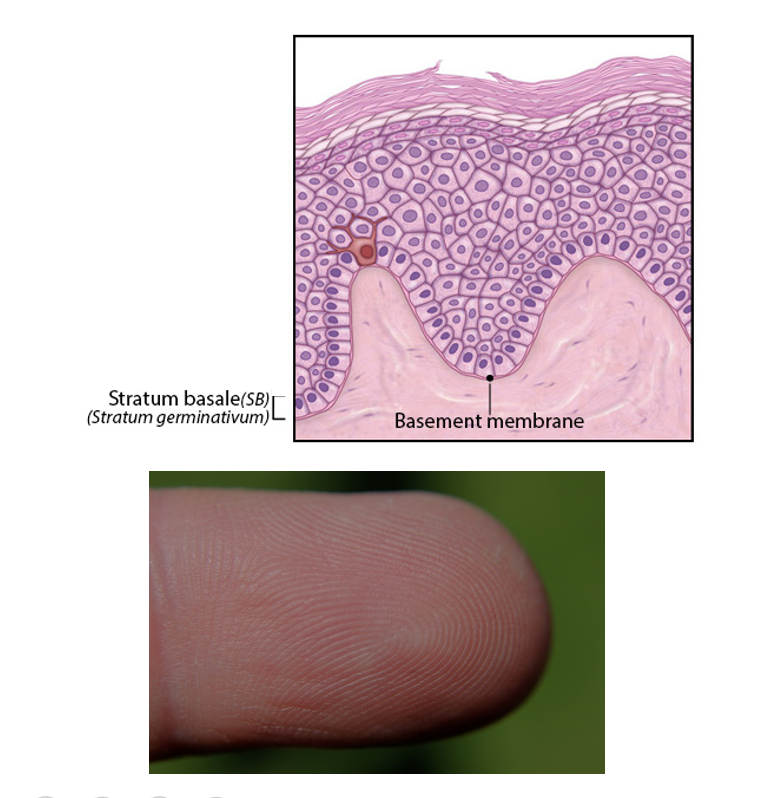
11
New cards
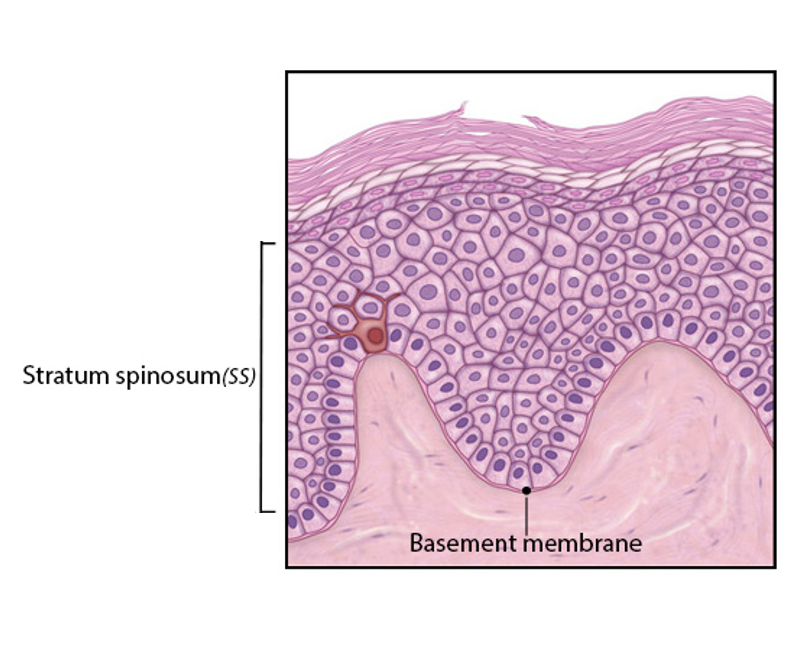
Stratum Spinosum
-overlies the stratum basale
-several layers thick
-keratinocytes from basale differentiate into non-dividing, specialized keratinocytes
-attached to neighbors by desmosomes results in spiny appearance
-several layers thick
-keratinocytes from basale differentiate into non-dividing, specialized keratinocytes
-attached to neighbors by desmosomes results in spiny appearance
12
New cards
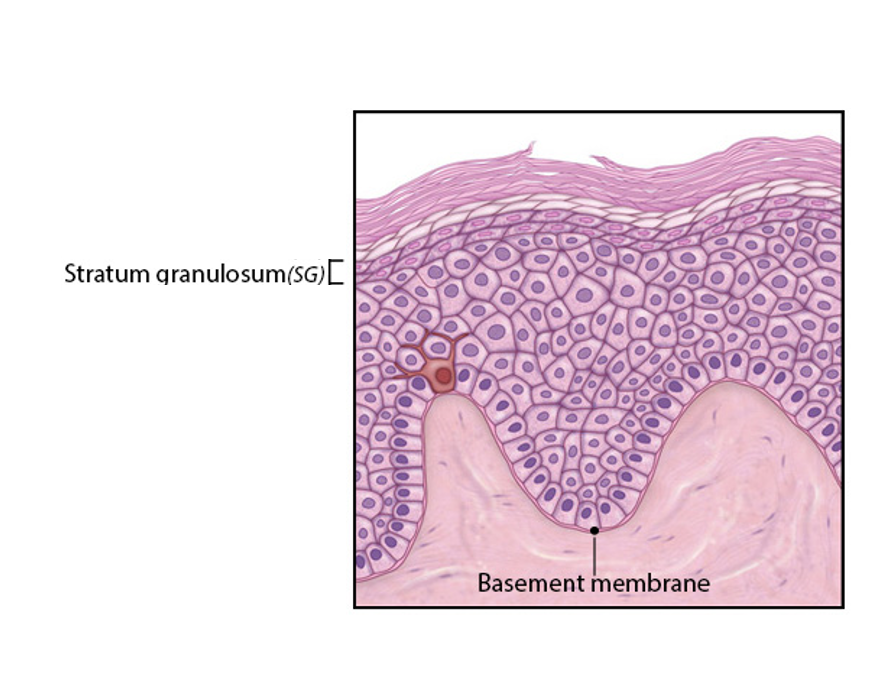
Stratum Granulosum
-3 to 5 layers thick
-keratinization
*(keratinocytes produce keratohyalin (precursor to keratin) granules)
*(nucleus and organelles begin to disintegrate)
*(cells begin to die, due to lack of organelles & being pushed further away from source of nutrients)
-won't be complete until after keratinocytes rise to superficial layer
-keratinization
*(keratinocytes produce keratohyalin (precursor to keratin) granules)
*(nucleus and organelles begin to disintegrate)
*(cells begin to die, due to lack of organelles & being pushed further away from source of nutrients)
-won't be complete until after keratinocytes rise to superficial layer
13
New cards
Stratum Lucidum
-thin, clear layer about 2-3 cell layers thick
*(protects against friction)
*(found only in thick skin on palms of hands and soles of feet)
-cells have become flattened and featureless
-filled with eleidin (an intermediate protein formed by keratohyalin) during keratin maturation
*(helps protect skin from UV light)
*(protects against friction)
*(found only in thick skin on palms of hands and soles of feet)
-cells have become flattened and featureless
-filled with eleidin (an intermediate protein formed by keratohyalin) during keratin maturation
*(helps protect skin from UV light)
14
New cards
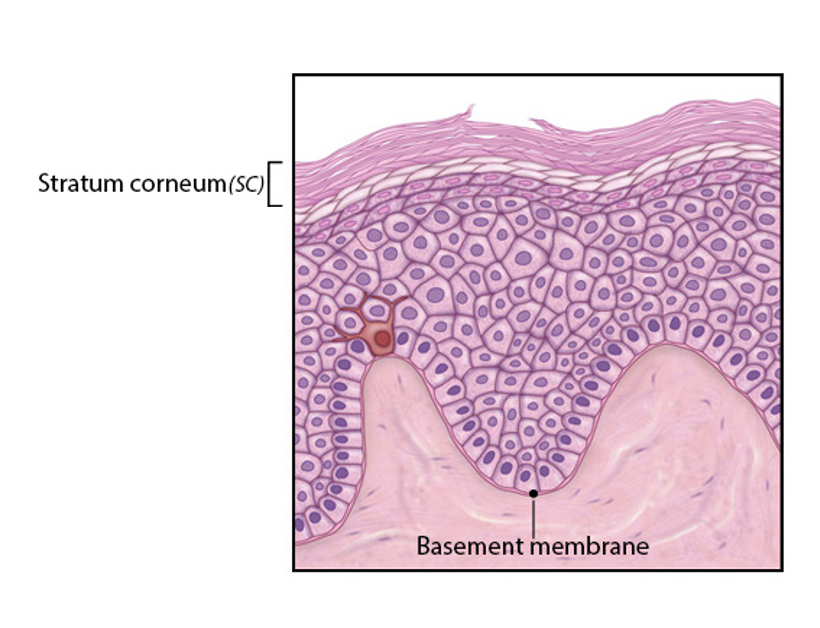
Stratum Corneum
