MS - based
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Write an equation for the reaction that occurs when the calcium carbonate is heated.
Include state symbols. [1]
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Barium chloride solution is used as a test for the sulfate ion.
Write an ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when this test is done.
Include state symbols. [2]
Ba 2+ (aq) + SO4 2-(aq) → BaSO4 (s)
Why are the bond enthalpies in described as average values? [1]
(Bond enthalpies/they are averaged) over different molecules that contain that bond
The larger bond enthalpy of C=O compared with C–O implies that the C=O bond is shorter. Explain why double bonds are shorter than single bonds between the same atoms. [2]
Double bonds have two pairs of e- AND single bonds have only one pair. There is a greater force of attraction between the shared e- and the bonded nuclei in the double bond.
State the types of particle that cause the transfer of charge through the wire and the solutions.
The wire_______________________________________________.
The solutions___________________________________________.
The wire - electrons
The solutions - ions
Explain how this mRNA sequence enables these two amino acids to form the correct primary structure in a protein.
The amino acids are joined to t-RNA with an anti-codon
these attach to codon / triplet on mRNA
Describe the feature of the amino acid structure that allows optical isomerism to occur.
A carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it
The formula of the species present in the aqueous solution of alanine is H3N+CH(CH3)COO–. Name this type of species
Zwitter ion
Excess chlorine is added to acidified seawater, forming aqueous bromine.
Write an ionic equation for the reaction of chlorine with bromide ions and explain how it shows that chlorine is more reactive than bromine
2Br- + Cl2 → Br2 + 2Cl-
Chlorine gains e- from bromide ions / chlorine displace bromine
Some of the hazards of transporting bromine are similar to those of transporting chlorine. Suggest three hazards of transporting bromine in a road tanker
Volatile / corrosive / toxic or poisonous

Ether
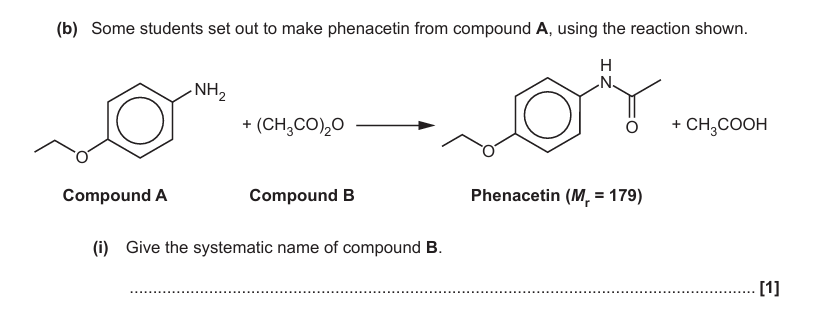
Ethanoic anhydride

The same AND Kc does not vary with pressure / only varies with temperature

Increased vibrational energy of bonds / bonds vibrate more. Increased KE / molecules move faster
Re-emit IR towards earth

2H2O → 4e- + 4H+ + O2
True fossil fuels are not sustainable / renewable / they produce CO2 / are not carbon neutral
Other named green method of producing electricity (eg wind, solar) can be used
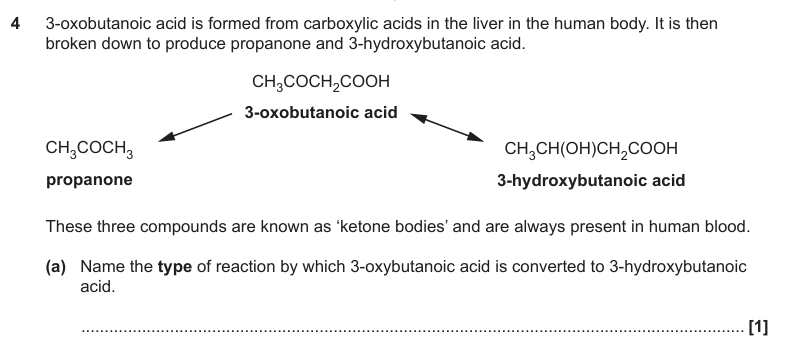
Reduction

