Chapter 9: Linear Momentum & Collisions
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Linear Momentum of a Part
p = mv
m = mass of particle (kg)
v = velocity of particle (m/s)
vector quantity: direction of the momentum is the same as velocity’s
depends on direction & magnitude
A particle with a high p, or linear momentum, is…
difficult to stop
large mass with high speed
Net Force of a particle
Fnet = Δp/Δt
The net force acting on a particle/object is equal to the rate of change of its momentum over time.
A greater net force will cause a greater change in momentum; net force changes momentum
Connected to Newton’s 2nd Law: F = ma
Force is equal to a…
change in momentum
A 0.12-kg ball is moving at 6 m/s when it is hit by a bat, causing it to reverse direction and have a speed of 14 m/s. What is the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball?
m = 0.12 kg
vi = 6 m/s
vf = -14 m/s
change in magnitude = |Δp| = pf - pi = mvf - mvi = 0.12 kg(6 - (-14)) = 2.4 kg*m/s
Impulse
changes momentum
J = Δp = FnetΔt
net force produces impulse

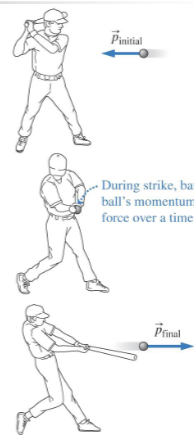
Explain what is happening.
Impulse occurs when a net force acts over a period of time, resulting in a change in momentum. In this context, the ball undergoes a significant momentum change due to the impact from the bat.
Bat changes ball’s momentum by exerting a force over a time interval. Strike reverses ball’s momentum.
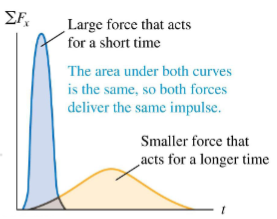
A moderate force will break an egg. However, an egg dropped on the road usually breaks, while one dropped on the grass usually doesn’t break. This is because for the egg dropped on the grass…
a. the change in momentum is greater
b. the change in momentum is less
c. the time interval for stopping is greater
d. the time interval for stopping is less
c. the time interval for stopping is greater
FΔt = Δp
Egg m = 1 kg, v = 10
Grass: t = 5, concrete: t = 1
Force is 5x greater for egg on concrete
change in momentum - same: egg goes from moving → stopped
grass stops egg more slowly & spreads force off
Conservation of Momentum
when no external forces act on a system consisting of 2 objects that collide with each other, the total momentum of the system remains constant in time
total momentum before collision = total momentum after collision
can be generalized to any number of objects
applies to the system (inelastic or elastic as long as no outside force)
pi = pf
m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
Momentum is conserved…
in ANY collision → elastic OR inelastic as long as it is closed and isolated (no outside forces acting on it)
Elastic Collision
KE of the system is conserved
total KE is unhanged
both momentum & KE are conserved
in a conserved & isolated system
typically have 2 unknowns: solve equations simultaneously
m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
½ m1v1i² + ½ m2v2i² = ½ m1v1f² + ½ m2v2f²
What simpler equation can be used in place of the KE equation in elastic collision momentum conservation?
v1i - v2i = -(v1f - v2f)
or
v1i + v1f = v2i + v2f
Newton’s Cradle is an example of…
elastic collision
momentum & kinetic energy are conserved
A 20-g bullet moving at 1000 m/s is fired through a 1-kg block of wood emerging at a speed of 100 m/s. If the block had been originally at rest and is free to move, what is its resulting speed?
Bullet
m1 = 20 g = 0.02 kg
v1i = 1000 m/s
v1f = 100 m/s
Block
m2 = 1 kg
v2i = 0 m/s
v2f = ?
inelastic → momentum is conserved!!
pi = pf
m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
(0.02 kg)(1000 m/s) + (1 kg)(0 m/s) = (0.02 kg)(100 m/s) + (1 kg)(v2f)
20 = 2 + v2f
v2f = 18 m/s
Elastic vs. Inelastic Collision
Elastic:
pi = pf
Ki = Kf
v1i + v1f = v2i + v2f
ex: billiard ball, gas molecules
Inelastic:
pi = pf
Ki
=KfKE not conserved
ex: car crash
Inelastic Collision
some energy is transferred from kinetic energy to other forms (thermal, energy of sound, etc.) → KE is not conserved
Includes perfectly inelastic collisions
Perfectly Inelastic Collisions
objects stick together
include all velocity directions and move with a common velocity after the collision
the “after” collision combines the masses
conservation of momentum becomes:
m1v1i + m2v2i = (m1+ m2)vf
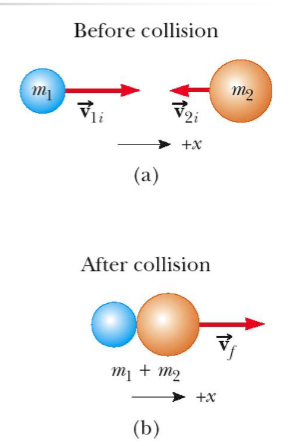
A 2500-kg truck moving at 10.00 m/s strikes a car waiting at a traffic light, hooking bumpers. the two continue to move together at 7.00 m/s. What was the mass of the struck car?