-most superficial layer
-individual keratinocyte from stratum basale to strata corneum exists for about 4 weeks
*(lost due to desaquamation)
-15 to 30 layers of dead, scaly interlocked keratinized cells
*(cells are anucleate)
*(tightly packed together)
*(contain large amounts of keratin)
-protective, durable overcoat
*(thickened plasma membrane enhanced by special glycoproteins waterproofs the strata corneum)
*(relatively insensitive to biological, chemical, and physical assault)
-individual keratinocyte from stratum basale to strata corneum exists for about 4 weeks
*(lost due to desaquamation)
-15 to 30 layers of dead, scaly interlocked keratinized cells
*(cells are anucleate)
*(tightly packed together)
*(contain large amounts of keratin)
-protective, durable overcoat
*(thickened plasma membrane enhanced by special glycoproteins waterproofs the strata corneum)
*(relatively insensitive to biological, chemical, and physical assault)
15
New cards
Thick Skin
-5 layers (contains stratum lucidum
-found on palms of hands and soles of feet
-contains sweat glands
-lacks hair follicles and sebaceous glands
-found on palms of hands and soles of feet
-contains sweat glands
-lacks hair follicles and sebaceous glands
16
New cards
Thin Skin
-4 layers (lacks stratum lucidum)
-covers most of the body
-contains sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands
-covers most of the body
-contains sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands
17
New cards
Epidermal dendritic (Langerhans')
-found within strata spinosum and granulosum
-phagocytic cell capable of stimulating immune response
-phagocytic cell capable of stimulating immune response
18
New cards
Melanin
-only pigment made in the skin
-delivered to keratinocytes within melanosomes
-everyone has the same relative number of melanocytes
-varying shades of skin color reflects the amount of melanin produced and retained