Gas liquid chromatography / GLC
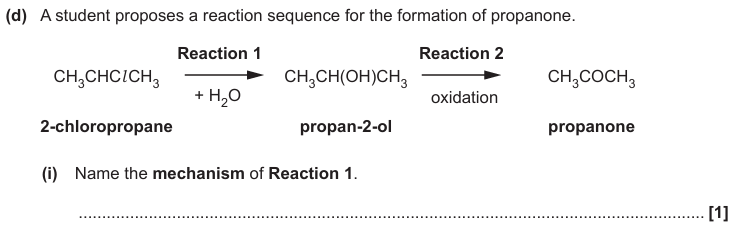
Nucleophilic substitution

Warm / Heat with acidified dichromate
Green colour

Cyan(o)hydrin

Photochemical smog / respiration difficulties
nitrogen oxides /NOx, CO and hydrocarbons are toxic and removed
mostly / incompletely / but not to zero
CO2 is still polluting AND greenhouse effect

Conditions: UV light
Type of bond fission: homolytic
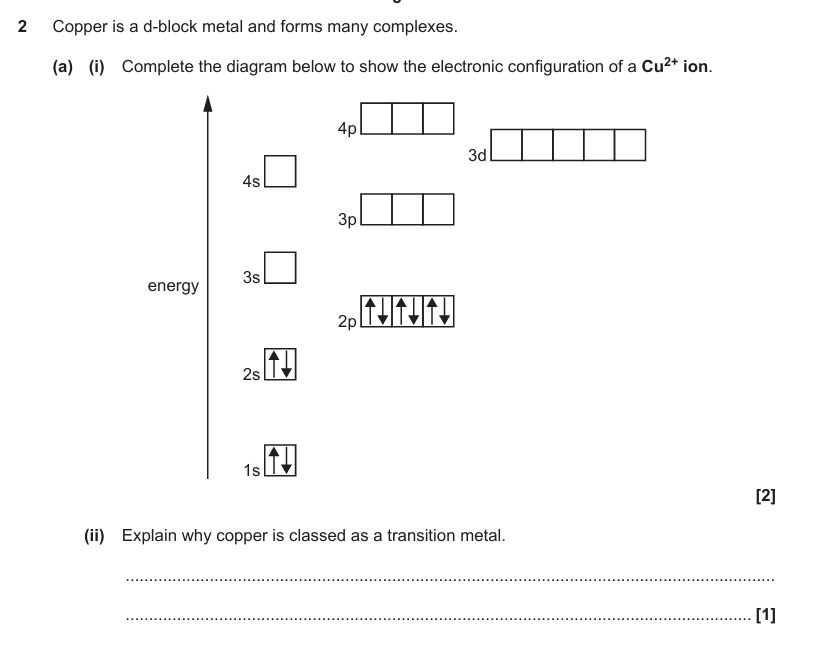
Forms an ion with an incomplete / partially filled d subshell / orbital
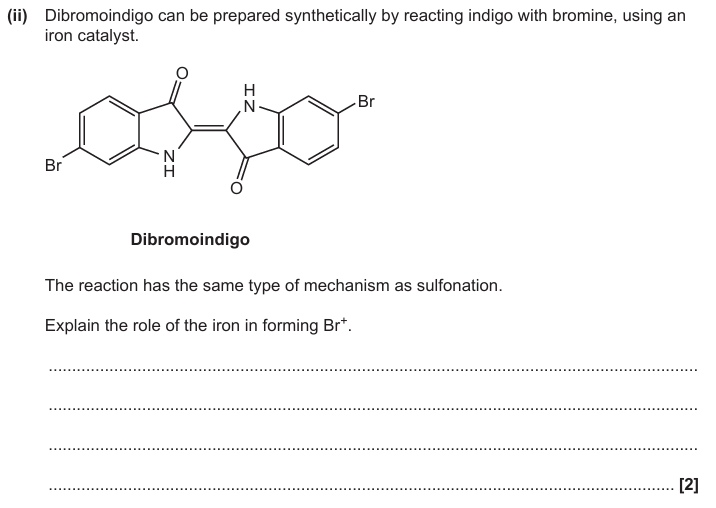
Fe reacts with Br2 to form FeBr3 / equation
FeBr3 + Br2 → FeBr4- + Br+

The chlorine gains / attracts an e- more easily than bromine
The outer/valence e- are further from the nucleus / experience weaker nuclear attraction in bromine

2Br- → Br2 + 2e-

This question is between Br and I
Add concentrated ammonia solution
Bromide partially soluble AND iodide insoluble

Use phosphoric acid / H3PO4

2HBr + H2SO4 → SO2 + Br2 + 2H2O

The C-F bond is more polar than the C-Cl bond as F is more electronegative
The C-Cl bond has a lower bond enthalpy / easier to break than the C-F bond
So, chlorine atoms / radicals are released.

