OCR GCSE Computer Science - Paper 1 Key terms
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:05 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Performs operations on data e.g. Addition, subtraction
2
New cards
Control Unit (CU)
Coordinating activities of the CPU
3
New cards
Registers
Quick, small stores of data within the CPU
4
New cards
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Holds memory address for data or a instruction about to be used by the CPU
5
New cards
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Holds actual data or instruction
6
New cards
Accumulator
Stores results of calculations performed in the ALU
7
New cards
Program Counter (PC)
Holds memory address of the instruction for each cycle
8
New cards
Fetch
The next instruction is retrieved by CPU from main memory
9
New cards
Decode
The instruction is broken down and decided so computer can understand
10
New cards
Execute
The CPU performs what the instructions told
11
New cards
Embedded System
A computer system built within a large device e.g. Camera, washer, car
12
New cards
Volatile
Memory loses its data when power of
13
New cards
Non-volatile
Memory retains its data when power is lost
14
New cards
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Read/write - function is to load open programs and operating system data currently in use - volatile
15
New cards
Read Only Memory (ROM)
Can only be read, can't be changed, stores essential programs to be run in order to boot the computer - non-volatile
16
New cards
Buses
Collection of wires that carry signals between various components of the computer system
17
New cards
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Processes all of the data and instructions that make the system work - can be effected by clock speed, number of cores, cache size
18
New cards
Clock speed
How fast the computer does the FDE cycle - a clock speed of 3Ghz means that 3 billion FDE cycles run every second
19
New cards
Virtual memory
Virtual memory needed when the RAM is full so a temporary section is made which acts like a part of RAM
20
New cards
Flash memory
Solid state storage, non-volatile, more reliable/durable but can only be overwritten a limited number of times
21
New cards
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Handles graphics and image processing
22
New cards
Optical storage
CD, DVD, Blue-ray
ADV: cheap,easy to transport
DIS: slow, less storage than hard drives, stored data degrades over time, cannot be written over
ADV: cheap,easy to transport
DIS: slow, less storage than hard drives, stored data degrades over time, cannot be written over
23
New cards
Magnetic storage
Hard drives
ADV: fast access, stores large amounts of data, low cost
DIS: not very portable, easily be broken
ADV: fast access, stores large amounts of data, low cost
DIS: not very portable, easily be broken
24
New cards
Solid State storage
USB, flash memory, SD
ADV: fast, small, light, easily potable, quiet
DIS: more expensive, storage capacity less, limited number erase/write cycles
ADV: fast, small, light, easily potable, quiet
DIS: more expensive, storage capacity less, limited number erase/write cycles
25
New cards
Cloud storage
Data is stored on multiple servers in a remote location
ADV: secure, can be accessed anywhere, no need to buy hardware, backed up by host
DIS: needs internet, download and upload can be affected by internet connection, potential security issues, unclear who owns data in the cloud, could be expensive
ADV: secure, can be accessed anywhere, no need to buy hardware, backed up by host
DIS: needs internet, download and upload can be affected by internet connection, potential security issues, unclear who owns data in the cloud, could be expensive
26
New cards
Operating System
essential software that links the hardware and other software together and generally manages the computer system
27
New cards
Command-line Interface
Text commands where user has to type in command
28
New cards
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
uses icons and other visual indicators to navigate and issue commands
29
New cards
Utility Software
maintains a computer
30
New cards
Defragmentation Software
reorganises data on the hard drive to put fragmented files back together and moves files to collect all the free space
31
New cards
Backup Software
Full Backup - a copy is taken from from every file on the system
Incremental Backup - only files created or edited since last backup are copied
Incremental Backup - only files created or edited since last backup are copied
32
New cards
Compression Software
reduces file size so they take up less space on hard disk
33
New cards
Encryption Software
scrambles data to stop others from accessing it
34
New cards
Open Source Software
source code is made freely available and users can modify it
ADV: free, ,made for greater good, can be adapted
DIS: small, buggy, security holes, no warranties, no customer support
ADV: free, ,made for greater good, can be adapted
DIS: small, buggy, security holes, no warranties, no customer support
35
New cards
Proprietary Software
only the compiled code is released and the source code is kept a secret
ADV: warranties, well-tested, reliable, cheaper
DIS: expensive, software may not fit user needs
ADV: warranties, well-tested, reliable, cheaper
DIS: expensive, software may not fit user needs
36
New cards
Personal Area Network (PAN)
within the range of an individual person, eg connecting bluetooth headphones to a phone
37
New cards
Local Area Network (LAN)
a network that connects devices close to each other e.g. school, house
38
New cards
Wide Area Network (WAN)
a network within a large geographical area e.g. internet
39
New cards
Bandwidth
amount of data that can be transferred in a given time
40
New cards
Network Interface Card (NIC)
hardware that allows a device to connect to a network
41
New cards
Switch
connects devices on a LAN - is intelligent and routes data where it needs to go
42
New cards
Router
responsible for transmitting data between networks
43
New cards
Ethernet
a set of standards for connecting computers
44
New cards
Client-server Network
client has connection to server, servers can backup and store centrally but can be expensive and difficult to maintain

45
New cards
Peer-to-peer Network
no central server, each computer equal in responsibility, have to work as both server and a client.