-freckles and pigmented moles are local accumulations of melanin
-delivered to keratinocytes within melanosomes
-everyone has the same relative number of melanocytes
-varying shades of skin color reflects the amount of melanin produced and retained
-freckles and pigmented moles are local accumulations of melanin
19
New cards
Eumelanin
-black/brown pigment
20
New cards
Pheomelanin
-red/yellow pigment
21
New cards
Carotene
-yellow/orange pigment found in certain plants
-accumulates in the stratum corneum & fatty tissues of the hypodermis
-accumulates in the stratum corneum & fatty tissues of the hypodermis
22
New cards
Tactile discs
-Merkel (tactile) cells (in stratum basale)
-mechanoreceptors
-small receptive fields
-response to tactile stimulation help determine shape and texture of object
*(fine touch)
*(pressure)
-mechanoreceptors
-small receptive fields
-response to tactile stimulation help determine shape and texture of object
*(fine touch)
*(pressure)
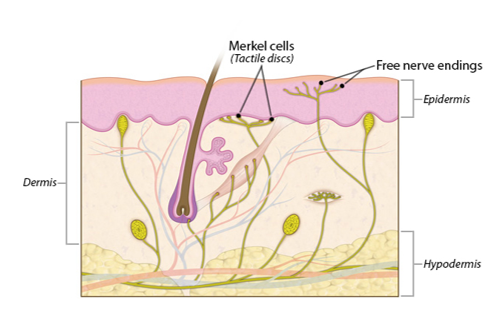
23
New cards
Free nerve endings
-responsible for pain
-tickling (light touch)
-itching (noxious stimuli)
-tickling (light touch)
-itching (noxious stimuli)
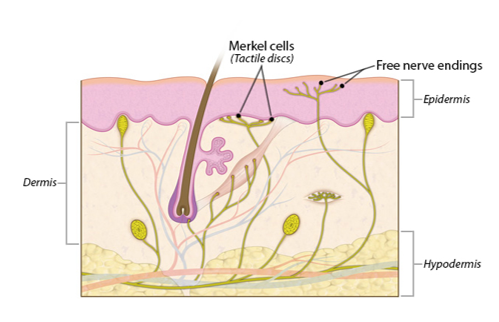
24
New cards
Epidermis produces Vitamin D
-vitamin D3 produced in the skin on exposure to UV light from a cholesterol precursor
*(may also be absorbed in diet)
-converted to its active form by 2 enzymatic reactions
*(one in liver)
*(one in kidney)
-increases intestinal reabsorption of Ca2+ and (PO4)3-
*(may also be absorbed in diet)
-converted to its active form by 2 enzymatic reactions
*(one in liver)
*(one in kidney)
-increases intestinal reabsorption of Ca2+ and (PO4)3-
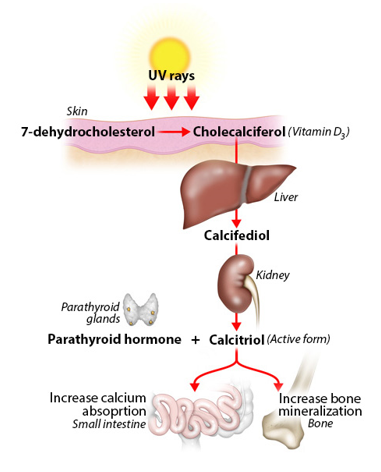
25
New cards
Dermis
-cells are typical of those found in CT proper
-richly innervated, vascularized
-possesses lymphatic vessels
-2 layers