Effervescence
A colourless solution forms
Change in temperature
Solid disappears / dissolves

Choice of ethanol
Dissolve in minimum volume of hot solvent
Filter when hot and cool / leave to crystallise
Collect crystals by filtering under reduced pressure
Wash with cold solvent and dry
Pharmacophore
Warm with Benedict solution - blue to orange/red precipitate
or
Warm with H+/Cr2O7 2- - orange to green

To prevent loss of reactants / products

Iron (III) oxide

e- are excited to higher energy levels by heat from flame
They drop emitting photons OR light of specific frequency / wavelength

More than one d configuration is stable
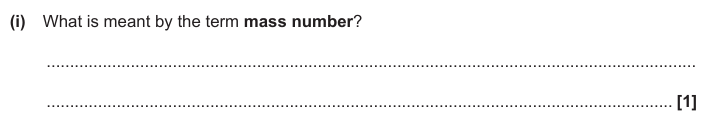
Number of protons plus neutrons

Answer part (ii)
Abundance/% of isotope below 56 is bigger than abundance/% of isotopes above 56
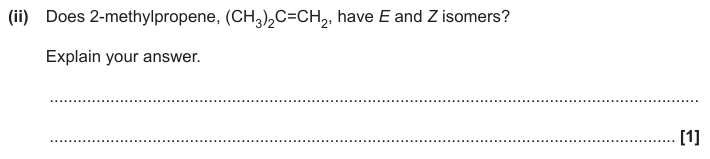
No, because 2 of same groups on each / one C

Thiosulfate reacts with the iodine until thiosulfate is used up
Iodine reacts to form blue-black colour with starch

Condensation / water is formed

Secondary structure
Hydrogen bonds

Hydrogen bonds broken in tertiary structure
So active site destroyed/ changes shape

Correct for low/initial [substrate] first order wrt low/initial [substrate]
At higher [substrate] becomes zero order / rate does not depend on [substrate]

Earth

Allows ion flow between half-cells
Completes circuit

Warm with NaOH AND ammonia gas turns red litmus paper blue

Colourless gas turns to a brown gas

Ba ions are Ba 2+ and sulfate is SO4 2-

C2H5Cl + NH3 → C2N5NH2 + HCl

C-Cl is more polar than C-I
Bond strength more important and C-I bond is weaker than C-Cl
Ppt forms faster with iodoethane

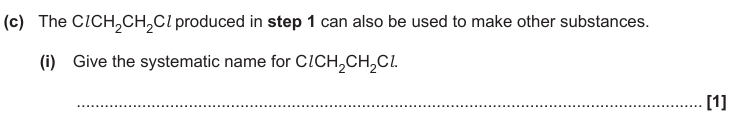
1,1,1-trichloroethane
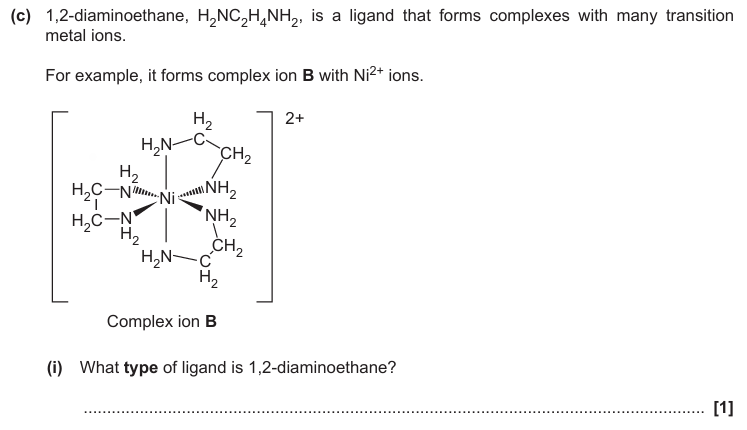
Bidentate
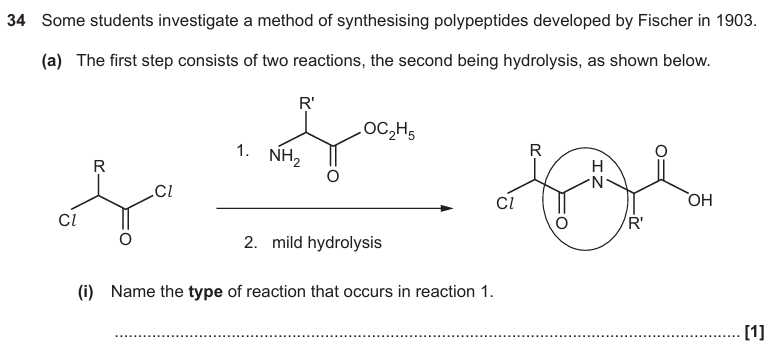
Condensation