46
New cards
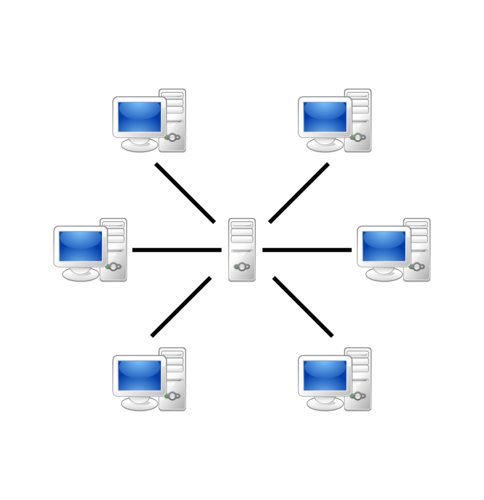
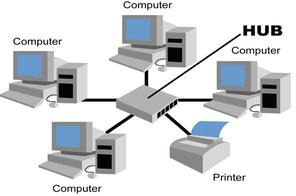
Star Topology
All devices connected to central switch or server controlling the network
ADV: better performance, rest of network not affected in one fails, simple to add more devices
DIS: wire needed for all devices, expensive
ADV: better performance, rest of network not affected in one fails, simple to add more devices
DIS: wire needed for all devices, expensive
47
New cards
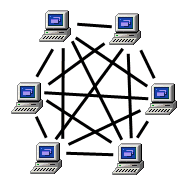
Mesh Topology
Devices correctly directly or indirectly to all other devices. No need for central server. Data sent along fastest route.
ADV: faster
DIS: expensive
ADV: faster
DIS: expensive
48
New cards
MAC Address
assigned to all devices, unique and cannot be changed, permanent, identifies the actual device. Used for communication on the same network
49
New cards
IP Address
assigned either manually or automatic, the location of your device on the internet. Static IP addresses are permanent and used to connect printers in a LAN or websites on the Internet. Dynamic addresses are allocated by a server each time the device accesses a network
50
New cards
Packet Switching
split data into packets to be sent across the network, each packet given a number order of data, each router reads packet header and decides which way to send it according to IP rules, packets then arrive and reassemble them in the right order.
51
New cards
TCP/IP
sets of rules for how devices connect on the network. Responsible for splitting data into packets and reassembling them.
52
New cards
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
used to access websites and communicate with web servers
53
New cards
HTTPS
more secure - encryption
54
New cards
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
used to access, edit and move files between devices
55
New cards
Post Office Protocol (POP3)
used to retrieve emails from a server, holds until download - then deletes from server
56
New cards
Internet Message Access (IMAP)
used to retrieve emails, server holds until you actually delete it- only download a copy. Allows email to be synchronised across multiple devices.
57
New cards
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
used to send emails, used to transfer emails between servers
58
New cards
Layer
Group of protocols which ahve similar functions. Self-contained. Each layer serves the layer above.
ADV: breaks network communication into manageable pieces. Self-contained so a layer can be changed without affecting other layers. Forces companies to create compatible hardware/software.
ADV: breaks network communication into manageable pieces. Self-contained so a layer can be changed without affecting other layers. Forces companies to create compatible hardware/software.