*(papillary layer)
*(reticular layer)
-richly innervated, vascularized
-possesses lymphatic vessels
-2 layers
*(papillary layer)
*(reticular layer)
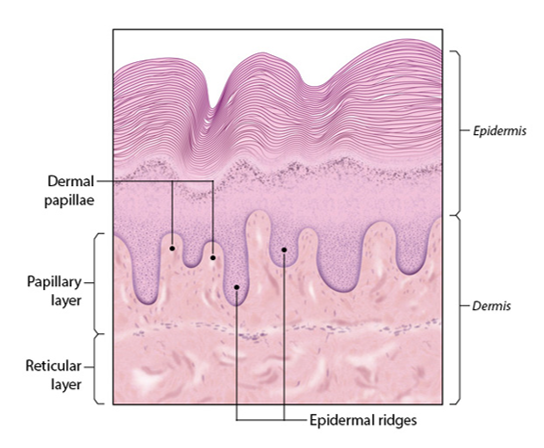
26
New cards
Papillary layer
-located near the superior surface
-areolar CT
-areolar CT
27
New cards
Dermal papillae
-small projections indenting into epidermis
-contains free nerve endings = pain receptors, touch receptors
-interdigit with epidermal ridges to increase area of contact and interlock the 2 layers
-contains free nerve endings = pain receptors, touch receptors
-interdigit with epidermal ridges to increase area of contact and interlock the 2 layers
28
New cards
Reticular layer
-dense irregular CT underlying the papillary layer of the dermis
*(mostly collagen fibers running parallel to the skin surface) -> creates "cleavage lines"
*(contains elastin providing elasticity)
-highly vascularized and innervated
*(nerves allow us to distinguish diff. types of sensory stimuli)
*(blood vessels supply nutrients for dermis and epidermis)
*(blood vessels also play a role in temp. regulation)
-possesses flexure lines
*(dermal folds where dermis is tightly secured to deeper structures)
*(mostly collagen fibers running parallel to the skin surface) -> creates "cleavage lines"
*(contains elastin providing elasticity)
-highly vascularized and innervated
*(nerves allow us to distinguish diff. types of sensory stimuli)
*(blood vessels supply nutrients for dermis and epidermis)
*(blood vessels also play a role in temp. regulation)
-possesses flexure lines
*(dermal folds where dermis is tightly secured to deeper structures)
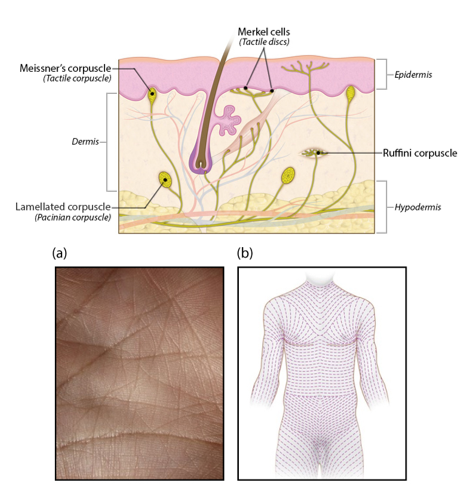
29
New cards
Meissner's (tactile) corpuscle
-dermal papillae
-light touch, pressure, and vibrations
-light touch, pressure, and vibrations
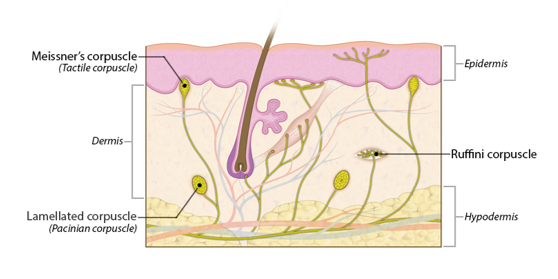
30
New cards
Pacinian (lamellated) corpuscle