Select a solvent in which the product is much more soluble at high temperature
Dissolve solid in minimum volume of hot solvent
Filter when hot to remove insoluble impurities
Then cool and collect purer solid by (vacuume?) filtration
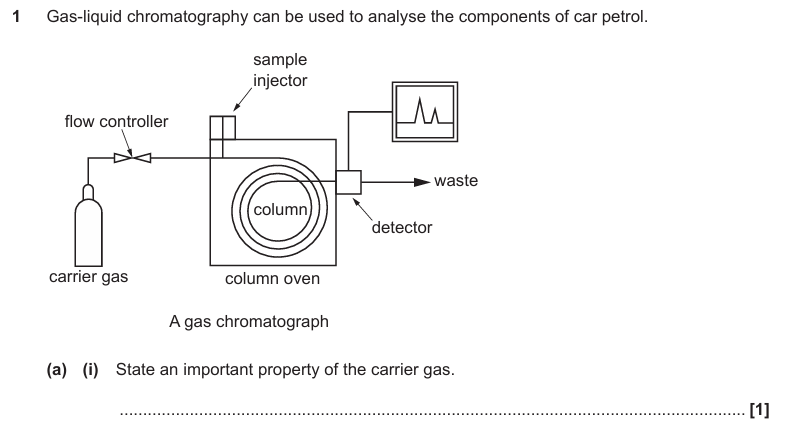
Inert / unreactive
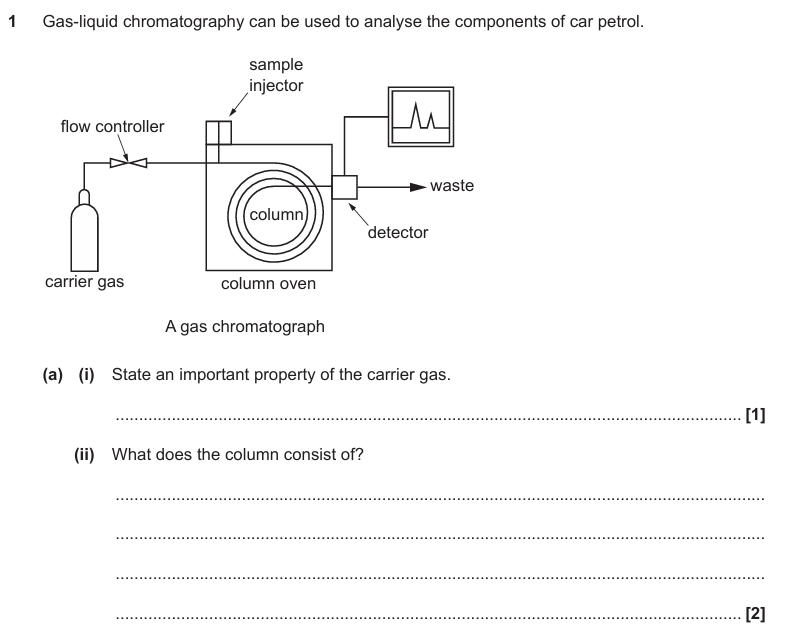
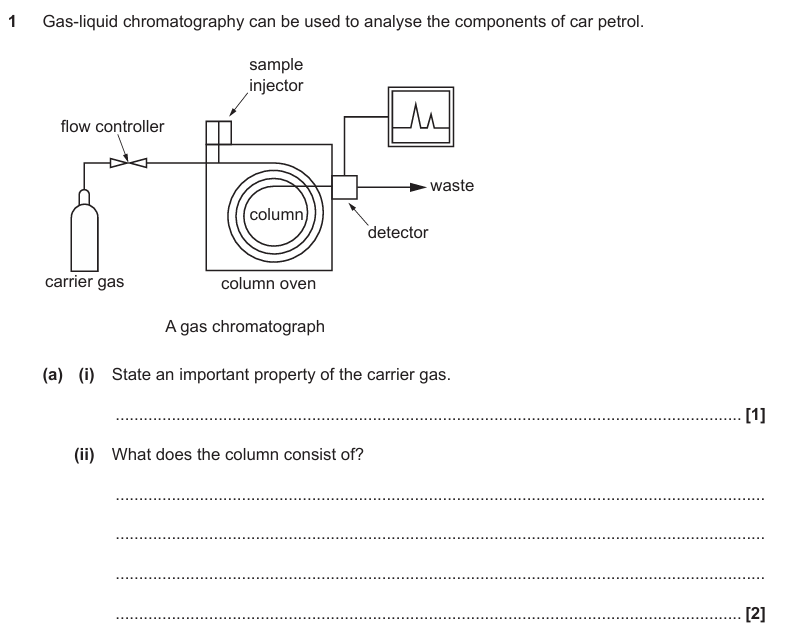
Answer part (ii)
High-boiling liquid
Porous support

