B1.1: Carbohydrates And Lipids
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Why is carbon described as the “backbone” of life?
Carbon forms stable covalent bonds and can bond to up to four atoms, so it can make chains, rings and branched molecules.
What is a covalent bond?
A bond where two atoms share electrons.
How many covalent bonds can a carbon atom form?
Four single bonds, or a mix of single and double bonds.
What types of elements does carbon commonly bond with in biology?
C, H, O, N, P, S (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur).
What is a macromolecule?
A large molecule made from many small subunits (monomers) joined together.
What is a monomer?
A small, repeating unit that can be joined to form a polymer.
What is a polymer?
A large molecule made of many monomers joined together.
What are the 4 main classes of biological macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
What is a condensation reaction?
A reaction that joins monomers together, forming a covalent bond and releasing water.
What bond forms between two glucose molecules in a condensation reaction?
A 1,4-glycosidic bond.
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
A reaction that uses water to break a covalent bond in a polymer, forming smaller units.
How does water take part in hydrolysis?
The –H from water attaches to one monomer and the –OH to the other, breaking the bond.
Relationship between condensation and hydrolysis.
They are reverse processes: condensation builds polymers, hydrolysis breaks them.
What is a monosaccharide?
The simplest carbohydrate, a single sugar unit that cannot be broken down further by hydrolysis.
What is a hexose sugar? Give an example.
A sugar with 6 carbons; examples: glucose, fructose, galactose.
What is a pentose sugar? Give an example.
A sugar with 5 carbons; example: ribose.
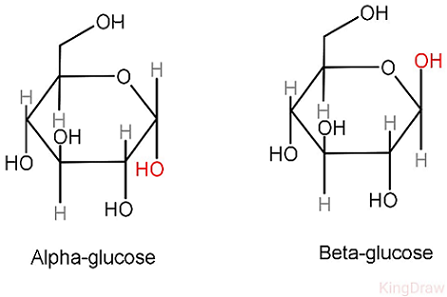
What are the two isomers of glucose?
Alpha-glucose (α-glucose) and beta-glucose (β-glucose).
How do α-glucose and β-glucose differ?
The –OH on carbon 1 points down in α-glucose and up in β-glucose.
Why is glucose soluble in water?
It has many polar –OH groups, so it can form hydrogen bonds with water.
Why is glucose’s solubility important in humans?
It can be transported in blood plasma to cells, especially the brain.
Why is glucose considered stable?
It’s a ring structure with –OH groups in positions that make it chemically stable.
What happens when glucose is oxidised in respiration?
It is broken down to CO₂ and H₂O, releasing energy to make ATP.
What is a polysaccharide?
A large carbohydrate made of many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds.
Which monosaccharide is used to build starch and glycogen?
Alpha-glucose.
Name the two components of starch.
Amylose and amylopectin.
Why is starch a good storage molecule in plants?
It is compact, insoluble (doesn’t affect osmosis), and can be broken down to glucose when needed.
Where is starch stored in plants?
In seeds, roots, and storage organs.
What is glycogen?
The animal storage polysaccharide of glucose.
Structure of glycogen.
Highly branched α-glucose polymer (more branches than amylopectin).
Why is glycogen good for animals?
Highly branched → rapid hydrolysis to release glucose; compact and insoluble.
Main storage sites of glycogen in humans.
Liver (blood glucose control) and muscles (energy for contraction).
What monosaccharide makes up cellulose?
β-glucose.
How is cellulose different from starch/glycogen?
Made from β-glucose, forming straight, unbranched chains.
How are cellulose chains arranged?
They form long chains that group into microfibrils held together by hydrogen bonds.
What property does cellulose give plant cell walls?
High tensile strength → structural support and resistance to osmotic pressure.
What is a glycoprotein?
A protein with carbohydrate chains attached.
Give two roles of glycoproteins on cell membranes.
Cell–cell recognition (acting as “markers”)
Receptors or ligands in cell signalling
(also structural support and adhesion).
What determines the ABO blood groups?
Different glycoprotein/glycolipid antigens on the surface of red blood cells (A, B or none).
Which blood type has both A and B antigens?
AB blood group.
Which blood type has no A or B antigens?
O blood group.
Why is blood type compatibility important?
The immune system can attack “foreign” antigens, causing clumping and possibly organ failure.
What are lipids?
Hydrophobic, mostly non-polar molecules such as fats, oils, waxes and steroids.
Do lipids dissolve in water?
No, they are insoluble in water, but dissolve in non-polar solvents.
What is a triglyceride made from?
One glycerol + three fatty acids joined by condensation → three ester bonds + three waters.
What is an ester bond?
The bond formed between glycerol and a fatty acid in lipids.
What is a phospholipid made from?
Glycerol + two fatty acids + a phosphate group.
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic and which is hydrophobic?
Head (phosphate) is hydrophilic, tails (fatty acids) are hydrophobic.
Why are triglycerides good for long-term energy storage?
They store a lot of energy per gram, are insoluble, and can be stored as droplets in adipose tissue.
How do triglycerides help with temperature regulation?
They act as thermal insulators (e.g. blubber in whales).
What is a fatty acid?
A molecule with a carboxyl group (–COOH) and a long hydrocarbon chain.
What is a saturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with no C=C double bonds; all carbons have single bonds.
Properties of saturated fatty acids at room temperature.
Straight chains, pack closely, usually solid (e.g. butter, lard).
What is a monounsaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with one C=C double bond in its hydrocarbon chain.
What is a polyunsaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with two or more C=C double bonds.
How do unsaturated fatty acids behave at room temperature?
The kinks from double bonds stop tight packing → usually liquid oils.
How does the number of double bonds affect melting point?
More double bonds → lower melting point.
What is a cis unsaturated fatty acid?
The H atoms around the C=C double bond are on the same side, causing a kink.
What is a trans unsaturated fatty acid?
The H atoms around the C=C are on opposite sides, so the chain is more straight.
Which type (cis or trans) occurs naturally?
Cis unsaturated fatty acids.
How are most trans fats produced?
Industrially, not usually found in nature.
Where are triglycerides stored in animals?
In fat tissue as oil droplets.
Give two functions of triglycerides in fat tissue.
Long-term energy store
Thermal insulation (and also protection around organs).
What is the basic structure of a steroid molecule?
Four fused carbon rings (three 6-carbon rings + one 5-carbon ring).
Are steroids generally polar or non-polar?
Mostly non-polar (hydrophobic).
How do steroid hormones cross the cell membrane?
They diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer because they are non-polar.
What is one role of cholesterol in membranes?
It helps control membrane fluidity and stability.