-reticular layer of dermis
-deep pressure & vibration
-deep pressure & vibration
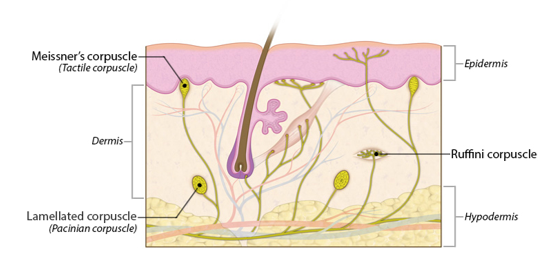
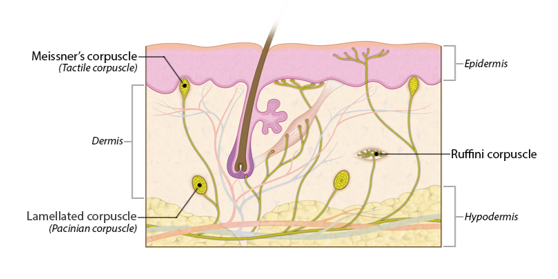
31
New cards
Ruffiini corpuscle
-reticular layer among collagen bundles
-pressure and skin distortion
-pressure and skin distortion
32
New cards
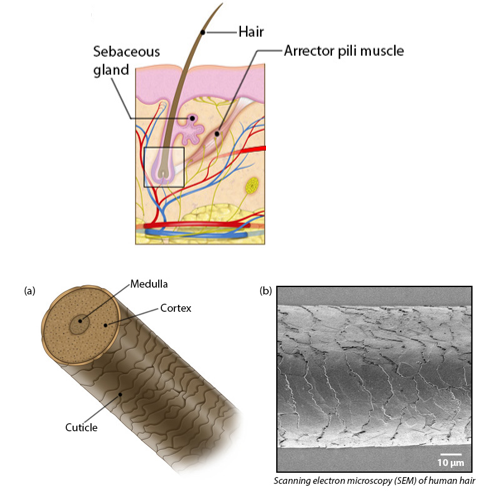
Hair
-flexible strands of dead keratinized cells produced by the hair follicle
*("hard keratin")
*(tougher and more durable)
*(individual cells do not flake off)
*("hard keratin")
*(tougher and more durable)
*(individual cells do not flake off)
33
New cards
Function of ___
-protection
*(head) sunburn and injury
*(nasal and ear) traps particles
*(eyes) prevent sweat and particles from endangering the eye
-heat retention
*(acts like a cap to prevent heat from escaping scalp)
-sensory reception
*(tactile receptors that detect light touch)
-visual identification
*(determining age and sex)
*(identifying individuals)
-chemical signal dispersion
*(pheromones in axillary and pubic regions)
-protection
*(head) sunburn and injury
*(nasal and ear) traps particles
*(eyes) prevent sweat and particles from endangering the eye
-heat retention
*(acts like a cap to prevent heat from escaping scalp)
-sensory reception
*(tactile receptors that detect light touch)
-visual identification
*(determining age and sex)
*(identifying individuals)
-chemical signal dispersion
*(pheromones in axillary and pubic regions)
Hair
34
New cards
Shaft (structure of hair)
-projects above skin surface
-dead epithelial cells
-dead epithelial cells
35
New cards
Root (structure of hair)
-lies below the skin surface
-dead epithelial cells
-dead epithelial cells
36
New cards
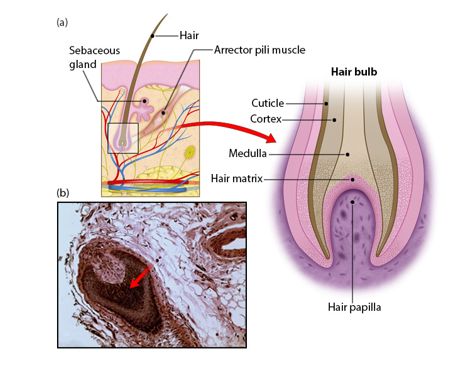
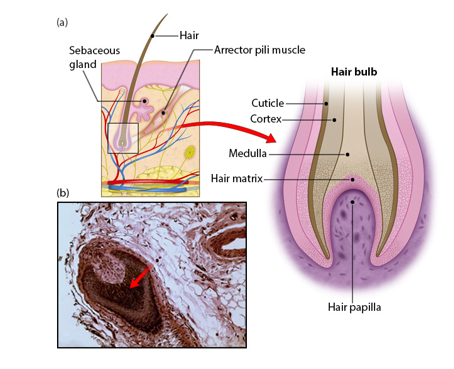
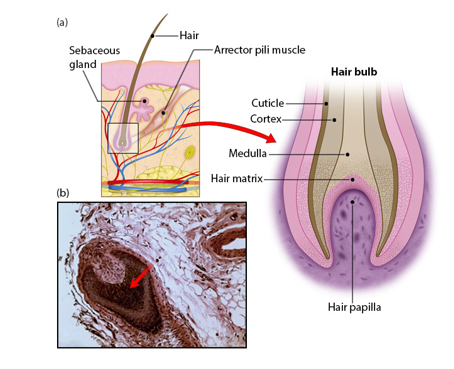
Hair bulb (structure of hair)
-region at base of hair follicle