Delocalised electrons
Above and below plane of benzene ring

Benzene has electrophilic substitution and ethene has electrophilic addition

Complementary colour / blue is absorbed
Student incorrect because molecule does not emit light
Yellow colour is what is left after absorption

Entropy is number of ways of arranging particles / associated energy quanta
KIO3 solid / ionic lattice lower entropy than ion in solution

Same number / two of moles of gas on each side of the equation
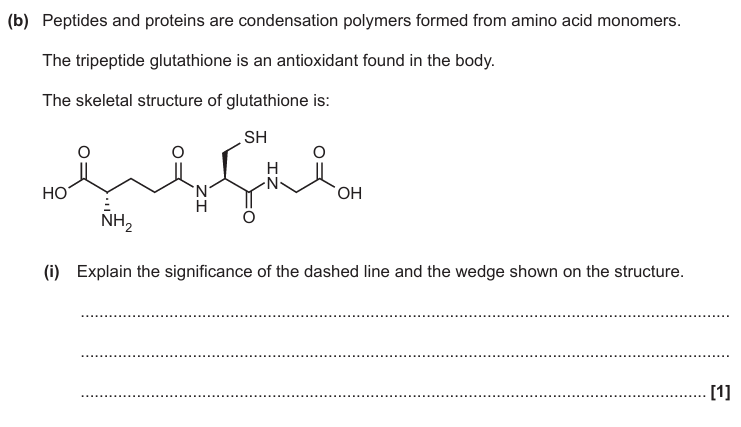
Dashed line is bond/ part of molecule going behind plane of paper
Wedge bond/ part of molecule coming in front of plane of paper