59
New cards
Application Layer
Allows software to communicate with network using protocols, eg browser communicates with WWW using http or https
60
New cards
Transport Layer
controlling data flow - splitting data into packets and checks data sent/delivered correctly, uses TCP
61
New cards
Network (Internet) Layer
Makes connections between networks, adds IP address headers to packets, using IP
62
New cards
Data link Layer
passing data over physical network, eg Ethernet
63
New cards
Domain Name Server (DNS)
translates websites' domain name into its IP address
64
New cards
Virtual Network
network that is entirely software based, created by partitioning of some physical network
65
New cards
Blagging
invented scenario to engage a targeted victim in a manner that increases the chance the victim will divulge information
66
New cards
Phishing
used to gain personal information for purposes of identity theft, using fraudulent e-mail messages that appear to come from legitimate businesses.
67
New cards
Shouldering
used to obtain information such as personal identification numbers (PINs), passwords and other confidential data by looking over the victim's shoulder.
68
New cards
Malware
malicious software - computer programs designed to infiltrate and damage computers without the users consent.
69
New cards
Virus
program loaded onto a user's computer without the user's knowledge and performs malicious actions. It can self-replicate, inserting itself onto other programs or files, infecting them in the process.
70
New cards
Worm
program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. Often, it uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it.
71
New cards
Trojan Horse
program which misleads users of its true intent.
72
New cards
Spyware
aims to gather information about a person or organization without their knowledge
73
New cards
Adware
unwanted advertisements to the user of a computer
74
New cards
Brute Force Attack
trail and error to gain information
75
New cards
Denial of Service Attack (DOS)
hacker stop users from accessing a part of a network, flooding network with useless traffic making computer very slow
76
New cards
Data Interception And Theft
The unauthorized taking or interception of computer-based information. Data theft is the act of stealing computer-based information from an unknowing victim with the intent of compromising privacy or obtaining confidential information.
77
New cards
SQL Injection
SQL is a programming language used to search and query databases. An injection adds SQL commands for example to a login to access a database
78
New cards
Penetration Testing
organisations employ specialists to simulate potential attacks on their network
79
New cards
Anti-malware Software
designed to find and stop malware from damaging a network
80
New cards
Encryption
data is scrambled so that it is meaningless to anyone who does not have the key to decrypt it
81
New cards
Freedom of Information Act
allows members of the public to access information held by a public organisation
82
New cards
Data Protection Act
Law to protect use of data by organisations. 8 principles. Replaced by GDPR. Data must be held securely, kept up to date and not transferred outside the EEA.
83
New cards
Computer Misuse Act
Law against computer misuse, covers unauthorised access to data, changing/editing data and spreading viruses
84
New cards
Copyright Act
protect intellectual property - anything someone has created
85
New cards
Cache
Very fast memory, close to CPU. Stores regularly used data for quick access. Low capacity and very expensive.
86
New cards
Cores
A multi-core processor will have 2, 4 or 8 processors which can process data independently of the rest. The more cores, the more instructions can be processed, so the faster the data can be processed
87
New cards
Comparing storage
Cost, speed, capacity,
portability, reliability
portability, reliability
88
New cards
Fibre optic cable
Data transmitted as light. High speed but expensive. Do not suffer from interference and can transmit data over long distances
89
New cards
Copper wire (coaxial)
Data transmitted over copper wires. Subject to interference. Traditional phone networks use copper.
90
New cards
Wi-fi
Radio waves transmit data. Easy to set up wireless network and generally cheaper. Limited range and subject to interference between channels and blocking by physical objects, eg walls.
91
New cards
Internet
A global network connecting millions of computers, making it possible to exchange information. Biggest WAN.
92
New cards
URL
Uniform Resource Locator - addresses used to access web servers
93
New cards
Ethical
What is considered right and wrong by society
94
New cards
Legal
What is considered right and wrong in the eyes of the law
95
New cards
Cultural
How groups of people with particular beliefs are affected
96
New cards
Environmental
Impact on the natural world
97
New cards
Stakeholder
A person/group of people who are affected by the actions of a company/organisation
98
New cards
Privacy issues
Social media, employee monitoring, cookies, sharing of data
99
New cards
Censorship
Controlling what people can access on the Internet
100
New cards
Surveillance
Monitoring what people do on the Internet