-located deep in dermis
-consists of living epithelial cells
-origin of hair
-located deep in dermis
-consists of living epithelial cells
-origin of hair
37
New cards
Hair papilla (structure of hair)
-possessing capillaries supplying nutrients and nerves (root hair plexus) of hair
-hair matrix contains cells that become the hair shaft
-contain hard keratin proteins
-hair matrix contains cells that become the hair shaft
-contain hard keratin proteins
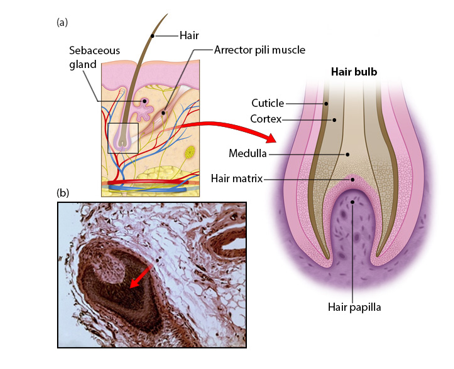
38
New cards
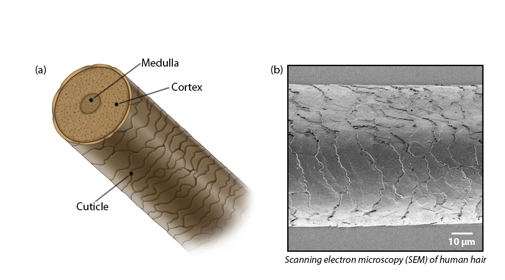
Medulla (structure of hair)
-innermost portion
-remnant of the matrix
-loosely arranged cells containing soft, flexible keratin and air pockets
-remnant of the matrix
-loosely arranged cells containing soft, flexible keratin and air pockets
39
New cards
Cortex (structure of hair)
-external to the medulla
-several layers of flattened cells
-hard keratin
-several layers of flattened cells
-hard keratin
40
New cards
Cuticle (structure of hair)
-outer layer consisting of a single layer of cells
-overlap one another (like shingles) away from the root
-overlap one another (like shingles) away from the root
41
New cards
Hair follicle
-folds down from the epidermis into the dermis
-wall has 2 layers
*(connective tissue root sheath)
*(epithelial root sheath)
-arrector pili muscle
-wall has 2 layers
*(connective tissue root sheath)
*(epithelial root sheath)
-arrector pili muscle
42
New cards
Connective tissue root sheath
-derived from the dermis
43
New cards
Epithelial root sheath
-derived from the epidermis
44
New cards
Arrector pili muscle
-responsible for contraction of the hair follicle
45
New cards
Anagen
-active phase
-producing new hairs
-pushes club hair out of follicle
-producing new hairs
-pushes club hair out of follicle
46
New cards
Catagen
-end of active phase
47
New cards
Telogen
-resting phase for the follicle
48