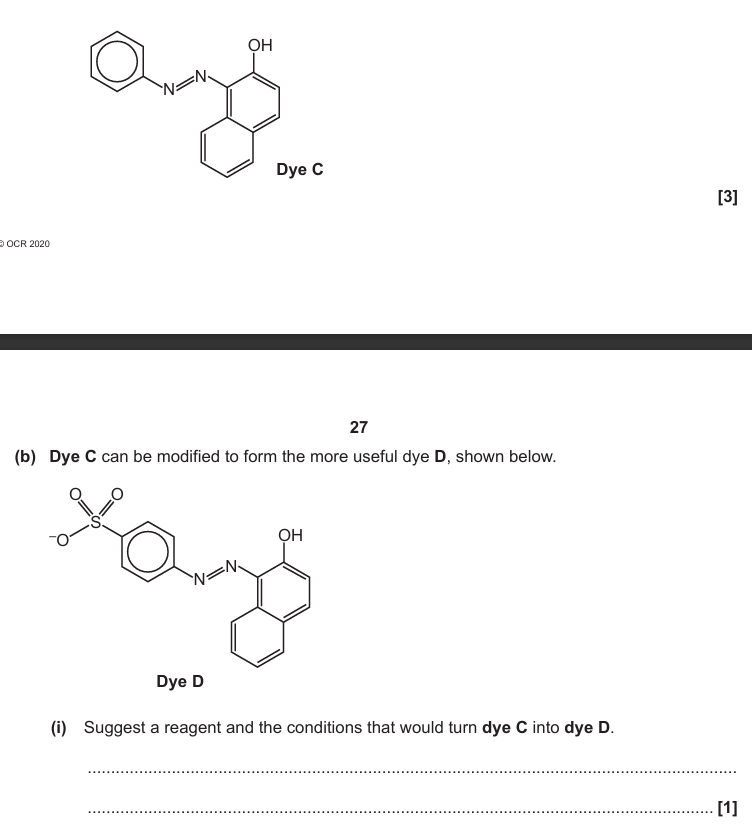
A part of a molecular structure that is responsible for a particular biological or pharmacological/medicinal activity
Explain the terms chiral and enantiomer
Chiral - asymmetric part of structure giving rise to asymmetry
Enantiomers - nonsuperimposable mirror images

Colourless gas turns brown

N2 + O2 → 2NO

Chlorine and bromine are toxic

Orange/brown solution forms

Simple molecules with weak pd-pd forces / intermolecular bonds between

2HBr + H2SO4 → Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O
1,2-dichloroethane
Concentrated sulfuric acid and reflux
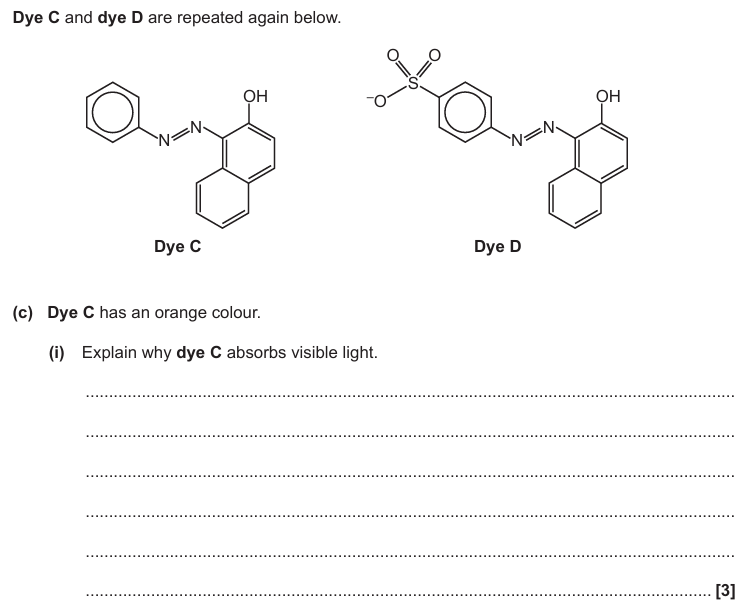
e- in the extended delocalised system
e- move to higher energy levels
E=hv

Complementary colour is seen / frequencies not absorbed are seen

White precipitate
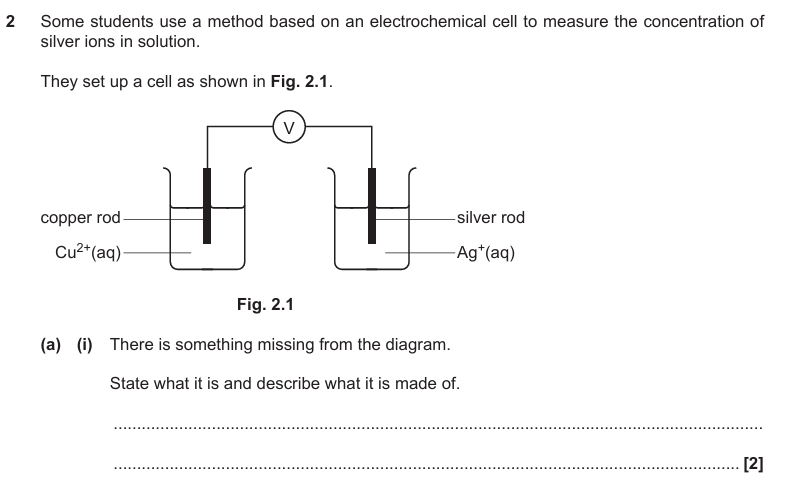
Salt bridge
Filter paper and potassium nitrate