m1 = 2500 kg
v1i = 10 m/s
m2 = ?
v2i = 0 m/s
vf = 7 m/s
perfectly inelastic collision
m1v1i + m2v2i = (m1+ m2)vf
(2500 kg)(10 m/s) + (m2)(0 m/s) = (2500 kg + m2)(7 m/s)
25,000 = (2500 kg + m2)(7 m/s)
m2 = 1071 kg
The ballistic pendulum was used to measure the speeds of the bullets before electronic timing devices were developed. The version shown in the figure consists of a large block of wood of mass M = 5.4 kg, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass m = 9.5 g is fired into the block, coming quickly to rest. The block + bullet then swing upward, their center of mass rising a vertical distance h = 6.3 cm before the pendulum comes momentarily to rest at the end of its arc. What is the speed of the bullet just prior to the collision?
There are 2 events here. The bullet collides with the block. Then the bullet-block system swings upward by height h.
Event 1: Inelastic Collision
In this event, the bullet embeds itself into the block, resulting in a perfectly inelastic collision where the total momentum before collision is conserved, but kinetic energy is not.
m1v1i + m2v2i = (m1+ m2)vf
(0.0095 kg)(v1i) + (5.4 kg)(0 m/s) = (5.4095 kg)(vf)
Event 2: The bullet-block system then rises to height h → energy is conserved in this event AFTER the collision
Ei = Ef
KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf
PEi = 0
KEf = 0
½ (M + m)V² = (M + m)gh
½ V² = gh
v = sqrt(2gh)
Step 3: Plug In
(0.0095 kg)(v1i) + (5.4 kg)(0 m/s) = (5.4095 kg)(sqrt(2(9.8)(0.063 m)))
v1i = 632 m/s
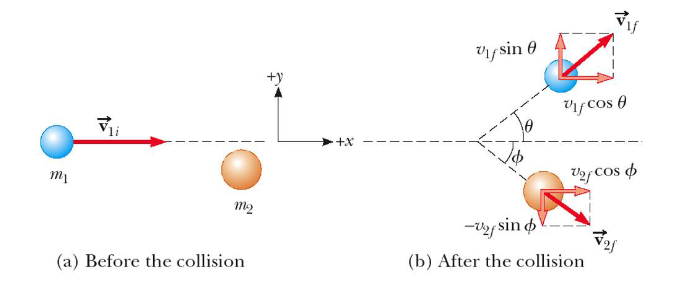
Glancing Collisions
the “after” velocities have x & y components
momentum is conserved in the x direction & y direction
apply conservation of momentum separately to each direction
the objects move at an angle to each other, resulting in different post-collision directions
Center of Mass
the point that moves as though all of the system’s mass is concentrated there & all external forces are applied there
location is important for stability
If we draw a line straight down from COM & it falls inside the base → it is in stable equilibrium and will balance
If it falls outside the base → it is unstable
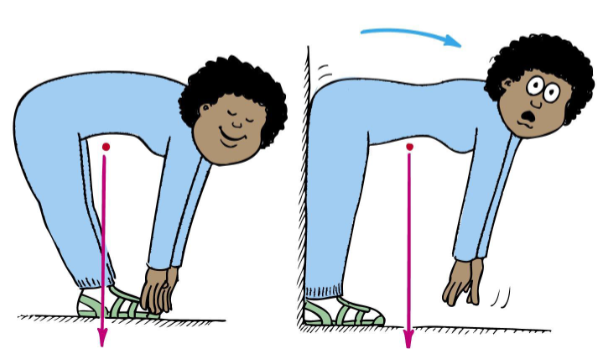
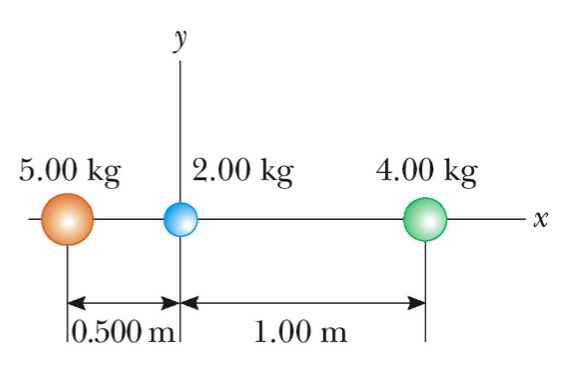
Where is the COM?
xcom = (m1x1 + m2x2 + m3×3) / (m1 + m2 + m3)
xcom = ((5)(0.5) + (2)(0) +(4)(1)) / (5 + 2 + 4) = 0.136 m

Change in momentum = impulse = Δp
Δp = FΔt
mass changes acceleration, not Δp, so it is not relevant here
A=D > B=C