New cards
Club hairs
-hair follicle is inactive
49
New cards
Lanugo hair
-fine, downy hair found on a fetus (third trimester)
50
New cards
Vellus hair
-replaces lanugo hair
-fine, pale body hair
-fine, pale body hair
51
New cards
Terminal hair
-darker, thicker hair located on the head, axillary, and pubic regions
-face and chest of adult males
-hair growth is dependent on nutrition and hormones
-face and chest of adult males
-hair growth is dependent on nutrition and hormones
52
New cards
Shaft shape determines the
-appearance of the hair
53
New cards
Ribbonlike
-kinky hair
54
New cards
Round
-straight and coarse
55
New cards
Oval
-wavy hair
56
New cards
Hair pigment is made in the melanocytes
-found at the base of the follicle
57
New cards
Gray hair
-diminished melanin production
58
New cards
White hair
-no melanin production
59
New cards
Nails
-scalelike modifications of the stratum corneum
*(compromised of hard keratin)
-protect the distal tips of the digits
-assist in grasping objects
*(compromised of hard keratin)
-protect the distal tips of the digits
-assist in grasping objects
60
New cards
3 parts of the nail
-nail plate
-nail bed
*(underlies the nail plate)
-nail matric
*(actively growing part of the nail)
*(produces nail bed)
-nail bed
*(underlies the nail plate)
-nail matric
*(actively growing part of the nail)
*(produces nail bed)
61
New cards
Lunula (structure of the nail)
-"white crescent"
-most proximal portion of the nail plate
-most proximal portion of the nail plate
62
New cards
Eponychium ("Cuticle")
-thin strip of epithelium that protects the matrix
63
New cards
Sebaceous glands
-secretions
*(secrete an oily substance called sebum)
*(bactericidal)
*(stimulated by hormones)
-function as holocrine glands
-usually secrete into hair follicles
-secretions soften and lubricate hair and skin
*(prevent excessive water loss)
*(prevent bacterial growth)