298K
Concentration of solutions 1 moldm^-3

HPO4 2-
Proton acceptor
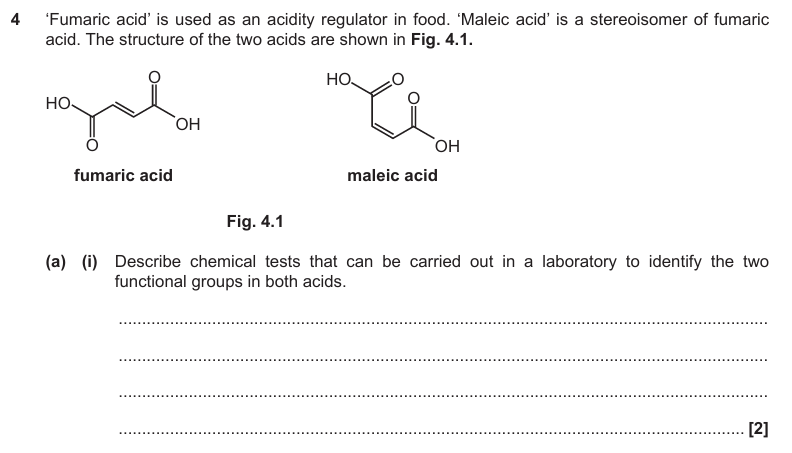
C=C decolorises bromine water
COOH will fizz with carbonate
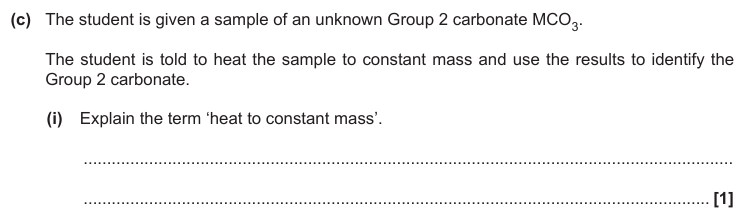
Heating until there is no further change to mass
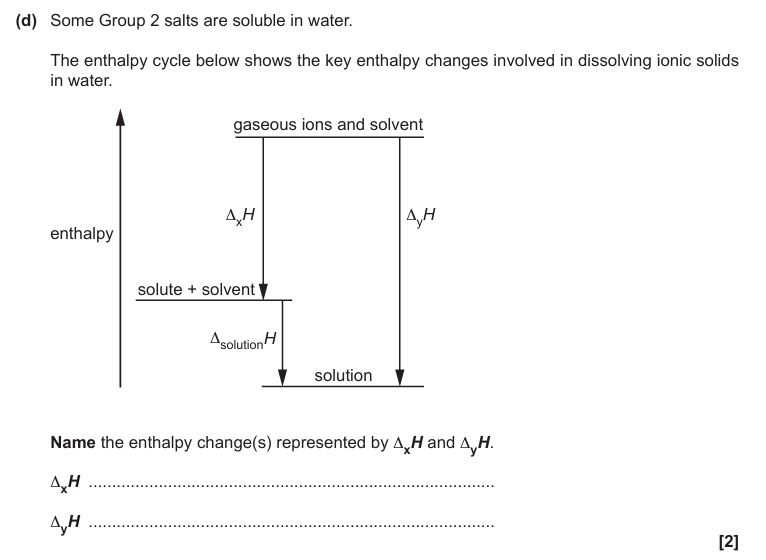
Lattice enthalpy
Hydration enthalpies of cation + anion in the solvent

Unsaturated - C=C present
Cis - adjacent parts of chain next to each other around double bond

Incomplete combustion
Evaporation of fuel
Evaporation of water
Non-standard conditions