*(secrete an oily substance called sebum)
*(bactericidal)
*(stimulated by hormones)
-function as holocrine glands
-usually secrete into hair follicles
-secretions soften and lubricate hair and skin
*(prevent excessive water loss)
*(prevent bacterial growth)
64
New cards
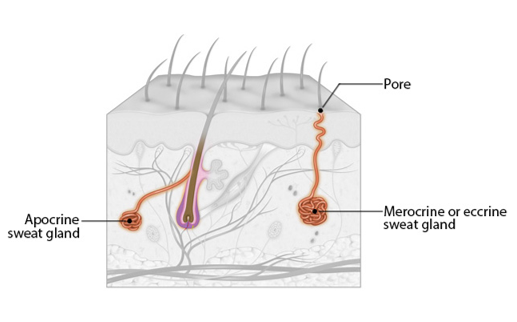
Sudoriferous glands (sweat glands)
-scattered over the whole body (excluding nipples & genitals)
-two types
*(Merocrine (Eccrine) sweat glands)
*(Apocrine sweat glands)
-two types
*(Merocrine (Eccrine) sweat glands)
*(Apocrine sweat glands)
65
New cards
Structure of Aprocrine sweat gland
-located in axillary & anogenital regions
-ducts empty into hair follicles
-ducts empty into hair follicles
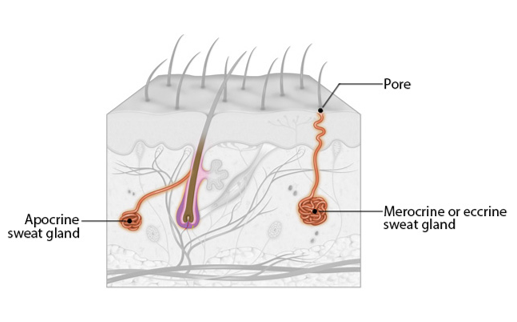
66
New cards
Secretion of Apocrine sweat gland
-same basic components as eccrine sweat + some fatty substances & proteins
-secretions are odorless but when decomposed by bacteria on the skin = body odor
-secretions are odorless but when decomposed by bacteria on the skin = body odor
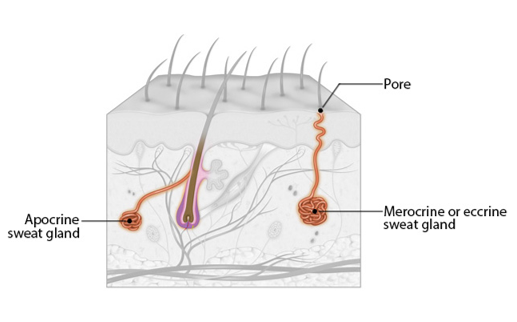
67
New cards
Merocrine sweat glands
-abundant on palms, soles, and forehead
-sweat: hypotonic filtrate of the blood
*(99% H2O)
-3 functions
-completely sympathetically regulated
*(emotionally-induced sweating)
-sweat: hypotonic filtrate of the blood
*(99% H2O)
-3 functions
-completely sympathetically regulated
*(emotionally-induced sweating)
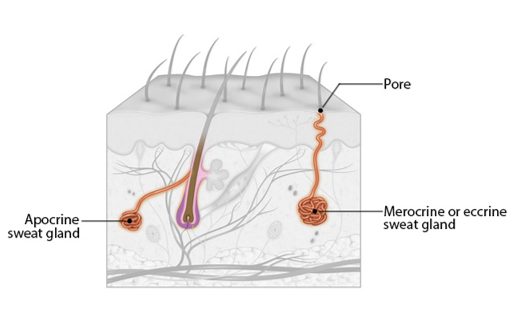
68
New cards
3 functions of Merocrine sweat glands
-thermoregulation
*(primary role of sweat is to prevent overheating of body)
-excretion
*(salts & metabolic wastes, such as urea)
-protection
*(antibodies & derminidin (anti-bacterial peptide))
*(primary role of sweat is to prevent overheating of body)
-excretion
*(salts & metabolic wastes, such as urea)
-protection
*(antibodies & derminidin (anti-bacterial peptide))