Rate of forward reaction = rate of backwards
Closed system
Overall concentrations remain constant

Brown gas

Reflux with HCl or NaOH

e- excited to higher energy levels by heat
Fall and release energy / visible light
Frequency of energy / light proportional to gap between energy level / Calc by E=hv

Sr2+ are larger and attract less
Sr 2+ have lower charge density
They distort / polarise the CO3 2- less
Thermal stability of SrCO3 is higher

s block

Answer part (ii)
Sr2+ and Rb2+ / Sr loses 2e- and Rb loses 1e-
More delocalised e- in Sr
Sr2+ attracts more e- in metallic structure more strongly

Chlorine has a greater attraction for e- than iodine

Adsorption of reactant molecules on catalyst surface
Bonds break within reactants
New bonds form
Desorption of product molecules off surface of catalyst
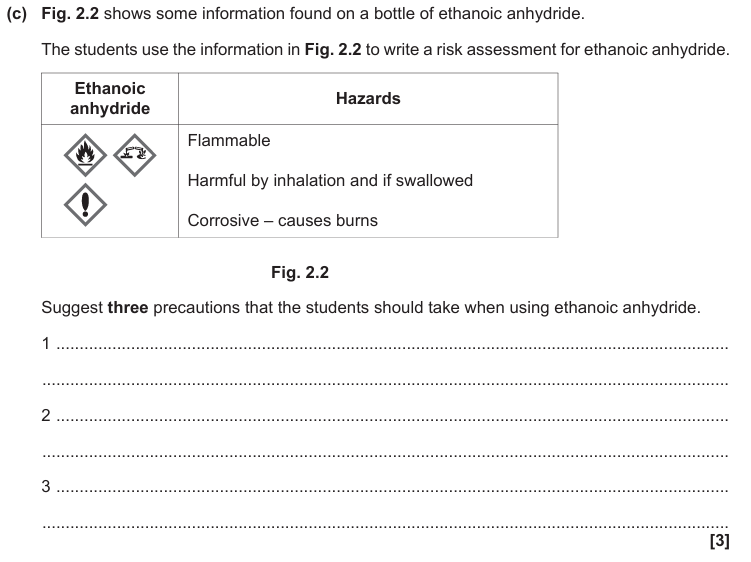
Keep away from flames
Use in fume cupboard
Wear protective gloves
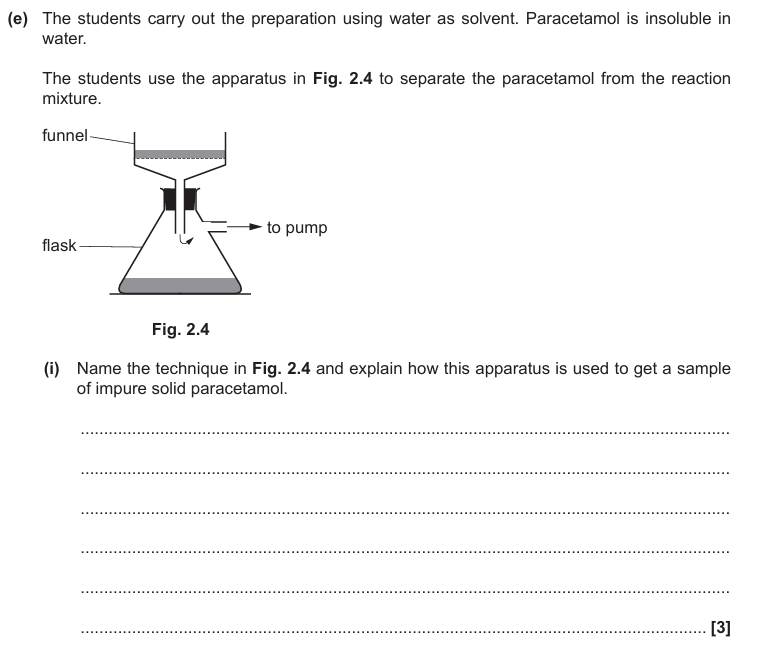
Vacuum filtration
Dampen filter paper
Wash solid/paracetamol with water
Suck to remove water/solvent
Crude paracetamol/solid left on filter paper